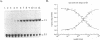Abstract
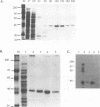
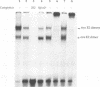
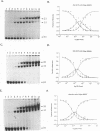
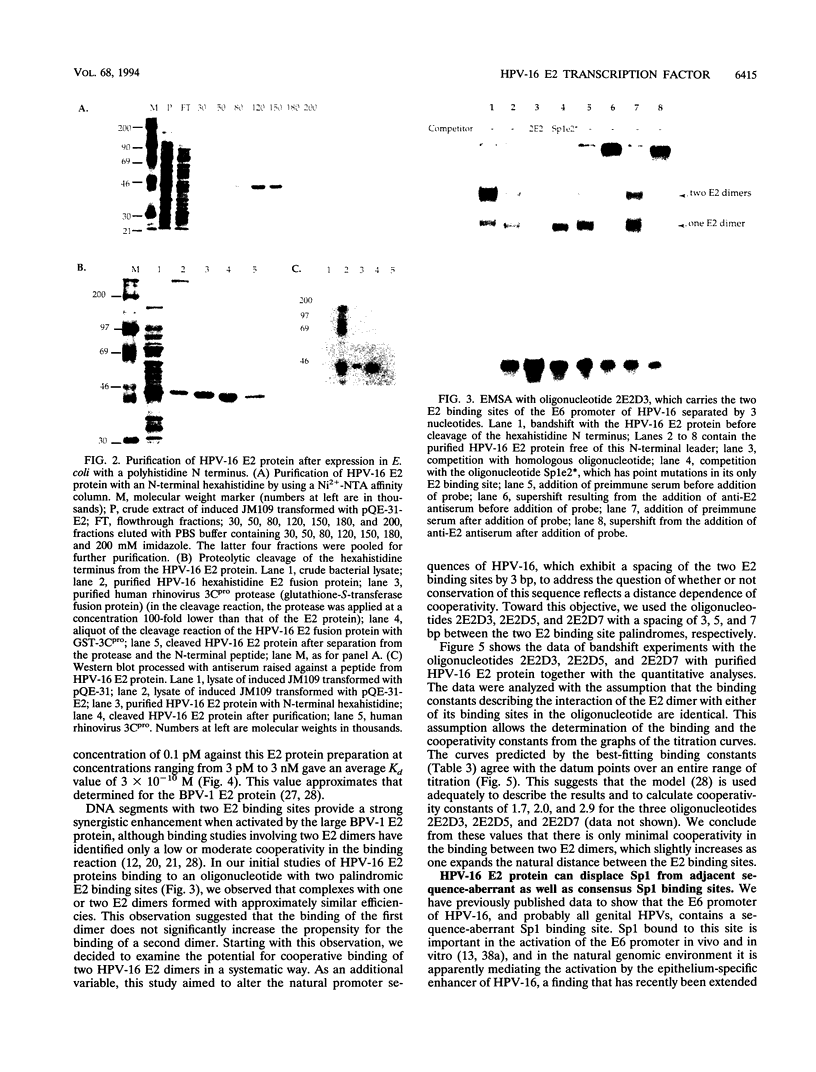
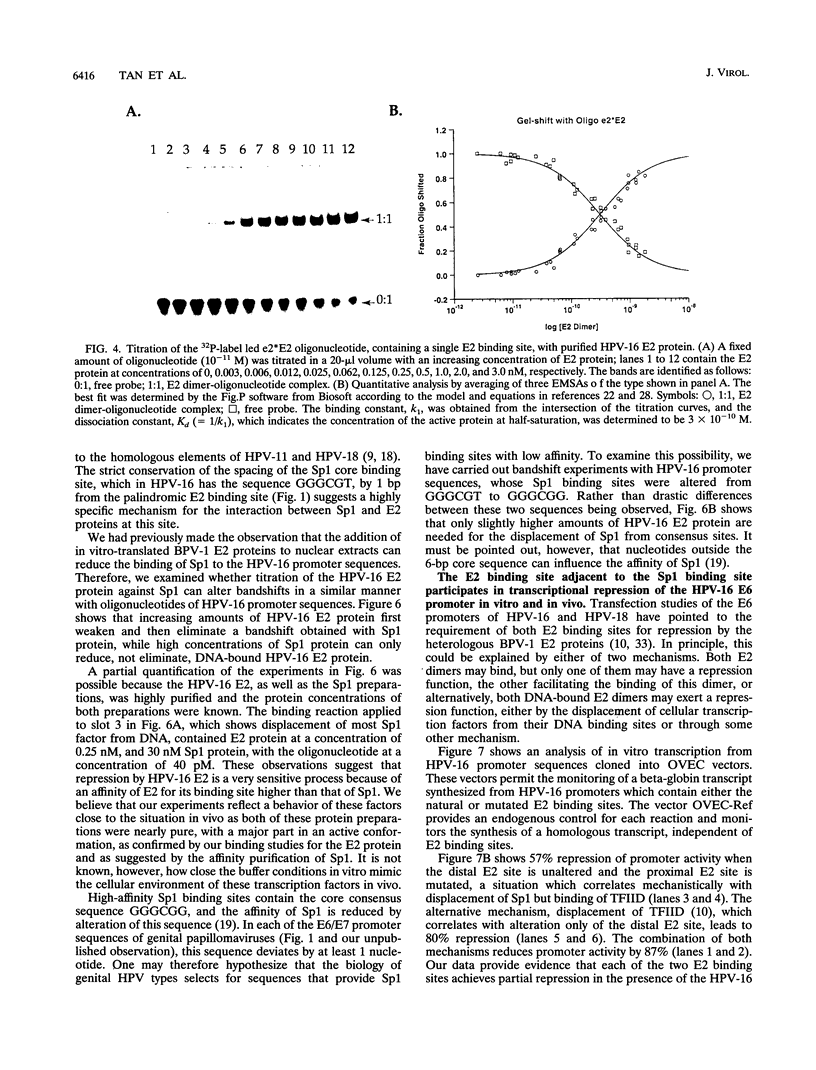
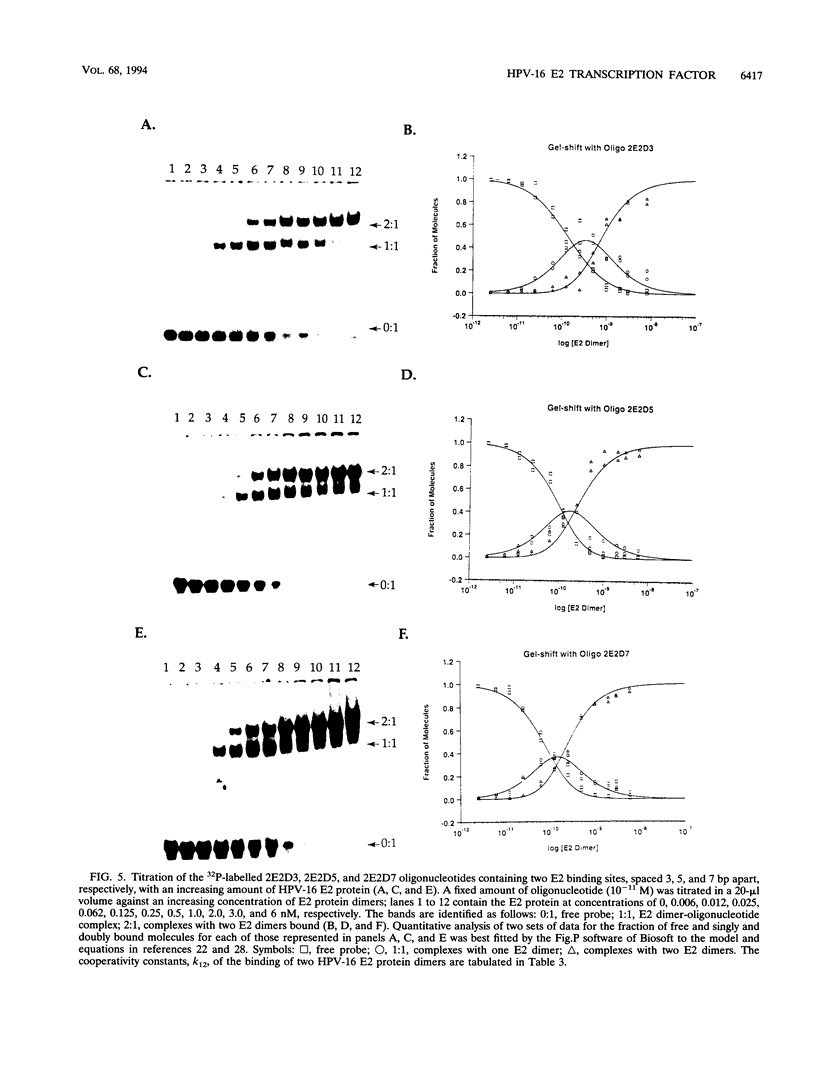
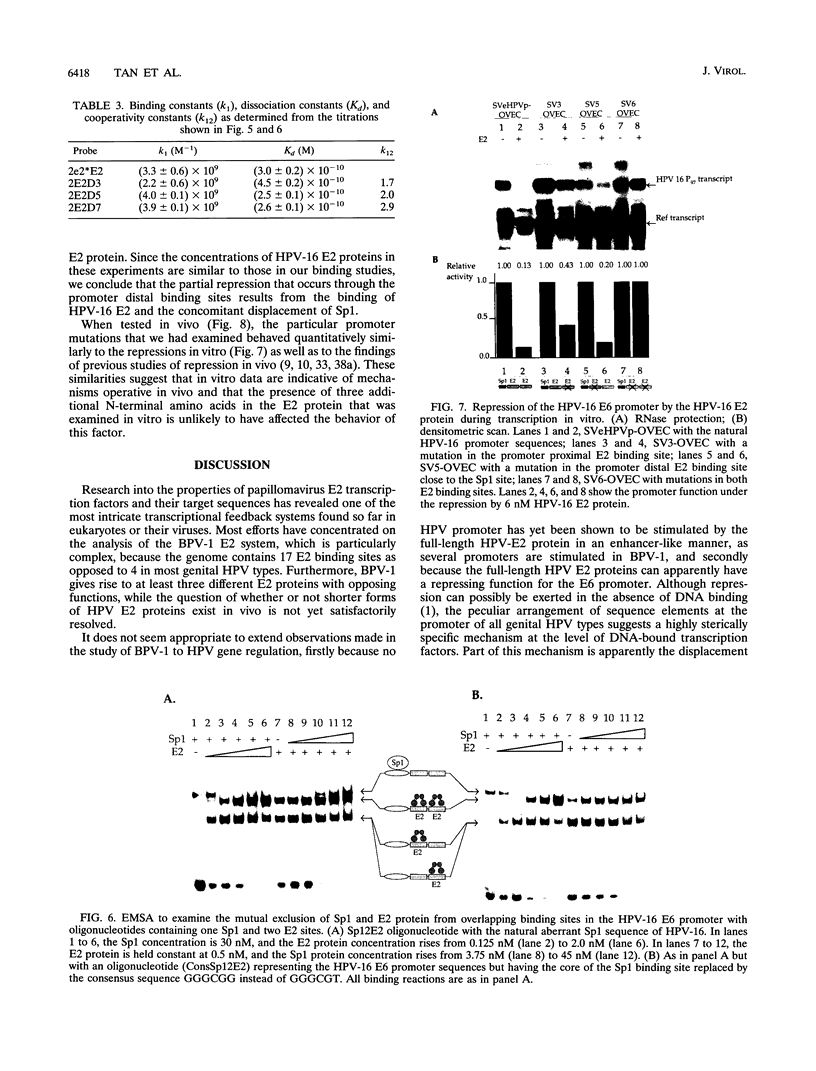
The E6 promoters of all genital human papillomaviruses have a characteristic alignment of transcription factor binding sites. Activation of the basic transcription complex at the TATA box depends upon a sequence-aberrant Sp1 site. Repression of E6 promoters is achieved by two binding sites for the viral E2 protein positioned between the Sp1 site and the TATA box. We have purified the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 protein after expression in Escherichia coli and studied its binding and repression properties with oligonucleotides representing the homologous promoter sequences. A Kd value of 3 x 10(-10) M indicated binding properties expected for a native protein. We found low cooperativity in the binding of two E2 dimers to flanking sites, both when these sites were separated by 3 nucleotides, as in the natural promoter, and when they were further apart. E2 protein, bound close to the distal Sp1 site, displaced the Sp1 factor even when the aberrant sequence was replaced by a typical Sp1 core recognition site. The high affinity of E2 protein for its binding site even led to Sp1 displacement at concentrations of E2 protein nearly 2 orders of magnitude lower than those of Sp1. Functional analyses of mutated E6 promoter sequences showed repression by this distal E2 binding site in the complete absence of binding to the proximal E2 binding site. From our findings and observations published by others, we conclude that each of the E2 binding sites in the E6 promoter of genital human papillomaviruses plays a separate role by displacing the transcription factors Sp1 and TFIID.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barsoum J., Prakash S. S., Han P., Androphy E. J. Mechanism of action of the papillomavirus E2 repressor: repression in the absence of DNA binding. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3941–3945. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3941-3945.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernard H. U., Apt D. Transcriptional control and cell type specificity of HPV gene expression. Arch Dermatol. 1994 Feb;130(2):210–215. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenowitz M., Senear D. F., Shea M. A., Ackers G. K. Quantitative DNase footprint titration: a method for studying protein-DNA interactions. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:132–181. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan S. Y., Bernard H. U., Ong C. K., Chan S. P., Hofmann B., Delius H. Phylogenetic analysis of 48 papillomavirus types and 28 subtypes and variants: a showcase for the molecular evolution of DNA viruses. J Virol. 