Abstract
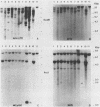
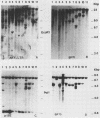
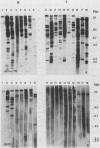
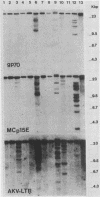
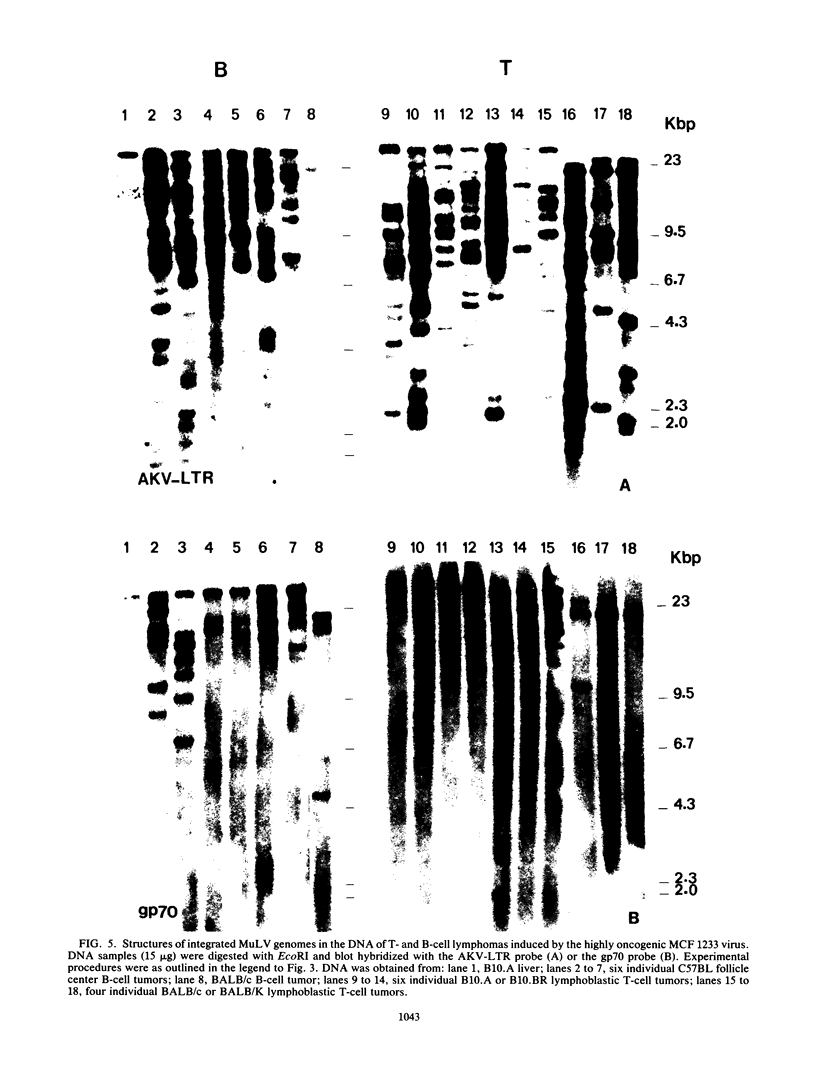
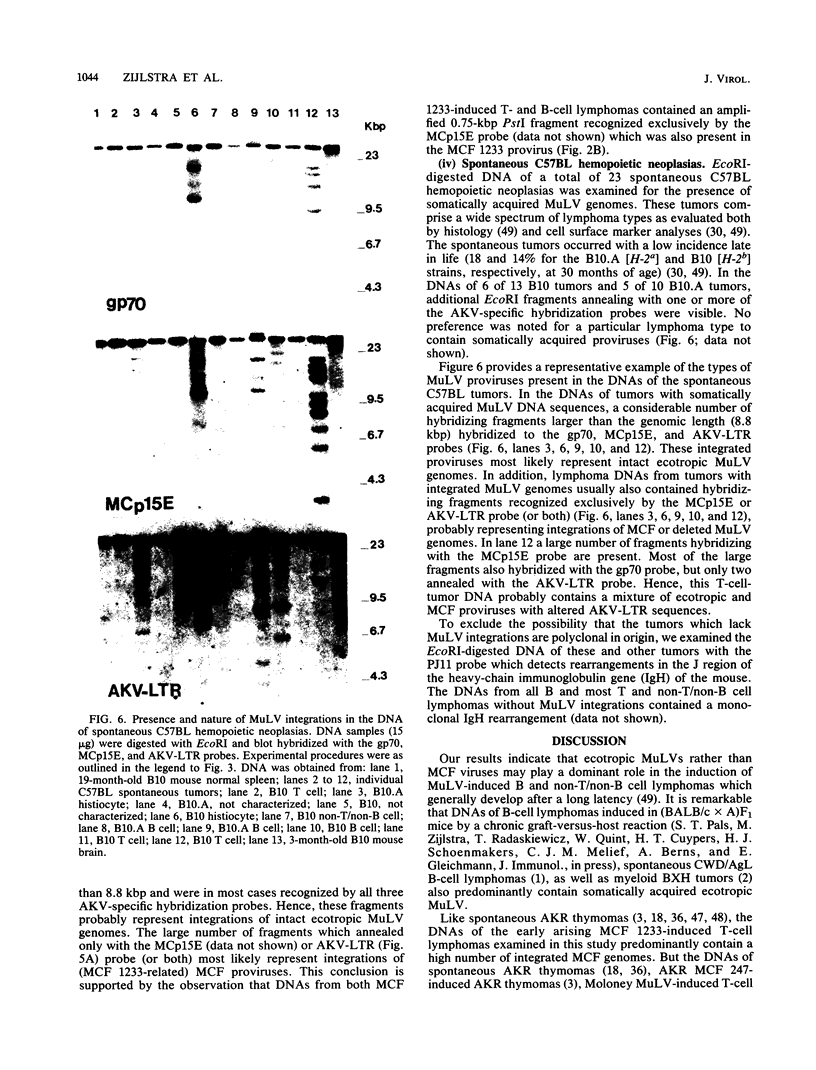
Structures of somatically acquired murine leukemia virus (MuLV) genomes present in the DNA of a large panel of MuLV-induced C57BL and BALB/c B and non-T/non-B cell lymphomas were compared with those present in MuLV-induced T-cell lymphomas induced in the same low-"spontaneous"-lymphoma-incidence mice. Analyses were performed with probes specific for the gp70, p15E, and U3-long terminal repeat (LTR) regions of ecotropic AKV MuLV and a mink cell focus-forming virus (MCF)-LTR probe annealing with U3-LTR sequences of a unique endogenous xenotropic MuLV, which also hybridizes with U3-LTR sequences of a substantial portion of somatically acquired MCF genomes in spontaneous AKR thymomas. The DNAs of both T- and B-cell tumors induced by neonatal inoculation with the highly oncogenic C57BL-derived MCF 1233 virus predominantly contain integrated MCF proviruses. In contrast, the DNAs of more slowly developing B and non-T/non-B cell lymphomas induced by poorly oncogenic ecotropic or MCF C57BL MuLV isolates mostly contain somatically acquired ecotropic MuLV genomes. Approximately 50% of the spontaneous C57BL lymphoma DNAs contain somatically acquired MuLV genomes. None of the integrated MuLV proviruses annealed with the MCF-LTR probe, which indicates a clear difference in LTR structure with a substantial portion of the somatically acquired MuLV genomes present in the DNA of spontaneous AKR thymomas. This study stresses a dominant role of MuLV with ecotropic gp70 and LTR sequences in the development of slowly arising MuLV-induced B and non-T/non-B cell lymphomas.
