Abstract
Consistent with their postulated origin from endosymbiotic cyanobacteria, chloroplasts of plants and algae have ribosomes whose component RNAs and proteins are strikingly similar to those of eubacteria. Comparison of the secondary structures of 16S rRNAs of chloroplasts and bacteria has been particularly useful in identifying highly conserved regions likely to have essential functions. Comparative analysis of ribosomal protein sequences may likewise prove valuable in determining their roles in protein synthesis. This review is concerned primarily with the RNAs and proteins that constitute the chloroplast ribosome, the genes that encode these components, and their expression. It begins with an overview of chloroplast genome structure in land plants and algae and then presents a brief comparison of chloroplast and prokaryotic protein-synthesizing systems and a more detailed analysis of chloroplast rRNAs and ribosomal proteins. A description of the synthesis and assembly of chloroplast ribosomes follows. The review concludes with discussion of whether chloroplast protein synthesis is essential for cell survival.
Full text
PDF
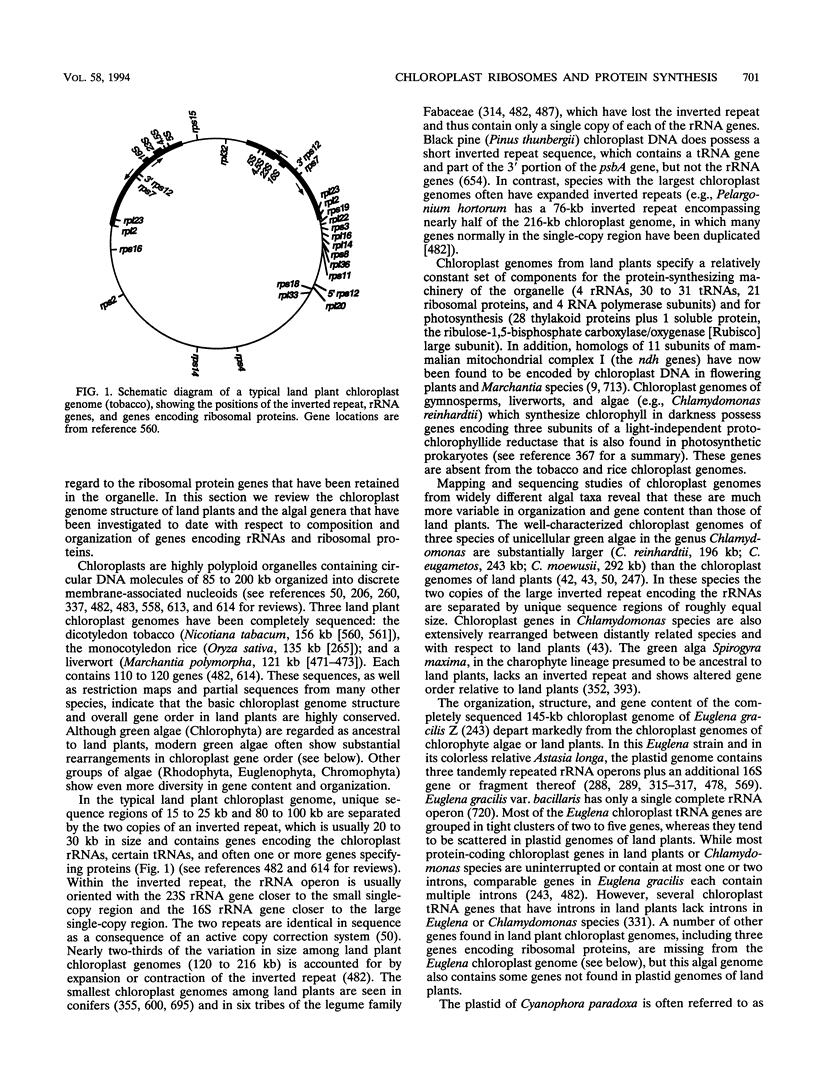





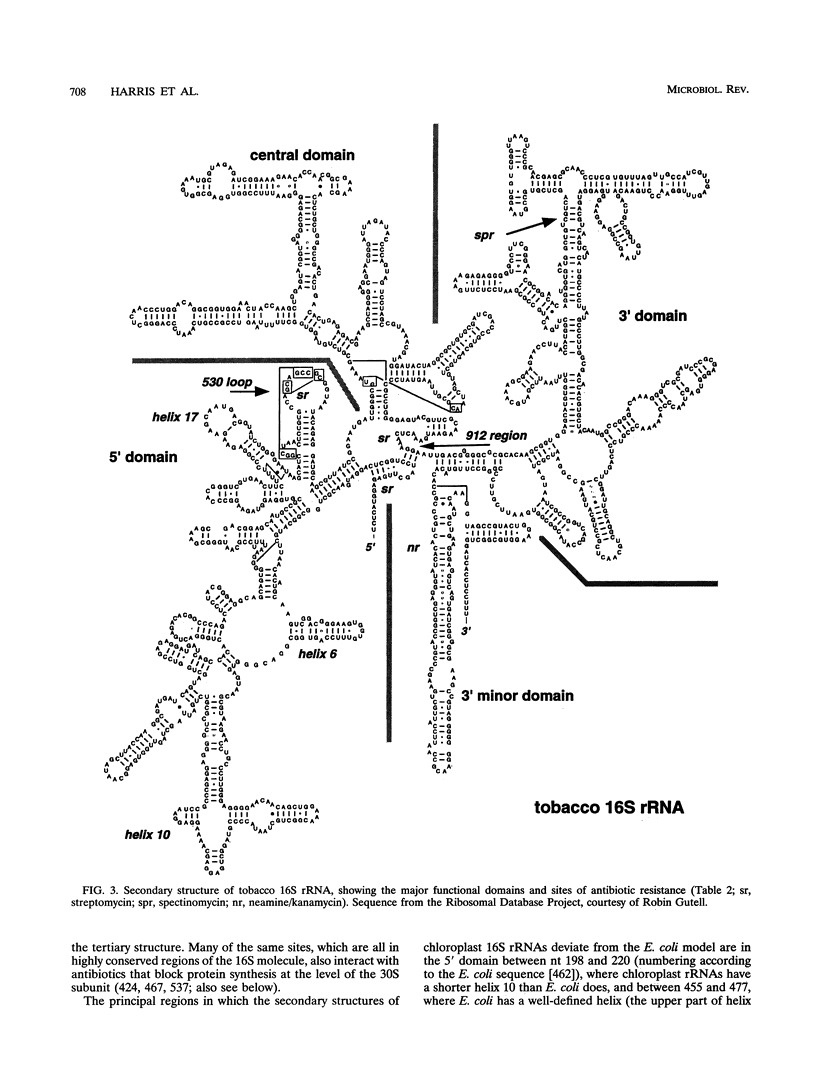

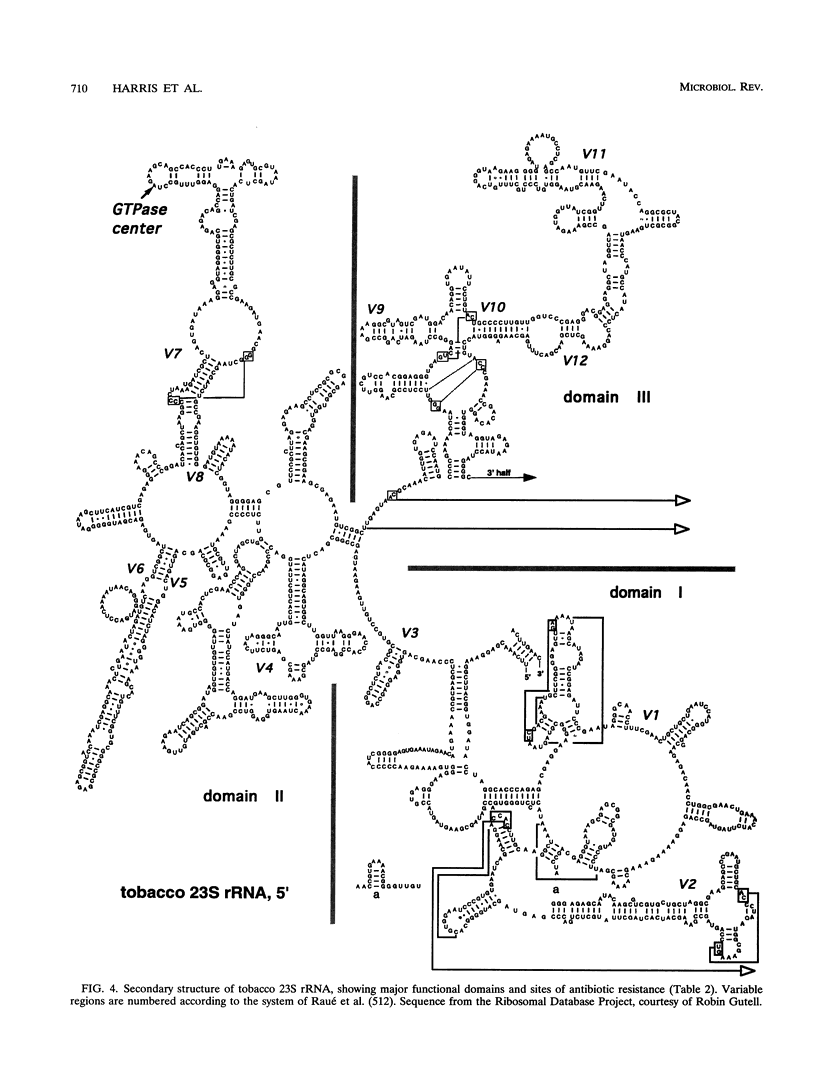


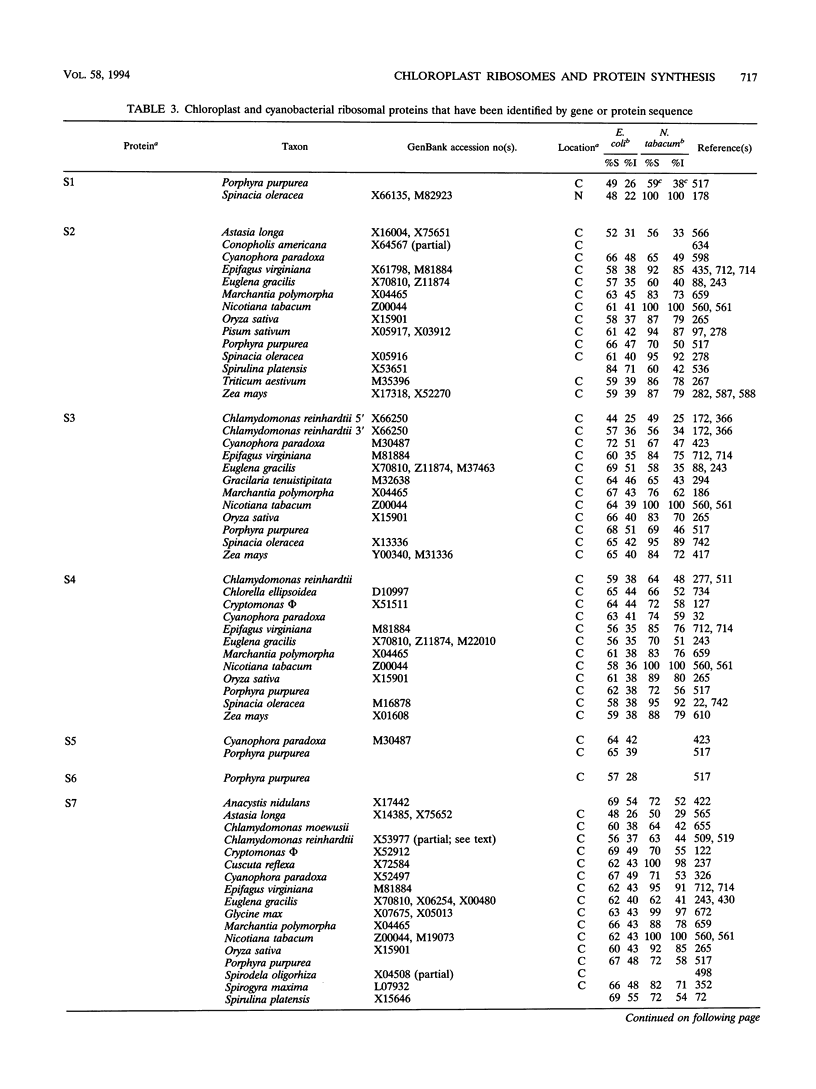
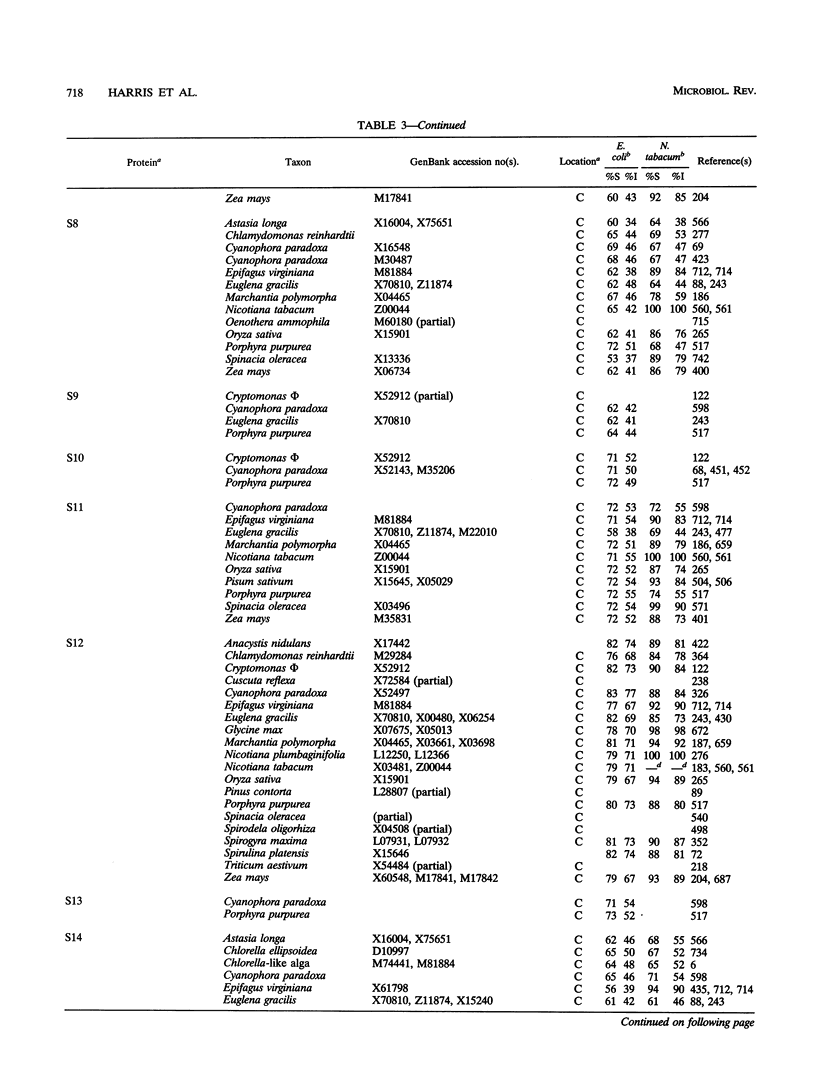
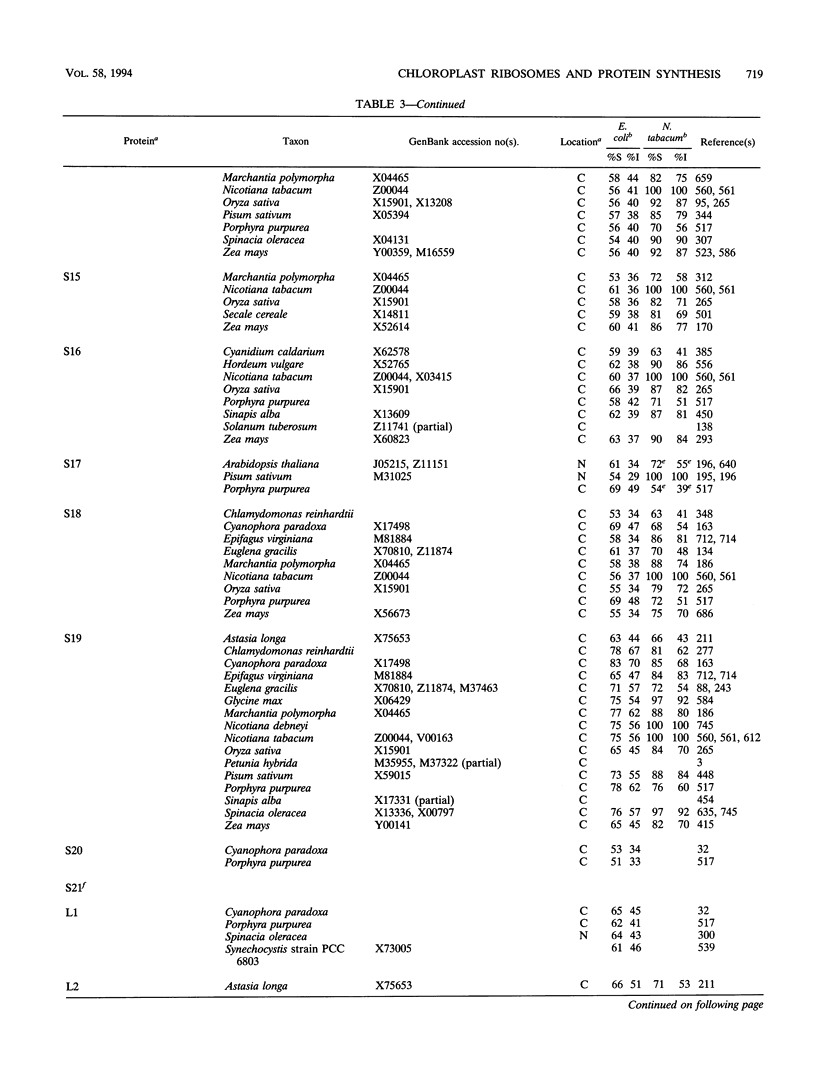
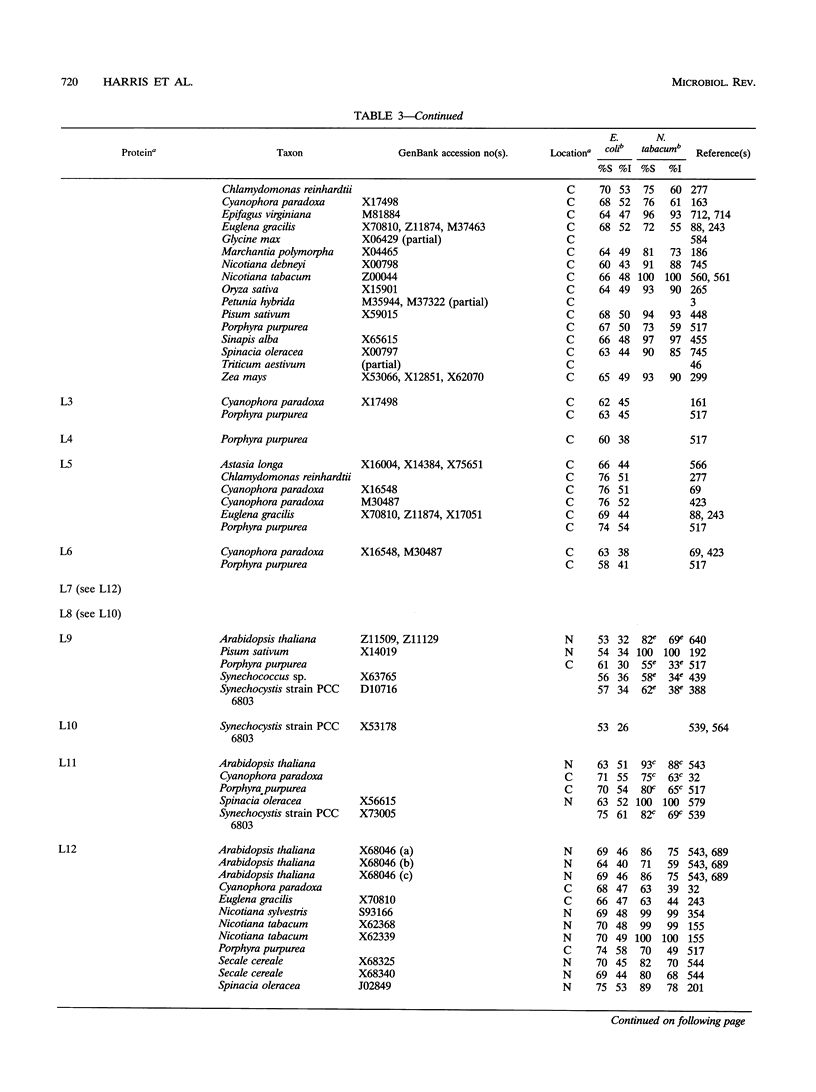































Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akkaya M. S., Breitenberger C. A. Light regulation of protein synthesis factor EF-G in pea chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Dec;20(5):791–800. doi: 10.1007/BF00027150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akkaya M. S., Welcsh P. L., Wolfe M. A., Duerr B. K., Becktel W. J., Breitenberger C. A. Purification and N-terminal sequence analysis of pea chloroplast protein synthesis factor EF-G. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1994 Jan;308(1):109–117. doi: 10.1006/abbi.1994.1016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich J., Cherney B. W., Merlin E., Christopherson L. The role of insertions/deletions in the evolution of the intergenic region between psbA and trnH in the chloroplast genome. Curr Genet. 1988 Aug;14(2):137–146. doi: 10.1007/BF00569337. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alksne L. E., Anthony R. A., Liebman S. W., Warner J. R. An accuracy center in the ribosome conserved over 2 billion years. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 15;90(20):9538–9541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.20.9538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allen J. F. Control of gene expression by redox potential and the requirement for chloroplast and mitochondrial genomes. J Theor Biol. 1993 Dec 21;165(4):609–631. doi: 10.1006/jtbi.1993.1210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson D. I., Andersson S. G., Kurland C. G. Functional interactions between mutated forms of ribosomal proteins S4, S5 and S12. Biochimie. 1986 May;68(5):705–713. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(86)80164-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arizmendi J. M., Runswick M. J., Skehel J. M., Walker J. E. NADH: ubiquinone oxidoreductase from bovine heart mitochondria. A fourth nuclear encoded subunit with a homologue encoded in chloroplast genomes. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 27;301(3):237–242. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80248-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audren H., Bisanz-Seyer C., Briat J. F., Mache R. Structure and transcription of the 5S rRNA gene from spinach chloroplasts. Curr Genet. 1987;12(4):263–269. doi: 10.1007/BF00435288. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audren H., Mache R. Nucleotide sequence of the spinach chloroplast 4.5S ribosomal RNA gene and of its 5' flanking region including the 3' end of the 23S rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9533–9533. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeza L., Bertrand A., Mache R., Lerbs-Mache S. Characterization of a protein binding sequence in the promoter region of the 16S rRNA gene of the spinach chloroplast genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 11;19(13):3577–3581. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.13.3577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldauf S. L., Manhart J. R., Palmer J. D. Different fates of the chloroplast tufA gene following its transfer to the nucleus in green algae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jul;87(14):5317–5321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.14.5317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldauf S. L., Palmer J. D. Evolutionary transfer of the chloroplast tufA gene to the nucleus. Nature. 1990 Mar 15;344(6263):262–265. doi: 10.1038/344262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barkan A. Nuclear Mutants of Maize with Defects in Chloroplast Polysome Assembly Have Altered Chloroplast RNA Metabolism. Plant Cell. 1993 Apr;5(4):389–402. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.4.389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch M. Correlation of chloroplast and bacterial ribosomal proteins by cross-reactions of antibodies specific to purified Escherichia coli ribosomal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 10;260(1):237–241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartsch M., Kimura M., Subramanian A. R. Purification, primary structure, and homology relationships of a chloroplast ribosomal protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6871–6875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu M. K., Wilson H. J. Mercury risk from teeth. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):109–109. doi: 10.1038/349109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendich A. J. Why do chloroplasts and mitochondria contain so many copies of their genome? Bioessays. 1987 Jun;6(6):279–282. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benzinger E. A., Hepburn A. G. The sequence of the chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA gene of soybean (Glycine max Merr.). Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10124–10124. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berends Sexton T., Jones J. T., Mullet J. E. Sequence and transcriptional analysis of the barley ctDNA region upstream of psbD-psbC encoding trnK(UUU), rps16, trnQ(UUG), psbK, psbI, and trnS(GCU). Curr Genet. 1990 May;17(5):445–454. doi: 10.1007/BF00334526. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsland K. J., Haselkorn R. Evolutionary relationships among eubacteria, cyanobacteria, and chloroplasts: evidence from the rpoC1 gene of Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(11):3446–3455. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.11.3446-3455.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin N., Claesens F., Pahverk H., Ehrenberg M. Kinetic properties of Escherichia coli ribosomes with altered forms of S12. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):1011–1027. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90466-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin N., Richter A. A., Ehrenberg M., Dahlberg A. E., Kurland C. G. Ribosomal RNA and protein mutants resistant to spectinomycin. EMBO J. 1990 Mar;9(3):735–739. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08167.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisanz-Seyer C., Mache R. Organization and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the plastid-specific S22 ribosomal protein from spinach. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):337–341. doi: 10.1007/BF00034960. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blamire J., Flechtner V. R., Sager R. Regulation of nuclear DNA replication by thechloroplast in Chlamydomonas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2867–2871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blowers A. D., Klein U., Ellmore G. S., Bogorad L. Functional in vivo analyses of the 3' flanking sequences of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast rbcL and psaB genes. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Apr;238(3):339–349. doi: 10.1007/BF00291992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonen L., Doolittle W. F., Fox G. E. Cyanobacterial evolution: results of 16S ribosomal ribonucleic acid sequence analyses. Can J Biochem. 1979 Jun;57(6):879–888. doi: 10.1139/o79-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonham-Smith P. C., Bourque D. P. Translation of chloroplast-encoded mRNA: potential initiation and termination signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):2057–2080. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.2057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonny C., Montandon P. E., Marc-Martin S., Stutz E. Analysis of streptomycin-resistance of Escherichia coli mutants. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Jun 13;1089(2):213–219. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(91)90010-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borbely G., Simoncsits A. 3'-Terminal conserved loops of 16S rRNAs from the cyanobacterium Synechococcus AN PCC 6301 and maize chloroplast differ only in two bases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1981 Aug 14;101(3):846–852. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(81)91827-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boudreau E., Otis C., Turmel M. Conserved gene clusters in the highly rearranged chloroplast genomes of Chlamydomonas moewusii and Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Feb;24(4):585–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00023556. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Barker R. F., Dyer T. A. In wheat ctDNA, segments of ribosomal protein genes are dispersed repeats, probably conserved by nonreciprocal recombination. Curr Genet. 1988 Aug;14(2):127–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00569336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowman C. M., Dyer T. A. 4.5S ribonucleic acid, a novel ribosome component in the chloroplasts of flowering plants. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):605–613. doi: 10.1042/bj1830605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Chloroplast transformation in Chlamydomonas. Methods Enzymol. 1993;217:510–536. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(93)17087-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breidenbach E., Leu S., Michaels A., Boschetti A. Synthesis of EF-Tu and distribution of its mRNA between stroma and thylakoids during the cell cycle of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Apr 6;1048(2-3):209–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90058-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitenberger C. A., Graves M. C., Spremulli L. L. Evidence for the nuclear location of the gene for chloroplast elongation factor G. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Apr 15;194(1):265–270. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90617-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitenberger C. A., Spremulli L. L. Purification of Euglena gracilis chloroplast elongation factor G and comparison with other prokaryotic and eukaryotic translocases. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 25;255(20):9814–9820. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briat J. F., Dron M., Loiseaux S., Mache R. Structure and transcription of the spinach chloroplast rDNA leader region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6865–6878. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Atmadja J., Stiege W., Schüler D. A detailed model of the three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA in situ in the 30 S subunit. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jan 5;199(1):115–136. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R. RNA-protein interactions in the Escherichia coli ribosome. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):927–936. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90134-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R., Stiege W. Structure and function of ribosomal RNA. Biochem J. 1985 Jul 1;229(1):1–17. doi: 10.1042/bj2290001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brimacombe R. Structure-function correlations (and discrepancies) in the 16S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli. Biochimie. 1992 Apr;74(4):319–326. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(92)90109-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Britschgi T. B., Giovannoni S. J. Phylogenetic analysis of a natural marine bacterioplankton population by rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jun;57(6):1707–1713. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.6.1707-1713.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):201–204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Dull T. J., Sleeter D. D., Noller H. F. Gene organization and primary structure of a ribosomal RNA operon from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1981 May 15;148(2):107–127. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90508-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brosius J., Palmer M. L., Kennedy P. J., Noller H. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4801–4805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunel C., Romby P., Westhof E., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Three-dimensional model of Escherichia coli ribosomal 5 S RNA as deduced from structure probing in solution and computer modeling. J Mol Biol. 1991 Sep 5;221(1):293–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)80220-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. A., Schluchter W. M., Stirewalt V. L. Ferredoxin and ribosomal protein S10 are encoded on the cyanelle genome of Cyanophora paradoxa. Gene. 1991 Feb 15;98(2):169–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90170-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. A., Stirewalt V. L. The cyanelle genome of Cyanophora paradoxa encodes ribosomal proteins not encoded by the chloroplasts genomes of higher plants. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80026-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubunenko M. G., Schmidt J., Subramanian A. R. Protein substitution in chloroplast ribosome evolution. A eukaryotic cytosolic protein has replaced its organelle homologue (L23) in spinach. J Mol Biol. 1994 Jul 1;240(1):28–41. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bubunenko M. G., Subramanian A. R. Recognition of novel and divergent higher plant chloroplast ribosomal proteins by Escherichia coli ribosome during in vivo assembly. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jul 8;269(27):18223–18231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buttarelli F. R., Calogero R. A., Tiboni O., Gualerzi C. O., Pon C. L. Characterization of the str operon genes from Spirulina platensis and their evolutionary relationship to those of other prokaryotes. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):97–104. doi: 10.1007/BF00330947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bömmer D., Haberhausen G., Zetsche K. A large deletion in the plastid DNA of the holoparasitic flowering plant Cuscuta reflexa concerning two ribosomal proteins (rpl2, rpl23), one transfer RNA (trnI) and an ORF 2280 homologue. Curr Genet. 1993 Jul-Aug;24(1-2):171–176. doi: 10.1007/BF00324682. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capel M. S., Bourque D. P. Characterization of Nicotiana tabacum chloroplast and cytoplasmic ribosomal proteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7746–7755. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carol P., Li Y. F., Mache R. Conservation and evolution of the nucleus-encoded and chloroplast-specific ribosomal proteins in pea and spinach. Gene. 1991 Jul 22;103(2):139–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90266-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carol P., Rozier C., Lazaro E., Ballesta J. P., Mache R. Erythromycin and 5S rRNA binding properties of the spinach chloroplast ribosomal protein CL22. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Feb 11;21(3):635–639. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.3.635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cedergren R., Gray M. W., Abel Y., Sankoff D. The evolutionary relationships among known life forms. J Mol Evol. 1988 Dec;28(1-2):98–112. doi: 10.1007/BF02143501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cerutti H., Jagendorf A. T. Nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene from pea (Pisum sativum L.). Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;17(1):125–126. doi: 10.1007/BF00036812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. C., Cheng M. C., Chen S. C. Characterization of the promoter of rice plastid psaA-psaB-rps14 operon and the DNA-specific binding proteins. Plant Cell Physiol. 1993 Jun;34(4):577–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X., Kindle K., Stern D. Initiation codon mutations in the Chlamydomonas chloroplast petD gene result in temperature-sensitive photosynthetic growth. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3627–3635. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06036.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Cushman J. C., Price C. A., Hallick R. B. Organization of ribosomal protein genes rpl23, rpl2, rps19, rpl22 and rps3 on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome. Curr Genet. 1988 Sep;14(3):275–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00376748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Complex RNA maturation pathway for a chloroplast ribosomal protein operon with an internal tRNA cistron. Plant Cell. 1990 Jul;2(7):659–671. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.7.659. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein operon: a new chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L5 and description of a novel organelle intron category designated group III. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7591–7608. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copertino D. W., Christopher D. A., Hallick R. B. A mixed group II/group III twintron in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal protein S3 gene: evidence for intron insertion during gene evolution. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6491–6497. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copertino D. W., Shigeoka S., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast group III twintron excision utilizing multiple 5'- and 3'-splice sites. EMBO J. 1992 Dec;11(13):5041–5050. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05611.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corry M. J., Payne P. I., Dyer T. A. The nucleotide sequence of 5 S rRNA from the blue-green alga Anacystis nidulans. FEBS Lett. 1974 Sep 15;46(1):63–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(74)80335-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cozens A. L., Walker J. E. Pea chloroplast DNA encodes homologues of Escherichia coli ribosomal subunit S2 and the beta'-subunit of RNA polymerase. Biochem J. 1986 Jun 1;236(2):453–460. doi: 10.1042/bj2360453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cseplö A., Etzold T., Schell J., Schreier P. H. Point mutations in the 23 S rRNA genes of four lincomycin resistant Nicotiana plumbaginifolia mutants could provide new selectable markers for chloroplast transformation. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):295–299. doi: 10.1007/BF00337724. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cséplö A., Eigel L., Horváth G. V., Medgyesy P., Herrmann R. G., Koop H. U. Subcellular location of lincomycin resistance in Nicotiana mutants. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):163–170. doi: 10.1007/BF00277108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui Z., Mason T. L. A single nucleotide substitution at the rib2 locus of the yeast mitochondrial gene for 21S rRNA confers resistance to erythromycin and cold-sensitive ribosome assembly. Curr Genet. 1989 Oct;16(4):273–279. doi: 10.1007/BF00422114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté J. C., Wu R. Sequence of the chloroplast rps14 gene encoding the chloroplast ribosomal protein S14 from rice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 25;17(4):1780–1780. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.4.1780. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Côté V., Mercier J. P., Lemieux C., Turmel M. The single group-I intron in the chloroplast rrnL gene of Chlamydomonas humicola encodes a site-specific DNA endonuclease (I-ChuI). Gene. 1993 Jul 15;129(1):69–76. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90697-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dabbs E. R. Mutants lacking individual ribosomal proteins as a tool to investigate ribosomal properties. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):639–645. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90043-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danon A., Mayfield S. P. Light regulated translational activators: identification of chloroplast gene specific mRNA binding proteins. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(13):3993–4001. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04974.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day A., Ellis T. H. Chloroplast DNA deletions associated with wheat plants regenerated from pollen: possible basis for maternal inheritance of chloroplasts. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):359–368. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90014-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Stasio E. A., Dahlberg A. E. Effects of mutagenesis of a conserved base-paired site near the decoding region of Escherichia coli 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Mar 5;212(1):127–133. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90309-A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney T. P., Cattolico R. A. Chloroplast ribosomal DNA organization in the chromophytic alga Olisthodiscus luteus. Curr Genet. 1989 Mar;15(3):221–229. doi: 10.1007/BF00435509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delaney T. P., Cattolico R. A. Sequence and secondary structure of chloroplast 16S rRNA from the chromophyte alga Olisthodiscus luteus, as inferred from the gene sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6328–6328. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Berns D. Phylogeny of the 5S ribosomal RNA from Synechococcus lividus II: the cyanobacterial/chloroplast 5S RNAs form a common structural class. J Mol Evol. 1984;21(4):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF02115651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andersen J., Sprouse H. M., Dudock B. The nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2801–2805. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delihas N., Andresini W., Andersen J., Berns D. Structural features unique to the 5 S ribosomal RNAs of the thermophilic cyanobacterium Synechococcus lividus II and the green plant chloroplasts. J Mol Biol. 1982 Dec 15;162(3):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90401-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux R., Loeblich A. R., 3rd, Fox G. E. Higher plant origins and the phylogeny of green algae. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jul;31(1):18–24. doi: 10.1007/BF02101788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorne A. M., Eneas-Filho J., Heizmann P., Mache R. Comparison of ribosomal proteins of chloroplast from spinach and of E. coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;193(1):129–134. doi: 10.1007/BF00327425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E. A secY homologue is found in the plastid genome of Cryptomonas phi. FEBS Lett. 1992 Feb 17;298(1):93–96. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80029-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Doolittle W. F. Complete nucleotide sequence of the 23S rRNA gene of the Cyanobacterium, Anacystis nidulans. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3373–3386. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Durnford D. G. Nucleotide sequence of the genes for ribosomal protein S4 and tRNA(Arg) from the chlorophyll c-containing alga Cryptomonas phi. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 11;18(7):1903–1903. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.7.1903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Durnford D. G. Sequence analysis of the plastid rDNA spacer region of the chlorophyll c-containing alga Cryptomonas phi. DNA Seq. 1990;1(1):55–62. doi: 10.3109/10425179009041347. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E. Eukaryote-eukaryote endosymbioses: insights from studies of a cryptomonad alga. Biosystems. 1992;28(1-3):57–68. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(92)90008-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Murphy C. A., Spencer D. F., Gray M. W. Cryptomonad algae are evolutionary chimaeras of two phylogenetically distinct unicellular eukaryotes. Nature. 1991 Mar 14;350(6314):148–151. doi: 10.1038/350148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E., Turner S. Molecular evidence for the origin of plastids from a cyanobacterium-like ancestor. J Mol Evol. 1991 Sep;33(3):267–273. doi: 10.1007/BF02100678. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglas S. E. Unusual organization of a ribosomal protein operon in the plastid genome of Cryptomonas phi: evolutionary considerations. Curr Genet. 1991 Apr;19(4):289–294. doi: 10.1007/BF00355057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douglass J., Steyn L. M. A ribosomal gene mutation in streptomycin-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis isolates. J Infect Dis. 1993 Jun;167(6):1505–1506. doi: 10.1093/infdis/167.6.1505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douthwaite S., Aagaard C. Erythromycin binding is reduced in ribosomes with conformational alterations in the 23 S rRNA peptidyl transferase loop. J Mol Biol. 1993 Aug 5;232(3):725–731. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drager R. G., Hallick R. B. A complex twintron is excised as four individual introns. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2389–2394. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drager R. G., Hallick R. B. A novel Euglena gracilis chloroplast operon encoding four ATP synthase subunits and two ribosomal proteins contains 17 introns. Curr Genet. 1993 Mar;23(3):271–280. doi: 10.1007/BF00351506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dragon F., Brakier-Gingras L. Interaction of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S7 with 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1199–1203. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dron M., Rahire M., Rochaix J. D. Sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene and its surrounding regions of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7609–7620. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dujon B. Group I introns as mobile genetic elements: facts and mechanistic speculations--a review. Gene. 1989 Oct 15;82(1):91–114. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90034-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durocher V., Gauthier A., Bellemare G., Lemieux C. An optional group I intron between the chloroplast small subunit rRNA genes of Chlamydomonas moewusii and C. eugametos. Curr Genet. 1989 Apr;15(4):277–282. doi: 10.1007/BF00447043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyer T. A., Bowman C. M. Nucleotide sequences of chloroplast 5S ribosomal ribonucleic acid in flowering plants. Biochem J. 1979 Dec 1;183(3):595–604. doi: 10.1042/bj1830595. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger F., Rochaix J. D. Characterization of the cleavage site and the recognition sequence of the I-CreI DNA endonuclease encoded by the chloroplast ribosomal intron of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Jan;236(2-3):409–414. doi: 10.1007/BF00277141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dürrenberger F., Rochaix J. D. Chloroplast ribosomal intron of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: in vitro self-splicing, DNA endonuclease activity and in vivo mobility. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3495–3501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04913.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberly S. L., Spremulli G. H., Spremulli L. L. Light induction of the Euglena chloroplast protein synthesis elongation factors: relative effectiveness of different wavelength ranges. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Mar;245(2):338–347. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90224-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards K., Kössel H. The rRNA operon from Zea mays chloroplasts: nucleotide sequence of 23S rDNA and its homology with E.coli 23S rDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2853–2869. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egebjerg J., Douthwaite S., Garrett R. A. Antibiotic interactions at the GTPase-associated centre within Escherichia coli 23S rRNA. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):607–611. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03415.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Gewely M. R., Helling R. B., Dibbits J. G. Sequence and evolution of the regions between thr rrn operons in the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis bacillaris. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;194(3):432–443. doi: 10.1007/BF00425555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhag G. A., Bourque D. P. Nuclear-encoded chloroplast ribosomal protein L27 of Nicotiana tabacum: cDNA sequence and analysis of mRNA and genes. Biochemistry. 1992 Jul 28;31(29):6856–6864. doi: 10.1021/bi00144a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhag G. A., Bourque D. P. Nuclear-encoded tobacco chloroplast ribosomal protein L24. Protein identification, sequence analysis of cDNAs encoding its cytoplasmic precursor, and mRNA and genomic DNA analysis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Oct 25;267(30):21705–21711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elhag G. A., Thomas F. J., McCreery T. P., Bourque D. P. Nuclear-encoded chloroplast ribosomal protein L12 of Nicotiana tabacum: characterization of mature protein and isolation and sequence analysis of cDNA clones encoding its cytoplasmic precursor. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):689–697. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A., Wolters J. Collection of published 5S, 5.8S and 4.5S ribosomal RNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986;14 (Suppl):r1–59. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.suppl.r1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ettayebi M., Prasad S. M., Morgan E. A. Chloramphenicol-erythromycin resistance mutations in a 23S rRNA gene of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):551–557. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.551-557.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard J. L., Johnson C., Janssen I., Löffelhardt W., Weil J. H., Kuntz M. The cyanelle genome of Cyanophora paradoxa, unlike the chloroplast genome, codes for the ribosomal L3 protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1115–1119. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard J. L., Kuntz M., Straus N. A., Weil J. H. A class-I intron in a cyanelle tRNA gene from Cyanophora paradoxa: phylogenetic relationship between cyanelles and plant chloroplasts. Gene. 1988 Nov 15;71(1):115–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90083-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evrard J. L., Kuntz M., Weil J. H. The nucleotide sequence of five ribosomal protein genes from the cyanelles of Cyanophora paradoxa: implications concerning the phylogenetic relationship between cyanelles and chloroplasts. J Mol Evol. 1990 Jan;30(1):16–25. doi: 10.1007/BF02102449. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E. The extrachromosomal DNAs of apicomplexan parasites. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1994;48:81–104. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.48.100194.000501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feagin J. E., Werner E., Gardner M. J., Williamson D. H., Wilson R. J. Homologies between the contiguous and fragmented rRNAs of the two Plasmodium falciparum extrachromosomal DNAs are limited to core sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Feb 25;20(4):879–887. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.4.879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon K., Mason T. L. Structure and regulation of a nuclear gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae that specifies MRP7, a protein of the large subunit of the mitochondrial ribosome. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;8(9):3636–3646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.9.3636. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzky B., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and map positions of the duplicated gene for chloroplast ribosomal protein S15 in Zea mays (maize). Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jun 11;18(11):3407–3407. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.11.3407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S. E., Surzycki S. J. Chloroplast RNA polymerase genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii exhibit an unusual structure and arrangement. Curr Genet. 1992 May;21(6):485–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00351659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fong S. E., Surzycki S. J. Organization and structure of plastome psbF, psbL, petG and ORF712 genes in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1992 May;21(6):527–530. doi: 10.1007/BF00351664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox L., Erion J., Tarnowski J., Spremulli L., Brot N., Weissbach H. Euglena gracilis chloroplast EF-Ts. Evidence that it is a nuclear-coded gene product. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6018–6019. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox T. D. Natural variation in the genetic code. Annu Rev Genet. 1987;21:67–91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.21.120187.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis M. A., Balint R. F., Dudock B. S. A novel variety of 4.5 S RNA from Codium fragile chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 5;262(4):1848–1854. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzetti B., Carol P., Mache R. Characterization and RNA-binding properties of a chloroplast S1-like ribosomal protein. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 25;267(27):19075–19081. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzetti B., Zhou D. X., Mache R. Structure and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the plastid CS1 ribosomal protein from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4153–4157. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freyssinet G. Determination of the site of synthesis of some Euglena cytoplasmic and chloroplast ribosomal proteins. Exp Cell Res. 1978 Aug;115(1):207–219. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(78)90418-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Edelman M., Aviv D., Galun E. The molecular basis for rRNA-dependent spectinomycin resistance in Nicotiana chloroplasts. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3233–3237. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02640.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Edelman M., Koller B., Goloubinoff P., Galun E. The enigma of the gene coding for ribosomal protein S12 in the chloroplasts of Nicotiana. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):883–898. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiwara S., Kawachi M., Inouye I., Someya J. The gene for ribosomal protein L27 is located on the plastid rather than the nuclear genome of the chlorophyll c-containing alga Pleurochrysis carterae. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Jan;24(1):253–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00040594. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuzawa H., Kohchi T., Sano T., Shirai H., Umesono K., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H., Ohyama K. Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. III. Gene organization of the large single copy region from rbcL to trnI(CAU). J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):333–351. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Nierhaus K., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXXVII. Determination of allelle types and amino acid exchanges in protein S12 of three streptomycin-resistant mutants of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Dec 6;287(2):282–291. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90377-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Puls W., Schiltz E., Reinbolt J., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. XXXI. Comparative studies on altered proteins S4 of six Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence. Mol Gen Genet. 1972;115(2):131–139. doi: 10.1007/BF00277293. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funatsu G., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. 33. Location of amino-acid replacements in protein S12 isolated from Escherichia coli mutants resistant to streptomycin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jul 28;68(3):547–550. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili S., Fromm H., Aviv D., Edelman M., Galun E. Ribosomal protein S12 as a site for streptomycin resistance in Nicotiana chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):289–292. doi: 10.1007/BF00331280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Baldauf S. L., Calie P. J., Weeden N. F., Palmer J. D. Transfer of rpl22 to the nucleus greatly preceded its loss from the chloroplast and involved the gain of an intron. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3073–3078. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07859.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Key J. L. Isolation of nuclear encoded plastid ribosomal protein cDNAs. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Feb;202(2):186–193. doi: 10.1007/BF00331635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S. Nucleotide sequences of cDNAs encoding four complete nuclear-encoded plastid ribosomal proteins. Curr Genet. 1988 Nov;14(5):519–528. doi: 10.1007/BF00521278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gantt J. S., Thompson M. D. Plant cytosolic ribosomal protein S11 and chloroplast ribosomal protein CS17. Their primary structures and evolutionary relationships. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2763–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Moore D. J., Rangachari K., Williamson D. H., Wilson R. J. Sequence and organization of large subunit rRNA genes from the extrachromosomal 35 kb circular DNA of the malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 11;21(5):1067–1071. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.5.1067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Moore D. J., Spencer D. F., Gray M. W., Williamson D. H., Wilson R. J. Organisation and expression of small subunit ribosomal RNA genes encoded by a 35-kilobase circular DNA in Plasmodium falciparum. Mol Biochem Parasitol. 1991 Sep;48(1):77–88. doi: 10.1016/0166-6851(91)90166-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. A group I intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos encodes a double-strand endonuclease that cleaves the homing site of this intron. Curr Genet. 1991 Jan;19(1):43–47. doi: 10.1007/BF00362086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier A., Turmel M., Lemieux C. Mapping of chloroplast mutations conferring resistance to antibiotics in Chlamydomonas: evidence for a novel site of streptomycin resistance in the small subunit rRNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):192–197. doi: 10.1007/BF00337710. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Subramanian A. R. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L12 is encoded in the nucleus: construction and identification of its cDNA clones and nucleotide sequence including the transit peptide. Biochemistry. 1989 Apr 18;28(8):3525–3529. doi: 10.1021/bi00434a056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Subramanian A. R. Enhanced translational utilization of chloroplast ribosomal protein mRNAs from two AUG codons shown by site-directed mutation. Biochemistry. 1990 Nov 20;29(46):10562–10566. doi: 10.1021/bi00498a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Subramanian A. R. Expression and functional assembly into bacterial ribosomes of a nuclear-encoded chloroplast ribosomal protein with a long NH2-terminal extension. FEBS Lett. 1991 Aug 19;288(1-2):72–76. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)81005-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giese K., Subramanian A. R., Larrinua I. M., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequence, promoter analysis, and linkage mapping of the unusually organized operon encoding ribosomal proteins S7 and S12 in maize chloroplast. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15251–15255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E., Hauser C. R. Translational regulation of gene expression in chloroplasts and mitochondria. Annu Rev Genet. 1994;28:71–93. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.28.120194.000443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmartin P. M., Sarokin L., Memelink J., Chua N. H. Molecular light switches for plant genes. Plant Cell. 1990 May;2(5):369–378. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.5.369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giovannoni S. J., Turner S., Olsen G. J., Barns S., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. Evolutionary relationships among cyanobacteria and green chloroplasts. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3584–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3584-3592.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gockel G., Baier S., Hachtel W. Plastid ribosomal protein genes from the nonphotosynthetic flagellate Astasia longa. Plant Physiol. 1994 Aug;105(4):1443–1444. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.4.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold J. C., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast initiation factor 2. Identification and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 5;260(28):14897–14900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golden B. L., Hoffman D. W., Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. Ribosomal protein S17: characterization of the three-dimensional structure by 1H and 15N NMR. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 30;32(47):12812–12820. doi: 10.1021/bi00210a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graack H. R., Grohmann L., Kitakawa M., Schäfer K. L., Kruft V. YmL9, a nucleus-encoded mitochondrial ribosomal protein of yeast, is homologous to L3 ribosomal proteins from all natural kingdoms and photosynthetic organelles. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jun 1;206(2):373–380. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16937.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Kössel H., Stutz E. Sequencing of 16S--23S spacer in a ribosomal RNA operon of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA reveals two tRNA genes. Nature. 1980 Aug 28;286(5776):908–910. doi: 10.1038/286908a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf L., Roux E., Stutz E., Kössel H. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene coding for the 16S rRNA: homologies to E. coli and Zea mays chloroplast 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6369–6381. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. C., Hird S. M., Dyer T. A. Nucleotide sequence of a wheat chloroplast gene encoding the proteolytic subunit of an ATP-dependent protease. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Dec;15(6):947–950. doi: 10.1007/BF00039435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W., Doolittle W. F. Has the endosymbiont hypothesis been proven? Microbiol Rev. 1982 Mar;46(1):1–42. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.1.1-42.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Organelle origins and ribosomal RNA. Biochem Cell Biol. 1988 May;66(5):325–348. doi: 10.1139/o88-042. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. Origin and evolution of organelle genomes. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Dec;3(6):884–890. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90009-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray M. W. The endosymbiont hypothesis revisited. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;141:233–357. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg B. M., Narita J. O., DeLuca-Flaherty C., Gruissem W., Rushlow K. A., Hallick R. B. Evidence for two RNA polymerase activities in Euglena gracilis chloroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14880–14887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gruissem W., Elsner-Menzel C., Latshaw S., Narita J. O., Schaffer M. A., Zurawski G. A subpopulation of spinach chloroplast tRNA genes does not require upstream promoter elements for transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7541–7556. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gualerzi C. O., Pon C. L. Initiation of mRNA translation in prokaryotes. Biochemistry. 1990 Jun 26;29(25):5881–5889. doi: 10.1021/bi00477a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R. Collection of small subunit (16S- and 16S-like) ribosomal RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3051–3054. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Fox G. E. A compilation of large subunit RNA sequences presented in a structural format. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r175–r269. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Gray M. W., Schnare M. N. A compilation of large subunit (23S and 23S-like) ribosomal RNA structures: 1993. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3055–3074. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Larsen N., Woese C. R. Lessons from an evolving rRNA: 16S and 23S rRNA structures from a comparative perspective. Microbiol Rev. 1994 Mar;58(1):10–26. doi: 10.1128/mr.58.1.10-26.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutell R. R., Weiser B., Woese C. R., Noller H. F. Comparative anatomy of 16-S-like ribosomal RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1985;32:155–216. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberhausen G., Valentin K., Zetsche K. Organization and sequence of photosynthetic genes from the plastid genome of the holoparasitic flowering plant Cuscuta reflexa. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):154–161. doi: 10.1007/BF00299148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haberhausen G., Zetsche K. Functional loss of all ndh genes in an otherwise relatively unaltered plastid genome of the holoparasitic flowering plant Cuscuta reflexa. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Jan;24(1):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00040588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Hong L., Drager R. G., Favreau M. R., Monfort A., Orsat B., Spielmann A., Stutz E. Complete sequence of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 25;21(15):3537–3544. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.15.3537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallick R. B., Lipper C., Richards O. C., Rutter W. J. Isolation of a transcriptionally active chromosome from chloroplasts of Euglena gracilis. Biochemistry. 1976 Jul 13;15(14):3039–3045. doi: 10.1021/bi00659a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada T., Ishikawa R., Niizeki M., Saito K. Pollen-derived rice calli that have large deletions in plastid DNA do not require protein synthesis in plastids for growth. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00587572. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. H., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Chloroplast ribosome biogenesis in Chlamydomonas. Selection and characterization of mutants blocked in ribosome formation. J Cell Biol. 1974 Oct;63(1):160–179. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.1.160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. H., Burkhart B. D., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Antibiotic resistance mutations in the chloroplast 16S and 23S rRNA genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: correlation of genetic and physical maps of the chloroplast genome. Genetics. 1989 Oct;123(2):281–292. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.2.281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori T., Margulies M. M. Synthesis of large subunit of ribulosebisphosphate carboxylase by thylakoid-bound polyribosomes from spinach chloroplasts. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Feb 1;244(2):630–640. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90631-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heizmann P., Doly J., Hussein Y., Nicolas P., Nigon V., Bernardi G. The chloroplast genome of bleached mutants of Euglena gracilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 May 29;653(3):412–415. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Held W. A., Ballou B., Mizushima S., Nomura M. Assembly mapping of 30 S ribosomal proteins from Escherichia coli. Further studies. J Biol Chem. 1974 May 25;249(10):3103–3111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herdenberger F., Pillay D. T., Steinmetz A. Sequence of the trnH gene and the inverted repeat structure deletion site of the broad bean chloroplast genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1297–1297. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernández Torres J., Breitenberger C. A., Spielmann A., Stutz E. Cloning and sequencing of a soybean nuclear gene coding for a chloroplast translation elongation factor EF-G. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Aug 19;1174(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90114-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herold M., Nowotny V., Dabbs E. R., Nierhaus K. H. Assembly analysis of ribosomes from a mutant lacking the assembly-initiator protein L24: lack of L24 induces temperature sensitivity. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 May;203(2):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00333967. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Bao Y., Thompson A. J., Chen Y. F. Self-splicing of the Chlamydomonas chloroplast psbA introns. Plant Cell. 1991 Oct;3(10):1095–1107. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.10.1095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrin D. L., Chen Y. F., Schmidt G. W. RNA splicing in Chlamydomonas chloroplasts. Self-splicing of 23 S preRNA. J Biol Chem. 1990 Dec 5;265(34):21134–21140. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess W. R., Prombona A., Fieder B., Subramanian A. R., Börner T. Chloroplast rps15 and the rpoB/C1/C2 gene cluster are strongly transcribed in ribosome-deficient plastids: evidence for a functioning non-chloroplast-encoded RNA polymerase. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):563–571. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05688.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrand M., Hallick R. B., Passavant C. W., Bourque D. P. Trans-splicing in chloroplasts: the rps 12 loci of Nicotiana tabacum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):372–376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiratsuka J., Shimada H., Whittier R., Ishibashi T., Sakamoto M., Mori M., Kondo C., Honji Y., Sun C. R., Meng B. Y. The complete sequence of the rice (Oryza sativa) chloroplast genome: intermolecular recombination between distinct tRNA genes accounts for a major plastid DNA inversion during the evolution of the cereals. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jun;217(2-3):185–194. doi: 10.1007/BF02464880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman D. W., Davies C., Gerchman S. E., Kycia J. H., Porter S. J., White S. W., Ramakrishnan V. Crystal structure of prokaryotic ribosomal protein L9: a bi-lobed RNA-binding protein. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 1;13(1):205–212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06250.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoot S. B., Palmer J. D. Structural rearrangements, including parallel inversions, within the chloroplast genome of Anemone and related genera. J Mol Evol. 1994 Mar;38(3):274–281. doi: 10.1007/BF00176089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Lim B. L., Osawa S. Evolution of green plants as deduced from 5S rRNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):820–823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horjales E., Aqvist J., Leijonmarck M., Tapia O. Aspects of model building applied to the C-terminal domain of the L12 protein from chloroplast ribosomes: a molecular dynamics study. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 13;148(3):954–961. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80225-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosler J. P., Wurtz E. A., Harris E. H., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Relationship between Gene Dosage and Gene Expression in the Chloroplast of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1989 Oct;91(2):648–655. doi: 10.1104/pp.91.2.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. J. Plastid origin of an extrachromosomal DNA molecule from Plasmodium, the causative agent of malaria. J Theor Biol. 1992 Sep 21;158(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(05)80718-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. M., Yang W. P., Chen C. C., Lai Y. K., Lin T. Y. A point mutation in the chloroplast rps12 gene from Nicotiana plumbaginifolia confers streptomycin resistance. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;23(1):179–183. doi: 10.1007/BF00021429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudson G. S., Mason J. G., Holton T. A., Koller B., Cox G. B., Whitfeld P. R., Bottomley W. A gene cluster in the spinach and pea chloroplast genomes encoding one CF1 and three CF0 subunits of the H+-ATP synthase complex and the ribosomal protein S2. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 20;196(2):283–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90690-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huss V. A., Giovannoni S. J. Primary structure of the chloroplast small subunit ribosomal RNA gene from Chlorella vulgaris. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9487–9487. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höglund A. S., Gray J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for ribosomal protein S2 in wheat chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10590–10590. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10590. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igloi G. L., Döry I., Kössel H. Nucleotide and derived amino acid sequence of rps2 from maize chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 11;18(3):663–663. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Wittmann H. G. Amino acid replacements in proteins S5 and S12 of two Escherichia coli revertants from streptomycin dependence to independence. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Dec 14;127(1):19–32. doi: 10.1007/BF00267779. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenni B., Stutz E. Analysis of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA: mapping of a DNA sequence complementary to 16 s rRNA outside of the three rRNA gene sets. FEBS Lett. 1979 Jun 1;102(1):95–99. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(79)80936-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenni B., Stutz E. Physical mapping of the ribosomal DNA region of Euglena gracilis chloroplast DNA. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Jul 17;88(1):127–134. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12429.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. H., Kruft V., Subramanian A. R. Identification of a plastid-specific ribosomal protein in the 30 S subunit of chloroplast ribosomes and isolation of the cDNA clone encoding its cytoplasmic precursor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):12790–12795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson C. H., Subramanian A. R. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L15, like L1, L13 and L21, is significantly larger than its E. coli homologue. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80492-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanakari S., Timmler G., von Knoblauch K., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence, map position and transcript pattern of the intron-containing gene for maize chloroplast ribosomal protein S16. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):419–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00034971. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. S., Wu M., Chiang Y. M. Cloning and characterization of chloroplast ribosomal protein-encoding genes, rpl16 and rps3, of the marine macro-algae, Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):221–226. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90183-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao J. S., Wu M. The sequence of the plastid encoded rpl22 protein in marine macroalgae, Gracilaria tenuistipitata. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3067–3067. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karabin G. D., Narita J. O., Dodd J. R., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. Nucleotide sequence polymorphism in 5 S rRNA genes and 5 S rRNAs. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):14790–14796. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A., Shimada H., Kusuda M., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequences of two tRNAAsn genes from tobacco chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Nov 11;9(21):5601–5607. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.21.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato A., Takaiwa F., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Location and nucleotide sequence of the genes for tobacco chloroplast tRNAArg (ACG) and tRNALeu(UAG). Curr Genet. 1985;9(5):405–409. doi: 10.1007/BF00421612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kavousi M., Giese K., Larrinua I. M., McLaughlin W. E., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and map positions of the duplicated gene for maize (Zea mays) chloroplast ribosomal protein L2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 25;18(14):4244–4244. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.14.4244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller M., Burkard G., Bohnert H. J., Mubumbila M., Gordon K., Steinmetz A., Heiser D., Crouse E. J., Weil J. H. Transfer RNA genes associated with the 16S and 23S rRNA genes of Euglena chloroplast DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1980 Jul 16;95(1):47–54. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(80)90702-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keus R. J., Dekker A. F., van Roon M. A., Groot G. S. The nucleotide sequences of the regions flanking the genes coding for 23S, 16S and 4.5S ribosomal RNA on chloroplast DNA from Spirodela oligorhiza. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6465–6474. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keus R. J., Roovers D. J., Dekker A. F., Groot G. S. The nucleotide sequence of the 4.5S and 5S rRNA genes and flanking regions from Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3405–3410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keus R. J., Stam N. J., Zwiers T., de Heij H. T., Groot G. S. The nucleotide sequences of the genes coding for tRNAArgUCU, tRNAArgACG and tRNAAsnGUU on Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5639–5646. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J., Mullet J. E. Ribosome-binding sites on chloroplast rbcL and psbA mRNAs and light-induced initiation of D1 translation. Plant Mol Biol. 1994 Jun;25(3):437–448. doi: 10.1007/BF00043872. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Mason H. S., Mullet J. E. Light-regulated translation of chloroplast proteins. I. Transcripts of psaA-psaB, psbA, and rbcL are associated with polysomes in dark-grown and illuminated barley seedlings. J Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;106(2):289–301. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.2.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein R. R., Mullet J. E. Light-induced transcription of chloroplast genes. psbA transcription is differentially enhanced in illuminated barley. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1895–1902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein U., De Camp J. D., Bogorad L. Two types of chloroplast gene promoters in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3453–3457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Edwards K., Kössel H. Sequencing of the 16S-23S spacer in a ribosomal RNA operon of Zea mays chloroplast DNA reveals two split tRNA genes. Cell. 1981 Jul;25(1):203–213. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90245-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohchi T., Shirai H., Fukuzawa H., Sano T., Komano T., Umesono K., Inokuchi H., Ozeki H., Ohyama K. Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. IV. Inverted repeat and small single copy regions. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):353–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90004-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohchi T., Umesono K., Ogura Y., Komine Y., Nakahigashi K., Komano T., Yamada Y., Ozeki H., Ohyama K. A nicked group II intron and trans-splicing in liverwort, Marchantia polymorpha, chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10025–10036. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koller B., Delius H. Parts of the sequence between the complete rRNA operons are repeated on either side of the extra 16 S rRNA gene in chloroplast DNA of Euglena gracilis strain Z. FEBS Lett. 1982 Apr 19;140(2):198–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80893-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo J. S., Spremulli L. L. Analysis of the translational initiation region on the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase (rbcL) messenger RNA. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7494–7500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koo J. S., Spremulli L. L. Effect of the secondary structure in the Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribulose-bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase messenger RNA on translational initiation. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7501–7508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostrzewa M., Zetsche K. Organization of plastid-encoded ATPase genes and flanking regions including homologues of infB and tsf in the thermophilic red alga Galdieria sulphuraria. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;23(1):67–76. doi: 10.1007/BF00021420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus B. L., Spremulli L. L. Chloroplast initiation factor 3 from Euglena gracilis. Identification and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4781–4784. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus B. L., Spremulli L. L. Evidence for the Nuclear Location of the Genes for Chloroplast IF-2 and IF-3 in Euglena. Plant Physiol. 1988 Dec;88(4):993–995. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.4.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraus M., Götz M., Löffelhardt W. The cyanelle str operon from Cyanophora paradoxa: sequence analysis and phylogenetic implications. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Oct;15(4):561–573. doi: 10.1007/BF00017831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhlemeier C. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression in plants. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):1–14. doi: 10.1007/978-94-011-2656-4_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuhsel M. G., Strickland R., Palmer J. D. An ancient group I intron shared by eubacteria and chloroplasts. Science. 1990 Dec 14;250(4987):1570–1573. doi: 10.1126/science.2125748. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumagai I., Pieler T., Subramanian A. R., Erdmann V. A. Nucleotide sequence and secondary structure analysis of spinach chloroplast 4.5 S RNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12924–12928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumano M., Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 23S rRNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Gene. 1983 Oct;24(2-3):219–225. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90082-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurland C. G. Translational accuracy and the fitness of bacteria. Annu Rev Genet. 1992;26:29–50. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.26.120192.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laboure A. M., Lescure A. M., Briat J. F. Evidence for a translation-mediated attenuation of a spinach chloroplast rDNA operon. Biochimie. 1988 Oct;70(10):1343–1352. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90005-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagrange T., Franzetti B., Axelos M., Mache R., Lerbs-Mache S. Structure and expression of the nuclear gene coding for the chloroplast ribosomal protein L21: developmental regulation of a housekeeping gene by alternative promoters. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Apr;13(4):2614–2622. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.4.2614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapadat M. A., Deerfield D. W., 2nd, Pedersen L. G., Spremulli L. L. Generation of potential structures for the G-domain of chloroplast EF-Tu using comparative molecular modeling. Proteins. 1990;8(3):237–250. doi: 10.1002/prot.340080306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen N. Higher order interactions in 23s rRNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 1;89(11):5044–5048. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.11.5044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Melançon P., Brakier-Gingras L. Mutations in the 915 region of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA reduce the binding of streptomycin to the ribosome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Jul 25;19(14):3973–3977. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.14.3973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehmbeck J., Stummann B. M., Henningsen K. W. Sequence of two regions of pea chloroplast DNA, one with the genes rps14, trnfM and trnG-GCC, and one with the genes trnP-UGG and trnW-CCA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3630–3630. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leijonmarck M., Liljas A., Subramanian A. R. Computed spatial homology between the L12 protein of chloroplast ribosome and 1.7 A structure of Escherichia coli L12 domain. Biochem Int. 1984 Jan;8(1):69–76. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux C., Boulanger J., Otis C., Turmel M. Nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7997–7997. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemieux C., Lee R. W. Nonreciprocal recombination between alleles of the chloroplast 23S rRNA gene in interspecific Chlamydomonas crosses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4166–4170. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4166. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerbs-Mache S. The 110-kDa polypeptide of spinach plastid DNA-dependent RNA polymerase: single-subunit enzyme or catalytic core of multimeric enzyme complexes? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jun 15;90(12):5509–5513. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.12.5509. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu S., White D., Michaels A. Cell cycle-dependent transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of chloroplast gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jul 30;1049(3):311–317. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90103-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li N, Cattolico R A. Chloroplast genome characterization in the red alga Griffithsia pacifica. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):343–351. doi: 10.1007/BF00329664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Itadani H., Sugita M., Sugiura M. cDNA cloning and sequencing of tobacco chloroplast ribosomal protein L12. FEBS Lett. 1992 Apr 6;300(3):199–202. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)80845-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligon P. J., Meyer K. G., Martin J. A., Curtis S. E. Nucleotide sequence of a 16S rRNA gene from Anabaena sp. strain PCC 7120. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4553–4553. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A. Comparative biochemistry and biophysics of ribosomal proteins. Int Rev Cytol. 1991;124:103–136. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)61525-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Q., Ma L., Burkhart W., Spremulli L. L. Isolation and characterization of cDNA clones for chloroplast translational initiation factor-3 from Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):9436–9444. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:297–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Little M. C., Hallick R. B. Chloroplast rpoA, rpoB, and rpoC genes specify at least three components of a chloroplast DNA-dependent RNA polymerase active in tRNA and mRNA transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 5;263(28):14302–14307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L-18 in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii is processed during ribosome assembly. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):588–591. doi: 10.1007/BF00330499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Chloroplast ribosomal protein gene rps12 of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Wild-type sequence, mutation to streptomycin resistance and dependence, and function in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 25;264(27):16100–16108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Huang C., Xu H. The unusual rps3-like orf712 is functionally essential and structurally conserved in Chlamydomonas. FEBS Lett. 1993 Dec 27;336(2):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80808-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu X. Q., Xu H., Huang C. Chloroplast chlB gene is required for light-independent chlorophyll accumulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;23(2):297–308. doi: 10.1007/BF00029006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou J. K., Cruz F. D., Wu M. Nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast ribosomal protein gene L14 in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3587–3587. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou J. K., Wu M., Chang C. H., Cuticchia A. J. Localization of a r-protein gene within the chloroplast DNA replication origin of Chlamydomonas. Curr Genet. 1987;11(6-7):537–541. doi: 10.1007/BF00384617. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luschnig C., Schweizer D. Nucleotide sequence of trnI(CAU) and rpl23 from Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplast genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jul 11;20(13):3511–3511. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.13.3511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lévesque M., Johnson D. A. Nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast 23S rRNA gene from alder (Alnus incana). Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Feb;18(3):601–602. doi: 10.1007/BF00040677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma L., Spremulli L. L. Immunological characterization of the complex forms of chloroplast translational initiation factor 2 from Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18356–18360. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacKay R. M., Salgado D., Bonen L., Stackebrandt E., Doolittle W. F. The 5S ribosomal RNAs of Paracoccus denitrificans and Prochloron. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2963–2970. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madsen L. H., Kreiberg J. D., Gausing K. A small gene family in barley encodes ribosomal proteins homologous to yeast YL17 and L22 from archaebacteria, eubacteria, and chloroplasts. Curr Genet. 1991 May;19(5):417–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00309605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maerz M., Wolters J., Hofmann C. J., Sitte P., Maier U. G. Plastid DNA from Pyrenomonas salina (Cryptophyceae): physical map, genes, and evolutionary implications. Curr Genet. 1992 Jan;21(1):73–81. doi: 10.1007/BF00318658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maid U., Zetsche K. A 16 kb small single-copy region separates the plastid DNA inverted repeat of the unicellular red alga Cyanidium caldarium: physical mapping of the IR-flanking regions and nucleotide sequences of the psbD-psbC, rps16, 5S rRNA and rpl21 genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Sep;19(6):1001–1010. doi: 10.1007/BF00040531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maid U., Zetsche K. Nucleotide sequence of the plastid 16S rRNA gene of the red alga Cyanidium caldarium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jul 11;18(13):3996–3996. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.13.3996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maid U., Zetsche K. Structural features of the plastid ribosomal RNA operons of two red algae: Antithamnion sp. and Cyanidium caldarium. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Apr;16(4):537–546. doi: 10.1007/BF00023420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier U. G. The four genomes of the alga Pyrenomonas salina (Cryptophyta). Biosystems. 1992;28(1-3):69–73. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(92)90009-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makosky P. C., Dahlberg A. E. Spectinomycin resistance at site 1192 in 16S ribosomal RNA of E. coli: an analysis of three mutants. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):885–889. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90216-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malakhov M. P., Wada H., Los D. A., Sakamoto T., Murata N. Structure of a cyanobacterial gene encoding the 50S ribosomal protein L9. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;21(5):913–918. doi: 10.1007/BF00027122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manhart J. R., Palmer J. D. The gain of two chloroplast tRNA introns marks the green algal ancestors of land plants. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):268–270. doi: 10.1038/345268a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manzara T., Hallick R. B. Nucleotide sequence of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein L20. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3927–3927. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann-Mulisch U., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and linkage map position of the genes for ribosomal proteins L14 and S8 in the maize chloroplast genome. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):507–514. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13728.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann-Mulisch U., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence of maize chloroplast rpS11 with conserved amino acid sequence between eukaryotes, bacteria and plastids. Biochem Int. 1988 Oct;17(4):655–664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markmann-Mulisch U., von Knoblauch K., Lehmann A., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence and linkage map position of the secX gene in maize chloroplast and evidence that it encodes a protein belonging to the 50S ribosomal subunit. Biochem Int. 1987 Nov;15(5):1057–1067. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowicz Y., Loiseaux-de Goër S., Mache R. Presence of a 16S rRNA pseudogene in the bi-molecular plastid genome of the primitive brown alga Pylaiella littoralis. Evolutionary implications. Curr Genet. 1988 Dec;14(6):599–608. doi: 10.1007/BF00434086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markowicz Y., Loiseaux-de Goër S. Plastid genomes of the Rhodophyta and Chromophyta constitute a distinct lineage which differs from that of the Chlorophyta and have a composite phylogenetic origin, perhaps like that of the Euglenophyta. Curr Genet. 1991 Nov;20(5):427–430. doi: 10.1007/BF00317073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Lemieux C. Cleavage pattern of the homing endonuclease encoded by the fifth intron in the chloroplast large subunit rRNA-encoding gene of Chlamydomonas eugametos. Gene. 1991 Aug 15;104(2):241–245. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90256-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall P., Lemieux C. The I-CeuI endonuclease recognizes a sequence of 19 base pairs and preferentially cleaves the coding strand of the Chlamydomonas moewusii chloroplast large subunit rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 11;20(23):6401–6407. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.23.6401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin W., Lagrange T., Li Y. F., Bisanz-Seyer C., Mache R. Hypothesis for the evolutionary origin of the chloroplast ribosomal protein L21 of spinach. Curr Genet. 1990 Dec;18(6):553–556. doi: 10.1007/BF00327027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxwell E. S., Liu J., Shively J. M. Nucleotide sequences of Cyanophora paradoxa cellular and cyanelle-associated 5S ribosomal RNAs: the cyanelle as a potential intermediate in plastid evolution. J Mol Evol. 1986;23(4):300–304. doi: 10.1007/BF02100638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElwain K. B., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. A nuclear mutation conferring thiostrepton resistance in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii affects a chloroplast ribosomal protein related to Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L11. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Dec;241(5-6):564–572. doi: 10.1007/BF00279898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFadden G. I., Gilson P. R., Douglas S. E. The photosynthetic endosymbiont in cryptomonad cells produces both chloroplast and cytoplasmic-type ribosomes. J Cell Sci. 1994 Feb;107(Pt 2):649–657. doi: 10.1242/jcs.107.2.649. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin W. E., Larrinua I. M. The sequence of the first exon and part of the intron of the maize plastid encoded rpl 16 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5896–5896. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin W. E., Larrinua I. M. The sequence of the maize plastid encoded rpl 22 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4356–4356. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4356. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin W. E., Larrinua I. M. The sequence of the maize plastid encoded rpl 23 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):8183–8183. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.8183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin W. E., Larrinua I. M. The sequence of the maize plastid encoded rps3 locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4689–4689. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaughlin W. E., Larrinua I. M. The sequence of the maize rps19 locus and of the inverted repeat/unique region junctions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 11;15(9):3932–3932. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.9.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Lemieux C., Brakier-Gingras L. A mutation in the 530 loop of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA causes resistance to streptomycin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9631–9639. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meng B. Y., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Genes for the ribosomal proteins S12 and S7 and elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu of the cyanobacterium, Anacystis nidulans: structural homology between 16S rRNA and S7 mRNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Mar;216(1):25–30. doi: 10.1007/BF00332226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalowski C. B., Pfanzagl B., Löffelhardt W., Bohnert H. J. The cyanelle S10 spc ribosomal protein gene operon from Cyanophora paradoxa. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Nov;224(2):222–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00271555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Chloramphenicol, erythromycin, carbomycin and vernamycin B protect overlapping sites in the peptidyl transferase region of 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1987 Aug;69(8):879–884. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with functional sites in 16S ribosomal RNA. Nature. 1987 Jun 4;327(6121):389–394. doi: 10.1038/327389a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Interaction of tRNA with 23S rRNA in the ribosomal A, P, and E sites. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):585–597. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90128-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Nicolas P., Schürmann P., Stutz E. Streptomycin-resistance of Euglena gracilis chloroplasts: identification of a point mutation in the 16S rRNA gene in an invariant position. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4299–4310. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. Nucleotide sequence of a Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome region coding for the elongation factor Tu; evidence for a spliced mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 10;11(17):5877–5892. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.17.5877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Stutz E. The genes for the ribosomal proteins S12 and S7 are clustered with the gene for the EF-Tu protein on the chloroplast genome of Euglena gracilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Mar 26;12(6):2851–2859. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.6.2851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montandon P. E., Wagner R., Stutz E. E. coli ribosomes with a C912 to U base change in the 16S rRNA are streptomycin resistant. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3705–3708. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04703.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano-Roditis L., McWilliams R., Glitz D. G., Olah T. V., Perrault A. R., Cooperman B. S. Placement of dinitrophenyl-modified ribosomal proteins in totally reconstituted Escherichia coli 30 S subunits. Localization of proteins S6, S13, S16, and S18 by immune electron microscopy. J Biol Chem. 1993 Sep 5;268(25):18701–18709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moon E., Wu R. Organization and nucleotide sequence of genes at both junctions between the two inverted repeats and the large single-copy region in the rice chloroplast genome. Gene. 1988 Oct 15;70(1):1–12. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morden C. W., Wolfe K. H., dePamphilis C. W., Palmer J. D. Plastid translation and transcription genes in a non-photosynthetic plant: intact, missing and pseudo genes. EMBO J. 1991 Nov;10(11):3281–3288. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan E. A., Ikemura T., Nomura M. Identification of spacer tRNA genes in individual ribosomal RNA transcription units of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2710–2714. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougel M., Allmang C., Eyermann F., Cachia C., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Minimal 16S rRNA binding site and role of conserved nucleotides in Escherichia coli ribosomal protein S8 recognition. Eur J Biochem. 1993 Aug 1;215(3):787–792. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1993.tb18093.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mougel M., Philippe C., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. The E. coli 16S rRNA binding site of ribosomal protein S15: higher-order structure in the absence and in the presence of the protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 11;16(7):2825–2839. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.7.2825. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein P. G., Klein R. R. Chlorophyll regulates accumulation of the plastid-encoded chlorophyll apoproteins CP43 and D1 by increasing apoprotein stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(11):4038–4042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.11.4038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullet J. E., Klein R. R. Transcription and RNA stability are important determinants of higher plant chloroplast RNA levels. EMBO J. 1987 Jun;6(6):1571–1579. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02402.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mural R. J. Fundamentals of light-regulated gene expression in plants. Subcell Biochem. 1991;17:191–211. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4613-9365-8_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T., Nishikawa K., Nemoto F., Kuchino Y., Nishimura S., Miyazawa T., Yokoyama S. Codon and amino-acid specificities of a transfer RNA are both converted by a single post-transcriptional modification. Nature. 1988 Nov 10;336(6195):179–181. doi: 10.1038/336179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama Y., Matsubayashi T., Sugita M., Sugiura M. Purification of chloroplast elongation factor Tu and cDNA analysis in tobacco: the existence of two chloroplast elongation factor Tu species. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Aug;22(5):767–774. doi: 10.1007/BF00027363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano K., Harel M., Takezawa M. Prediction of three-dimensional structure of Escherichia coli ribosomal RNA. J Theor Biol. 1988 Sep 17;134(2):199–256. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(88)80202-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagano Y., Ishikawa H., Matsuno R., Sasaki Y. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the ribosomal protein L2 gene in pea chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Sep;17(3):541–545. doi: 10.1007/BF00040653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neefs J. M., Van de Peer Y., De Rijk P., Chapelle S., De Wachter R. Compilation of small ribosomal subunit RNA structures. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Jul 1;21(13):3025–3049. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.13.3025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuhaus H., Scholz A., Link G. Structure and expression of a split chloroplast gene from mustard (Sinapis alba): ribosomal protein gene rps16 reveals unusual transcriptional features and complex RNA maturation. Curr Genet. 1989 Jan;15(1):63–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00445753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann-Spallart C., Brandtner M., Kraus M., Jakowitsch J., Bayer M. G., Maier T. L., Schenk H. E., Löffelhardt W. The petFI gene encoding ferredoxin I is located close to the str operon on the cyanelle genome of Cyanophora paradoxa. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jul 30;268(1):55–58. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80971-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neumann-Spallart C., Jakowitsch J., Kraus M., Brandtner M., Bohnert H. J., Löffelhardt W. rps10, unreported for plastid DNAs, is located on the cyanelle genome of Cyanophora paradoxa and is cotranscribed with the str operon genes. Curr Genet. 1991 Apr;19(4):313–315. doi: 10.1007/BF00355061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newman S. M., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W., Randolph-Anderson B. L., Johnson A. M., Harris E. H. Transformation of chloroplast ribosomal RNA genes in Chlamydomonas: molecular and genetic characterization of integration events. Genetics. 1990 Dec;126(4):875–888. doi: 10.1093/genetics/126.4.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., Link G. Nucleotide sequence of the mustard chloroplast genes trnH and rps19'. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Feb 25;18(4):1051–1051. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.4.1051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickelsen J., Link G. The 54 kDa RNA-binding protein from mustard chloroplasts mediates endonucleolytic transcript 3' end formation in vitro. Plant J. 1993 Apr;3(4):537–544. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.03040537.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickoloff J. A., Christopher D. A., Drager R. G., Hallick R. B. Nucleotide sequence of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genes for isoleucine, phenylalanine and cysteine transfer RNAs and ribosomal protein S14. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4882–4882. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4882. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H. Structure, assembly, and function of ribosomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1982;97:81–155. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68318-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nierhaus K. H. The assembly of prokaryotic ribosomes. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):739–755. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90054-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi K., Müller M., Schnier J. Spontaneous missense mutations in the rplX gene for ribosomal protein L24 from Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Oct;169(10):4854–4856. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.10.4854-4856.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Peptidyl transferase: protein, ribonucleoprotein, or RNA? J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(17):5297–5300. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.17.5297-5300.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Ribosomal RNA and translation. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:191–227. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.001203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F. Structure of ribosomal RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:119–162. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Connor M., Göringer H. U., Dahlberg A. E. A ribosomal ambiguity mutation in the 530 loop of E. coli 16S rRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Aug 25;20(16):4221–4227. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.16.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill C., Horváth G. V., Horváth E., Dix P. J., Medgyesy P. Chloroplast transformation in plants: polyethylene glycol (PEG) treatment of protoplasts is an alternative to biolistic delivery systems. Plant J. 1993 May;3(5):729–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogihara Y., Terachi T., Sasakuma T. Intramolecular recombination of chloroplast genome mediated by short direct-repeat sequences in wheat species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8573–8577. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohyama K., Fukuzawa H., Kohchi T., Sano T., Sano S., Shirai H., Umesono K., Shiki Y., Takeuchi M., Chang Z. Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. I. Cloning and gene identification. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):281–298. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90001-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oleinikov A. V., Perroud B., Wang B., Traut R. R. Structural and functional domains of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L7/L12. The hinge region is required for activity. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 15;268(2):917–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson M. O., Isaksson L. A. Analysis of rpsD mutations in Escherichia coli. I. Comparison of mutants with various alterations in ribosomal protein S4. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 1;169(3):251–257. doi: 10.1007/BF00382271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Gray P. W., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. I. The location of transfer RNA, 5 S, 16 S, and 23 S ribosomal RNA genes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10991–10996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast transfer RNA transcription units. II. Nucleotide sequence analysis of a tRNAVal-tRNAAsn-tRNAArg-tRNALeu gene cluster. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3265–3275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orozco E. M., Jr, Rushlow K. E., Dodd J. R., Hallick R. B. Euglena gracilis chloroplast ribosomal RNA transcription units. II. Nucleotide sequence homology between the 16 S--23 S ribosomal RNA spacer and the 16 S ribosomal RNA leader regions. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 25;255(22):10997–11003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa S., Jukes T. H., Watanabe K., Muto A. Recent evidence for evolution of the genetic code. Microbiol Rev. 1992 Mar;56(1):229–264. doi: 10.1128/mr.56.1.229-264.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osswald M., Greuer B., Brimacombe R. Localization of a series of RNA-protein cross-link sites in the 23S and 5S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli, induced by treatment of 50S subunits with three different bifunctional reagents. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6755–6760. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D. Green ancestry of malarial parasites? Curr Biol. 1992 Jun;2(6):318–320. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90887-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmer J. D., Thompson W. F. Chloroplast DNA rearrangements are more frequent when a large inverted repeat sequence is lost. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):537–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90170-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzinger H., Guillemaut P., Weil J. H., Pillay D. T. Adjustment of the tRNA population to the codon usage in chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1377–1386. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfitzinger H., Weil J. H., Pillay D. T., Guillemaut P. Codon recognition mechanisms in plant chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 May;14(5):805–814. doi: 10.1007/BF00016513. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phua S. H., Srinivasa B. R., Subramanian A. R. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L13 is encoded in the nucleus and is considerably larger than its bacterial homologue. Construction, immunoisolation, and nucleotide sequence (including transit peptide) its cDNA clone from an angiosperm. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):1968–1971. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Digweed M., Bartsch M., Erdmann V. A. Comparative structural analysis of cytoplasmic and chloroplastic 5S rRNA from spinach. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 11;11(3):591–604. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.3.591. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieler T., Erdmann V. A., Digweed M., Delihas N. Size heterogeneity in Spinacia oleracea (spinach) chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6579–6580. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinard R., Payant C., Melançon P., Brakier-Gingras L. The 5' proximal helix of 16S rRNA is involved in the binding of streptomycin to the ribosome. FASEB J. 1993 Jan;7(1):173–176. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.7.1.7678560. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posno M., Verweij W. R., Dekker I. C., de Waard P. M., Groot G. S. The genes encoding chloroplast ribosomal proteins S7 and S12 are located in the inverted repeat of Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplast DNA. Curr Genet. 1986;11(1):25–34. doi: 10.1007/BF00389422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Posno M., van Vliet A., Groot G. S. The gene for Spirodela oligorhiza chloroplast ribosomal protein homologous to E. coli ribosomal protein L16 is split by a large intron near its 5' end: structure and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 25;14(8):3181–3195. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.8.3181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Changchien L. M., Craven G. R., Noller H. F. Probing the assembly of the 3' major domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA. Quaternary interactions involving ribosomal proteins S7, S9 and S19. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):309–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90243-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers T., Stern S., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. Probing the assembly of the 3' major domain of 16 S rRNA. Interactions involving ribosomal proteins S2, S3, S10, S13 and S14. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jun 20;201(4):697–716. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90468-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purton S., Gray J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for ribosomal protein L36 in pea chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 11;15(21):9080–9080. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.21.9080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purton S., Gray J. C. Nucleotide sequence of the gene for ribosomal protein S11 in pea chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1873–1873. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1873. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purton S., Gray J. C. The plastid rpoA gene encoding a protein homologous to the bacterial RNA polymerase alpha subunit is expressed in pea chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 May;217(1):77–84. doi: 10.1007/BF00330945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan V., White S. W. The structure of ribosomal protein S5 reveals sites of interaction with 16S rRNA. Nature. 1992 Aug 27;358(6389):768–771. doi: 10.1038/358768a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randolph-Anderson B. L., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Electrophoretic and immunological comparisons of chloroplast and prokaryotic ribosomal proteins reveal that certain families of large subunit proteins are evolutionarily conserved. J Mol Evol. 1989 Jul;29(1):68–88. doi: 10.1007/BF02106183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Klootwijk J., Musters W. Evolutionary conservation of structure and function of high molecular weight ribosomal RNA. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1988;51(2):77–129. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(88)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raué H. A., Otaka E., Suzuki K. Structural comparison of 26S rRNA-binding ribosomal protein L25 from two different yeast strains and the equivalent proteins from three eubacteria and two chloroplasts. J Mol Evol. 1989 May;28(5):418–426. doi: 10.1007/BF02603077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith M., Munholland J. A High-Resolution Gene Map of the Chloroplast Genome of the Red Alga Porphyra purpurea. Plant Cell. 1993 Apr;5(4):465–475. doi: 10.1105/tpc.5.4.465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith M., Munholland J. The ribosomal RNA repeats are non-identical and directly oriented in the chloroplast genome of the red alga Porphyra purpurea. Curr Genet. 1993 Nov;24(5):443–450. doi: 10.1007/BF00351855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith M., Munholland J. Two amino-acid biosynthetic genes are encoded on the plastid genome of the red alga Porphyra umbilicalis. Curr Genet. 1993 Jan;23(1):59–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00336751. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson D., Boynton J. E., Gillham N. W. Cotranscription of the wild-type chloroplast atpE gene encoding the CF1/CF0 epsilon subunit with the 3' half of the rps7 gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and characterization of frameshift mutations in atpE. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):155–163. doi: 10.1007/BF00261715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Darlix J. L. Composite structure of the chloroplast 23 S ribosomal RNA genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Evolutionary and functional implications. J Mol Biol. 1982 Aug 15;159(3):383–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90290-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D. Post-transcriptional steps in the expression of chloroplast genes. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:1–28. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rochaix J. D., Rahire M., Michel F. The chloroplast ribosomal intron of Chlamydomonas reinhardii codes for a polypeptide related to mitochondrial maturases. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Feb 11;13(3):975–984. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.3.975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodermel S., Orlin P., Bogorad L. The transcription termination region between two convergently-transcribed photoregulated operons in the maize plastid chromosome contains rps14, trnR (UCU) and a putative trnfM pseudogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5493–5493. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romby P., Westhof E., Toukifimpa R., Mache R., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Higher order structure of chloroplastic 5S ribosomal RNA from spinach. Biochemistry. 1988 Jun 28;27(13):4721–4730. doi: 10.1021/bi00413a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romero D. P., Arredondo J. A., Traut R. R. Identification of a region of Escherichia coli ribosomal protein L2 required for the assembly of L16 into the 50 S ribosomal subunit. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 25;265(30):18185–18191. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosendahl G., Douthwaite S. Ribosomal proteins L11 and L10.(L12)4 and the antibiotic thiostrepton interact with overlapping regions of the 23 S rRNA backbone in the ribosomal GTPase centre. J Mol Biol. 1993 Dec 20;234(4):1013–1020. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roux E., Graf L., Stutz E. Nucleotide sequence of a 'truncated rRNA operon' of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 11;11(7):1957–1968. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.7.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozier C., Mache R. Binding of 16S rRNA to chloroplast 30S ribosomal proteins blotted on nitrocellulose. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 11;12(19):7293–7304. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.19.7293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan P. C., Lu M., Draper D. E. Recognition of the highly conserved GTPase center of 23 S ribosomal RNA by ribosomal protein L11 and the antibiotic thiostrepton. J Mol Biol. 1991 Oct 20;221(4):1257–1268. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90932-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rydén-Aulin M., Shaoping Z., Kylsten P., Isaksson L. A. Ribosome activity and modification of 16S RNA are influenced by deletion of ribosomal protein S20. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Mar;7(6):983–992. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01190.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakamoto W., Kindle K. L., Stern D. B. In vivo analysis of Chlamydomonas chloroplast petD gene expression using stable transformation of beta-glucuronidase translational fusions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Jan 15;90(2):497–501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.2.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanangelantoni A. M., Calogero R. C., Buttarelli F. R., Gualerzi C. O., Tiboni O. Organization and nucleotide sequence of the genes for ribosomal protein S2 and elongation factor Ts in Spirulina platensis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Jan 1;54(1-3):141–145. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90272-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santer M., Santer U., Nurse K., Bakin A., Cunningham P., Zain M., O'Connell D., Ofengand J. Functional effects of a G to U base change at position 530 in a highly conserved loop of Escherichia coli 16S RNA. Biochemistry. 1993 Jun 1;32(21):5539–5547. doi: 10.1021/bi00072a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Bubunenko M., Subramanian A. R. A novel operon organization involving the genes for chorismate synthase (aromatic biosynthesis pathway) and ribosomal GTPase center proteins (L11, L1, L10, L12: rplKAJL) in cyanobacterium Synechocystis PCC 6803. J Biol Chem. 1993 Dec 25;268(36):27447–27457. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Herfurth E., Subramanian A. R. Purification and characterization of seven chloroplast ribosomal proteins: evidence that organelle ribosomal protein genes are functional and that NH2-terminal processing occurs via multiple pathways in chloroplasts. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Nov;20(3):459–465. doi: 10.1007/BF00040605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Srinivasa B., Weglöhner W., Subramanian A. R. A small novel chloroplast ribosomal protein (S31) that has no apparent counterpart in the E. coli ribosome. Biochem Mol Biol Int. 1993 Jan;29(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J., Subramanian A. R. Sequence of the cyanobacterial tRNA(w) gene in Synechocystis PCC 6803: requirement of enzymatic 3' CCA attachment to the acceptor stem. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 May 25;21(10):2519–2519. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.10.2519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M., Pichl L., Lepper M., Feierabend J. Identification of the nuclear-encoded chloroplast ribosomal protein L12 of the monocotyledonous plant Secale cereale and sequencing of two different cDNAs with strong codon bias. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1993 Mar 20;1172(3):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(93)90230-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. J., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Processing of the precursor to a chloroplast ribosomal protein made in the cytosol occurs in two steps, one of which depends on a protein made in the chloroplast. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1093–1099. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. J., Myers A. M., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Chloroplast ribosomal proteins of Chlamydomonas synthesized in the cytoplasm are made as precursors. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jun;98(6):2011–2018. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.6.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt R. J., Richardson C. B., Gillham N. W., Boynton J. E. Sites of synthesis of chloroplast ribosomal proteins in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1983 May;96(5):1451–1463. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.5.1451. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt T. M., DeLong E. F., Pace N. R. Analysis of a marine picoplankton community by 16S rRNA gene cloning and sequencing. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4371–4378. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4371-4378.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnare M. N., Yepiz-Plascencia G. M., Copertino D. W., Hallick R. B., Gray M. W. 5'- and 3'-terminal sequences of the chloroplast 16S and 23S ribosomal RNAs of Euglena gracilis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Mar 25;20(6):1421–1421. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.6.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M., Darlix J. L., Erickson J., Rochaix J. D. Sequence organization of repetitive elements in the flanking regions of the chloroplast ribosomal unit of Chlamydomonas reinhardii. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8531–8541. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schön A., Krupp G., Gough S., Berry-Lowe S., Kannangara C. G., Söll D. The RNA required in the first step of chlorophyll biosynthesis is a chloroplast glutamate tRNA. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):281–284. doi: 10.1038/322281a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimada H., Sugiura M. Fine structural features of the chloroplast genome: comparison of the sequenced chloroplast genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):983–995. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinozaki K., Ohme M., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Hayashida N., Matsubayashi T., Zaita N., Chunwongse J., Obokata J., Yamaguchi-Shinozaki K. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tobacco chloroplast genome: its gene organization and expression. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2043–2049. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04464.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shivji M. S., Li N., Cattolico R. A. Structure and organization of rhodophyte and chromophyte plastid genomes: implications for the ancestry of plastids. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(1):65–73. doi: 10.1007/BF00299138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibold C., Subramanian A. R. Cloning and characterization of the genes for ribosomal proteins L10 and L12 from Synechocystis Sp. PCC 6803: comparison of gene clustering pattern and protein sequence homology between cyanobacteria and chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):61–68. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90142-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemeister G., Buchholz C., Hachtel W. Genes for ribosomal proteins are retained on the 73 kb DNA from Astasia longa that resembles Euglena chloroplast DNA. Curr Genet. 1990 Dec;18(5):457–464. doi: 10.1007/BF00309917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemeister G., Buchholz C., Hachtel W. Genes for the plastid elongation factor Tu and ribosomal protein S7 and six tRNA genes on the 73 kb DNA from Astasia longa that resembles the chloroplast DNA of Euglena. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Feb;220(3):425–432. doi: 10.1007/BF00391749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemeister G., Hachtel W. Organization and nucleotide sequence of ribosomal RNA genes on a circular 73 kbp DNA from the colourless flagellate Astasia longa. Curr Genet. 1990 May;17(5):433–438. doi: 10.1007/BF00334524. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siemeister G., Hachtel W. Structure and expression of a gene encoding the large subunit of ribulose-1,5-bisphosphate carboxylase (rbcL) in the colourless euglenoid flagellate Astasia longa. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 May;14(5):825–833. doi: 10.1007/BF00016515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigmund C. D., Ettayebi M., Morgan E. A. Antibiotic resistance mutations in 16S and 23S ribosomal RNA genes of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4653–4663. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sijben-Müller G., Hallick R. B., Alt J., Westhoff P., Herrmann R. G. Spinach plastid genes coding for initiation factor IF-1, ribosomal protein S11 and RNA polymerase alpha-subunit. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):1029–1044. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silk G. W., Wu M. Posttranscriptional accumulation of chloroplast tufA (elongation factor gene) mRNA during chloroplast development in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Oct;23(1):87–96. doi: 10.1007/BF00021422. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu C. H., Chiang K. S., Swift H. Characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear genomes in the colorless alga Polytoma. V. Molecular structure and heterogenity of leucoplast DNA. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 25;98(2):369–391. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80125-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu C., Chiang K., Swift H. Characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear genomes in the colorless alga Polytoma. III. Ribosomal RNA cistrons of the nucleus and leucoplast. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):383–392. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siu C., Swift H., Chiang K. Characterization of cytoplasmic and nuclear genomes in the colorless alga Polytoma. II. General characterization of organelle nucleic acids. J Cell Biol. 1976 May;69(2):371–382. doi: 10.1083/jcb.69.2.371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smooker P. M., Kruft V., Subramanian A. R. A ribosomal protein is encoded in the chloroplast DNA in a lower plant but in the nucleus in angiosperms. Isolation of the spinach L21 protein and cDNA clone with transit and an unusual repeat sequence. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16699–16703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smooker P. M., Schmidt J., Subramanian A. R. The nuclear:organelle distribution of chloroplast ribosomal proteins genes. Features of a cDNA clone encoding the cytoplasmic precursor of L11. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):845–851. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. C., Jouannic S., Loiseaux-de Goër S. Sequence, proposed secondary structure, and phylogenetic analysis of the chloroplast 5S rRNA gene of the brown alga Pylaiella littoralis (L.) Kjellm. J Mol Evol. 1992 Mar;34(3):246–253. doi: 10.1007/BF00162973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville C. C., Jouannic S., Martin W. F., Kloareg B., Loiseaux-de Goër S. Secondary structure and phylogeny of the chloroplast 23S rRNA gene from the brown alga Pylaiella littoralis. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;21(5):779–787. doi: 10.1007/BF00027111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Specht T., Wolters J., Erdmann V. A. Compilation of 5S rRNA and 5S rRNA gene sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Apr 25;18 (Suppl):2215–2230. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.suppl.2215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spielmann A., Roux E., von Allmen J. M., Stutz E. The soybean chloroplast genome: complete sequence of the rps19 gene, including flanking parts containing exon 2 of rpl2 (upstream), but rpl22 (downstream). Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1199–1199. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreedharan S. P., Beck C. M., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast elongation factor Tu. Purification and initial characterization. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):3126–3131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D. J., Rodermel S. R., Bogorad L., Subramanian A. R. Co-transcription pattern of an introgressed operon in the maize chloroplast genome comprising four ATP synthase subunit genes and the ribosomal rps2. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Mar;21(6):1069–1076. doi: 10.1007/BF00023603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl D., Rodermel S. R., Subramanian A. R., Bogorad L. Nucleotide sequence of a 3.46 kb region of maize chloroplast DNA containing the gene cluster rpoC2-rps2-atpI-atpH. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):3073–3074. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanzel M., Schön A., Sprinzl M. Discrimination against misacylated tRNA by chloroplast elongation factor Tu. Eur J Biochem. 1994 Jan 15;219(1-2):435–439. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1994.tb19956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub J. M., Maliga P. Accumulation of D1 polypeptide in tobacco plastids is regulated via the untranslated region of the psbA mRNA. EMBO J. 1993 Feb;12(2):601–606. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05692.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staub J. M., Maliga P. Long regions of homologous DNA are incorporated into the tobacco plastid genome by transformation. Plant Cell. 1992 Jan;4(1):39–45. doi: 10.1105/tpc.4.1.39. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steege D. A., Graves M. C., Spremulli L. L. Euglena gracilis chloroplast small subunit rRNA. Sequence and base pairing potential of the 3' terminus, cleavage by colicin E3. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10430–10439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Changchien L. M., Craven G. R., Noller H. F. Interaction of proteins S16, S17 and S20 with 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90241-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Powers T., Changchien L. M., Noller H. F. RNA-protein interactions in 30S ribosomal subunits: folding and function of 16S rRNA. Science. 1989 May 19;244(4906):783–790. doi: 10.1126/science.2658053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern S., Weiser B., Noller H. F. Model for the three-dimensional folding of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Nov 20;204(2):447–481. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90588-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson J. K., Drager R. G., Copertino D. W., Christopher D. A., Jenkins K. P., Yepiz-Plascencia G., Hallick R. B. Intercistronic group III introns in polycistronic ribosomal protein operons of chloroplasts. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):183–192. doi: 10.1007/BF00282464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss S. H., Palmer J. D., Howe G. T., Doerksen A. H. Chloroplast genomes of two conifers lack a large inverted repeat and are extensively rearranged. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(11):3898–3902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.11.3898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter G., Kössel H. Cotranscription and processing of 23S, 4.5S and 5S rRNA in chloroplasts from Zea mays. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Oct 25;12(20):7633–7647. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.20.7633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Molecular genetics of chloroplast ribosomal proteins. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 May;18(5):177–181. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R., Steinmetz A., Bogorad L. Maize chloroplast DNA encodes a protein sequence homologous to the bacterial ribosome assembly protein S4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5277–5286. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subramanian A. R. Structure and functions of ribosomal protein S1. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1983;28:101–142. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60085-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Murayama Y., Sugiura M. Structure and differential expression of two distinct genes encoding the chloroplast elongation factor Tu in tobacco. Curr Genet. 1994 Feb;25(2):164–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00309543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita M., Sugiura M. A putative gene of tobacco chloroplast coding for ribosomal protein similar to E. coli ribosomal protein S19. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1913–1918. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura M. The chloroplast genome. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 May;19(1):149–168. doi: 10.1007/BF00015612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun E., Wu B. W., Tewari K. K. In vitro analysis of the pea chloroplast 16S rRNA gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5650–5659. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Hajdukiewicz P., Maliga P. Stable transformation of plastids in higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8526–8530. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8526. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Maliga P. High-frequency plastid transformation in tobacco by selection for a chimeric aadA gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):913–917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svab Z., Maliga P. Mutation proximal to the tRNA binding region of the Nicotiana plastid 16S rRNA confers resistance to spectinomycin. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):316–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00282483. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson P., Changchien L. M., Craven G. R., Noller H. F. Interaction of ribosomal proteins, S6, S8, S15 and S18 with the central domain of 16 S ribosomal RNA. J Mol Biol. 1988 Mar 20;200(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90242-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Kusuda M., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequence of chloroplast 4.5S rRNA from a fern, Dryopteris acuminata. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 10;10(7):2257–2260. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.7.2257. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. Nucleotide sequence of the 16S - 23S spacer region in an rRNA gene cluster from tobacco chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Apr 24;10(8):2665–2676. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.8.2665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 23-S rRNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1982 May;124(1):13–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05901.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequence of 4.5S ribosomal RNA from tobacco chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4125–4129. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takaiwa F., Sugiura M. The nucleotide sequence of chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA from a fern, Dryopteris acuminata. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5369–5373. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takemura M., Oda K., Yamato K., Ohta E., Nakamura Y., Nozato N., Akashi K., Ohyama K. Gene clusters for ribosomal proteins in the mitochondrial genome of a liverwort, Marchantia polymorpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jun 25;20(12):3199–3205. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.12.3199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Sugita M., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Genes for the eight ribosomal proteins are clustered on the chloroplast genome of tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum): similarity to the S10 and spc operons of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):6030–6034. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.6030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor F. J. An overview of the status of evolutionary cell symbiosis theories. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1987;503:1–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1987.tb40595.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor G. W., Wolfe K. H., Morden C. W., dePamphilis C. W., Palmer J. D. Lack of a functional plastid tRNA(Cys) gene is associated with loss of photosynthesis in a lineage of parasitic plants. Curr Genet. 1991 Dec;20(6):515–518. doi: 10.1007/BF00334780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas F., Massenet O., Dorne A. M., Briat J. F., Mache R. Expression of the rpl23, rpl2 and rps19 genes in spinach chloroplasts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 25;16(6):2461–2472. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.6.2461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. J., Herrin D. L. In vitro self-splicing reactions of the chloroplast group I intron Cr.LSU from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii and in vivo manipulation via gene-replacement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec 11;19(23):6611–6618. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.23.6611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson A. J., Yuan X., Kudlicki W., Herrin D. L. Cleavage and recognition pattern of a double-strand-specific endonuclease (I-creI) encoded by the chloroplast 23S rRNA intron of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Gene. 1992 Oct 1;119(2):247–251. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90278-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J., Cundliffe E. The binding of thiostrepton to 23S ribosomal RNA. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1131–1135. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90156-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson M. D., Jacks C. M., Lenvik T. R., Gantt J. S. Characterization of rps17, rp19 and rpl15: three nucleus-encoded plastid ribosomal protein genes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Mar;18(5):931–944. doi: 10.1007/BF00019207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiboni O., Di Pasquale G. Organization of genes for ribosomal proteins S7 and S12, elongation factors EF-Tu and EF-G in the cyanobacterium Spirulina platensis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Feb 27;908(2):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90050-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiller K., Eisermann A., Link G. The chloroplast transcription apparatus from mustard (Sinapis alba L.). Evidence for three different transcription factors which resemble bacterial sigma factors. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 23;198(1):93–99. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15990.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To K. Y., Lai Y. K., Feng T. Y., Chen C. C. Restriction endonuclease analysis of chloroplast DNA from streptomycin-resistant mutants of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia. Genome. 1992 Apr;35(2):220–224. doi: 10.1139/g92-033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- To K. Y., Liu C. I., Liu S. T., Chang Y. S. Detection of point mutations in the chloroplast genome by single-stranded conformation polymorphism analysis. Plant J. 1993 Jan;3(1):183–186. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-313x.1993.t01-10-00999.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. Sequence of a putative promoter region for the rRNA genes of tobacco chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 24;9(20):5399–5406. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.20.5399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohdoh N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of 16S ribosomal RNA gene from tobacco chloroplasts. Gene. 1982 Feb;17(2):213–218. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90074-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomioka N., Sugiura M. The complete nucleotide sequence of a 16S ribosomal RNA gene from a blue-green alga, Anacystis nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;191(1):46–50. doi: 10.1007/BF00330888. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonkyn J. C., Gruissem W. Differential expression of the partially duplicated chloroplast S10 ribosomal protein operon. Mol Gen Genet. 1993 Oct;241(1-2):141–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00280211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torazawa K., Hayashida N., Obokata J., Shinozaki K., Sugiura M. The 5' part of the gene for ribosomal protein S12 is located 30 kbp downstream from its 3' part in tobacco chloroplast genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Apr 11;14(7):3143–3143. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.7.3143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Troxler R. F., Zhang F., Hu J., Bogorad L. Evidence that sigma factors are components of chloroplast RNA polymerase. Plant Physiol. 1994 Feb;104(2):753–759. doi: 10.1104/pp.104.2.753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsudzuki J., Nakashima K., Tsudzuki T., Hiratsuka J., Shibata M., Wakasugi T., Sugiura M. Chloroplast DNA of black pine retains a residual inverted repeat lacking rRNA genes: nucleotide sequences of trnQ, trnK, psbA, trnI and trnH and the absence of rps16. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Mar;232(2):206–214. doi: 10.1007/BF00279998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turmel M., Boulanger J., Schnare M. N., Gray M. W., Lemieux C. Six group I introns and three internal transcribed spacers in the chloroplast large subunit ribosomal RNA gene of the green alga Chlamydomonas eugametos. J Mol Biol. 1991 Mar 20;218(2):293–311. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90713-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turmel M., Gutell R. R., Mercier J. P., Otis C., Lemieux C. Analysis of the chloroplast large subunit ribosomal RNA gene from 17 Chlamydomonas taxa. Three internal transcribed spacers and 12 group I intron insertion sites. J Mol Biol. 1993 Jul 20;232(2):446–467. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Inokuchi H., Shiki Y., Takeuchi M., Chang Z., Fukuzawa H., Kohchi T., Shirai H., Ohyama K., Ozeki H. Structure and organization of Marchantia polymorpha chloroplast genome. II. Gene organization of the large single copy region from rps'12 to atpB. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 20;203(2):299–331. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urbach E., Robertson D. L., Chisholm S. W. Multiple evolutionary origins of prochlorophytes within the cyanobacterial radiation. Nature. 