Abstract
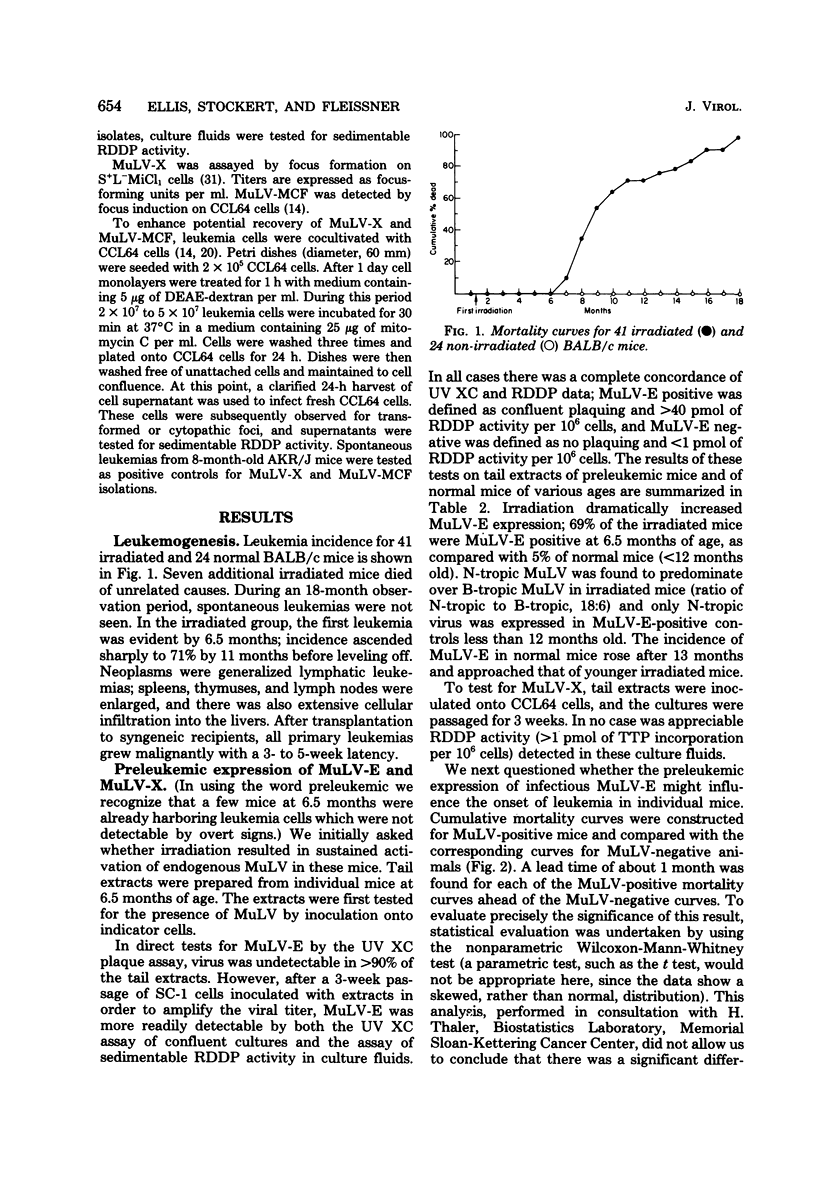
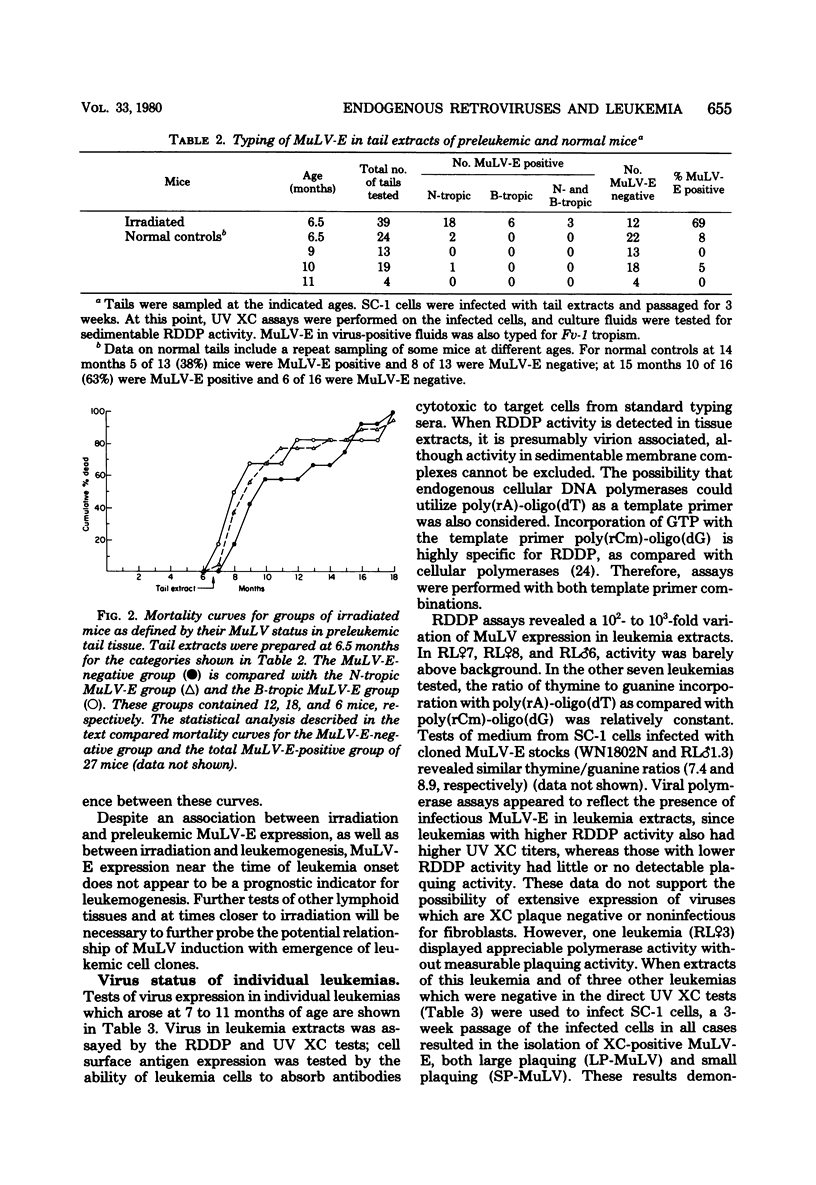
X-irradiation of BALB/c mice in the second month of life induced a high incidence of generalized lymphatic leukemia of T-cell origin, beginning at 7 months of age. Infectious ecotropic murine leukemia virus (B-tropic predominant over N-tropic) was isolable from all tumor extracts but exhibited a wide titer range among individual leukemias. Detection of infectious xenotropic virus usually required extensive amplification on indicator cells. Dual-tropic (mink cell focus-forming) virus has not been found in the leukemias. Expression of ecotropic virus in tail extracts prepared at 6.5 months of age, although greatly enhanced compared with unirradiated controls, was not found to be prognostic of tumor development in individual mice. We conclude that leukemogenesis does not show a simple dependence on infectious murine leukemia virus expression in these mice.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aaronson S. A., Stephenson J. R. Independent segregation of loci for activation of biologically distinguishable RNA C-type viruses in mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jul;70(7):2055–2058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.7.2055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnstein P., Levy J. A., Oshiro L. S., Price P. J., Suk W., Lennette E. H. Recovery of murine xenotropic type-C virus from C57L mice. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Dec;53(6):1787–1792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Teich N. M., Levine A. S., Rowe W. P. Evidence that the AKR murine-leukemia-virus genome is complete in DNA of the high-virus AKR mouse and incomplete in the DNA of the "virus-negative" NIH mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jan;71(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Lieberman M., Ihle J. N., Rosenthal P. N., Lung M. L., Kaplan H. S. Physicochemical, biological and serological properties of a leukemogenic virus isolated from cultured RadLV-induced lymphomas of C57BL/Ka mice. Virology. 1978 Oct 1;90(1):23–35. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Declève A., Sato C., Lieberman M., Kaplan H. S. Selective thymic localization of murine leukemia virus-related antigens in C57BL-Ka mice after inoculation with radiation virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Aug;71(8):3124–3128. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.8.3124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Hopkins N., Fleissner E. Biochemical analysis of murine leukemia viruses isolated from radiation-induced leukemias of strain BALB/c. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):661–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.661-670.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleissner E., Ikeda H., Tung J. S., Vitetta E. S., Tress E., Hardly W., Jr, Stockert E., Boyse E. A., Pincus T., O'Donnell P. Characterization of murine leukemia virus-specific proteins. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1057–1066. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Hilgers J. In vitro infection of lymphoid cells by thymotropic radiation leukemia virus grown in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Sep;72(9):3546–3550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.9.3546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M. Transient virus expression during murine leukemia induction by X-irradiation. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1977 Feb;58(2):251–257. doi: 10.1093/jnci/58.2.251. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haran-Ghera N. Spontaneous and induced preleukemia cells in C57BL/6 mice:brief communication. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1978 Mar;60(3):707–710. doi: 10.1093/jnci/60.3.707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Huebner R. J. Host-range restrictions of murine leukemia viruses in mouse embryo cell cultures. J Virol. 1970 Feb;5(2):221–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.5.2.221-225.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopkins N., Jolicoeur P. Variants of N-tropic leukemia virus derived from BALB/c mice. J Virol. 1975 Oct;16(4):991–999. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.4.991-999.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Joseph D. R., Pazmino N. H. Radiation leukemia in C57BL/6 mice. II. Lack of ecotropic virus expression in the majority of lymphomas. J Exp Med. 1976 Dec 1;144(6):1406–1423. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.6.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN H. S., BROWN M. B. Mortality of mice after total-body irradiation as influenced by alterations in total dose, fractionation, and periodicity of treatment. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1952 Feb;12(4):765–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan H. S. On the natural history of the murine leukemias: presidential address. Cancer Res. 1967 Aug;27(8):1325–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima K., Ikeda H., Hartley J. W., Stockert E., Rowe W. P., Old L. J. Changes in expression of murine leukemia virus antigens and production of xenotropic virus in the late preleukemic period in AKR mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIEBERMAN M., KAPLAN H. S. Leukemogenic activity of filtrates from radiation-induced lymphoid tumors of mice. Science. 1959 Aug 14;130(3372):387–388. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3372.387. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lilly F., Duran-Reynals M. L., Rowe W. P. Correlation of early murine leukemia virus titer and H-2 type with spontaneous leukemia in mice of the BALB/c times AKR cross: a genetic analysis. J Exp Med. 1975 Apr 1;141(4):882–889. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Modak M. J., Marcus S. L. Purification and properties of Rauscher leukemia virus DNA polymerase and selective inhibition of mammalian viral reverse transcriptase by inorganic phosphate. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):11–19. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nexø B. A., Ulrich K. Activation of C-type virus during chemically induced leukemogenesis in mice. Cancer Res. 1978 Mar;38(3):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E. Induction of GIX antigen and gross cell surface antigen after infection by ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia viruses in vitro. J Virol. 1976 Dec;20(3):545–554. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.3.545-554.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OLD L. J., BOYSE E. A. ANTIGENIC PROPERTIES OF EXPERIMENTAL LEUKEMIAS. I. SEROLOGICAL STUDIES IN VITRO WITH SPONTANEOUS AND RADIATION-INDUCED LEUKEMIAS. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1963 Oct;31:977–995. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obata Y., Ikeda H., Stockert E., Boyse E. A. Relation of GIX antigen of thymocytes to envelope glycoprotein of murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):188–197. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Boyse E. A., Stockert E. The G (Gross) leukemia antigen. Cancer Res. 1965 Jul;25(6):813–819. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J., Stockert E. Immunogenetics of cell surface antigens of mouse leukemia. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:127–160. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peebles P. T. An in vitro focus-induction assay for xenotropic murine leukemia virus, feline leukemia virus C, and the feline--primate viruses RD-114/CCC/M-7. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):288–291. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90427-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. L., Hartley J. W., Spahn G. J., Rabstein L. S., Whitmire C. E., Turner H. C., Huebner R. J. Prevalence of the group-specific (gs) antigen and infectious virus expressions of the murine C-type RNA viruses during the life span of BALB-cCr mice. Int J Cancer. 1972 Sep 15;10(2):283–289. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. L., Rabstein L. S., Spahn G. J., Madison R. M., Huebner R. J. Incidence of spontaneous neoplasms in breeding and retired breeder BALB-cCr mice throughout the natural life span. Int J Cancer. 1972 Sep 15;10(2):273–282. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters R. L., Spahn G. J., Rabstein L. S., Kelloff G. J., Huebner R. J. Murine C-type RNA virus from spontaneous neoplasms: in vitro host range and oncogenic potential. Science. 1973 Aug 17;181(4100):665–667. doi: 10.1126/science.181.4100.665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Nowinski R. C. Endogenous ecotropic mouse type C viruses deficient in replication and production of XC plaques. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):411–417. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.411-417.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P. Genetic factors in the natural history of murine leukemia virus infection: G. H. A. Clowes Memorial Lecture. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3061–3068. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pincus T. Quantitative studies of naturally occurring murine leukemia virus infection of AKR mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):429–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder H. W., Jr, Stockert E., Fleissner E. Characterization of molecular species carrying gross cell surface antigen. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):302–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.302-314.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Reynolds R. K., Aaronson S. A. Isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants of murine leukemia virus. Virology. 1972 Jun;48(3):749–756. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(72)90158-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockert E., Old L. J., Boyse E. A. The G-IX system. A cell surface allo-antigen associated with murine leukemia virus; implications regarding chromosomal integration of the viral genome. J Exp Med. 1971 Jun 1;133(6):1334–1355. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.6.1334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Arnstein P., Parks W. P., Lennette E. H., Huebner R. J. A type-C virus in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells after inoculation into NIH Swiss mice treated with antithymocyte serum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Mar;70(3):859–862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Sherr C. J., Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Melnick J. L. Type C viruses of baboons: isolation from normal cell cultures. Cell. 1974 May;2(1):55–61. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Transplantable murine tumors release mouse-tropic and xenotropic type-C viruses. Int J Cancer. 1975 Apr 15;15(4):555–560. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tung J. S., Vitetta E. S., Fleissner E., Boyse E. A. Biochemical evidence linking the GIX thymocyte surface antigen to the gp69/71 envelope glycoprotein of murine leukemia virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Jan 1;141(1):198–205. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vitetta E. S., Uhr J. W., Boyse E. A. Association of a beta2-microglobulin-like subunit with H-2 and TL alloantigens on murine thymocytes. J Immunol. 1975 Jan;114(1 Pt 1):252–254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


