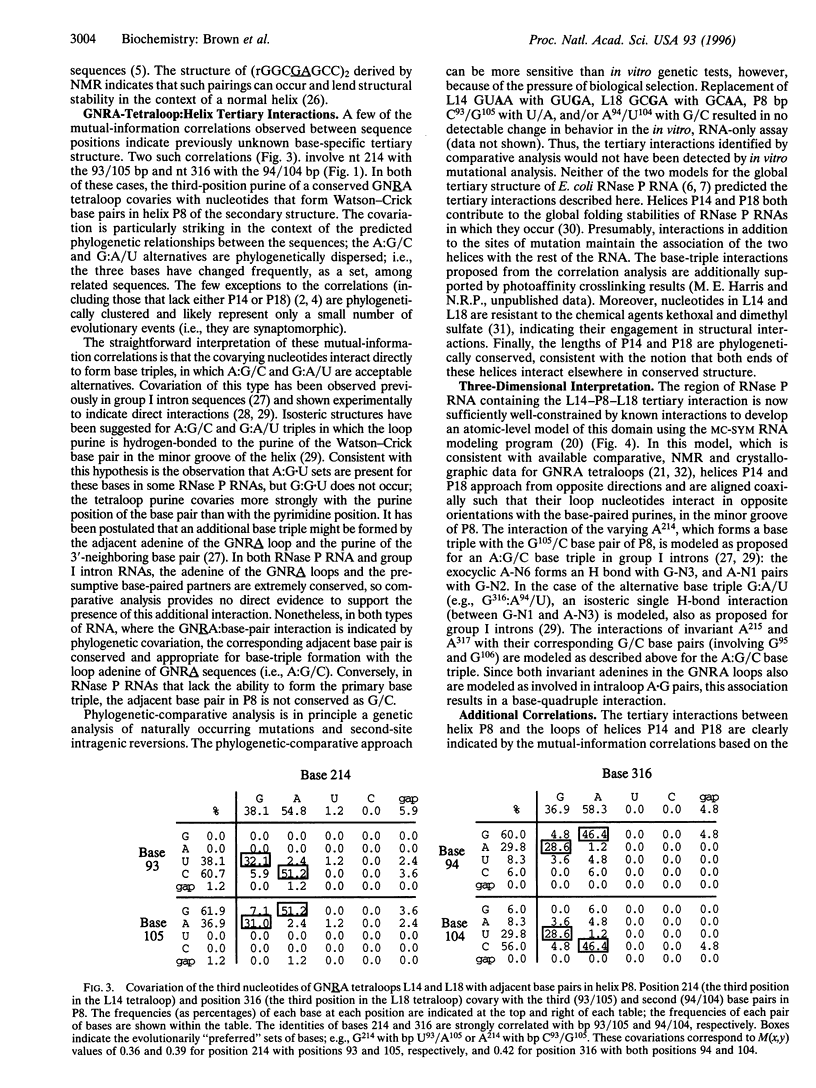
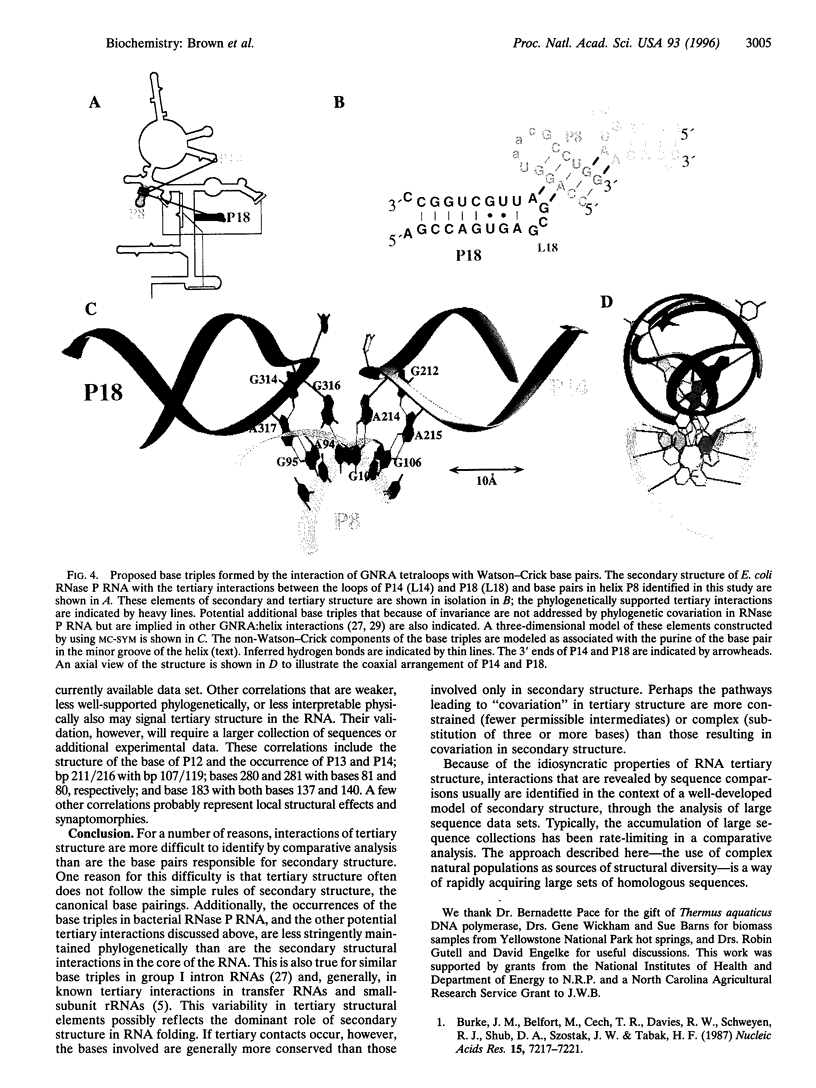
Abstract
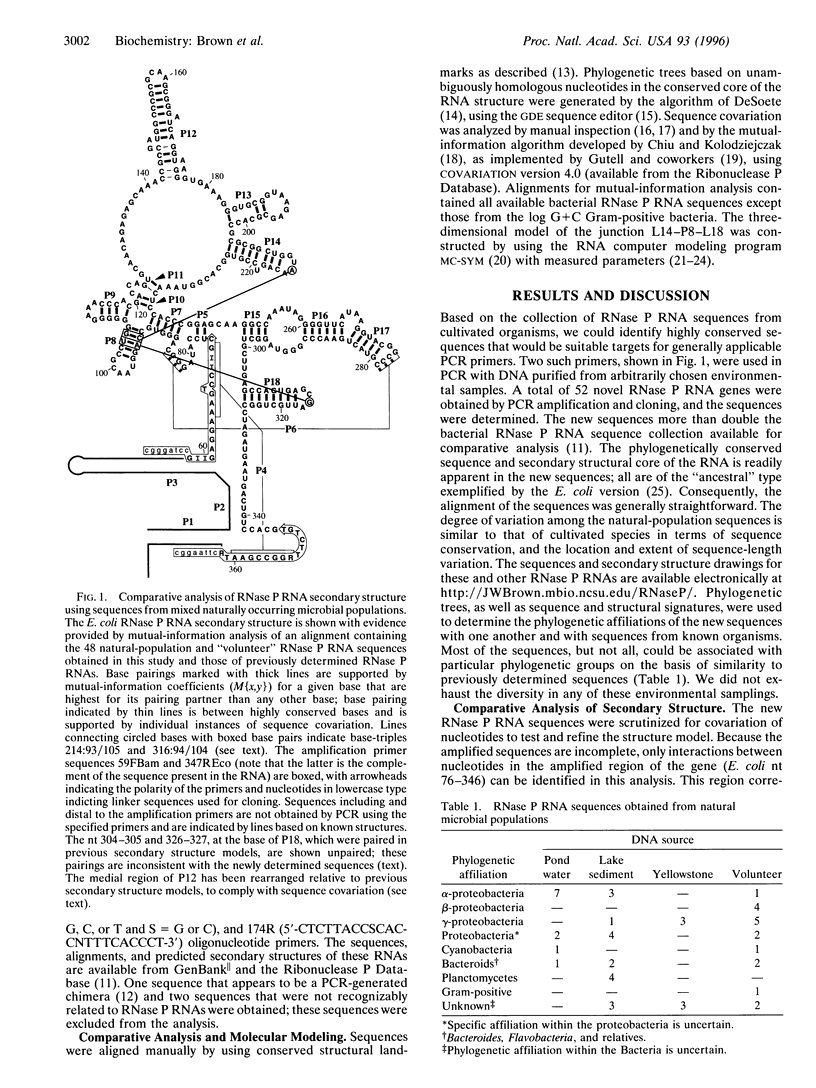
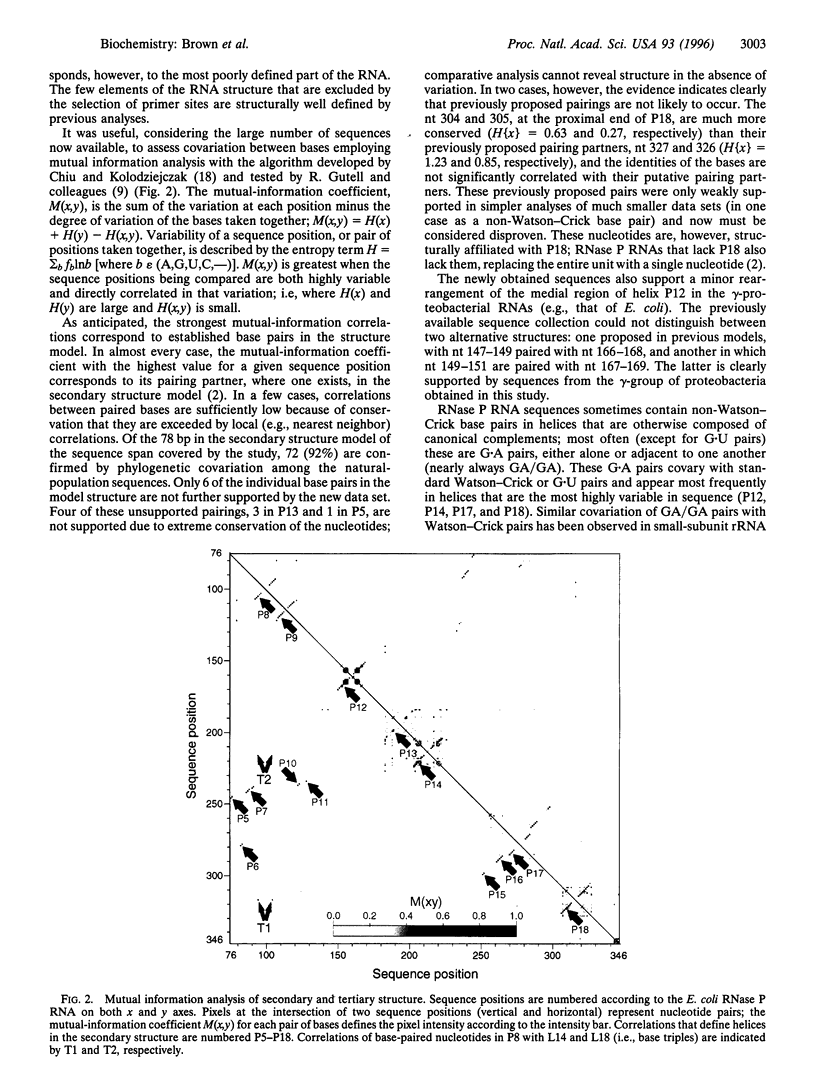
PCR amplification of template DNAs extracted from mixed, naturally occurring microbial populations, using oligonucleotide primers complementary to highly conserved sequences, was used to obtain a large collection of diverse RNase P RNA-encoding genes. An alignment of these sequences was used in a comparative analysis of RNase P RNA secondary and tertiary structure. The new sequences confirm the secondary structure model based on sequences from cultivated organisms (with minor alterations in helices P12 and P18), providing additional support for nearly every base pair. Analysis of sequence covariation using the entire RNase P RNA data set reveals elements of tertiary structure in the RNA; the third nucleotides (underlined) of the GNRA tetraloops L14 and L18 are seen to interact with adjacent Watson-Crick base pairs in helix P8, forming A:G/C or G:A/U base triples. These experiments demonstrate one way in which the enormous diversity of natural microbial populations can be used to elucidate molecular structure through comparative analysis.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barns S. M., Fundyga R. E., Jeffries M. W., Pace N. R. Remarkable archaeal diversity detected in a Yellowstone National Park hot spring environment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 1;91(5):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.5.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Haas E. S., Gilbert D. G., Pace N. R. The Ribonuclease P database. Nucleic Acids Res. 1994 Sep;22(17):3660–3662. doi: 10.1093/nar/22.17.3660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Haas E. S., Pace N. R. Characterization of ribonuclease P RNAs from thermophilic bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):671–679. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.671. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. W., Pace N. R. Ribonuclease P RNA and protein subunits from bacteria. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1451–1456. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burke J. M., Belfort M., Cech T. R., Davies R. W., Schweyen R. J., Shub D. A., Szostak J. W., Tabak H. F. Structural conventions for group I introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7217–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu D. K., Kolodziejczak T. Inferring consensus structure from nucleic acid sequences. Comput Appl Biosci. 1991 Jul;7(3):347–352. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/7.3.347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darr S. C., Zito K., Smith D., Pace N. R. Contributions of phylogenetically variable structural elements to the function of the ribozyme ribonuclease P. Biochemistry. 1992 Jan 21;31(2):328–333. doi: 10.1021/bi00117a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Larsen N., Woese C. R. Lessons from an evolving rRNA: 16S and 23S rRNA structures from a comparative perspective. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Mar;58(1):10–26. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.10-26.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Power A., Hertz G. Z., Putz E. J., Stormo G. D. Identifying constraints on the higher-order structure of RNA: continued development and application of comparative sequence analysis methods. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5785–5795. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas E. S., Brown J. W., Pitulle C., Pace N. R. Further perspective on the catalytic core and secondary structure of ribonuclease P RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Mar 29;91(7):2527–2531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.7.2527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris M. E., Nolan J. M., Malhotra A., Brown J. W., Harvey S. C., Pace N. R. Use of photoaffinity crosslinking and molecular modeling to analyze the global architecture of ribonuclease P RNA. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):3953–3963. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06711.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heus H. A., Pardi A. Structural features that give rise to the unusual stability of RNA hairpins containing GNRA loops. Science. 1991 Jul 12;253(5016):191–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1712983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger L., Michel F., Westhof E. Involvement of a GNRA tetraloop in long-range RNA tertiary interactions. J Mol Biol. 1994 Mar 11;236(5):1271–1276. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(94)90055-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger L., Westhof E., Michel F. Function of P11, a tertiary base pairing in self-splicing introns of subgroup IA. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1153–1164. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90925-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James B. D., Olsen G. J., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic comparative analysis of RNA secondary structure. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:227–239. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LaGrandeur T. E., Hüttenhofer A., Noller H. F., Pace N. R. Phylogenetic comparative chemical footprint analysis of the interaction between ribonuclease P RNA and tRNA. EMBO J. 1994 Sep 1;13(17):3945–3952. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N., Olsen G. J., Maidak B. L., McCaughey M. J., Overbeek R., Macke T. J., Marsh T. L., Woese C. R. The ribosomal database project. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3021–3023. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Major F., Turcotte M., Gautheret D., Lapalme G., Fillion E., Cedergren R. The combination of symbolic and numerical computation for three-dimensional modeling of RNA. Science. 1991 Sep 13;253(5025):1255–1260. doi: 10.1126/science.1716375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel F., Westhof E. Modelling of the three-dimensional architecture of group I catalytic introns based on comparative sequence analysis. J Mol Biol. 1990 Dec 5;216(3):585–610. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90386-Z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace N. R., Brown J. W. Evolutionary perspective on the structure and function of ribonuclease P, a ribozyme. J Bacteriol. 1995 Apr;177(8):1919–1928. doi: 10.1128/jb.177.8.1919-1928.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pley H. W., Flaherty K. M., McKay D. B. Model for an RNA tertiary interaction from the structure of an intermolecular complex between a GAAA tetraloop and an RNA helix. Nature. 1994 Nov 3;372(6501):111–113. doi: 10.1038/372111a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SantaLucia J., Jr, Turner D. H. Structure of (rGGCGAGCC)2 in solution from NMR and restrained molecular dynamics. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12612–12623. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torsvik V., Goksøyr J., Daae F. L. High diversity in DNA of soil bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Mar;56(3):782–787. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.3.782-787.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Altman S. Three-dimensional working model of M1 RNA, the catalytic RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 May 24;91(11):5133–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.11.5133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]