Abstract
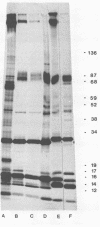
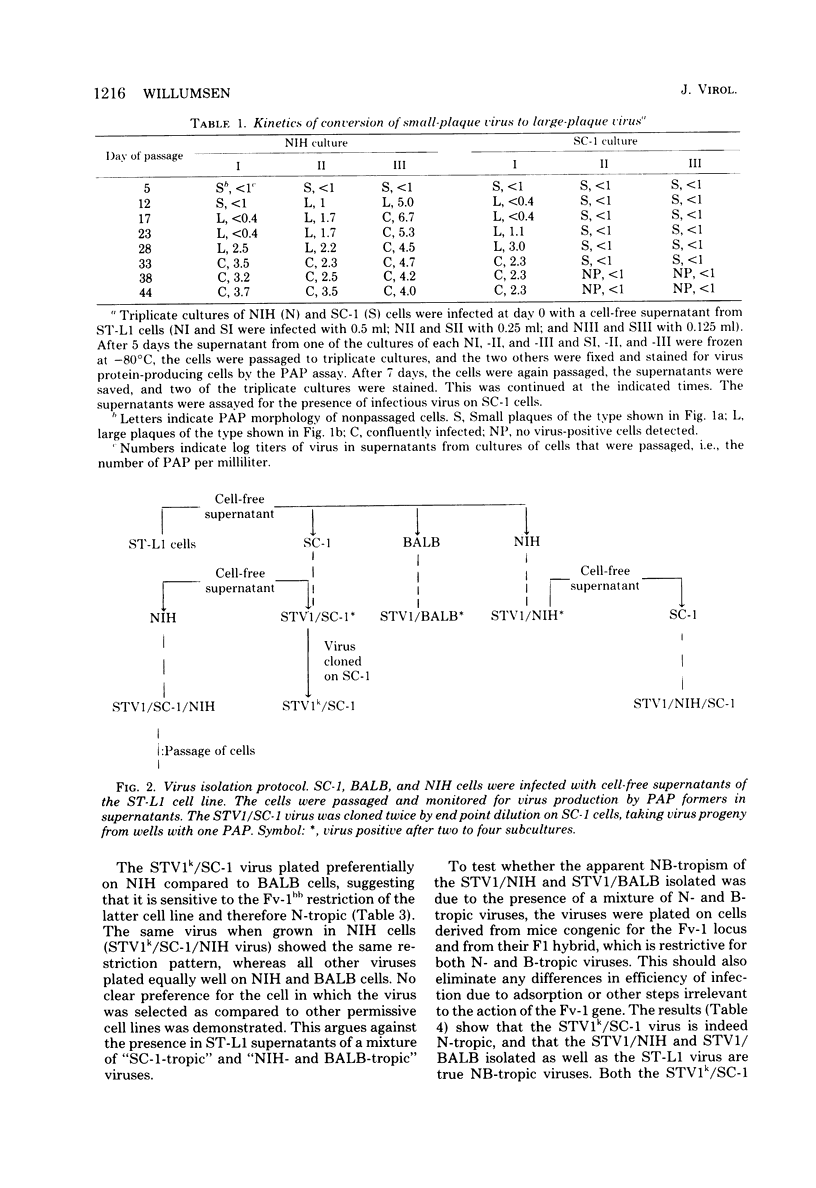
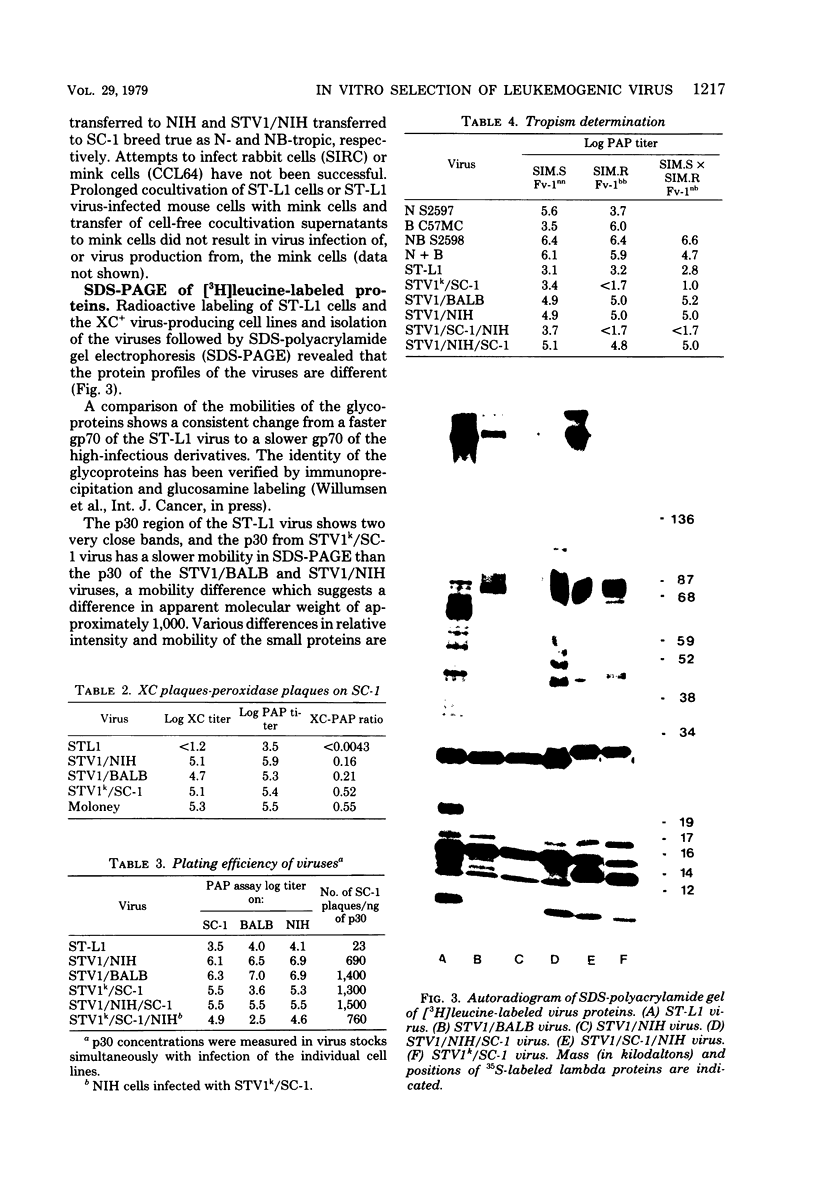
Low-infectious, nontransforming type C virus was isolated from an in vitro spontaneously transformed ST/a mouse cell line, ST-L1. The virus released by ST-L1 cells was NB-tropic and XC−. It gave rise to very small peroxidase antibody plaques (PAP) in cultures which initially were nonproducing. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-polyacrylamide gels of the structural proteins of the ST-L1 virus showed an envelope glycoprotein with an apparent mass of 65 kilodaltons (kdal). The mouse cells SC-1, BALB/3T3, and NIH/3T3 could be productively infected with cell-free supernatants from the ST-L1 cell line; however, virus was detected in supernatant fluids only after two to four subcultures of the infected cells. The virus thus produced was XC+ and a large plaque former. The virus released from infected SC-1 cells was N-tropic, whereas the viruses from infected NIH/3T3 and BALB/3T3 cells were NB-tropic. The structural proteins of the N- and NB-tropic viruses could be distinguished on SDS polyacrylamide gels, the major dissimilarity being a difference in the mobility of the p30. All these viruses had an envelope glycoprotein with an apparent mass of 70 kdal. The infectivity of the viruses, measured as PAP per nanogram of p30, was 30- to 60-fold lower for the virus released from the ST-L1 cell line than that of the viruses after passage in SC-1, NIH/3T3, and BALB/3T3 cells. None of the viruses could infect rabbit or mink cells. Inoculation of the viruses into newborn mice showed that the ST-L1 virus was non-leukemogenic, whereas the NB-tropic virus selected from this after passage in BALB/3T3 or NIH/3T3 cells was highly leukemogenic. Viruses isolated from leukemic animals were indistinguishable with respect to host range and protein mobilities in SDS gels from the ones with which the mice were inoculated. Although the SC-1-selected virus was highly infectious in vitro, it was only weakly, if at all, leukemogenic.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Development of 3T3-like lines from Balb-c mouse embryo cultures: transformation susceptibility to SV40. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):141–148. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittles A. H. The comparative analysis of three batches of foetal bovine serum used in tissue culture. Med Lab Technol. 1974 Jul;31(3):253–255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLarco J., Todaro G. J. Membrane receptors for murine leukemia viruses: characterization using the purified viral envelope glycoprotein, gp71. Cell. 1976 Jul;8(3):365–371. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Lieberman M., Kaplan H. S. In vivo interaction between RNA viruses isolated from the C57BL/Ka strain of mice. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):270–283. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90144-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Propagation in a fluid medium of a human epidermoid carcinoma, strain KB. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Jul;89(3):362–364. doi: 10.3181/00379727-89-21811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Gautsch J. W., Jensen F. C., Lerner R. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Biochemical evidence that MCF murine leukemia viruses are envelope (env) gene recombinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4676–4680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberger J. S., Stephenson J. R., Moloney W. C., Aaronson S. A. Different hematological diseases induced by type C viruses chemically activated from embryo cells of different mouse strains. Cancer Res. 1975 Jan;35(1):245–252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. Leukemogenic activity of thymotropic, ecotropic, and xenotropic radiation leukemia virus isolates. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):705–709. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.705-709.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hays E. F., Vredevoe D. L. A discrepancy in XC and oncogenicity assays for murine leukemia virus in AKR mice. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):726–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson I. C., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Mink cell line Mv 1 Lu (CCL 64). Focus formation and the generation of "nonproducer" transformed cell lines with murine and feline sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1974 Jul;60(1):282–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90386-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Jolicoeur P. Variants of N-tropic leukemia virus derived from BALB/c mice. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.991-999.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Schindler J., Hynes R. Six-NB-tropic murine leukemia viruses derived from a B-tropic virus of BALB/c have altered p30. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):309–318. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.309-318.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jainchill J. L., Aaronson S. A., Todaro G. J. Murine sarcoma and leukemia viruses: assay using clonal lines of contact-inhibited mouse cells. J Virol. 1969 Nov;4(5):549–553. doi: 10.1128/jvi.4.5.549-553.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murialdo H., Siminovitch L. The morphogenesis of bacteriophage lambda. IV. Identification of gene products and control of the expression of the morphogenetic information. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):785–823. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90162-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexo B. A. A plaque assay for murine leukemia virus using enzyme-coupled antibodies. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):849–852. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90504-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexø B. A., Krog H. H. C-type virus protein p30 in blood from inbred mice correlates with their later incidence of leukemia. Infect Immun. 1977 Feb;15(2):376–381. doi: 10.1128/iai.15.2.376-381.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexø B. A., Ulrich K. Activation of C-type virus during chemically induced leukemogenesis in mice. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Hays E. F., Doyle T., Linkhart S., Medeiros E., Pickering R. Oncornaviruses produced by murine leukemia cells in culture. Virology. 1977 Sep;81(2):363–370. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90152-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pincus T., Rowe W. P., Lilly F. A major genetic locus affecting resistance to infection with murine leukemia viruses. II. Apparent identity to a major locus described for resistance to friend murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1234–1241. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Nowinski R. C. Endogenous ecotropic mouse type C viruses deficient in replication and production of XC plaques. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):411–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.411-417.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Todaro G. J. Generation of oncogenic type C viruses: rapidly leukemogenic viruses derived from C3H mouse cells in vivo and in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2468–2472. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2468. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVOBODA J., CHYLE P., SIMKOVIC D., HILGERT I. Demonstration of the absence of infectious Rous virus in rat tumour XC, whose structurally intact cells produce Rous sarcoma when transferred to chicks. Folia Biol (Praha) 1963 Apr;9:77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler J., Hynes R., Hopkins N. Evidence for recombination between N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses: analysis of three virion proteins by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):700–700. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.700-.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh V., Blackstein M. E., Axelrad A. A. Inherited resistance to N- and B-tropic murine leukemia viruses in vitro: titration patterns in strains SIM and SIM.R congenic at the Fv-1 locus. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):473–480. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.473-480.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulrich K., Nexo J. A. Virus protein p30 in blood predicts development of leukaemia in mice injected with MuLV. Nature. 1977 Jun 23;267(5613):723–724. doi: 10.1038/267723a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]