Abstract
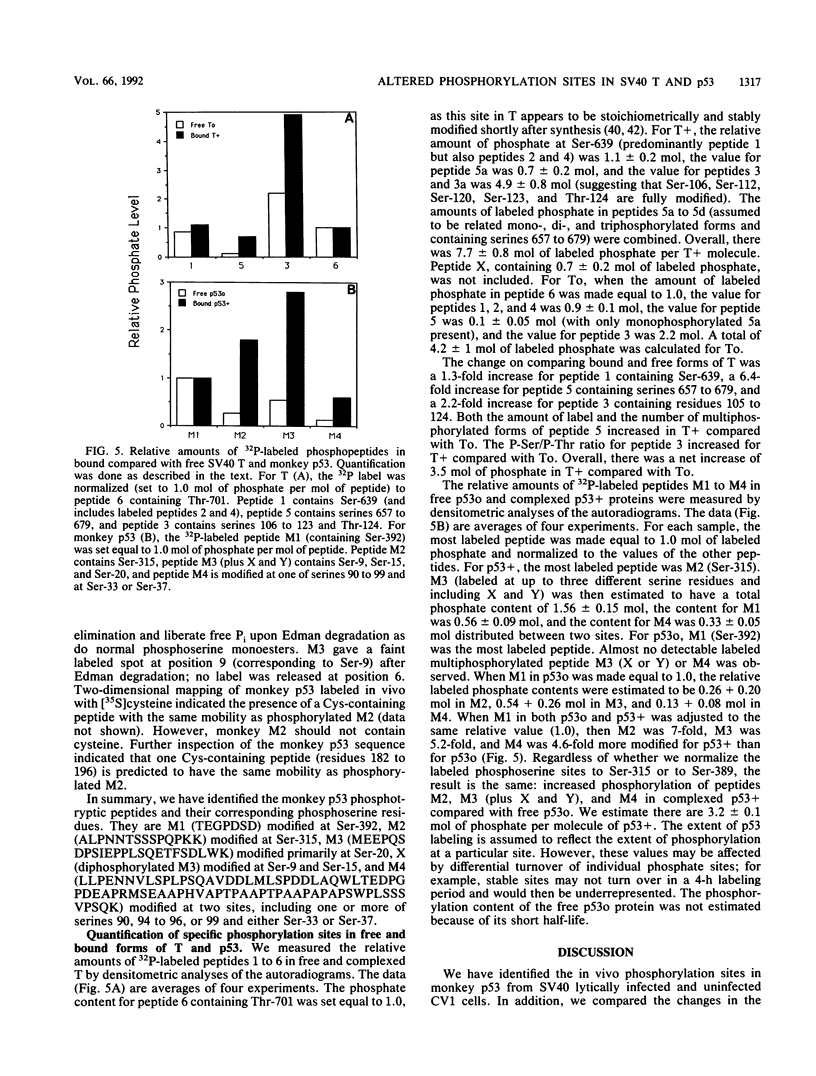
We have identified the phosphorylation sites in monkey p53 as well as specific changes in the phosphorylation state of free and complexed forms of simian virus 40 (SV40) large T antigen (T) and monkey p53 isolate from SV40 lytically infected CV1 cells. Phosphopeptide analyses of free T and p53 (To and p53o) and complexed T and p53 (T+ and p53+) fractions indicated several quantitative increases in the specific phosphorylation of complexed forms of both proteins. The N terminus of monkey p53+ is phosphorylated at Ser-9, Ser-15, Ser-20, either Ser-33 or Ser-37, and at least one of Ser-90 to Ser-99. The C-terminal sites are Ser-315 and Ser-392. On comparing p53+ with p53o, we found that labeling of the two N-terminal phosphotryptic peptides encompassing residues 1 to 20 and 33 to 101 was increased fivefold and that Ser-315 was sevenfold more labeled than was Ser-392. When T+ was compared with To, the N-terminal peptide containing phosphorylation sites Ser-106 through Thr-124 was twofold more labeled, the peptide containing Ser-657 through Ser-679 was sixfold more labeled and contained up to four phosphorylated serine residues, and Ser-639 and Thr-701 appeared unchanged. Overall, T+ molecules appeared to contain 3.5 mol more of labeled phosphate than did To, with the N-terminal peptide appearing fully phosphorylated. The phosphopeptide patterns obtained for lytic T+ and To fractions were nearly identical to those found for wild-type SV40 T (stably complexed with mouse p53) and mutant 5080 T (defective for p53 binding) expressed in transformed C3H10T1/2 cells (L. Tack, C. Cartwright, J. Wright, A. Srinivasan, W. Eckhart, K. Peden, and J. Pipas, J. Virol. 63:3362-3367, 1989). These results indicate that increases in specific phosphorylation sites in both T+ and p53+ correlate with the association of T with p53. The enhanced phosphorylation state may be a consequence of complex formation between T and p53 or reflect an increased affinity of p53 for highly phosphorylated forms of T.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Addison C., Jenkins J. R., Stürzbecher H. W. The p53 nuclear localisation signal is structurally linked to a p34cdc2 kinase motif. Oncogene. 1990 Mar;5(3):423–426. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bargonetti J., Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type but not mutant p53 immunopurified proteins bind to sequences adjacent to the SV40 origin of replication. Cell. 1991 Jun 14;65(6):1083–1091. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90560-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Friedman P. N., Marshak D. R., Prives C., Beach D. Human p53 is phosphorylated by p60-cdc2 and cyclin B-cdc2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4766–4770. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4766. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Buschhausen-Denker G., Patschinsky T., Steinmeyer K. Cell cycle control of p53 in normal (3T3) and chemically transformed (Meth A) mouse cells. II. Requirement for cell cycle progression. Oncogene. 1990 Nov;5(11):1701–1706. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanning E., Nowak B., Burger C. Detection and characterization of multiple forms of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):92–102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.92-102.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Jang S. K. Presence of a potent transcription activating sequence in the p53 protein. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1046–1049. doi: 10.1126/science.2144363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finlay C. A., Hinds P. W., Levine A. J. The p53 proto-oncogene can act as a suppressor of transformation. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1083–1093. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90045-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman P. N., Kern S. E., Vogelstein B., Prives C. Wild-type, but not mutant, human p53 proteins inhibit the replication activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9275–9279. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. V., Lane D. P. p53 and DNA polymerase alpha compete for binding to SV40 T antigen. Nature. 1987 Oct 1;329(6138):456–458. doi: 10.1038/329456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenspan D. S., Carroll R. B. Complex of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen and 48,000-dalton host tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):105–109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Tamowski S., Deppert W. Antigenic binding sites of monoclonal antibodies specific for simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1168–1172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1168-1172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Kinzler K. W., Bruskin A., Jarosz D., Friedman P., Prives C., Vogelstein B. Identification of p53 as a sequence-specific DNA-binding protein. Science. 