Abstract
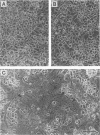
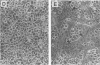
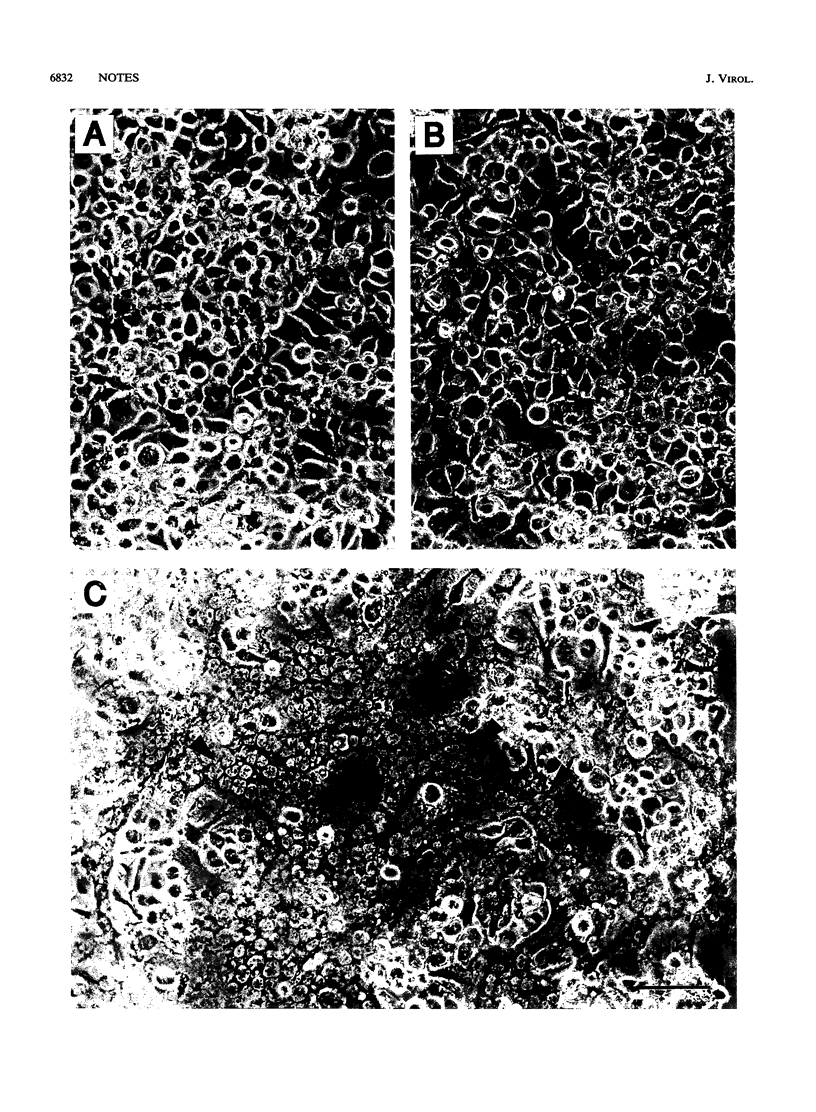
The baculovirus gp64 envelope glycoprotein is a major component of the envelope of the budded virus (BV) and is involved in BV entry into the host cell by endocytosis. To determine whether gp64 alone was sufficient to mediate membrane fusion, the Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus gp64 protein was transiently expressed in uninfected insect cells. Cells expressing the baculovirus gp64 protein were examined for membrane fusion activity by using a syncytium formation assay under various conditions of exposure to low pH. Cells expressing the gp64 protein mediated membrane fusion and syncytium formation in a pH-dependent manner. A pH of 5.5 or lower was required to induce membrane fusion. In addition, exposure of gp64-expressing cells to low pH for as little as 5 s was sufficient to induce gp64-mediated syncytium formation. These studies provide direct evidence that gp64 is a pH-dependent membrane fusion protein and suggest that gp64 is the protein responsible for fusion of the virion envelope with the endosome membrane during BV entry into the host cell by endocytosis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Blissard G. W., Quant-Russell R. L., Rohrmann G. F., Beaudreau G. S. Nucleotide sequence, transcriptional mapping, and temporal expression of the gene encoding p39, a major structural protein of the multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus of Orgyia pseudotsugata. Virology. 1989 Feb;168(2):354–362. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90276-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus diversity and molecular biology. Annu Rev Entomol. 1990;35:127–155. doi: 10.1146/annurev.en.35.010190.001015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus gp64 gene expression: analysis of sequences modulating early transcription and transactivation by IE1. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5820–5827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5820-5827.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Location, sequence, transcriptional mapping, and temporal expression of the gp64 envelope glycoprotein gene of the Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1989 Jun;170(2):537–555. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. B., Blissard G. W., Rohrmann G. F. Characterization of the infection cycle of the Orgyia pseudotsugata multicapsid nuclear polyhedrosis virus in Lymantria dispar cells. J Gen Virol. 1990 Dec;71(Pt 12):2841–2846. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-71-12-2841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Düzgüneş N., Pedroso de Lima M. C., Stamatatos L., Flasher D., Alford D., Friend D. S., Nir S. Fusion activity and inactivation of influenza virus: kinetics of low pH-induced fusion with cultured cells. J Gen Virol. 1992 Jan;73(Pt 1):27–37. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-1-27. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. The regulation of baculovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann A. W., Faulkner P. Monoclonal antibodies to baculovirus structural proteins: determination of specificities by Western blot analysis. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):432–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90214-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsh M., Helenius A. Virus entry into animal cells. Adv Virus Res. 1989;36:107–151. doi: 10.1016/S0065-3527(08)60583-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morse M. A., Marriott A. C., Nuttall P. A. The glycoprotein of Thogoto virus (a tick-borne orthomyxo-like virus) is related to the baculovirus glycoprotein GP64. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):640–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90030-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts T. E., Faulkner P. Fatty acid acylation of the 67K envelope glycoprotein of a baculovirus: Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):377–381. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohrmann G. F. Baculovirus structural proteins. J Gen Virol. 1992 Apr;73(Pt 4):749–761. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-73-4-749. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman L. E., Summers M. D. Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: comparative infectivity of the occluded, alkali-liberated, and nonoccluded forms. J Invertebr Pathol. 1977 Jul;30(1):102–103. doi: 10.1016/0022-2011(77)90045-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkman L. E. The 64K envelope protein of budded Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:103–118. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitford M., Stewart S., Kuzio J., Faulkner P. Identification and sequence analysis of a gene encoding gp67, an abundant envelope glycoprotein of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1989 Mar;63(3):1393–1399. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.3.1393-1399.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiley D. C., Skehel J. J. The structure and function of the hemagglutinin membrane glycoprotein of influenza virus. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:365–394. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]