Full text
PDF
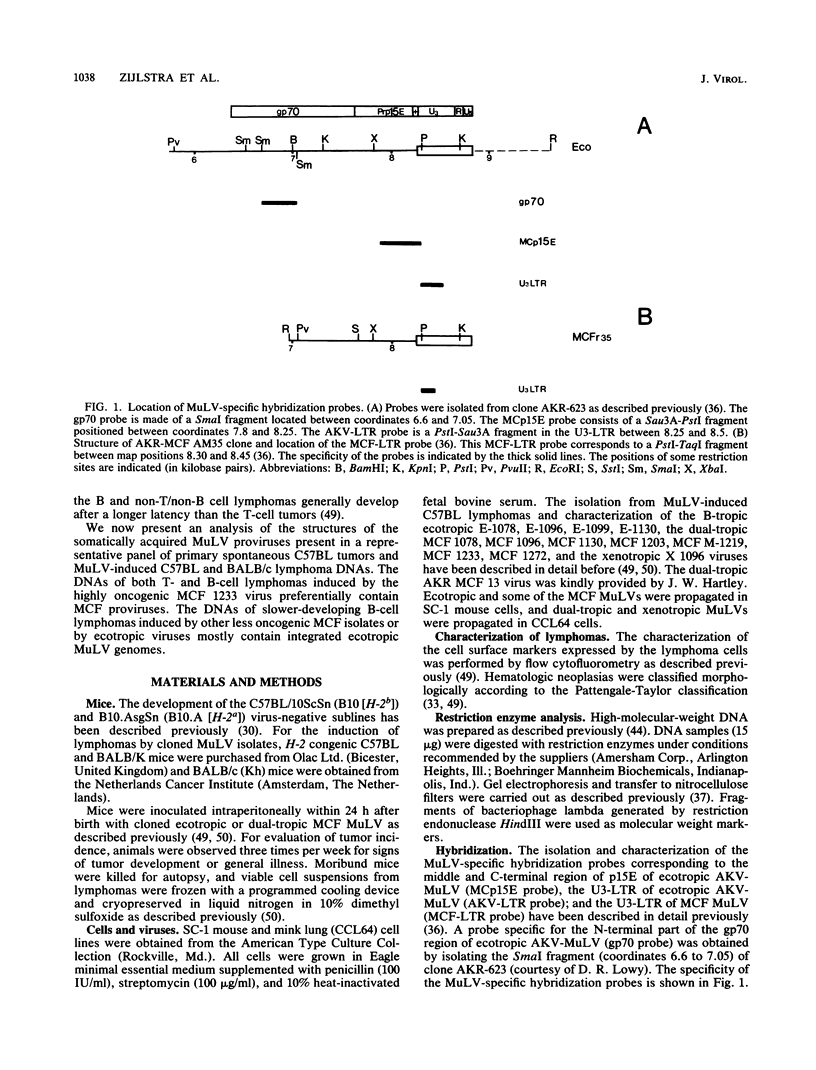

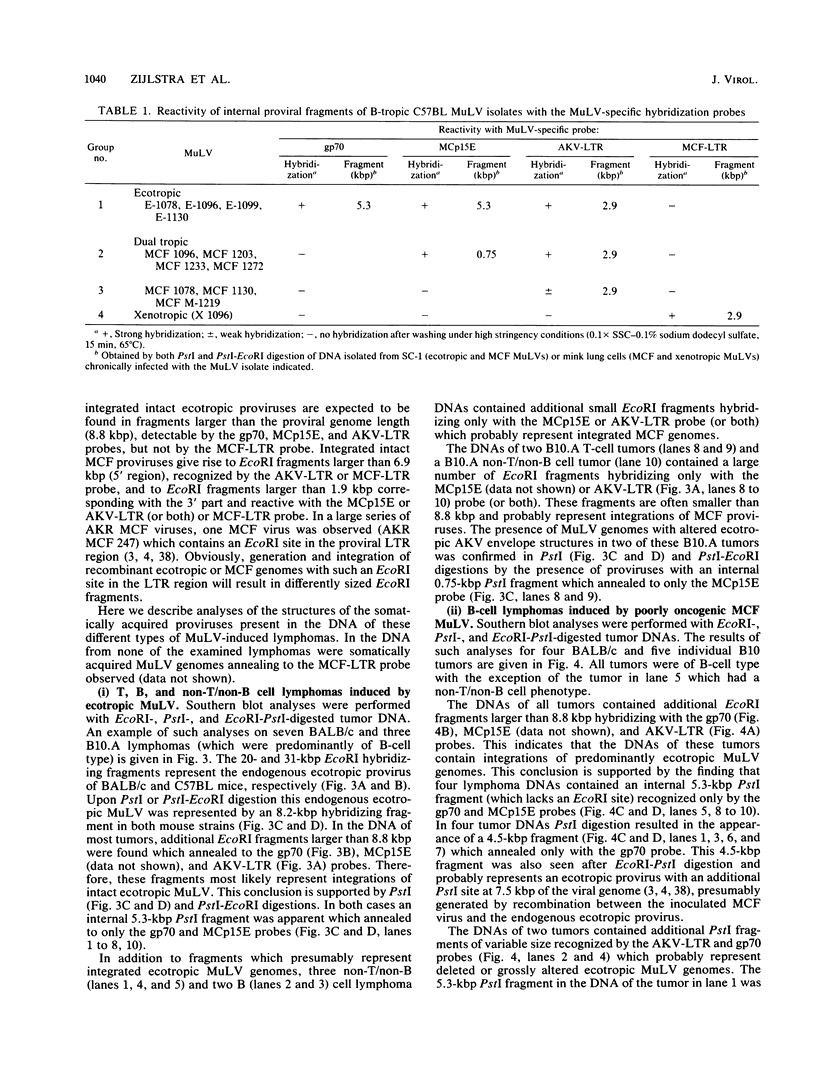
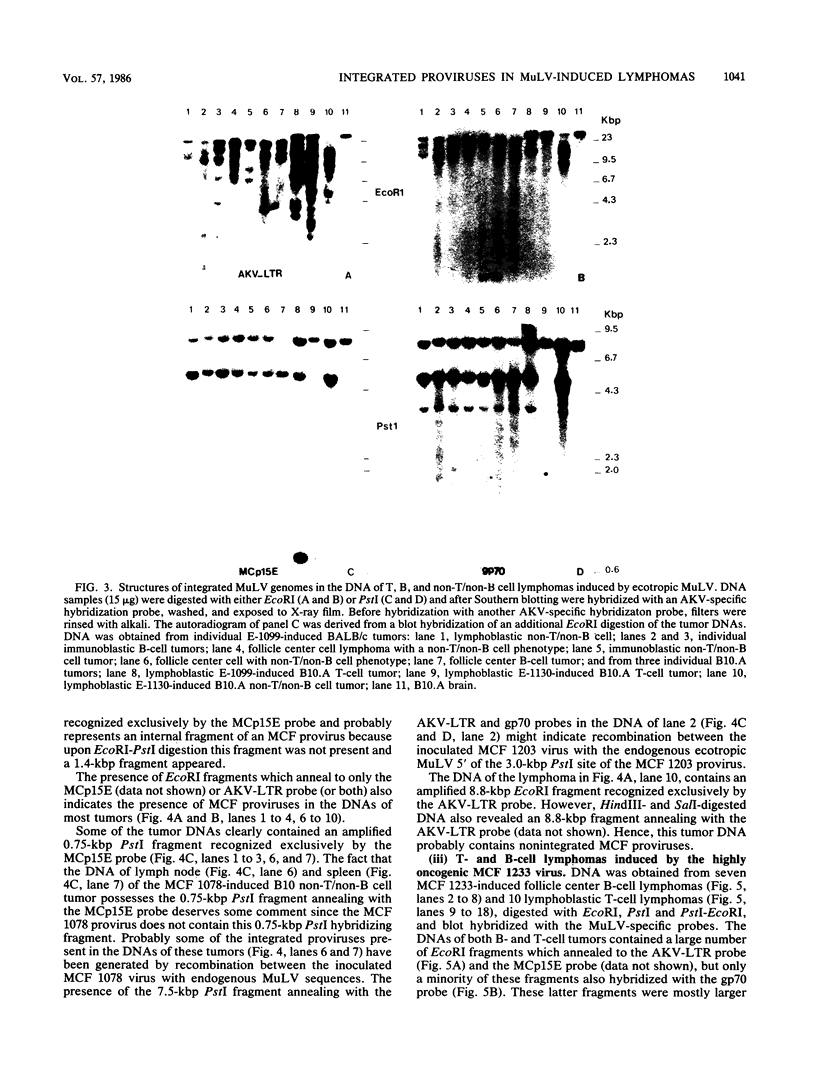
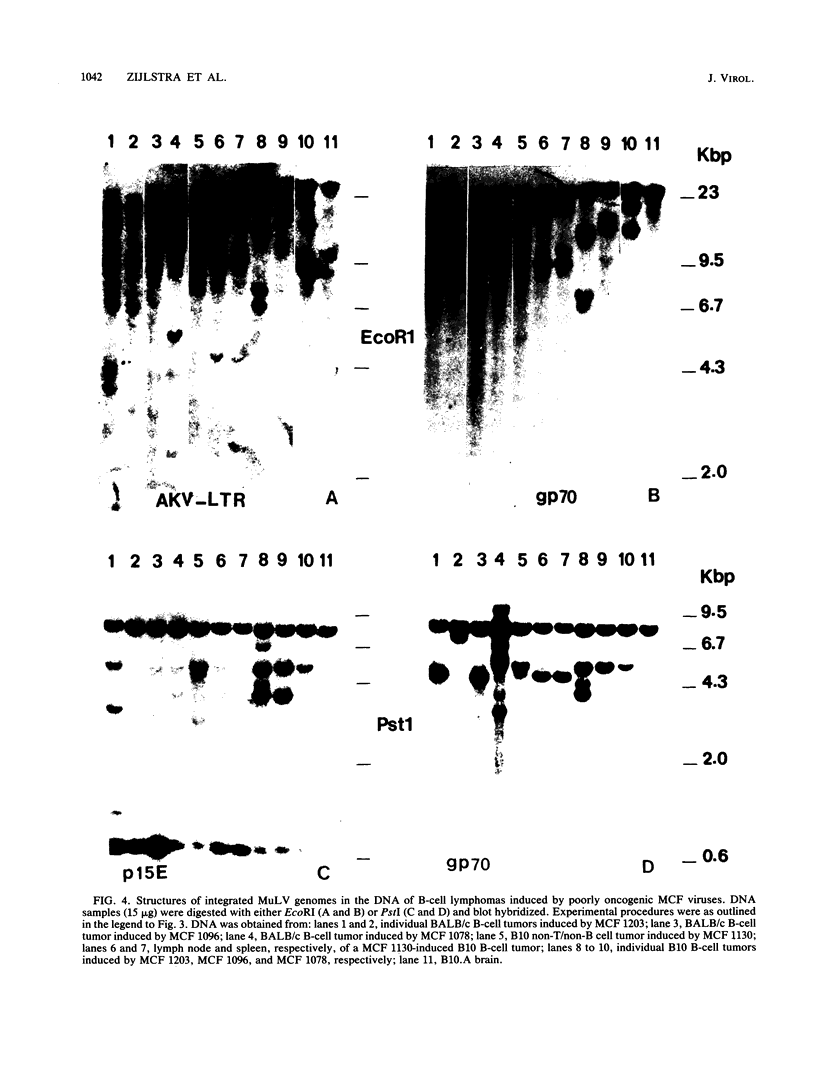



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel J. M., Bedigian H. G. Expression of murine leukemia viruses in B-cell lymphomas of CWD/Agl mice. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):691–694. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.691-694.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedigian H. G., Johnson D. A., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Evans R. Spontaneous and induced leukemias of myeloid origin in recombinant inbred BXH mice. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):586–594. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.586-594.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Genetic study of lymphoma induction by AKR mink cell focus-inducing virus in AKR x NFS crosses. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):450–457. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corcoran L. M., Adams J. M., Dunn A. R., Cory S. Murine T lymphomas in which the cellular myc oncogene has been activated by retroviral insertion. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):113–122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90306-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Villemur R., Jolicoeur P. The high leukemogenic potential of Gross passage A murine leukemia virus maps in the region of the genome corresponding to the long terminal repeat and to the 3' end of env. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):24–32. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.24-32.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green N., Hiai H., Elder J. H., Schwartz R. S., Khiroya R. H., Thomas C. Y., Tsichlis P. N., Coffin J. M. Expression of leukemogenic recombinant viruses associated with a recessive gene in HRS/J mice. J Exp Med. 1980 Aug 1;152(2):249–264. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.2.249. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerrero I., Calzada P., Mayer A., Pellicer A. A molecular approach to leukemogenesis: mouse lymphomas contain an activated c-ras oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(1):202–205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.1.202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Patch V. Genomic masking and rescue of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses: role of pseudotype virions in viral lymphomagenesis. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):583–591. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.583-591.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas M., Reshef T. Non-thymic malignant lymphomas induced in C57BL/6 mice by cloned dualtropic viruses isolated from hematopoietic stromal cell lines. Eur J Cancer. 1980 Jul;16(7):909–917. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(80)90329-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Perlmutter A. P., Gilbert W. Monoclonal AKR/J thymic leukemias contain multiple JH immunoglobulin gene rearrangements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7433–7436. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7433. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jolicoeur P., Rassart E., Sankar-Mistry P. Strong selection for cells containing new ecotropic recombinant murine leukemia virus provirus after propagation of C57BL/6 radiation-induced thymoma cells in vitro or in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Sep;3(9):1675–1679. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.9.1675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J. P., Kaplan H. S., Fry K. E. Characterization of an infective molecular clone of the B-tropic, ecotropic BL/Ka(B) murine retrovirus genome. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):217–225. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.217-225.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G. Specific chromosomal translocations and the genesis of B-cell-derived tumors in mice and men. Cell. 1983 Feb;32(2):311–315. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90449-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langdon W. Y., Theodore T. S., Buckler C. E., Stimpfling J. H., Martin M. A., Morse H. C., 3rd Relationship between a retroviral germ line reintegration and a new mutation at the ashen locus in B10.F mice. Retroviral integration and an ashen mutation. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):183–190. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90437-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Celander D., Crowther R. L., Patarca R., Perkins D. W., Haseltine W. A. Determination of the leukaemogenicity of a murine retrovirus by sequences within the long terminal repeat. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):467–470. doi: 10.1038/308467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J., Crowther R., Klimenko S., Haseltine W. Molecular cloning of a highly leukemogenic, ecotropic retrovirus from an AKR mouse. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):943–951. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.943-951.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcu K. B., Banerji J., Penncavage N. A., Lang R., Arnheim N. 5' flanking region of immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region genes displays length heterogeneity in germlines of inbred mouse strains. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):187–196. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90167-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath M. S., Weissman I. L. AKR leukemogenesis: identification and biological significance of thymic lymphoma receptors for AKR retroviruses. Cell. 1979 May;17(1):65–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90295-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melief C. J., Vlug A., de Goede R. E., de Bruyne C., Barendsen W., de Greeve P. Naturally occurring leukemia viruses in H-2 congenic C57BL mice. I. High lymphoma incidence following milk-borne transmission of virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 May;64(5):1179–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newcomb E. W., Binari R., Fleissner E. A comparative analysis of radiation- and virus-induced leukemias in BALB/c mice. Virology. 1985 Jan 15;140(1):102–112. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90449-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowinski R. C., Pickering R., O'Donnell P. V., Pinter A., Hammerling U. Selective neutralization of ecotropic murine leukemia virus by monoclonal antibodies: localization of a site on the gp70 protein associated with ecotropism. Virology. 1981 May;111(1):84–92. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90655-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Taylor C. R. Experimental models of lymphoproliferative disease. The mouse as a model for human non-Hodgkin's lymphomas and related leukemias. Am J Pathol. 1983 Nov;113(2):237–265. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pattengale P. K., Taylor C. R., Twomey P., Hill S., Jonasson J., Beardsley T., Haas M. Immunopathology of B-cell lymphomas induced in C57BL/6 mice by dualtropic murine leukemia virus (MuLV). Am J Pathol. 1982 Jun;107(3):362–377. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen F. S., Crowther R. L., Tenney D. Y., Reimold A. M., Haseltine W. A. Novel leukaemogenic retroviruses isolated from cell line derived from spontaneous AKR tumour. Nature. 1981 Jul 9;292(5819):167–170. doi: 10.1038/292167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Cuypers T., Maandag E. R., Selten G., Berns A. Generation of AKR mink cell focus-forming viruses: a conserved single-copy xenotrope-like provirus provides recombinant long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):432–438. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.432-438.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Quax W., van der Putten H., Berns A. Characterization of AKR murine leukemia virus sequences in AKR mouse substrains and structure of integrated recombinant genomes in tumor tissues. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rands E., Lowy D. R., Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. Restriction endonuclease mapping of ecotropic murine leukemia viral DNAs: size and sequence heterogeneity of the long terminal repeat. Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):445–452. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90451-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rassart E., Sankar-Mistry P., Lemay G., DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. New class of leukemogenic ecotropic recombinant murine leukemia virus isolated from radiation-induced thymomas of C57BL/6 mice. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):565–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.565-575.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rein A. Interference grouping of murine leukemia viruses: a distinct receptor for the MCF-recombinant viruses in mouse cells. Virology. 1982 Jul 15;120(1):251–257. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selten G., Cuypers H. T., Zijlstra M., Melief C., Berns A. Involvement of c-myc in MuLV-induced T cell lymphomas in mice: frequency and mechanisms of activation. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 20;3(13):3215–3222. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02281.