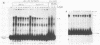Abstract
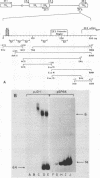
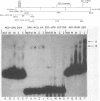
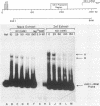
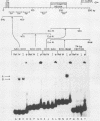
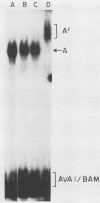
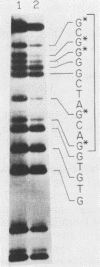
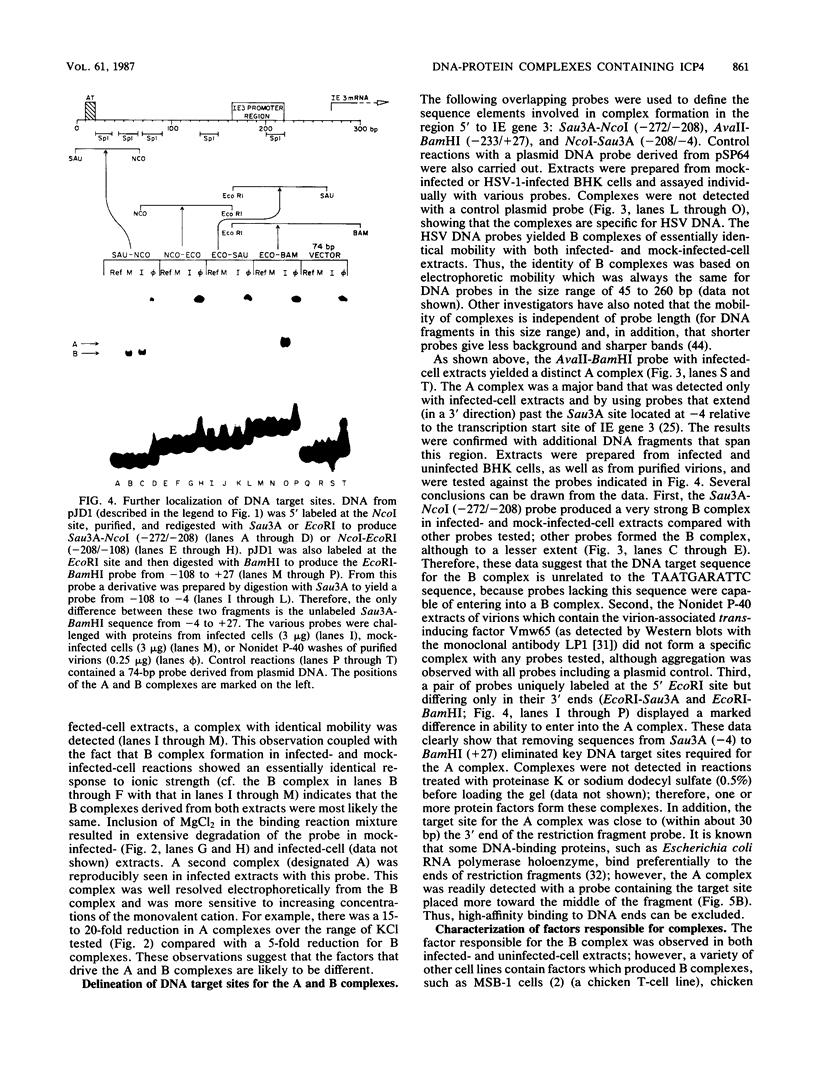
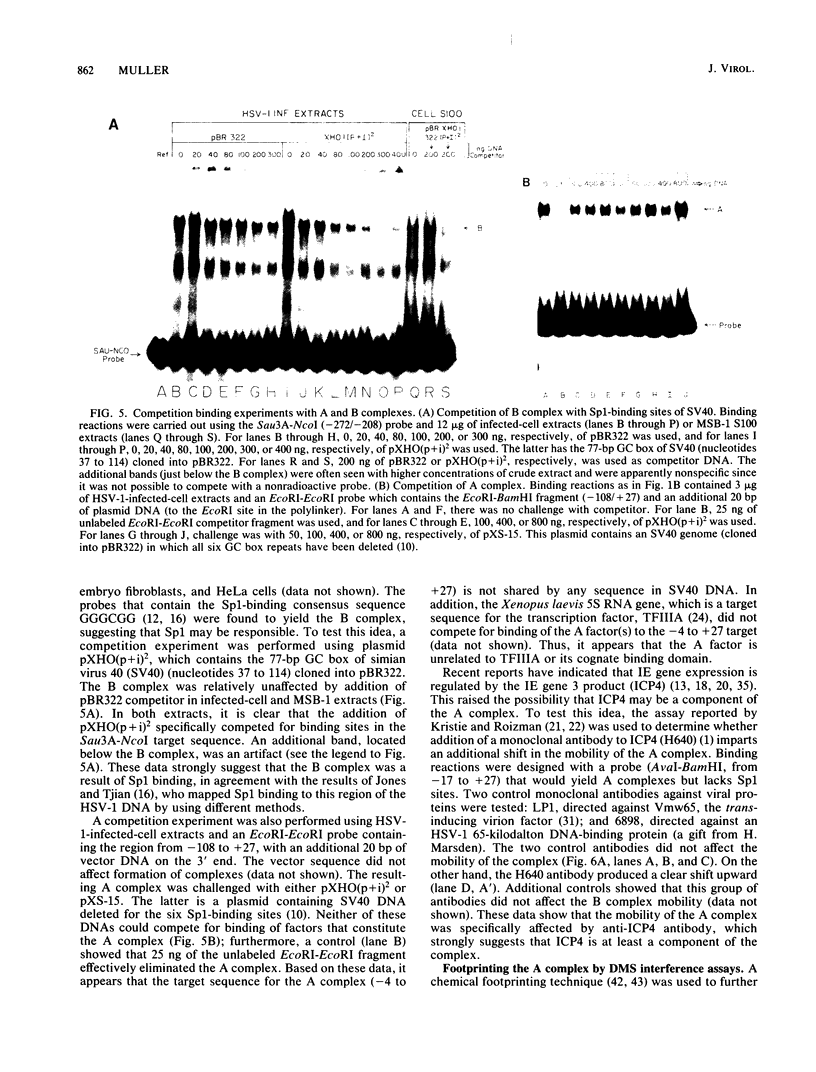
A gel electrophoresis DNA-binding assay was used to detect proteins from herpes simplex virus type 1-infected and uninfected cells that specifically bind the upstream region of immediate-early (IE) gene 3. The assay is based on the altered electrophoretic mobility of DNA-protein complexes relative to that of free DNA in native gels. A series of end-labeled overlapping DNA fragments spanning a region from -272 to +27 (relative to the 5' terminus of the IE gene 3 mRNA) were used as probes. Two complexes were identified (referred to as A and B) which were driven by different protein factors. Formation of the A complex required infected-cell proteins extracted at any time from 2 to 16 h postinfection; a 0.5 to 1 M NaCl extract of infected cells, and a DNA probe that contained the sequences from -4 to +27 (relative to the 5' terminus of IE gene 3 mRNA). The protein that drove the formation of the A complex is not related to transcription factors TFIIIA or Sp1 or their cognate binding domains since neither the 5S RNA gene nor the GC box of simian virus 40 could compete for proteins that induced formation of the A complex. Through the use of monoclonal antibodies, the complex was shown to contain the IE gene 3 product, ICP4. A more detailed localization of the DNA-binding site in vitro by using chemical footprinting revealed that binding occurs over the sequence from -10 to +3 relative to the mRNA terminus. The binding of ICP4 to its own transcription start site may explain the repression of IE gene transcription which attends the onset of early (beta) gene expression and suggests an autoregulatory mechanism for gene control in herpes simplex virus type 1. The B complex was readily detected in uninfected cells (of a number of different cell lines), as well as in infected cells, with a probe containing the IE consensus sequence TAATGARATTC (where R is a purine) and two nested copies of the Sp1 binding motif GGGCGG; however, complexes were also detected with probes that lack the IE consensus sequence but contain Sp1 sites. These data suggest that the B complex contains the promoter-specific factor Sp1, and competition experiments with the clustered Sp1 binding domains from simian virus 40 confirmed this idea.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackermann M., Braun D. K., Pereira L., Roizman B. Characterization of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha proteins 0, 4, and 27 with monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):108–118. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.108-118.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akiyama Y., Kato S. Two cell lines from lymphomas of Marek's disease. Biken J. 1974 Sep;17(3):105–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Preston C. M. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene 3: DNA sequences required for enhancer-like activity and response to trans-activation by a virion polypeptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):929–943. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordingley M. G., Campbell M. E., Preston C. M. Functional analysis of a herpes simplex virus type 1 promoter: identification of far-upstream regulatory sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2347–2365. