Abstract
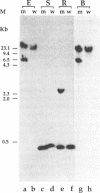
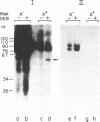
DNA sequences, that control expression of the spliced leader (SL) RNA gene in the parasitic protozoan Leishmania amazonensis, were mapped by block substitution mutagenesis. In the absence of a functional in vitro system for transcription, no promoter elements have yet been identified in this organism. We therefore developed an alternative in vivo approach, in which the SL RNA gene was tagged and then subjected to a series of linker scanning mutations. Each tagged and mutated SL RNA construct was introduced into parasite cells via the pX transfection vector, and was examined for expression of the tagged SL RNA followed by characterization of its transcriptional start site. The replacement of a critical DNA element was expected to prevent expression of the tagged SL RNA. We found that the putative SL RNA promoter is complex and includes two elements: one is located upstream to the coding region, between positions -30 to -70; and the other is located between -10 to +10, and includes transcribed sequences. In addition to the functional relationship between the SL RNA and vertebrate U snRNAs, we found structural similarities in their regulatory elements, which may possibly indicate a common evolutionary ancestry for these molecules.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agabian N. Trans splicing of nuclear pre-mRNAs. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1157–1160. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90674-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agami R., Shapira M. Nucleotide sequence of the spliced leader RNA gene from Leishmania mexicana amazonensis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1804–1804. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellofatto V., Cooper R., Cross G. A. Discontinuous transcription in Leptomonas seymouri: presence of intact and interrupted mini-exon gene families. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7437–7456. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Thomas J. Cis and trans mRNA splicing in C. elegans. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruzik J. P., Van Doren K., Hirsh D., Steitz J. A. Trans splicing involves a novel form of small nuclear ribonucleoprotein particles. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):559–562. doi: 10.1038/335559a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbon P., Murgo S., Ebel J. P., Krol A., Tebb G., Mattaj L. W. A common octamer motif binding protein is involved in the transcription of U6 snRNA by RNA polymerase III and U2 snRNA by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Oct 9;51(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curotto de Lafaille M. A., Laban A., Wirth D. F. Gene expression in Leishmania: analysis of essential 5' DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):2703–2707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.2703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das G., Henning D., Wright D., Reddy R. Upstream regulatory elements are necessary and sufficient for transcription of a U6 RNA gene by RNA polymerase III. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):503–512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02838.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lange T., Liu A. Y., Van der Ploeg L. H., Borst P., Tromp M. C., Van Boom J. H. Tandem repetition of the 5' mini-exon of variant surface glycoprotein genes: a multiple promoter for VSG gene transcription? Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):891–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90546-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grondal E. J., Evers R., Kosubek K., Cornelissen A. W. Characterization of the RNA polymerases of Trypanosoma brucei: trypanosomal mRNAs are composed of transcripts derived from both RNA polymerase II and III. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3383–3389. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08502.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Maroney P. A., Ayers D. G., Shambaugh J. D., Nilsen T. W. Transcription of a nematode trans-spliced leader RNA requires internal elements for both initiation and 3' end-formation. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1915–1921. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08318.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannon G. J., Maroney P. A., Denker J. A., Nilsen T. W. Trans splicing of nematode pre-messenger RNA in vitro. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1247–1255. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90689-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan G., Turner M. J., Cordingley J. S. Ribosomal RNA genes of Trypanosoma brucei: mapping the regions specifying the six small ribosomal RNAs. Gene. 1984 Jan;27(1):75–86. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90240-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Lucito R. Elements required for transcription initiation of the human U2 snRNA gene coincide with elements required for snRNA 3' end formation. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3125–3134. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03179.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krause M., Hirsh D. A trans-spliced leader sequence on actin mRNA in C. elegans. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):753–761. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90613-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel G. R., Pederson T. Upstream elements required for efficient transcription of a human U6 RNA gene resemble those of U1 and U2 genes even though a different polymerase is used. Genes Dev. 1988 Feb;2(2):196–204. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.2.196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laban A., Wirth D. F. Transfection of Leishmania enriettii and expression of chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9119–9123. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9119. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Kooter J. M., Loosbroek N., Borst P. Mature mRNAs of Trypanosoma brucei possess a 5' cap acquired by discontinuous RNA synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jun 25;13(12):4253–4266. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.12.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laird P. W., Zomerdijk J. C., de Korte D., Borst P. In vivo labelling of intermediates in the discontinuous synthesis of mRNAs in Trypanosoma brucei. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):1055–1062. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04858.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Coburn C. M., McMahon-Pratt D., Beverley S. M. Development of a stable Leishmania expression vector and application to the study of parasite surface antigen genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9736–9740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobo S. M., Ifill S., Hernandez N. cis-acting elements required for RNA polymerase II and III transcription in the human U2 and U6 snRNA promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 May 25;18(10):2891–2899. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.10.2891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Dathan N. A., Parry H. D., Carbon P., Krol A. Changing the RNA polymerase specificity of U snRNA gene promoters. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):435–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90029-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattaj I. W., Lienhard S., Jiricny J., De Robertis E. M. An enhancer-like sequence within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter facilitates the formation of stable transcription complexes. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):163–167. doi: 10.1038/316163a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally K. P., Agabian N. Trypanosoma brucei spliced-leader RNA methylations are required for trans splicing in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Nov;12(11):4844–4851. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.11.4844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli S., Agami R., Shapira M. Leishmania mexicana amazonensis: effect of heat shock on the spliced leader RNA and its ribonucleoprotein particle SL RNP. Exp Parasitol. 1993 Feb;76(1):59–67. doi: 10.1006/expr.1993.1007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaeli S., Roberts T. G., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Isolation of distinct small ribonucleoprotein particles containing the spliced leader and U2 RNAs of Trypanosoma brucei. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 25;265(18):10582–10588. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milhausen M., Nelson R. G., Sather S., Selkirk M., Agabian N. Identification of a small RNA containing the trypanosome spliced leader: a donor of shared 5' sequences of trypanosomatid mRNAs? Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):721–729. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90267-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Landfear S. M., Wirth D. F. Cloning and characterization of a Leishmania gene encoding a RNA spliced leader sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Sep 25;14(18):7341–7360. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.18.7341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. I., Wirth D. F. trans splicing in Leishmania enriettii and identification of ribonucleoprotein complexes containing the spliced leader and U2 equivalent RNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2597–2603. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy W. J., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Identification of a novel Y branch structure as an intermediate in trypanosome mRNA processing: evidence for trans splicing. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):517–525. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90616-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. G., Parsons M., Barr P. J., Stuart K., Selkirk M., Agabian N. Sequences homologous to the variant antigen mRNA spliced leader are located in tandem repeats and variable orphons in trypanosoma brucei. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):901–909. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90547-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W., Shambaugh J., Denker J., Chubb G., Faser C., Putnam L., Bennett K. Characterization and expression of a spliced leader RNA in the parasitic nematode Ascaris lumbricoides var. suum. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3543–3547. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsen T. W. Trans-splicing in nematodes. Exp Parasitol. 1989 Nov;69(4):413–416. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(89)90191-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry K. L., Watkins K. P., Agabian N. Trypanosome mRNAs have unusual "cap 4" structures acquired by addition of a spliced leader. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8190–8194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajkovic A., Davis R. E., Simonsen J. N., Rottman F. M. A spliced leader is present on a subset of mRNAs from the human parasite Schistosoma mansoni. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8879–8883. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudenko G., Le Blancq S., Smith J., Lee M. G., Rattray A., Van der Ploeg L. H. Procyclic acidic repetitive protein (PARP) genes located in an unusually small alpha-amanitin-resistant transcription unit: PARP promoter activity assayed by transient DNA transfection of Trypanosoma brucei. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3492–3504. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapira M., Pinelli E. Heat-shock protein 83 of Leishmania mexicana amazonensis is an abundant cytoplasmic protein with a tandemly repeated genomic arrangement. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):231–236. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15107.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmen K. A., Waldschmidt R., Bernués J., Parry H. D., Seifart K. H., Mattaj I. W. Proximal sequence element factor binding and species specificity in vertebrate U6 snRNA promoters. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 20;223(4):873–884. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90249-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutton R. E., Boothroyd J. C. Evidence for trans splicing in trypanosomes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90617-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takacs A. M., Denker J. A., Perrine K. G., Maroney P. A., Nilsen T. W. A 22-nucleotide spliced leader sequence in the human parasitic nematode Brugia malayi is identical to the trans-spliced leader exon in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7932–7936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebb G., Bohmann D., Mattaj I. W. Only two of the four sites of interaction with nuclear factors within the Xenopus U2 gene promoter are necessary for efficient transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6437–6453. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tebb G., Mattaj I. W. Positionally exact initiation is required for the formation of a stable RNA polymerase II transcription complex in vivo. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3785–3792. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03263.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. D., Conrad R. C., Blumenthal T. The C. elegans trans-spliced leader RNA is bound to Sm and has a trimethylguanosine cap. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):533–539. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90075-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullu E., Tschudi C. Trans splicing in trypanosomes requires methylation of the 5' end of the spliced leader RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10074–10078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;153:3–11. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)53044-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K., Hanson S., Landfear S., Ullman B. Nucleotide sequence of the Leishmania donovani medRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Oct 25;19(20):5787–5787. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.20.5787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]