1992 Oct;66(10):5714–5725. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.10.5714-5725.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiang C. M., Dong G., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Control of human papillomavirus type 11 origin of replication by the E2 family of transcription regulatory proteins. J Virol. 1992 Sep;66(9):5224–5231. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.9.5224-5231.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemens K. R., Wolf V., McBryant S. J., Zhang P., Liao X., Wright P. E., Gottesfeld J. M. Molecular basis for specific recognition of both RNA and DNA by a zinc finger protein. Science. 1993 Apr 23;260(5107):530–533. doi: 10.1126/science.8475383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong G., Broker T. R., Chow L. T. Human papillomavirus type 11 E2 proteins repress the homologous E6 promoter by interfering with the binding of host transcription factors to adjacent elements. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1115–1127. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1115-1127.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dostatni N., Lambert P. F., Sousa R., Ham J., Howley P. M., Yaniv M. The functional BPV-1 E2 trans-activating protein can act as a repressor by preventing formation of the initiation complex. Genes Dev. 1991 Sep;5(9):1657–1671. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.9.1657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier J. M., Dillner J., Yaniv M. Structural analysis of the human papillomavirus type 16-E2 transactivator with antipeptide antibodies reveals a high mobility region linking the transactivation and the DNA-binding domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Dec;19(25):7073–7079. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.25.7073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gauthier J. M., Dostatni N., Lusky M., Yaniv M. Two DNA-bound E2 dimers are required for strong transcriptional activation and for cooperation with cellular factors in most cells. New Biol. 1991 May;3(5):498–509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gloss B., Bernard H. U. The E6/E7 promoter of human papillomavirus type 16 is activated in the absence of E2 proteins by a sequence-aberrant Sp1 distal element. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5577–5584. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5577-5584.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ham J., Dostatni N., Gauthier J. M., Yaniv M. The papillomavirus E2 protein: a factor with many talents. Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Nov;16(11):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90172-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hegde R. S., Grossman S. R., Laimins L. A., Sigler P. B. Crystal structure at 1.7 A of the bovine papillomavirus-1 E2 DNA-binding domain bound to its DNA target. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):505–512. doi: 10.1038/359505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A., Roeder R. G. Purification of his-tagged proteins in non-denaturing conditions suggests a convenient method for protein interaction studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6337–6338. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holt S. E., Schuller G., Wilson V. G. DNA binding specificity of the bovine papillomavirus E1 protein is determined by sequences contained within an 18-base-pair inverted repeat element at the origin of replication. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1094–1102. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1094-1102.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoppe-Seyler F., Butz K. Activation of human papillomavirus type 18 E6-E7 oncogene expression by transcription factor Sp1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Dec 25;20(24):6701–6706. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.24.6701. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight J. D., Li R., Botchan M. The activation domain of the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein mediates association of DNA-bound dimers to form DNA loops. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 15;88(8):3204–3208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.8.3204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert P. F., Dostatni N., McBride A. A., Yaniv M., Howley P. M., Arcangioli B. Functional analysis of the papilloma virus E2 trans-activator in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):38–48. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.38. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Moal M. A., Yaniv M., Thierry F. The bovine papillomavirus type 1 (BPV1) replication protein E1 modulates transcriptional activation by interacting with BPV1 E2. J Virol. 1994 Feb;68(2):1085–1093. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.2.1085-1093.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Clerc R. G., Brenowitz M., Sharp P. A. The Oct-2 protein binds cooperatively to adjacent octamer sites. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1625–1638. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li R., Knight J. D., Jackson S. P., Tjian R., Botchan M. R. Direct interaction between Sp1 and the BPV enhancer E2 protein mediates synergistic activation of transcription. Cell. 1991 May 3;65(3):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90467-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McBride A. A., Romanczuk H., Howley P. M. The papillomavirus E2 regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 5;266(28):18411–18414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohr I. J., Clark R., Sun S., Androphy E. J., MacPherson P., Botchan M. R. Targeting the E1 replication protein to the papillomavirus origin of replication by complex formation with the E2 transactivator. Science. 