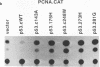
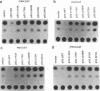
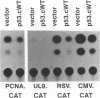
Abstract
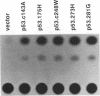
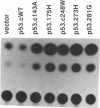
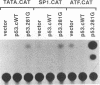
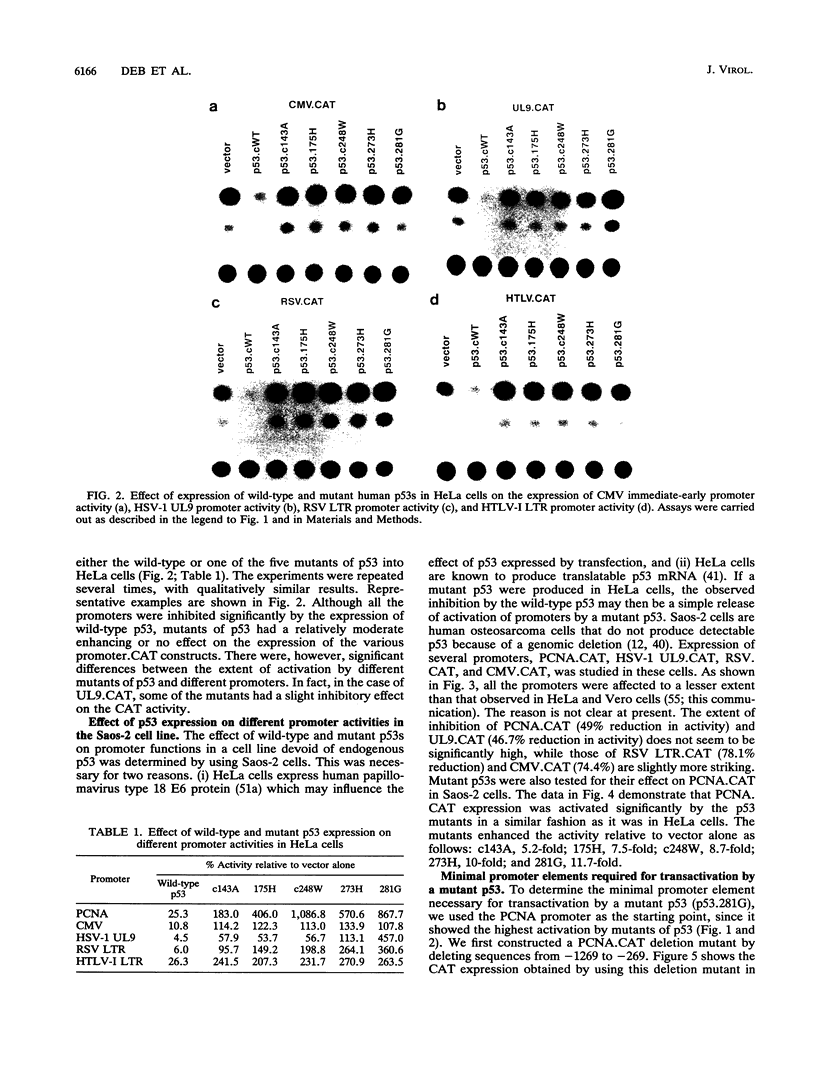
Wild-type p53 has recently been shown to repress transcription from several cellular and viral promoters. Since p53 mutations are the most frequently reported genetic defects in human cancers, it becomes important to study the effects of mutations of p53 on promoter functions. We, therefore, have studied the effects of wild-type and mutant human p53 on the human proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) promoter and on several viral promoters, including the herpes simplex virus type 1 UL9 promoter, the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early promoter-enhancer, and the long terminal repeat promoters of Rous sarcoma virus and human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. HeLa cells were cotransfected with a wild-type or mutant p53 expression vector and a plasmid containing a chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene under viral (or cellular) promoter control. As expected, expression of the wild-type p53 inhibited promoter function. Expression of a p53 with a mutation at any one of the four amino acid positions 175, 248, 273, or 281, however, correlated with a significant increase of the PCNA promoter activity (2- to 11-fold). The viral promoters were also activated, although to a somewhat lesser extent. We also showed that activation by a mutant p53 requires a minimal promoter containing a lone TATA box. A more significant increase (25-fold) in activation occurs when the promoter contains a binding site for the activating transcription factor or cyclic AMP response element-binding protein. Using Saos-2 cells that do not express p53, we showed that activation by a mutant p53 was a direct enhancement. The mutant forms of p53 used in this study are found in various cancer cells. The activation of PCNA by mutant p53s may indicate a way to increase cell proliferation by the mutant p53s. Thus, our data indicate a possible functional role for the mutants of p53 found in cancer cells in activating several important loci, including PCNA.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Nigro J. M., Hamilton S. R., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., vanTuinen P., Ledbetter D. H., Barker D. F., Nakamura Y. Chromosome 17 deletions and p53 gene mutations in colorectal carcinomas. Science. 1989 Apr 14;244(4901):217–221. doi: 10.1126/science.2649981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker S. J., Markowitz S., Fearon E. R., Willson J. K., Vogelstein B. Suppression of human colorectal carcinoma cell growth by wild-type p53. Science. 1990 Aug 24;249(4971):912–915. doi: 10.1126/science.2144057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Sturzbecher H. W., Addison C., Palmer C., Rudge K., Jenkins J. R. Mouse p53 inhibits SV40 origin-dependent DNA replication. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):458–460. doi: 10.1038/329458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg M. D., Kelly T. J. Animal virus DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:671–717. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.003323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin K. V., Ueda K., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Modulation of activity of the promoter of the human MDR1 gene by Ras and p53. Science. 1992 Jan 24;255(5043):459–462. doi: 10.1126/science.1346476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Lomedico P. T., Ju G. Transcriptional interference in avian retroviruses--implications for the promoter insertion model of leukaemogenesis. Nature. 1984 Jan 19;307(5948):241–245. doi: 10.1038/307241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diller L., Kassel J., Nelson C. E., Gryka M. A., Litwak G., Gebhardt M., Bressac B., Ozturk M., Baker S. J., Vogelstein B. p53 functions as a cell cycle control protein in osteosarcomas. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5772–5781. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Michalovitz D., Eliyahu S., Pinhasi-Kimhi O., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can inhibit oncogene-mediated focus formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8763–8767. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8763. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eliyahu D., Raz A., Gruss P., Givol D., Oren M. Participation of p53 cellular tumour antigen in transformation of normal embryonic cells. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):646–649. doi: 10.1038/312646a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Tan T. H., Eliyahu D., Oren M., Levine A. J. Activating mutations for transformation by p53 produce a gene product that forms an hsc70-p53 complex with an altered half-life. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):531–539. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.531. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type, but not mutant, human p53 proteins inhibit the replication activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9275–9279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsberg D., Mechta F., Yaniv M., Oren M. Wild-type p53 can down-modulate the activity of various promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):9979–9983. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.9979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P. W., Finlay C. A., Quartin R. S., Baker S. J., Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B., Levine A. J. Mutant p53 DNA clones from human colon carcinomas cooperate with ras in transforming primary rat cells: a comparison of the "hot spot" mutant phenotypes. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):571–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinds P., Finlay C., Levine A. J. Mutation is required to activate the p53 gene for cooperation with the ras oncogene and transformation. J Virol. 1989 Feb;63(2):739–746. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.2.739-746.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollstein M., Sidransky D., Vogelstein B., Harris C. C. p53 mutations in human cancers. Science. 1991 Jul 5;253(5015):49–53. doi: 10.1126/science.1905840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., Gatti C., Travali S., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Regulation of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen cyclin and thymidine kinase mRNA levels by growth factors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10175–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Rudge K., Chumakov P., Currie G. A. The cellular oncogene p53 can be activated by mutagenesis. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):816–818. doi: 10.1038/317816a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Pietenpol J. A., Thiagalingam S., Seymour A., Kinzler K. W., Vogelstein B. Oncogenic forms of p53 inhibit p53-regulated gene expression. Science. 1992 May 8;256(5058):827–830. doi: 10.1126/science.1589764. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. S., Kao C. C., Bryant G. O., Liu X., Berk A. J. Adenovirus E1A activation domain binds the basic repeat in the TATA box transcription factor. Cell. 1991 Oct 18;67(2):365–376. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J., Momand J., Finlay C. A. The p53 tumour suppressor gene. Nature. 1991 Jun 6;351(6326):453–456. doi: 10.1038/351453a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lillie J. W., Loewenstein P. M., Green M. R., Green M. Functional domains of adenovirus type 5 E1a proteins. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1091–1100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90175-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu F., Green M. R. A specific member of the ATF transcription factor family can mediate transcription activation by the adenovirus E1a protein. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1217–1224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90686-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maekawa T., Sakura H., Kanei-Ishii C., Sudo T., Yoshimura T., Fujisawa J., Yoshida M., Ishii S. Leucine zipper structure of the protein CRE-BP1 binding to the cyclic AMP response element in brain. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2023–2028. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03610.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkin D., Li F. P., Strong L. C., Fraumeni J. F., Jr, Nelson C. E., Kim D. H., Kassel J., Gryka M. A., Bischoff F. Z., Tainsky M. A. Germ line p53 mutations in a familial syndrome of breast cancer, sarcomas, and other neoplasms. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1233–1238. doi: 10.1126/science.1978757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin K. J., Lillie J. W., Green M. R. Evidence for interaction of different eukaryotic transcriptional activators with distinct cellular targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 12;346(6280):147–152. doi: 10.1038/346147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez J., Georgoff I., Martinez J., Levine A. J. Cellular localization and cell cycle regulation by a temperature-sensitive p53 protein. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):151–159. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masuda H., Miller C., Koeffler H. P., Battifora H., Cline M. J. Rearrangement of the p53 gene in human osteogenic sarcomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7716–7719. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matlashewski G., Banks L., Pim D., Crawford L. Analysis of human p53 proteins and mRNA levels in normal and transformed cells. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 3;154(3):665–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09449.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Amin M., Sauve G. J., Appella E., Ullrich S. J., Romano J. W. Wild type human p53 is antiproliferative in SV40-transformed hamster cells. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):973–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Shields M. T., Lin D., Appella E., Ullrich S. J. Growth suppression induced by wild-type p53 protein is accompanied by selective down-regulation of proliferating-cell nuclear antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1958–1962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalovitz D., Halevy O., Oren M. Conditional inhibition of transformation and of cell proliferation by a temperature-sensitive mutant of p53. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):671–680. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90113-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. Analysis of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter and its response to adenovirus early region 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16116–16125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris G. F., Mathews M. B. The adenovirus E1A transforming protein activates the proliferating cell nuclear antigen promoter via an activating transcription factor site. J Virol. 1991 Dec;65(12):6397–6406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.12.6397-6406.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santhanam U., Ray A., Sehgal P. B. Repression of the interleukin 6 gene promoter by p53 and the retinoblastoma susceptibility gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 1;88(17):7605–7609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.17.7605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schärer E., Iggo R. Mammalian p53 can function as a transcription factor in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1539–1545. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seedorf K., Oltersdorf T., Krämmer G., Röwekamp W. Identification of early proteins of the human papilloma viruses type 16 (HPV 16) and type 18 (HPV 18) in cervical carcinoma cells. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):139–144. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04731.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soussi T., Caron de Fromentel C., May P. Structural aspects of the p53 protein in relation to gene evolution. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):945–952. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stillman B. Initiation of eukaryotic DNA replication in vitro. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1989;5:197–245. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.05.110189.001213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Subler M. A., Martin D. W., Deb S. Inhibition of viral and cellular promoters by human wild-type p53. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4757–4762. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4757-4762.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi T., Nau M. M., Chiba I., Birrer M. J., Rosenberg R. K., Vinocour M., Levitt M., Pass H., Gazdar A. F., Minna J. D. p53: a frequent target for genetic abnormalities in lung cancer. Science. 1989 Oct 27;246(4929):491–494. doi: 10.1126/science.2554494. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan T. H., Wallis J., Levine A. J. Identification of the p53 protein domain involved in formation of the simian virus 40 large T-antigen-p53 protein complex. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):574–583. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.574-583.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B. Cancer. A deadly inheritance. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):681–682. doi: 10.1038/348681a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. D., Gralla J. D. Differential ability of proximal and remote element pairs to cooperate in activating RNA polymerase II transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4561–4571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weintraub H., Hauschka S., Tapscott S. J. The MCK enhancer contains a p53 responsive element. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4570–4571. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zambetti G. P., Olson D., Labow M., Levine A. J. A mutant p53 protein is required for maintenance of the transformed phenotype in cells transformed with p53 plus ras cDNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 1;89(9):3952–3956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.9.3952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]