Abstract
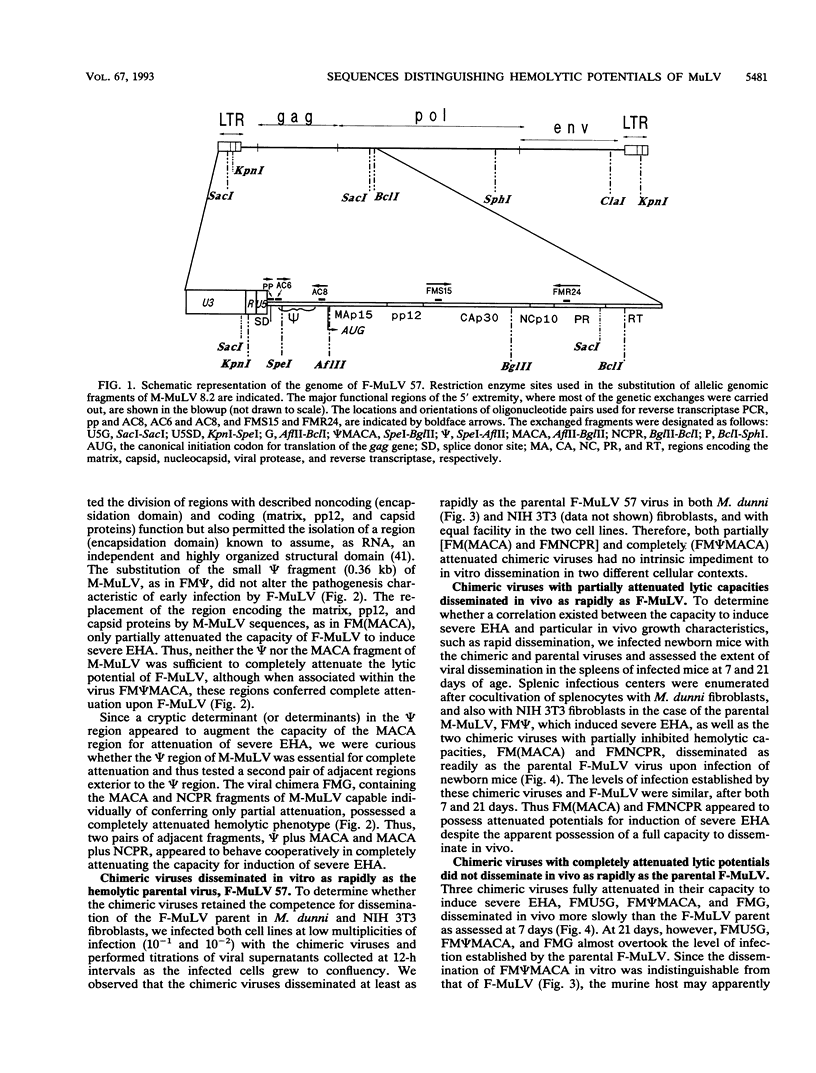
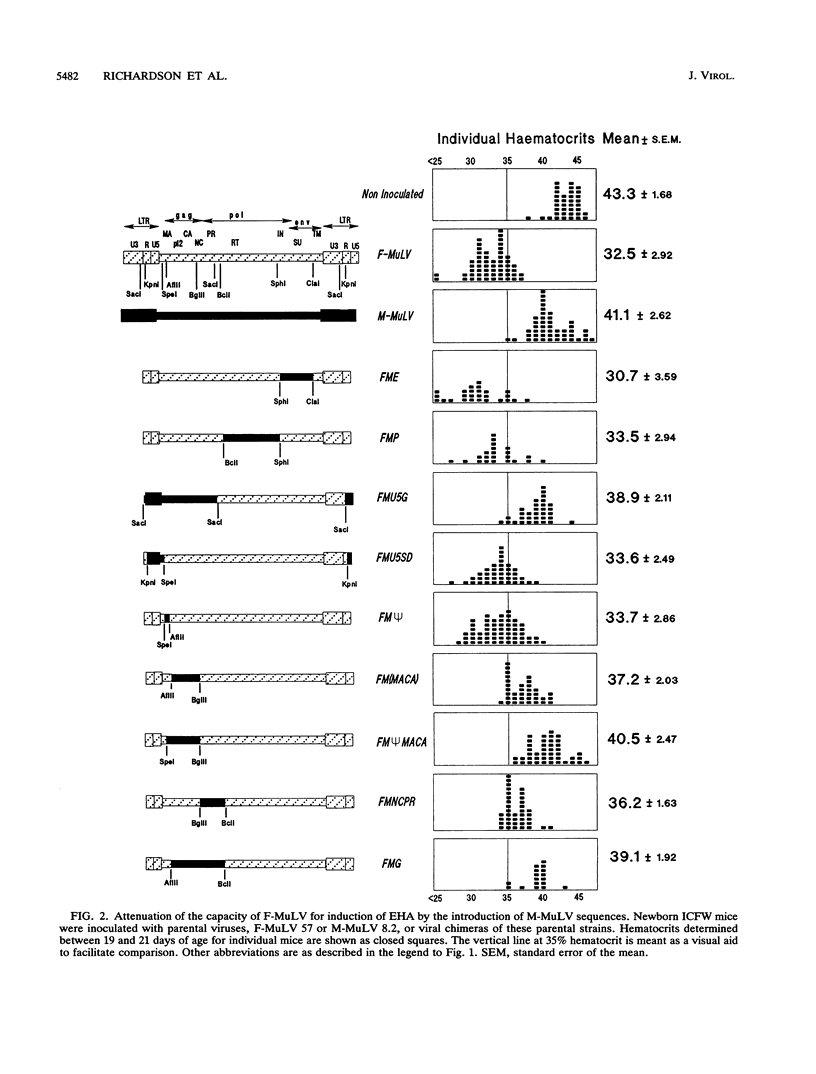
Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses (F- and M-MuLV) induce distinct diseases in hematopoietic tissues following inoculation of newborn mice of susceptible strains. F-MuLV induces erythroleukemia preceded by severe early hemolytic anemia; M-MuLV induces thymomas and only very mild hemolysis. The major viral determinant of severe early hemolytic anemia residues in the env gene, but sequences located outside this gene can modulate this effect. By means of genetic chimeras of F- and M-MuLV, we have found that although they are confined to the 5' portion of the env gene intron, sequences that determine the distinctive hemolytic potentials of F- and M-MuLV are widely distributed over a region spanning the RNA encapsidation domain, the gag gene, and the portion of the pol gene encoding the viral protease. Within this large region, two fragments of M-MuLV, a 1.3-kb region encoding the matrix, pp12, and capsid proteins and a 0.8-kb region encoding the nucleocapsid and the viral protease, were capable, individually, of partially attenuating the capacity of F-MuLV for induction of severe early hemolytic anemia. In association, these two fragments conferred complete attenuation. Moreover, a second pair of adjacent fragments within this large region appeared to behave cooperatively to confer complete attenuation; a 0.36-kb region roughly corresponding to the encapsidation domain, although not detectably altering hemolytic potential on its own, deepened the attenuation conferred by the adjacent 1.3-kb region. Whether capable of inducing severe early hemolytic anemia or not and despite different efficiencies of induction of recombinant polytropic viruses, all chimeric viruses retained the erythroleukemogenicity of the F-MuLV parent.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brody B. A., Rhee S. S., Sommerfelt M. A., Hunter E. A viral protease-mediated cleavage of the transmembrane glycoprotein of Mason-Pfizer monkey virus can be suppressed by mutations within the matrix protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3443–3447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bösze Z., Thiesen H. J., Charnay P. A transcriptional enhancer with specificity for erythroid cells is located in the long terminal repeat of the Friend murine leukemia virus. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1615–1623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Portis J. L., Wehrly K., Nishio J. Effect of murine host genotype on MCF virus expression, latency, and leukemia cell type of leukemias induced by Friend murine leukemia helper virus. Virology. 1983 Jul 15;128(1):221–233. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90332-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Wehrly K., Cloyd M., Britt W., Portis J., Collins J., Nishio J. Characterization of mouse monoclonal antibodies specific for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced erythroleukemia cells: friend-specific and FMR-specific antigens. Virology. 1981 Jul 15;112(1):131–144. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90619-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czub M., McAtee F. J., Portis J. L. Murine retrovirus-induced spongiform encephalomyelopathy: host and viral factors which determine the length of the incubation period. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3298–3305. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3298-3305.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Barrette M., Jolicoeur P. Physical mapping of the paralysis-inducing determinant of a wild mouse ecotropic neurotropic retrovirus. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):356–363. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.356-363.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L. H., Morrison R. P., Malik F. G., Portis J., Britt W. J. A neutralizable epitope common to the envelope glycoproteins of ecotropic, polytropic, xenotropic, and amphotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6176–6183. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6176-6183.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Nomura S., Bolognesi D. P. A novel murine oncornavirus with dual eco- and xenotropic properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Dec;72(12):5150–5155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.12.5150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu X. D., Katz R. A., Skalka A. M., Maniatis T. The role of branchpoint and 3'-exon sequences in the control of balanced splicing of avian retrovirus RNA. Genes Dev. 1991 Feb;5(2):211–220. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.2.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S., Traktman P., Baltimore D. Isolation and properties of Moloney murine leukemia virus mutants: use of a rapid assay for release of virion reverse transcriptase. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):239–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.239-248.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golub E. I., Kim H., Volsky D. J. Transfection of DNA into adherent cells by DEAE-dextran/DMSO method increases drastically if the cells are removed from surface and treated in suspension. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4902–4902. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirsch I., Salaun D., Brichacek B., Chermann J. C. HIV1 cytopathogenicity-genetic difference between direct cytotoxic and fusogenic effect. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):647–654. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90031-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. At least four viral genes contribute to the leukemogenicity of murine retrovirus MCF 247 in AKR mice. J Virol. 1985 Jan;53(1):158–165. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.1.158-165.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang L. S., Park J., Gilboa E. Role of intron-contained sequences in formation of moloney murine leukemia virus env mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2289–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lander M. R., Chattopadhyay S. K. A Mus dunni cell line that lacks sequences closely related to endogenous murine leukemia viruses and can be infected by ectropic, amphotropic, xenotropic, and mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):695–698. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.695-698.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Baltimore D. Varying the position of a retrovirus packaging sequence results in the encapsidation of both unspliced and spliced RNAs. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):401–407. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.401-407.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally M. T., Beemon K. Intronic sequences and 3' splice sites control Rous sarcoma virus RNA splicing. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):6–11. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.6-11.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNally M. T., Gontarek R. R., Beemon K. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus intronic sequences that negatively regulate splicing. Virology. 1991 Nov;185(1):99–108. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90758-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., McKinney M. D., Agranovsky O. Contribution of the gag and pol sequences to the leukemogenicity of Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1985 Jun;54(3):864–868. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.3.864-868.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens R. J., Dubay J. W., Hunter E., Compans R. W. Human immunodeficiency virus envelope protein determines the site of virus release in polarized epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 1;88(9):3987–3991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.9.3987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paquette Y., Hanna Z., Savard P., Brousseau R., Robitaille Y., Jolicoeur P. Retrovirus-induced murine motor neuron disease: mapping the determinant of spongiform degeneration within the envelope gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(10):3896–3900. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.10.3896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., Czub S., Garon C. F., McAtee F. J. Neurodegenerative disease induced by the wild mouse ecotropic retrovirus is markedly accelerated by long terminal repeat and gag-pol sequences from nondefective Friend murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1990 Apr;64(4):1648–1656. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.4.1648-1656.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis J. L., Perryman S., McAtee F. J. The R-U5-5' leader sequence of neurovirulent wild mouse retrovirus contains an element controlling the incubation period of neurodegenerative disease. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):1877–1883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.1877-1883.