Abstract
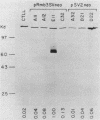
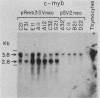
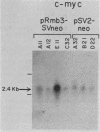
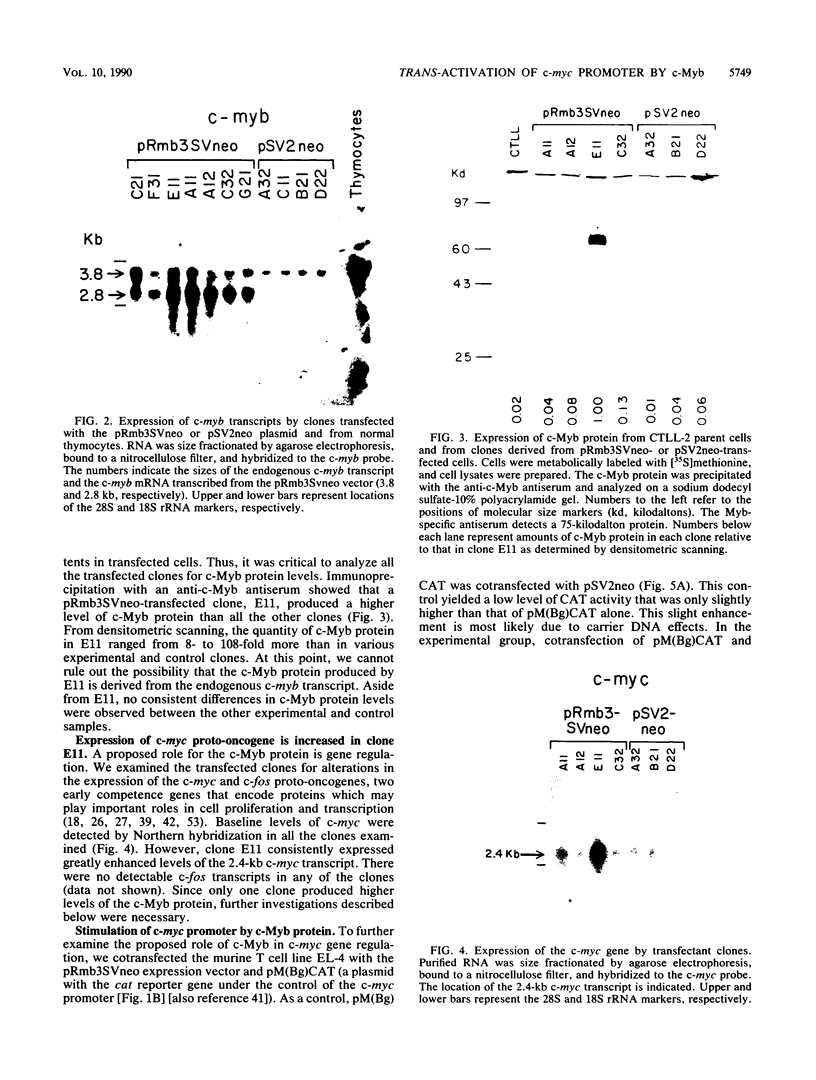
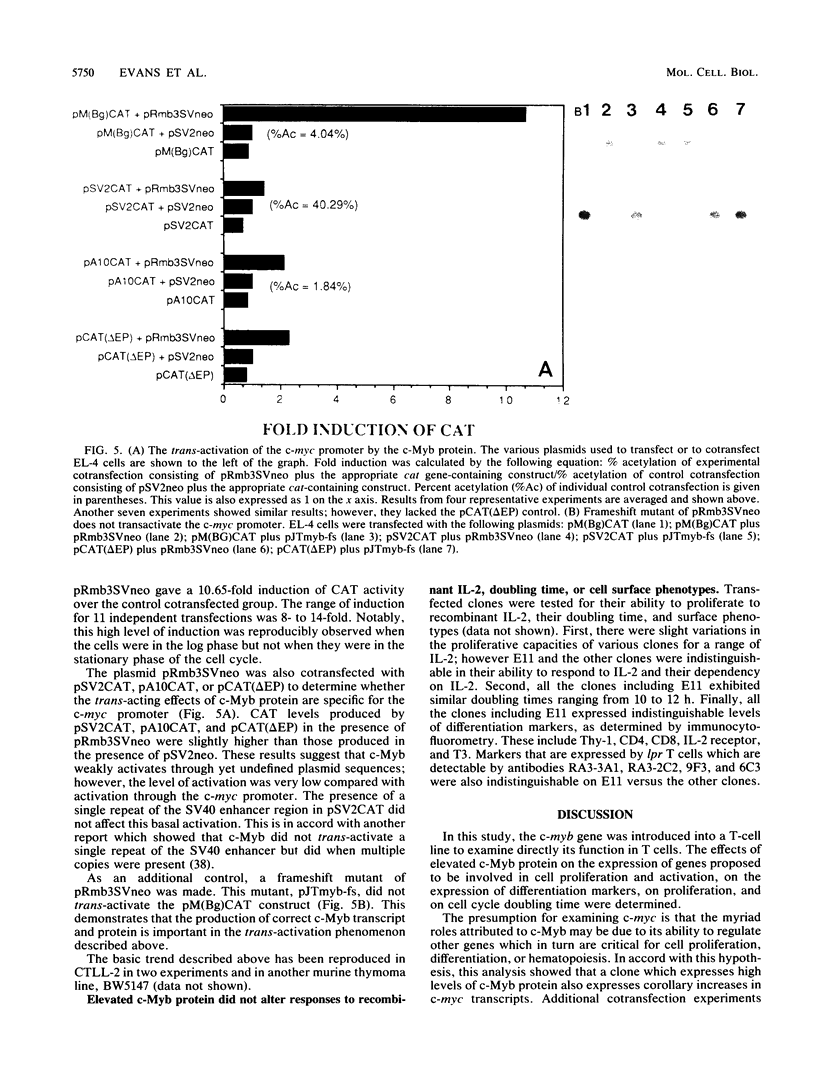
The function of c-Myb protein was revealed by transfecting an expression vector containing the entire c-Myb protein-coding sequence into the murine CTLL-2 T-cell line. Expressions of high levels of c-Myb protein did not alter the expression of several T-cell markers, c-fos mRNA expression, responses to interleukin-2, and growth characteristics of these cells. Interestingly, expression of the c-myc gene was drastically increased in this clone. Further, the c-myb expression plasmid, but not a frameshift mutant of c-myb, enhanced the expression of a hybrid construct of c-myc promoter linked to a reporter gene by 8- to 14-fold. These results demonstrate a role of c-Myb protein in c-myc gene expression.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alitalo K., Winqvist R., Lin C. C., de la Chapelle A., Schwab M., Bishop J. M. Aberrant expression of an amplified c-myb oncogene in two cell lines from a colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(14):4534–4538. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.14.4534. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bading H., Hansen J., Moelling K. Selective DNA binding of the human cellular myb protein isolated by immunoaffinity chromatography using a monoclonal antibody. Oncogene. 1987;1(4):395–401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biedenkapp H., Borgmeyer U., Sippel A. E., Klempnauer K. H. Viral myb oncogene encodes a sequence-specific DNA-binding activity. Nature. 1988 Oct 27;335(6193):835–837. doi: 10.1038/335835a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyle W. J., Lipsick J. S., Baluda M. A. Antibodies to the evolutionarily conserved amino-terminal region of the v-myb-encoded protein detect the c-myb protein in widely divergent metazoan species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4685–4689. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke M. F., Kukowska-Latallo J. F., Westin E., Smith M., Prochownik E. V. Constitutive expression of a c-myb cDNA blocks Friend murine erythroleukemia cell differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):884–892. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. A monoclonal antibody that recognizes B cells and B cell precursors in mice. J Exp Med. 1981 Feb 1;153(2):269–279. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coffman R. L., Weissman I. L. B220: a B cell-specific member of th T200 glycoprotein family. Nature. 1981 Feb 19;289(5799):681–683. doi: 10.1038/289681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colbère-Garapin F., Horodniceanu F., Kourilsky P., Garapin A. C. A new dominant hybrid selective marker for higher eukaryotic cells. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jul 25;150(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90321-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davignon J. L., Budd R. C., Ceredig R., Piguet P. F., MacDonald H. R., Cerottini J. C., Vassalli P., Izui S. Functional analysis of T cell subsets from mice bearing the lpr gene. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2423–2428. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Coker L. Z., Habbersett R. C., Treffinger J. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibody to an Ly-6-linked murine cell surface antigen: differential reactivity with T cell subpopulations and bone marrow cells. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2357–2365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dumont F. J., Habbersett R. C., Nichols E. A. A new lymphocyte surface antigen defined by a monoclonal antibody (9F3) to the T cell population expanding in MRL/Mp-lpr/lpr mice. J Immunol. 