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. Proviruses are adjacent to c-myc in some murine leukemia virus-induced lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2097–2101. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villemur R., Rassart E., DesGroseillers L., Jolicoeur P. Molecular cloning of viral DNA from leukemogenic Gross passage A murine leukemia virus and nucleotide sequence of its long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):539–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.539-546.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener F., Spira J., Babonits M., Klein G. Non-random duplication of chromosome 15 in T-cell leukemias induced in mice heterozygous for reciprocal and Robertsonian translocations. Int J Cancer. 1982 Oct 15;30(4):479–487. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Breda M. Lack of AKR ecotropic provirus amplification in AKR leukemic thymuses. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):808–815. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.808-815.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura F. K., Levine K. L. AKR thymic lymphomas involving mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses have a common region of provirus integration. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):576–584. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.576-584.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Schoenmakers H. J., Schinkel A. H., Hesselink W. G., Portis J. L., Melief C. J. Naturally occurring leukemia viruses in H-2 congenic C57BL mice. III. Characterization of C-type viruses isolated from lymphomas induced by milk transmission of B-ecotropic virus. Virology. 1983 Feb;125(1):47–63. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zijlstra M., de Goede R. E., Schoenmakers H., Radaszkiewicz T., Melief C. J. Ecotropic and dualtropic mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses can induce a wide spectrum of H-2 controlled lymphoma types. Virology. 1984 Oct 30;138(2):198–211. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90345-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., van Raaij J., Maandag E. R., Verma I. M., Berns A. M-MuLV-induced leukemogenesis: integration and structure of recombinant proviruses in tumors. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]