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C., Goff S., Gilboa E., Paskind M., Mitra S. W., Baltimore D. Structure of a cloned circular Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA molecule containing an inverted segment: implications for retrovirus integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3932–3936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Ellerbrok H., Pozo F., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Evans L. H., Chesebro B. Sequences in the U5-gag-pol region influence early and late pathogenic effects of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1990 May;64(5):2135–2140. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.5.2135-2140.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Evans L., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Chesebro B. Analysis of two strains of Friend murine leukemia viruses differing in ability to induce early splenomegaly: lack of relationship with generation of recombinant mink cell focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):389–393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.389-393.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Nishio J., Wehrly K., Lodmell D., Chesebro B. Use of a focal immunofluorescence assay on live cells for quantitation of retroviruses: distinction of host range classes in virus mixtures and biological cloning of dual-tropic murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):110–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90187-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., Sola B., Evans L., Nishio J., Hayes S. F., Nathanson K., Garon C. F., Chesebro B. Hemolytic anemia and erythroleukemia, two distinct pathogenic effects of Friend MuLV: mapping of the effects to different regions of the viral genome. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):851–859. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90800-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sitbon M., d'Auriol L., Ellerbrok H., André C., Nishio J., Perryman S., Pozo F., Hayes S. F., Wehrly K., Tambourin P. Substitution of leucine for isoleucine in a sequence highly conserved among retroviral envelope surface glycoproteins attenuates the lytic effect of the Friend murine leukemia virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 1;88(13):5932–5936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.13.5932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Renjifo B., Golemis E., Fredrickson T. N., Hartley J. W., Hopkins N. Mutation of the core or adjacent LVb elements of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer alters disease specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):233–242. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevenson M., Haggerty S., Lamonica C., Mann A. M., Meier C., Wasiak A. Cloning and characterization of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 variants diminished in the ability to induce syncytium-independent cytolysis. J Virol. 1990 Aug;64(8):3792–3803. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.8.3792-3803.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiesen H. J., Bösze Z., Henry L., Charnay P. A DNA element responsible for the different tissue specificities of Friend and Moloney retroviral enhancers. J Virol. 1988 Feb;62(2):614–618. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.2.614-618.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tounekti N., Mougel M., Roy C., Marquet R., Darlix J. L., Paoletti J., Ehresmann B., Ehresmann C. Effect of dimerization on the conformation of the encapsidation Psi domain of Moloney murine leukemia virus RNA. J Mol Biol. 1992 Jan 5;223(1):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90726-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wendling F., Moreau-Gachelin F., Tambourin P. Emergence of tumorigenic cells during the course of Friend virus leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3614–3618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu X., Yuan X., Matsuda Z., Lee T. H., Essex M. The matrix protein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 is required for incorporation of viral envelope protein into mature virions. J Virol. 1992 Aug;66(8):4966–4971. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.4966-4971.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Mareuil J., Brichacek B., Salaun D., Chermann J. C., Hirsch I. The human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) gag gene product p18 is responsible for enhanced fusogenicity and host range tropism of the highly cytopathic HIV-1-NDK strain. J Virol. 1992 Nov;66(11):6797–6801. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.11.6797-6801.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


