Abstract
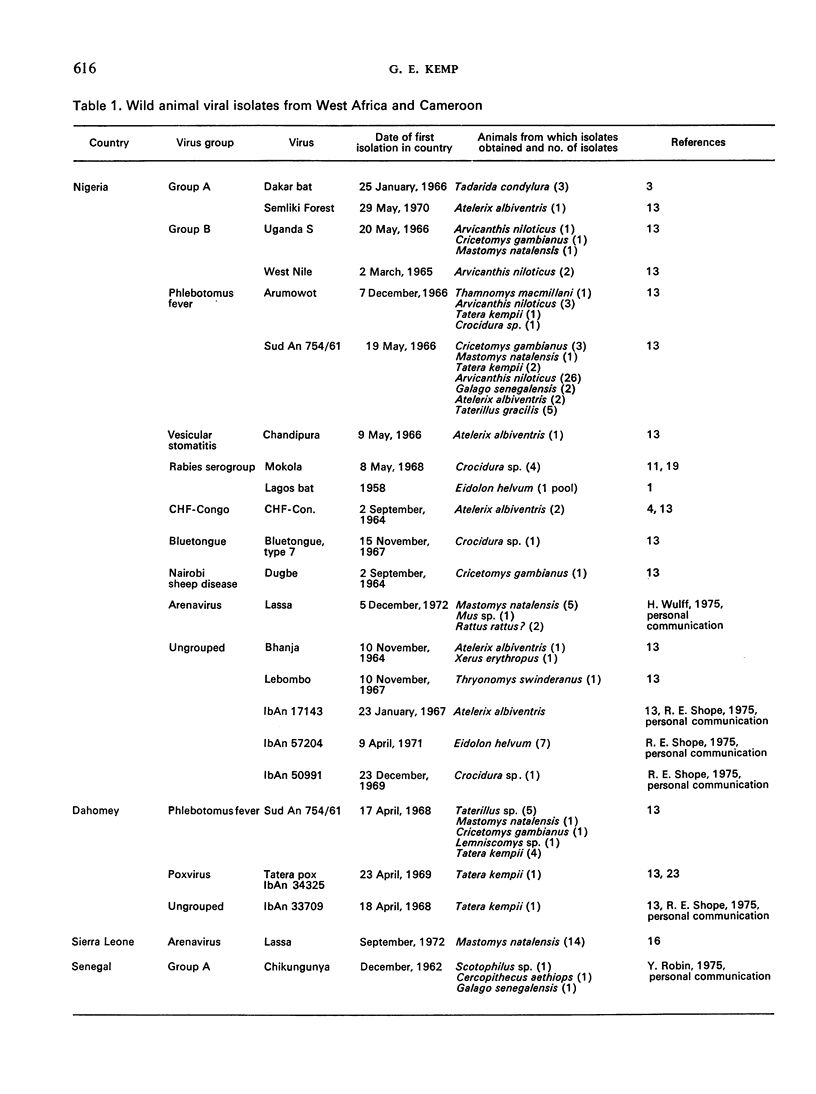
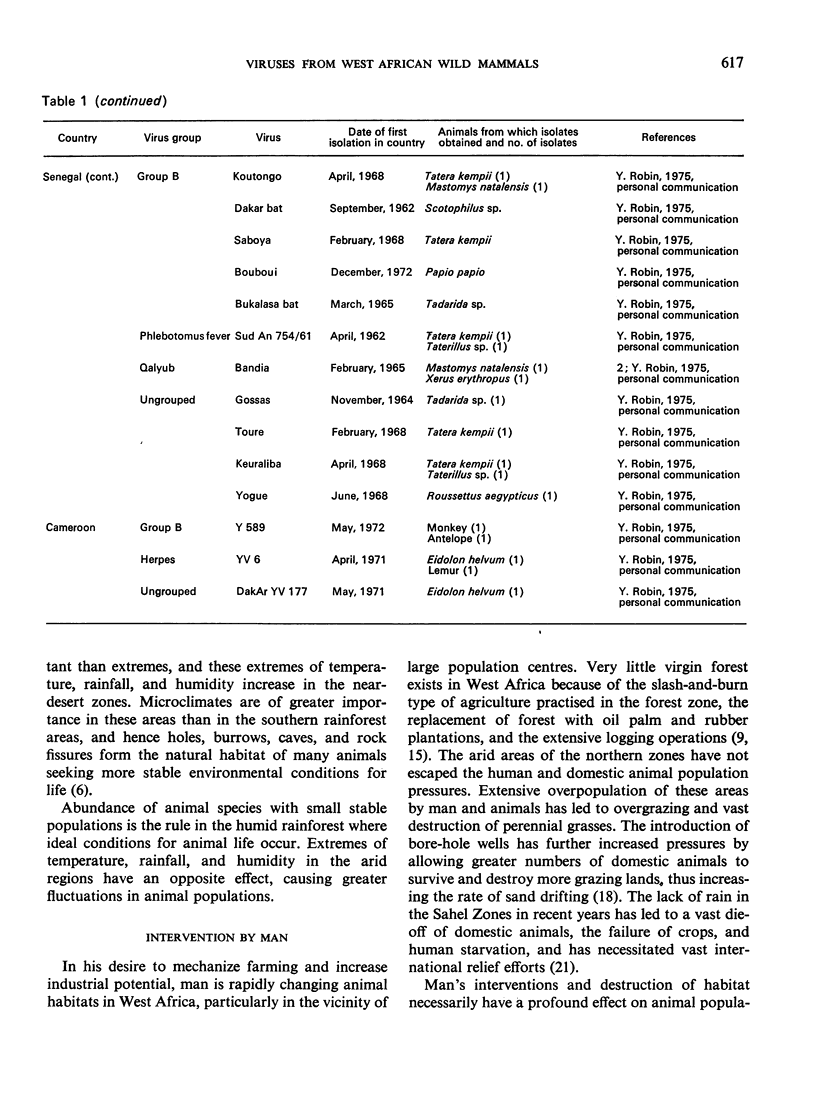
At least thirty-seven different viruses have been isolated from wild mammals in West Africa since 1962. Some of these, including Lassa virus, are already known to cause serious human morbidity and mortality. Crimean haemorrhagic fever-Congo virus, Dugbe virus, Mokola virus, and a smallpox-like agent from a gerbil in Dahomey are briefly discussed. An account of social and ecologic factors affecting man, domestic animals, and their interaction with wild mammals is given.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOULGER L. R., PORTERFIELD J. S. Isolation of a virus from Nigerian fruit bats. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1958 Sep;52(5):421–424. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(58)90127-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BRES P., CHAMBON L. TECHNIQUES POUR L''ETUDE DE L'INFESTATION NATURELLE DES CHAUVES-SOURIS PAR LES ARBOVIRUS. INT'ER ET 'EPID'EMIOLOGIQUE AU S'EN'EGAL. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1964 Jul;107:34–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brès P., Cornet M., Robin Y. Le virus de la Forét de Bandia (IPD-A 611), nouveau prototype d'arbovirus isolé au Sénégal. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1967 Nov;113(5):739–747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Causey O. R., Kemp G. E., Madbouly M. H., David-West T. S. Congo virus from domestic livestock, African hedgehog, and arthropods in Nigeria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1970 Sep;19(5):846–850. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1970.19.846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Familusi J. B., Moore D. L. Isolation of a rabies related virus from the cerebrospinal fluid of a child with 'aseptic meningitis'. Afr J Med Sci. 1972 Jan;3(1):93–96. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. E., Causey O. R., Causey C. E. Virus isolations from trade cattle, sheep, goats and swine at Ibadan, Nigeria, 1964-68. Bull Epizoot Dis Afr. 1971 Jun;19(2):131–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. E., Causey O. R., Moore D. L., O'Connor E. H. Viral isolates from livestock in northern Nigeria: 1966-1970. Am J Vet Res. 1973 May;34(5):707–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp G. E., Causey O. R., Moore D. L., Odelola A., Fabiyi A. Mokola virus. Further studies on IbAn 27377, a new rabies-related etiologic agent of zoonosis in nigeria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1972 May;21(3):356–359. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monath T. P., Kemp G. E. Importance of nonhuman primates in yellow fever epidemiology in Nigeria. Trop Geogr Med. 1973 Mar;25(1):28–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore D. L., Causey O. R., Carey D. E., Reddy S., Cooke A. R., Akinkugbe F. M., David-West T. S., Kemp G. E. Arthropod-borne viral infections of man in Nigeria, 1964-1970. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1975 Mar;69(1):49–64. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1975.11686983. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shope R. E., Murphy F. A., Harrison A. K., Causey O. R., Kemp G. E., Simpson D. I., Moore D. L. Two African viruses serologically and morphologically related to rabies virus. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):690–692. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.690-692.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


