Abstract
Fifty two strains of anaerobic bacteria isolated from the upper gut of patients with small intestinal bacterial overgrowth were screened for phospholipase activity. Bacteroides melaninogenicus spp intermedius had the greatest activity. The effects of culture supernatants of this organism and deoxycholate on intestinal calcium absorption and disaccharidase activity were studied using a rat closed loop model. The supernatant decreased the in vitro uptake of calcium by 15% (p less than 0.001). Deoxycholate reduced calcium uptake by 16% (p less than 0.001). Combined culture supernatant and deoxycholate reduced calcium uptake by 39% (p less than 0.001) suggesting a potentiation of supernatant activity by deoxycholate. Culture supernatant and deoxycholate, both alone and combined, significantly reduced lactase, sucrase, and maltase activity. Electron microscopic evidence showed degeneration of microvilli, disruption of mitochondrial structure, and swelling of the endoplasmic reticulum after exposure of the intestinal loops to the supernatant or deoxycholate.
Full text
PDF

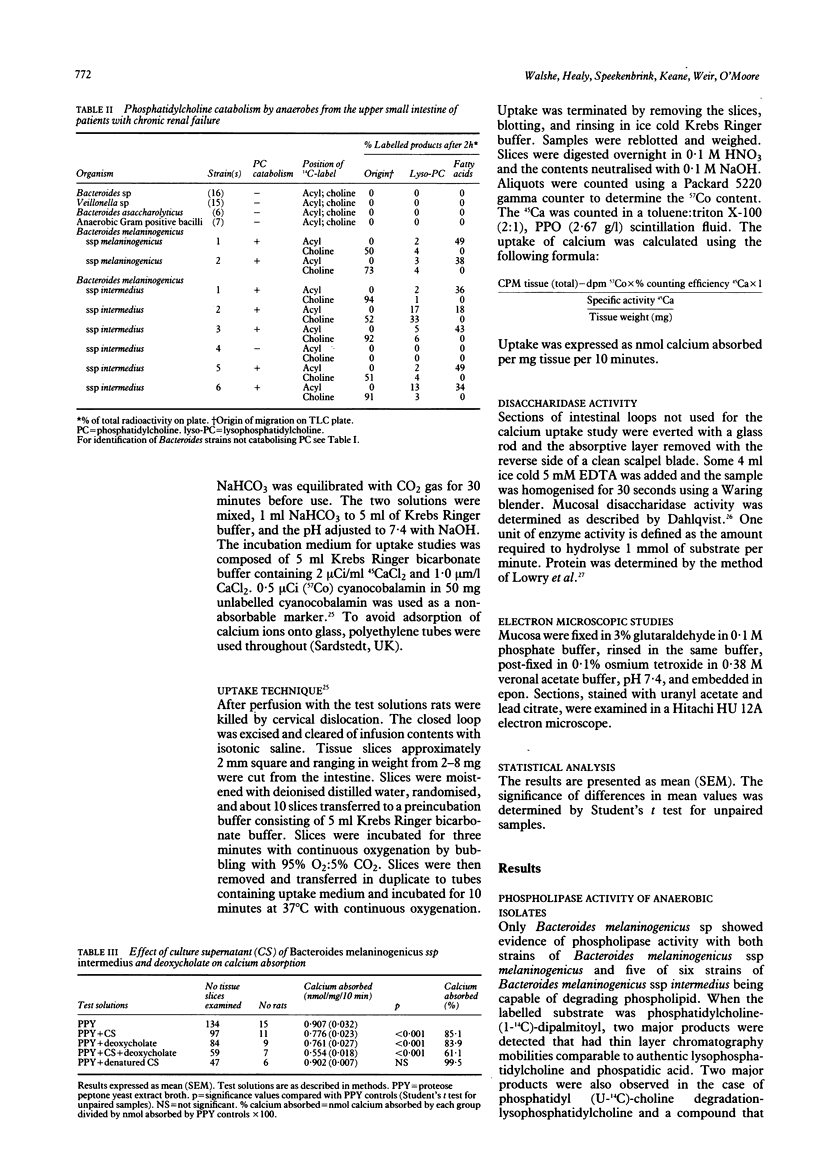
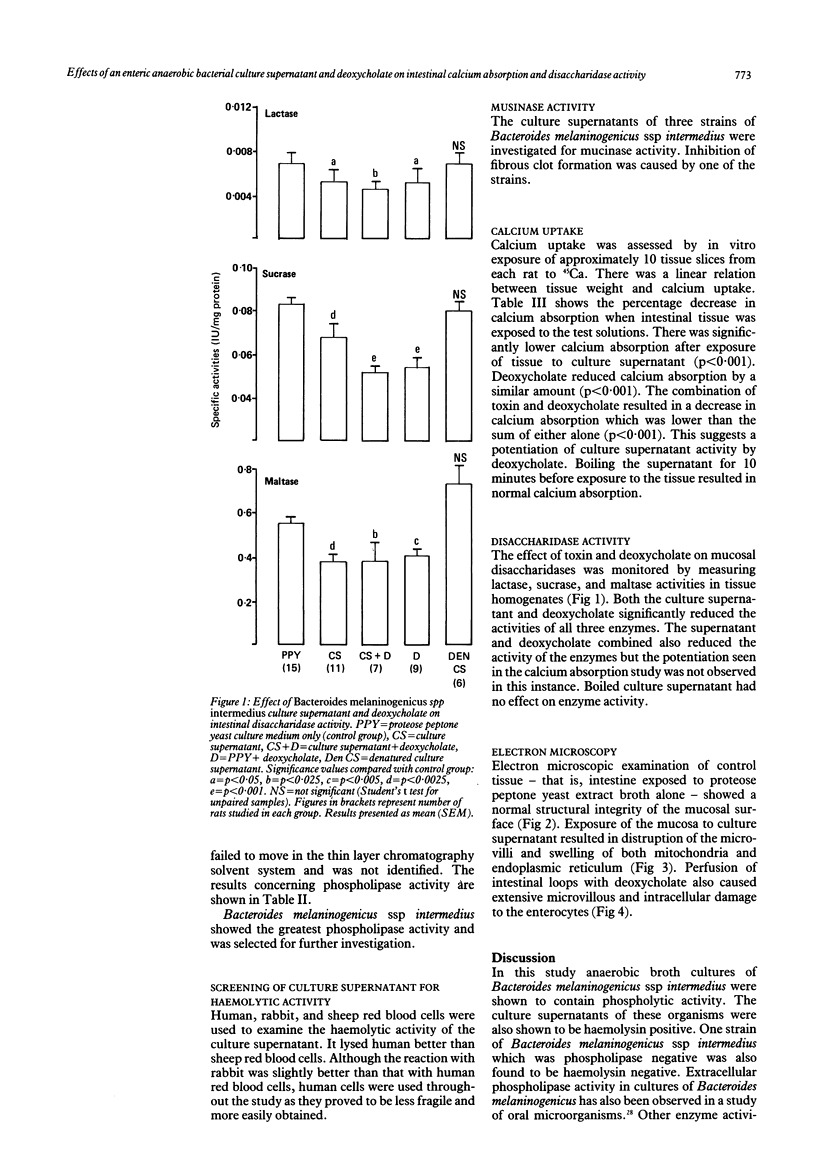



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bikle D. D. Calcium absorption and vitamin D metabolism. Clin Gastroenterol. 1983 May;12(2):379–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bordier P., Zingraff J., Gueris J., Jungers P., Marie P., Pechet M., Rasmussen H. The effect of 1alpha(OH)D3 and 1alpha,25(OH)2D3 on the bone in patients with renal osteodystrophy. Am J Med. 1978 Jan;64(1):101–107. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(78)90184-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bricker N. S., Slatopolsky E., Reiss E., Avioli L. V. Caclium, phosphorus, and bone in renal disease and transplantation. Arch Intern Med. 1969 May;123(5):543–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOKE W. T., COX E. V., FONE D. J., MEYNELL M. J., GADDIE R. The clinical and metabolic significance of jejunal diverticula. Gut. 1963 Jun;4:115–131. doi: 10.1136/gut.4.2.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chernov A. J., Doe W. F., Gompertz D. Intrajejunal volatile fatty acids in the stagnant loop syndrome. Gut. 1972 Feb;13(2):103–106. doi: 10.1136/gut.13.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coburn J. W., Hartenbower D. L., Brickman A. S. Advances in vitamin D metabolism as they pertain to chronic renal disease. Am J Clin Nutr. 1976 Nov;29(11):1283–1299. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/29.11.1283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Compston J. E., Horton L. W., Laker M. F., Merrett A. L., Woodhead J. S., Gazet J. C., Pilkington T. R. Treatment of bone disease after jejunoileal bypass for obesity with oral 1 alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3. Gut. 1980 Aug;21(8):669–674. doi: 10.1136/gut.21.8.669. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAHLQVIST A. METHOD FOR ASSAY OF INTESTINAL DISACCHARIDASES. Anal Biochem. 1964 Jan;7:18–25. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(64)90115-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAWSON A. M., ISSELBACHER K. J. Studies on lipid metabolism in the small intestine with observations on the role of bile salts. J Clin Invest. 