1992 Jan 16;355(6357):267–270. doi: 10.1038/355267a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ursin V. M., Becker C. K., Shewmaker C. K. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a tobacco chloroplast translational elongation factor, EF-Tu. Plant Physiol. 1993 Jan;101(1):333–334. doi: 10.1104/pp.101.1.333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van de Peer Y., Neefs J. M., De Wachter R. Small ribosomal subunit RNA sequences, evolutionary relationships among different life forms, and mitochondrial origins. J Mol Evol. 1990 May;30(5):463–476. doi: 10.1007/BF02101118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Eynde H., De Baere R., De Roeck E., Van de Peer Y., Vandenberghe A., Willekens P., De Wachter R. The 5S ribosomal RNA sequences of a red algal rhodoplast and a gymnosperm chloroplast. Implications for the evolution of plastids and cyanobacteria. J Mol Evol. 1988;27(2):126–132. doi: 10.1007/BF02138372. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van den Eynde H., De Baere R., De Wachter R. Sequence and secondary structure of Porphyra umbilicalis 5S rRNA. Relevance for the evolutionary origin of red algae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 25;16(22):10919–10919. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.22.10919. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vannuffel P., Di Giambattista M., Morgan E. A., Cocito C. Identification of a single base change in ribosomal RNA leading to erythromycin resistance. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 25;267(12):8377–8382. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vera A., Matsubayashi T., Sugiura M. Active transcription from a promoter positioned within the coding region of a divergently oriented gene: the tobacco chloroplast rpl32 gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):151–156. doi: 10.1007/BF00587573. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vera A., Yokoi F., Sugiura M. The existence of pre-mature 16S rRNA species in plastid ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1993 Jul 19;327(1):29–31. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81032-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel D. W., Hartmann R. K., Bartsch M., Subramanian A. R., Kleinow W., O'Brien T. W., Pieler T., Erdmann V. A. Reconstitution of 50 S ribosomal subunits from Bacillus stearothermophilus with 5 S RNA from spinach chloroplasts and low-Mr RNA from mitochondria of Locusta migratoria and bovine liver. FEBS Lett. 1984 Apr 9;169(1):67–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80291-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Koyama K., Maki Y., Shimoi Y., Tanaka A., Tsuji H. A 5 kDa protein (SCS23) from the 30 S subunit of the spinach chloroplast ribosome. FEBS Lett. 1993 Mar 15;319(1-2):115–118. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80048-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Sako T. Primary structures of and genes for new ribosomal proteins A and B in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1987 Mar;101(3):817–820. doi: 10.1093/jb/101.3.817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walleczek J., Schüler D., Stöffler-Meilicke M., Brimacombe R., Stöffler G. A model for the spatial arrangement of the proteins in the large subunit of the Escherichia coli ribosome. EMBO J. 1988 Nov;7(11):3571–3576. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03234.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Roney W. B., Alston R. L., Spremulli L. L. Initiation complex formation on Euglena chloroplast 30S subunits in the presence of natural mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):9735–9747. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.9735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang C. C., Spremulli L. L. Chloroplast translational initiation factor 3. Purification and characterization of multiple forms from Euglena gracilis. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 15;266(26):17079–17083. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. J., Davis N. W., Gegenheimer P. Novel mechanisms for maturation of chloroplast transfer RNA precursors. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1567–1574. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S. L., Liu X. Q. The plastid genome of Cryptomonas phi encodes an hsp70-like protein, a histone-like protein, and an acyl carrier protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10783–10787. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward D. M., Weller R., Bateson M. M. 16S rRNA sequences reveal numerous uncultured microorganisms in a natural community. Nature. 1990 May 3;345(6270):63–65. doi: 10.1038/345063a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson J. C., Surzycki S. J. Extensive sequence homology in the DNA coding for elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli and the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii chloroplast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2264–2267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weglöhner W., Subramanian A. R. A heptapeptide repeat contributes to the unusual length of chloroplast ribosomal protein S18. Nucleotide sequence and map position of the rpl33-rps18 gene cluster in maize. FEBS Lett. 1991 Feb 25;279(2):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80147-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weglöhner W., Subramanian A. R. Multicopy GTPase center protein L12 of Arabidopsis chloroplast ribosome is encoded by a clustered nuclear gene family with the expressed members closely linked to tRNA(Pro) genes. J Biol Chem. 1994 Mar 11;269(10):7330–7336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weglöhner W., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence of a region of maize chloroplast DNA containing the 3' end of clpP, exon 1 of rps12 and rpl20 and their cotranscription. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):415–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00034970. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weglöhner W., Subramanian A. R. Nucleotide sequence of maize chloroplast rpl32: completing the apparent set of plastid ribosomal protein genes and their tentative operon organization. Plant Mol Biol. 1993 Feb;21(3):543–548. doi: 10.1007/BF00028811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weijland A., Parmeggiani A. Toward a model for the interaction between elongation factor Tu and the ribosome. Science. 1993 Feb 26;259(5099):1311–1314. doi: 10.1126/science.8446899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R., Bateson M. M., Heimbuch B. K., Kopczynski E. D., Ward D. M. Uncultivated cyanobacteria, Chloroflexus-like inhabitants, and spirochete-like inhabitants of a hot spring microbial mat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3964–3969. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3964-3969.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller R., Weller J. W., Ward D. M. 16S rRNA sequences of uncultivated hot spring cyanobacterial mat inhabitants retrieved as randomly primed cDNA. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Apr;57(4):1146–1151. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.4.1146-1151.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westhof E., Romby P., Romaniuk P. J., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Computer modeling from solution data of spinach chloroplast and of Xenopus laevis somatic and oocyte 5 S rRNAs. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):417–431. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90264-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wildeman A. G., Nazar R. N. Nucleotide sequence of wheat chloroplastid 4.5 S ribonucleic acid. Sequence homologies in 4.5 S RNA species. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11896–11900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson S. E., Doolittle W. F. Genes for tRNAIle and tRNAAla in the spacer between the 16S and 23S rRNA genes of a blue-green alga: strong homology to chloroplast tRNA genes and tRNA genes of the E. coli rrnD gene cluster. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 11;11(1):225–235. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.1.225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilmotte A., Van der Auwera G., De Wachter R. Structure of the 16 S ribosomal RNA of the thermophilic cyanobacterium Chlorogloeopsis HTF ('Mastigocladus laminosus HTF') strain PCC7518, and phylogenetic analysis. FEBS Lett. 1993 Feb 8;317(1-2):96–100. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)81499-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Fry M., Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Williamson D. H. Subcellular fractionation of the two organelle DNAs of malaria parasites. Curr Genet. 1992 Apr;21(4-5):405–408. doi: 10.1007/BF00351702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson R. J., Gardner M. J., Feagin J. E., Williamson D. H. Have malaria parasites three genomes? Parasitol Today. 1991 Jun;7(6):134–136. doi: 10.1016/0169-4758(91)90276-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpee C. F., Morgan R., Wrobel R. L. Loss of transfer RNA genes from the plastid 16S-23S ribosomal RNA gene spacer in a parasitic plant. Curr Genet. 1992 Apr;21(4-5):417–422. doi: 10.1007/BF00351704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpee C. F., Morgan R., Wrobel R. An aberrant plastid ribosomal RNA gene cluster in the root parasite Conopholis americana. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Jan;18(2):275–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00034955. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wimpee C. F., Wrobel R. L., Garvin D. K. A divergent plastid genome in Conopholis americana, an achlorophyllous parasitic plant. Plant Mol Biol. 1991 Jul;17(1):161–166. doi: 10.1007/BF00036822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Gupta R., Siegel R. B., Stahl D. A., Kop J., Crawford N., Brosius J., Gutell R., Hogan J. J. Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Katz-Downie D. S., Morden C. W., Palmer J. D. Evolution of the plastid ribosomal RNA operon in a nongreen parasitic plant: accelerated sequence evolution, altered promoter structure, and tRNA pseudogenes. Plant Mol Biol. 1992 Apr;18(6):1037–1048. doi: 10.1007/BF00047707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Morden C. W., Ems S. C., Palmer J. D. Rapid evolution of the plastid translational apparatus in a nonphotosynthetic plant: loss or accelerated sequence evolution of tRNA and ribosomal protein genes. J Mol Evol. 1992 Oct;35(4):304–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00161168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Morden C. W., Palmer J. D. Function and evolution of a minimal plastid genome from a nonphotosynthetic parasitic plant. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 15;89(22):10648–10652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.22.10648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe K. H., Morden C. W., Palmer J. D. Ins and outs of plastid genome evolution. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1991 Dec;1(4):523–529. doi: 10.1016/s0959-437x(05)80202-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfson R., Higgins K. G., Sears B. B. Evidence for replication slippage in the evolution of Oenothera chloroplast DNA. Mol Biol Evol. 1991 Sep;8(5):709–720. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolstenholme D. R. Animal mitochondrial DNA: structure and evolution. Int Rev Cytol. 1992;141:173–216. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock J., Moazed D., Cannon M., Davies J., Noller H. F. Interaction of antibiotics with A- and P-site-specific bases in 16S ribosomal RNA. EMBO J. 1991 Oct;10(10):3099–3103. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07863.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodson S. A., Cech T. R. Reverse self-splicing of the tetrahymena group I intron: implication for the directionality of splicing and for intron transposition. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):335–345. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90971-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H., Wower I., Zimmermann R. A. Mutagenesis of ribosomal protein S8 from Escherichia coli: expression, stability, and RNA-binding properties of S8 mutants. Biochemistry. 1993 May 11;32(18):4761–4768. doi: 10.1021/bi00069a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaguchi M., Wittmann H. G., Cábezon T., De Wilde M., Villarroel R., Herzog A., Bollen A. Cooperative control of translational fidelity by ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli. II. Localization of amino acid replacements in proteins S5 and S12 altered in double mutants resistant to neamine. Mol Gen Genet. 1975 Dec 23;142(1):35–43. doi: 10.1007/BF00268753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T. Nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast 16S rRNA gene from the unicellular green alga Chlorella ellipsoidea. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9865–9865. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T. Repetitive sequence-mediated rearrangements in Chlorella ellipsoidea chloroplast DNA: completion of nucleotide sequence of the large inverted repeat. Curr Genet. 1991 Feb;19(2):139–147. doi: 10.1007/BF00326295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Shimaji M. An intron in the 23S rRNA gene of the Chlorella chloroplasts: complete nucleotide sequence of the 23S rRNA gene. Curr Genet. 1987;11(5):347–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00378176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Shimaji M. Peculiar feature of the organization of rRNA genes of the Chlorella chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3827–3839. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamano Y., Ohyama K., Komano T. Nucleotide sequences of chloroplast 5S ribosomal RNA from cell suspension cultures of the liverworts Marchantia polymorpha and Jungermannia subulata. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jun 11;12(11):4621–4624. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.11.4621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yepiz-Plascencia G. M., Jenkins M. E., Hallick R. B. Nucleotide sequence of the Euglena gracilis chloroplast 23S rRNA gene of the rrnC operon. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 11;16(19):9340–9340. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.19.9340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yesalis C. E., 3rd, Norwood G. J., Lipson D. P., Helling D. K., Burmeister L. F., Fisher W. P. Use and costs under the Iowa capitation drug program. Health Care Financ Rev. 1981 Sep;3(1):127–136. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi F., Sugiura M. Tobacco chloroplast ribosomes contain a homologue of E. coli ribosomal protein L28. FEBS Lett. 1992 Aug 24;308(3):258–260. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(92)81287-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi F., Tanaka M., Wakasugi T., Sugiura M. The chloroplast gene for ribosomal protein CL23 is functional in tobacco. FEBS Lett. 1991 Apr 9;281(1-2):64–66. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80359-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokoi F., Vassileva A., Hayashida N., Torazawa K., Wakasugi T., Sugiura M. Chloroplast ribosomal protein L32 is encoded in the chloroplast genome. FEBS Lett. 1990 Dec 10;276(1-2):88–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80514-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Macklis R., Steitz J. A. Sequence of the 16 S-23 s spacer region in two ribosomal RNA operons of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 10;254(9):3264–3271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu W., Zhang D., Spreitzer R. J. Sequences of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii Chloroplast Genes Encoding tRNA and Ribosomal Protein L20. Plant Physiol. 1992 Oct;100(2):1079–1080. doi: 10.1104/pp.100.2.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Li Y. F., Rocipon M., Mache R. Sequence-specific interaction between S1F, a spinach nuclear factor, and a negative cis-element conserved in plastid-related genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Nov 25;267(33):23515–23519. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Mache R. Presence in the stroma of chloroplasts of a large pool of a ribosomal protein not structurally related to any Escherichia coli ribosomal protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Oct;219(1-2):204–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00261178. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou D. X., Quigley F., Massenet O., Mache R. Cotranscription of the S10- and spc-like operons in spinach chloroplasts and identification of three of their gene products. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Apr;216(2-3):439–445. doi: 10.1007/BF00334388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou X. Q., Liu W. Y., Wang M. Q. Comparative study on the evolution of chloroplast ribosomal 5S RNA of a living fossil plant, Cycas revoluta Thumb. FEBS Lett. 1988 Aug 1;235(1-2):30–34. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)81228-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Bottomley W., Whitfeld P. R. Junctions of the large single copy region and the inverted repeats in Spinacia oleracea and Nicotiana debneyi chloroplast DNA: sequence of the genes for tRNAHis and the ribosomal proteins S19 and L2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 24;12(16):6547–6558. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.16.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- dePamphilis C. W., Palmer J. D. Loss of photosynthetic and chlororespiratory genes from the plastid genome of a parasitic flowering plant. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):337–339. doi: 10.1038/348337a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Allmen J. M., Stutz E. Complete sequence of 'divided' rps12 (r-protein S12) and rps7 (r-protein S7) gene in soybean chloroplast DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 11;15(5):2387–2387. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.5.2387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Allmen J. M., Stutz E. The soybean chloroplast genome: nucleotide sequence of a region containing tRNA-Val (GAC) and 16S rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Feb 11;16(3):1200–1200. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.3.1200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