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalrymple M. A., McGeoch D. J., Davison A. J., Preston C. M. DNA sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gene whose product is responsible for transcriptional activation of immediate early promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 11;13(21):7865–7879. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.21.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faber S. W., Wilcox K. W. Association of the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein ICP4 with specific nucleotide sequences in DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Aug 11;14(15):6067–6083. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.15.6067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm M., Berg P. Deletion mapping of DNA regions required for SV40 early region promoter function in vivo. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(5):457–481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Tjian R. Sp1 binds to promoter sequences and activates herpes simplex virus 'immediate-early' gene transcription in vitro. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):179–182. doi: 10.1038/317179a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Ruyechan W. T., Roizman B., Halliburton I. W. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus: demonstration of regions of obligatory and nonobligatory identity within diploid regions of the genome by sequence replacement and insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: nuclear retention of nontranslated viral RNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4322–4326. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Alpha 4, the major regulatory protein of herpes simplex virus type 1, is stably and specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes and of selected other viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. DNA-binding site of major regulatory protein alpha 4 specifically associated with promoter-regulatory domains of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4700–4704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang J. C., Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Transcriptional regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene is mediated through an enhancer-type sequence. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):389–395. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01817.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Differentiation between alpha promoter and regulator regions of herpes simplex virus 1: the functional domains and sequence of a movable alpha regulator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4917–4921. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: the alpha 27 gene promoter-thymidine kinase chimera is positively regulated in converted L cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1015-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. In vitro transcription: whole-cell extract. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:568–582. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01038-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Donald S., Brauer D. H. Complete DNA sequence of the short repeat region in the genome of herpes simplex virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Feb 25;14(4):1727–1745. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.4.1727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean C., Buckmaster A., Hancock D., Buchan A., Fuller A., Minson A. Monoclonal antibodies to three non-glycosylated antigens of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):297–305. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Direct evidence for the preferential binding of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme to the ends of deoxyribonucleic acid restriction fragments. Biochemistry. 1983 Oct 25;22(22):5169–5176. doi: 10.1021/bi00291a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muller M. T., Bolles C. S., Parris D. S. Association of type I DNA topoisomerase with herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1565–1574. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murchie M. J., McGeoch D. J. DNA sequence analysis of an immediate-early gene region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome (map coordinates 0.950 to 0.978). J Gen Virol. 1982 Sep;62(Pt 1):1–15. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-62-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Three trans-acting regulatory proteins of herpes simplex virus modulate immediate-early gene expression in a pathway involving positive and negative feedback regulation. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):723–733. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.723-733.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pellett P. E., McKnight J. L., Jenkins F. J., Roizman B. Nucleotide sequence and predicted amino acid sequence of a protein encoded in a small herpes simplex virus DNA fragment capable of trans-inducing alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(17):5870–5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.17.5870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Tedder D. G., Betz J. L., Wilcox K. W., Beard P. Regulation of transcription in vitro from herpes simplex virus genes. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):950–959. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.950-959.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Abnormal properties of an immediate early polypeptide in cells infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):357–369. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.357-369.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puga A., Gomez-Marquez J., Brayton P. R., Cantin E. M., Long L. K., Barbacid M., Notkins A. L. The immediate-early enhancer element of herpes simplex virus type 1 can replace a regulatory region of the c-Ha-ras1 oncogene required for transformation. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):879–881. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.879-881.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sacks W. R., Greene C. C., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Herpes simplex virus type 1 ICP27 is an essential regulatory protein. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):796–805. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.796-805.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss F., Varshavsky A. A protein binds to a satellite DNA repeat at three specific sites that would be brought into mutual proximity by DNA folding in the nucleosome. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):889–901. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90424-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Clements J. B. A herpes simplex virus type 1 function continuously required for early and late virus RNA synthesis. Nature. 1980 May 29;285(5763):329–330. doi: 10.1038/285329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]