1960 May;39:730–740. doi: 10.1172/JCI104090. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M. Effects of bile salts on intermediate metabolism of the intestinal mucosa. Fed Proc. 1967 Nov-Dec;26(6):1589–1598. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncombe V. M., Watts R. W., Peters T. J. In-vitro calcium uptake by jejunal biopsy specimens from patients with idiopathic hypercalciuria. Lancet. 1980 Dec 20;2(8208-8209):1334–1336. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(80)92399-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis H. A., Pierides A. M., Feest T. G., Ward M. K., Kerr D. N. Histopathology of renal osteodystrophy with particular reference to the effects of 1alpha-hydroxyvitamin D3 in patients treated by long-term haemodialysis. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 1977 Dec;7 (Suppl):31s–38s. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.1977.tb03359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRETER R. The serologic character of cholera Vibrio mucinase. J Infect Dis. 1955 Nov-Dec;97(3):238–245. doi: 10.1093/infdis/97.3.238. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gertner J. M., Lilburn M., Domenech M. 25-Hydroxycholecalciferol absorption in steatorrhoea and postgastrectomy osteomalacia. Br Med J. 1977 May 21;1(6072):1310–1312. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.6072.1310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbach S. L., Tabaqchali S. Bacteria, bile, and the small bowel. Gut. 1969 Dec;10(12):963–972. doi: 10.1136/gut.10.12.963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Oshin A., Barker J., Glasgow E. F. Bacteria, bile salts, and intestinal monosaccharide malabsorption. Gut. 1971 Sep;12(9):683–692. doi: 10.1136/gut.12.9.683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Burke V., Thomas J. A., Stone D. E. Effect of microorganisms isolated from the upper gut of malnourished children on intestinal sugar absorption in vivo. Am J Clin Nutr. 1975 Aug;28(8):841–845. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/28.8.841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M. Mechanisms of malabsorption in the "Contaminated Small-Bowel syndrome". Nahrung. 1984;28(6-7):659–666. doi: 10.1002/food.19840280630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gracey M., Papadimitriou J., Bower G. Ultrastructural changes in the small intestines of rats with self-filling blind loops. Gastroenterology. 1974 Oct;67(4):646–651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoskins L. C. Bacterial degradation of gastrointestinal mucins. II. Bacterial origin of fecal ABH(O) blood group antigen-destroying enzymes. Gastroenterology. 1968 Feb;54(2):218–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs P. E., Kim Y. S. The contaminated small bowel syndrome. Am J Med. 1979 Dec;67(6):1049–1057. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(79)90647-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonas A., Krishnan C., Forstner G. Pathogenesis of mucosal injury in the blind loop syndrome. Gastroenterology. 1978 Nov;75(5):791–795. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. E., Toskes P. P. Small intestine bacterial overgrowth. Gastroenterology. 1979 May;76(5 Pt 1):1035–1055. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klipstein F. A., Holdeman L. V., Corcino J. J., Moore W. E. Enterotoxigenic intestinal bacteria in tropical sprue. Ann Intern Med. 1973 Nov;79(5):632–641. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-79-5-632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusama H., Craig J. P. Production of Biologically Active Substances by Two Strains of Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1970 Jan;1(1):80–87. doi: 10.1128/iai.1.1.80-87.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamabadusuriya S. P., Guiraldes E., Harries J. T. Influence of mixtures of taurocholate, fatty acids, and monolein on the toxic effects of deoxycholate in rat jejunum in vivo. Gastroenterology. 1975 Aug;69(2):463–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low-Beer T. S., Schneider R. E., Dobbins W. O. Morphological changes of the small-intestinal mucosa of guinea pig and hamster following incubation in vitro and perfusion in vivo with unconjugated bile salts. Gut. 1970 Jun;11(6):486–492. doi: 10.1136/gut.11.6.486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manicourt D. H., Orloff S. Osteomalacia complicating a blind loop syndrome from congenital megaesophagus-megaduodenum. J Rheumatol. 1979 Jan-Feb;6(1):57–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. P., Marriott C., Kellaway I. W. Direct effect of bile salts and phospholipids on the physical properties of mucus. Gut. 1978 Feb;19(2):103–107. doi: 10.1136/gut.19.2.103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menge H., Köhn R., Dietermann K. H., Lorenz-Meyer H., Riecken E. O., Robinson J. W. Structural and functional alterations in the mucosa of self-filling intestinal blind loops in rats. Clin Sci (Lond) 1979 Feb;56(2):121–131. doi: 10.1042/cs0560121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol phospholipids and cell surface receptor function. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 25;415(1):81–47. doi: 10.1016/0304-4157(75)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A., 3rd, Li S. T., Bronner F. Characterization of calcium binding to brush-border membranes from rat duodenum. Biochem J. 1982 Dec 15;208(3):773–781. doi: 10.1042/bj2080773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neale G., Antcliff A. C., Welbourn R. B., Mollin D. L., Booth C. C. Protein malnutrition after partial gastrectomy. Q J Med. 1967 Oct;36(144):469–494. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudek W., Haque R. U. Extracellular enzymes of the genus Bacteroides. J Clin Microbiol. 1976 Nov;4(5):458–460. doi: 10.1128/jcm.4.5.458-460.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simenhoff M. L., Saukkonen J. J., Burke J. F., Wesson L. G., Jr, Schaedler R. W., Gordon S. J. Bacterial populations of the small intestine in uremia. Nephron. 1978;22(1-3):63–68. doi: 10.1159/000181424. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabaqchali S. The pathophysiological role of small intestinal bacterial flora. Scand J Gastroenterol Suppl. 1970;6:139–163. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toskes P. P., Giannella R. A., Jervis H. R., Rout W. R., Takeuchi A. Small intestinal mucosal injury in the experimental blind loop syndrome. Light- and electron-microscopic and histochemical studies. Gastroenterology. 1975 May;68(5 Pt 1):1193–1203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]