1991 Jun 21;252(5013):1708–1711. doi: 10.1126/science.2047879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kienzle H., Baack M., Knippers R. Effects of the cellular p53 protein on Simian-virus-40-T-antigen-catalyzed DNA unwinding in vitro. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Sep 1;184(1):181–186. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15005.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klausing K., Scheidtmann K. H., Baumann E. A., Knippers R. Effects of in vitro dephosphorylation on DNA-binding and DNA helicase activities of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1258–1265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1258-1265.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. The p53 protein and its interactions with the oncogene products of the small DNA tumor viruses. Virology. 1990 Aug;177(2):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90505-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. Tumor suppressor genes. Bioessays. 1990 Feb;12(2):60–66. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin J. Y., Simmons D. T. Stable T-p53 complexes are not required for replication of simian virus 40 in culture or for enhanced phosphorylation of T antigen and p53. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2066–2072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2066-2072.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McVey D., Brizuela L., Mohr I., Marshak D. R., Gluzman Y., Beach D. Phosphorylation of large tumour antigen by cdc2 stimulates SV40 DNA replication. Nature. 1989 Oct 12;341(6242):503–507. doi: 10.1038/341503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Eckhart W. Mutation of the serine 312 phosphorylation site does not alter the ability of mouse p53 to inhibit simian virus 40 DNA replication in vivo. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1734–1744. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1734-1744.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Eckhart W. Phosphorylation of p53 in normal and simian virus 40-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):461–465. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meek D. W., Simon S., Kikkawa U., Eckhart W. The p53 tumour suppressor protein is phosphorylated at serine 389 by casein kinase II. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3253–3260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07524.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milner J., Cook A., Mason J. p53 is associated with p34cdc2 in transformed cells. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2885–2889. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07478.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Deppert W. Phosphorylation of p53 in primary, immortalised and transformed Balb/c mouse cells. Oncogene. 1990 Jul;5(7):1071–1076. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Farber J. M., Pipas J. M. Mutants with changes within or near a hydrophobic region of simian virus 40 large tumor antigen are defective for binding cellular protein p53. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):13–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90398-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C. The replication functions of SV40 T antigen are regulated by phosphorylation. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):735–738. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90179-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raycroft L., Wu H. Y., Lozano G. Transcriptional activation by wild-type but not transforming mutants of the p53 anti-oncogene. Science. 1990 Aug 31;249(4972):1049–1051. doi: 10.1126/science.2144364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigaudy P., Eckhart W. Nucleotide sequence of a cDNA encoding the monkey cellular phosphoprotein p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8375–8375. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V. p53, a transformation-related cellular-encoded protein, can be used as a biochemical marker for the detection of primary mouse tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2613–2617. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad A., Anderson C. W., Carroll R. B. Mapping of phosphomonoester and apparent phosphodiester bonds of the oncogene product p53 from simian virus 40-transformed 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):897–901. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samad A., Carroll R. B. The tumor suppressor p53 is bound to RNA by a stable covalent linkage. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Mar;11(3):1598–1606. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.3.1598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Buck M., Schneider J., Kalderon D., Fanning E., Smith A. E. Biochemical characterization of phosphorylation site mutants of simian virus 40 large T antigen: evidence for interaction between amino- and carboxy-terminal domains. J Virol. 1991 Mar;65(3):1479–1490. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.3.1479-1490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Echle B., Walter G. Simian virus 40 large T antigen is phosphorylated at multiple sites clustered in two separate regions. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):116–133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.116-133.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Haber A. Simian virus 40 large T antigen induces or activates a protein kinase which phosphorylates the transformation-associated protein p53. J Virol. 1990 Feb;64(2):672–679. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.2.672-679.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Hardung M., Echle B., Walter G. DNA-binding activity of simian virus 40 large T antigen correlates with a distinct phosphorylation state. J Virol. 1984 Apr;50(1):1–12. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.1.1-12.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H. Phosphorylation of simian virus 40 large T antigen: cytoplasmic and nuclear phophorylation sites differ in their metabolic stability. Virology. 1986 Apr 15;150(1):85–95. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidtmann K. H., Virshup D. M., Kelly T. J. Protein phosphatase 2A dephosphorylates simian virus 40 large T antigen specifically at residues involved in regulation of DNA-binding activity. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2098–2101. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2098-2101.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider J., Fanning E. Mutations in the phosphorylation sites of simian virus 40 (SV40) T antigen alter its origin DNA-binding specificity for sites I or II and affect SV40 DNA replication activity. J Virol. 1988 May;62(5):1598–1605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.5.1598-1605.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stürzbecher H. W., Maimets T., Chumakov P., Brain R., Addison C., Simanis V., Rudge K., Philp R., Grimaldi M., Court W. p53 interacts with p34cdc2 in mammalian cells: implications for cell cycle control and oncogenesis. Oncogene. 1990 Jun;5(6):795–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Cartwright C. A., Wright J. H., Eckhart W., Peden K. W., Srinivasan A., Pipas J. M. Properties of a simian virus 40 mutant T antigen substituted in the hydrophobic region: defective ATPase and oligomerization activities and altered phosphorylation accompany an inability to complex with cellular p53. J Virol. 1989 Aug;63(8):3362–3367. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.8.3362-3367.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Wright J. H., Deb S. P., Tegtmeyer P. The p53 complex from monkey cells modulates the biochemical activities of simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1310–1317. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1310-1317.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tack L. C., Wright J. H., Gurney E. G. Characterization of simian virus 40 large T antigen by using different monoclonal antibodies: T-p53 complexes are preferentially ATPase active and adenylylated. J Virol. 1988 Mar;62(3):1028–1037. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.3.1028-1037.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Roy F., Fransen L., Fiers W. Metabolic turnover of phosphorylation sites in simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):442–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.442-446.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang E. H., Friedman P. N., Prives C. The murine p53 protein blocks replication of SV40 DNA in vitro by inhibiting the initiation functions of SV40 large T antigen. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):379–392. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90913-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]