1990 Dec 21;250(4988):1694–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2176744. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monini P., Blitz I. L., Cassai E. Cooperative DNA binding of the bovine papillomavirus E2 transcriptional activator is antagonized by truncated E2 polypeptides. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5668–5676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5668-5676.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monini P., Grossman S. R., Pepinsky B., Androphy E. J., Laimins L. A. Cooperative binding of the E2 protein of bovine papillomavirus to adjacent E2-responsive sequences. J Virol. 1991 Apr;65(4):2124–2130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.4.2124-2130.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moskaluk C., Bastia D. DNA bending is induced in an enhancer by the DNA-binding domain of the bovine papillomavirus E2 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Mar;85(6):1826–1830. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.6.1826. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps W. C., Howley P. M. Transcriptional trans-activation by the human papillomavirus type 16 E2 gene product. J Virol. 1987 May;61(5):1630–1638. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.5.1630-1638.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prakash S. S., Grossman S. R., Pepinsky R. B., Laimins L. A., Androphy E. J. Amino acids necessary for DNA contact and dimerization imply novel motifs in the papillomavirus E2 trans-activator. Genes Dev. 1992 Jan;6(1):105–116. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Remm M., Brain R., Jenkins J. R. The E2 binding sites determine the efficiency of replication for the origin of human papillomavirus type 18. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 25;20(22):6015–6021. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.22.6015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanczuk H., Thierry F., Howley P. M. Mutational analysis of cis elements involved in E2 modulation of human papillomavirus type 16 P97 and type 18 P105 promoters. J Virol. 1990 Jun;64(6):2849–2859. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.6.2849-2859.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandler A. B., Vande Pol S. B., Spalholz B. A. Repression of bovine papillomavirus type 1 transcription by the E1 replication protein. J Virol. 1993 Sep;67(9):5079–5087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.9.5079-5087.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman L., Alloul N. Human papillomavirus type 16 expresses a variety of alternatively spliced mRNAs putatively encoding the E2 protein. Virology. 1992 Dec;191(2):953–959. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90271-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Byrne J. C., Howley P. M. Evidence for cooperativity between E2 binding sites in E2 trans-regulation of bovine papillomavirus type 1. J Virol. 1988 Sep;62(9):3143–3150. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.9.3143-3150.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenlund A., Botchan M. R. The E2 trans-activator can act as a repressor by interfering with a cellular transcription factor. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):123–136. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sverdrup F., Khan S. A. Replication of human papillomavirus (HPV) DNAs supported by the HPV type 18 E1 and E2 proteins. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):505–509. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.505-509.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan S. H., Gloss B., Bernard H. U. During negative regulation of the human papillomavirus-16 E6 promoter, the viral E2 protein can displace Sp1 from a proximal promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Jan 25;20(2):251–256. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.2.251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ustav E., Ustav M., Szymanski P., Stenlund A. The bovine papillomavirus origin of replication requires a binding site for the E2 transcriptional activator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):898–902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Pol S. B., Howley P. M. A bovine papillomavirus constitutive enhancer is negatively regulated by the E2 repressor through competitive binding for a cellular factor. J Virol. 1990 Nov;64(11):5420–5429. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.11.5420-5429.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. A., Leong L. E., Ng P. W., Tan S. H., Waller S., Murphy D., Porter A. G. Efficient and rapid affinity purification of proteins using recombinant fusion proteases. Biotechnology (N Y) 1994 Jun;12(6):601–605. doi: 10.1038/nbt0694-601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westin G., Gerster T., Müller M. M., Schaffner G., Schaffner W. OVEC, a versatile system to study transcription in mammalian cells and cell-free extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):6787–6798. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.6787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D., Sheng G., Lecuit T., Dostatni N., Desplan C. Cooperative dimerization of paired class homeo domains on DNA. Genes Dev. 1993 Nov;7(11):2120–2134. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.11.2120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J. H., Davidson I., Matthes H., Garnier J. M., Chambon P. Cloning, expression, and transcriptional properties of the human enhancer factor TEF-1. Cell. 1991 May 17;65(4):551–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90088-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang L., Li R., Mohr I. J., Clark R., Botchan M. R. Activation of BPV-1 replication in vitro by the transcription factor E2. Nature. 1991 Oct 17;353(6345):628–632. doi: 10.1038/353628a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]