1984 Aug;133(2):809–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrar J. J., Howard M., Fuller-Farrar J., Paul W. E. Biochemical and physicochemical characterization of mouse B cell growth factor: a lymphokine distinct from interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1838–1842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gewirtz A. M., Calabretta B. A c-myb antisense oligodeoxynucleotide inhibits normal human hematopoiesis in vitro. Science. 1988 Dec 2;242(4883):1303–1306. doi: 10.1126/science.2461588. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Smith K. A. Long term culture of tumour-specific cytotoxic T cells. Nature. 1977 Jul 14;268(5616):154–156. doi: 10.1038/268154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunning P., Ponte P., Okayama H., Engel J., Blau H., Kedes L. Isolation and characterization of full-length cDNA clones for human alpha-, beta-, and gamma-actin mRNAs: skeletal but not cytoplasmic actins have an amino-terminal cysteine that is subsequently removed. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 May;3(5):787–795. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.5.787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikura H., Honma Y., Honma C., Hozumi M., Black J. D., Kieber-Emmons T., Bloch A. Inhibition of messenger RNA transcriptional activity in ML-1 human myeloblastic leukemia cell nuclei by antiserum to a c-myb-specific peptide. Cancer Res. 1987 Feb 15;47(4):1052–1057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katzen A. L., Kornberg T. B., Bishop J. M. Isolation of the proto-oncogene c-myb from D. melanogaster. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):449–456. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80018-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Regulation of heat shock protein 70 gene expression by c-myc. Nature. 1984 Nov 15;312(5991):280–282. doi: 10.1038/312280a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Arnold H., Biedenkapp H. Activation of transcription by v-myb: evidence for two different mechanisms. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1582–1589. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1582. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H. Interaction of myb proteins with nuclear matrix in vitro. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):545–551. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Sippel A. E. The highly conserved amino-terminal region of the protein encoded by the v-myb oncogene functions as a DNA-binding domain. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2719–2725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02565.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsick J. S., Boyle W. J. c-myb protein expression is a late event during T-lymphocyte activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3358–3360. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malek T. R., Robb R. J., Shevach E. M. Identification and initial characterization of a rat monoclonal antibody reactive with the murine interleukin 2 receptor-ligand complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5694–5698. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5694. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse H. C., 3rd, Davidson W. F., Yetter R. A., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Coffman R. L. Abnormalities induced by the mutant gene Ipr: expansion of a unique lymphocyte subset. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2612–2615. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mountz J. D., Steinberg A. D., Klinman D. M., Smith H. R., Mushinski J. F. Autoimmunity and increased c-myb transcription. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1087–1089. doi: 10.1126/science.6494925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mushinski J. F., Potter M., Bauer S. R., Reddy E. P. DNA rearrangement and altered RNA expression of the c-myb oncogene in mouse plasmacytoid lymphosarcomas. Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):795–798. doi: 10.1126/science.6687762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishina Y., Nakagoshi H., Imamoto F., Gonda T. J., Ishii S. Trans-activation by the c-myb proto-oncogene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):107–117. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onclercq R., Gilardi P., Lavenu A., Cremisi C. c-myc products trans-activate the adenovirus E4 promoter in EC stem cells by using the same target sequence as E1A products. J Virol. 1988 Dec;62(12):4533–4537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.12.4533-4537.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauza C. D. Regulation of human T-lymphocyte gene expression by interleukin 2: immediate-response genes include the proto-oncogene c-myb. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):342–348. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remmers E. F., Yang J. Q., Marcu K. B. A negative transcriptional control element located upstream of the murine c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):899–904. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04301.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoyama C., Frunzio R., Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Transcriptional activation encoded by the v-fos gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3213–3217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Gardinier M. Expression of a proto-oncogene (proto-myb) in hemopoietic tissues of mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;4(7):1206–1212. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.7.1206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman P. A., Basta P. V., Moore T. L., Brown A. M., Ting J. P. Class II box consensus sequences in the HLA-DR alpha gene: transcriptional function and interaction with nuclear proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jan;9(1):50–56. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.1.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipp M. A., Reinherz E. L. Differential expression of nuclear proto-oncogenes in T cells triggered with mitogenic and nonmitogenic T3 and T11 activation signals. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 1;139(7):2143–2148. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slamon D. J., Boone T. C., Murdock D. C., Keith D. E., Press M. F., Larson R. A., Souza L. M. Studies of the human c-myb gene and its product in human acute leukemias. Science. 1986 Jul 18;233(4761):347–351. doi: 10.1126/science.3014652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern J. B., Smith K. A. Interleukin-2 induction of T-cell G1 progression and c-myb expression. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.3523754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Expression of the c-myb proto-oncogene during cellular proliferation. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):374–380. doi: 10.1038/319374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torelli G., Selleri L., Donelli A., Ferrari S., Emilia G., Venturelli D., Moretti L., Torelli U. Activation of c-myb expression by phytohemagglutinin stimulation in normal human T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2874–2877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torelli G., Venturelli D., Coló A., Zanni C., Selleri L., Moretti L., Calabretta B., Torelli U. Expression of c-myb protooncogene and other cell cycle-related genes in normal and neoplastic human colonic mucosa. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5266–5269. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weston K., Bishop J. M. Transcriptional activation by the v-myb oncogene and its cellular progenitor, c-myb. Cell. 1989 Jul 14;58(1):85–93. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90405-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yokota S., Yuan D., Katagiri T., Eisenberg R. A., Cohen P. L., Ting J. P. The expression and regulation of c-myb transcription in B6/lpr Lyt-2-, L3T4-T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1987 Oct 15;139(8):2810–2817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]