Abstract
Recent studies suggest that gut microbiomes of urban-industrialized societies are different from those of traditional peoples. Here, we examine the relationship between lifeways and gut microbiota through taxonomic and functional potential characterization of fecal samples from hunter-gatherer and traditional agriculturalist communities in Peru, and an urban-industrialized community from the US. We find that in addition to taxonomic and metabolic differences between urban and traditional lifestyles, hunter-gatherers form a distinct sub-group among traditional peoples. As observed in previous studies, we find that Treponema are characteristic of traditional gut microbiomes. Moreover, through genome reconstruction (2.2–2.5 MB, coverage depth 26-513×) and functional potential characterization, we discover these Treponema are diverse, fall outside of pathogenic clades, and are similar to Treponema succinifaciens, a known carbohydrate metabolizer in swine. Gut Treponema are found in non-human primates and all traditional peoples studied to date, suggesting they are symbionts lost in urban-industrialized societies.
INTRODUCTION
Understanding the human microbiome has the potential to transform health and medicine. Yet, despite large-scale sequencing efforts, the full extent of human gut microbial diversity remains underexplored. Extant people living traditional lifestyles are especially under-studied, limited to one population of hunter-gatherers from Tanzania1, and three rural agriculturalist communities in Burkina Faso2, Malawi, and Venezuela3. Studies of peoples maintaining traditional subsistence practices are critical for understanding the ancestral state of the human microbiome and providing a foundation for understanding how the human microbiome responds to urbanism and Westernization, especially regarding diseases of civilization, such as obesity and chronic inflammatory disorders. To date, only two studies have focused on the gut microbiomes of communities exclusively eating local, non-industrially produced foods: a study by De Filippo and colleagues 2 that focused on children up to six years old from Burkina Faso, whose diet was primarily composed of locally grown cereals, legumes and vegetables2, and a study by Schnorr and colleagues1 that explored the gut microbiome of African hunter-gatherers from Tanzania. A study on rural agriculturalist communities from Venezuela and Malawi3 included adults with more diverse diets, including industrial goods such as soda in Malawi, and milk products, canned products, and soda in Venezuela.
Because of their unique cultural, behavioral and ecological environment, we hypothesize that remote hunter-gatherer communities harbor novel microbiome profiles that depart from those previously described in urban and semi-urban settings, and that may be tailored to the specific dietary sources within each population. To test this hypothesis, here we use a combination of high throughput 16S rRNA gene amplicon sequencing, and shotgun metagenomic sequencing to characterize the gut microbiota of peoples from three different lifeways: traditional hunter-gatherers, traditional agriculturalists, and urban industrialized peoples. In addition to previously published data, we provide novel data from: (1) the Matses, a remote hunter-gatherer population from the Peruvian Amazon; (2) Tunapuco, a traditional agricultural community from the Andean highlands; and (3) residents of Norman, Oklahoma, a typical U.S. university community that serves as a comparative population following an urban industrialized lifestyle.
RESULTS
Diet and engagement
While both rural communities live within the national borders of Peru, the lifeways of the Matses and residents of Tunapuco are startlingly different. The Matses live at an elevation of 150 meters above sea level in a pocket of natural hyperdiversity that extends across the Brazilian border, and, until recently, the Matses have been geographically, historically, and socially, isolated4. The Matses are traditional hunter-gatherers whose subsistence focuses primarily on gathered tubers (Manihot spp.) and invasive plantains (Musa spp.) (Supplementary Table 1). Fish is their primary protein source, complemented by sporadic consumption of game meat (monkey, sloth, capybara, alligator, etc.). Consumption of dairy or processed food is very rare, and only as a result of sporadic visitors. In contrast, Tunapuco is situated in the central Andes, at an elevation between 2,500 and 3,100 meters above sea level. The diet of this rural agriculturalist community is based on local agricultural produce and homegrown small animals. Their main sources of nutrition include stem tubers such as potatoes (Solanum tuberosum spp.) and root tubers like oca (Oxalis tuberosa) and mashua (Tropaeolum tuberosum), which they eat at every meal. Tocosh, a typical dish of the central Andes made out of potatoes that have been fermented in wet soil, is eaten at least once a week by families in Tunapuco (Supplementary Table 2). Residents of Tunapuco eat fruits that they buy from lowland rural communities from the same region. Guinea pig, pork, lamb, and infrequent cow cheese are the main animal protein sources in their diet. Intake of dairy products and processed foods is limited, and rice and bread are the main products they buy to supplement their diet. Residents of Norman self-report diets typical of urban-industrial communities, with regular consumption of processed foods including canned fruits and vegetables, bread, and prepackaged meals. In addition, residents of Norman also reported regular dairy consumption in the form of milk, cheese, and other dairy products.
This study was conducted under the supervision of the University of Oklahoma and the Ethics Committee of the Peruvian National Institute of Health, in collaboration with the Matses and Tunapuco communities (Supplementary Fig. 1). Our model of research with indigenous populations consists of longitudinal engagement; through a Community Based Participatory Research was designed5 to ethically engage vulnerable indigenous communities in microbiome research (Methods). Our participants range from 1–52 years of age for the Matses, 3–63 years of age for Tunapuco, and 7–50 years of age for the Norman population. Body mass index, age, and sex of our participants are summarized in Supplementary Table 3.
Rural communities have higher richness
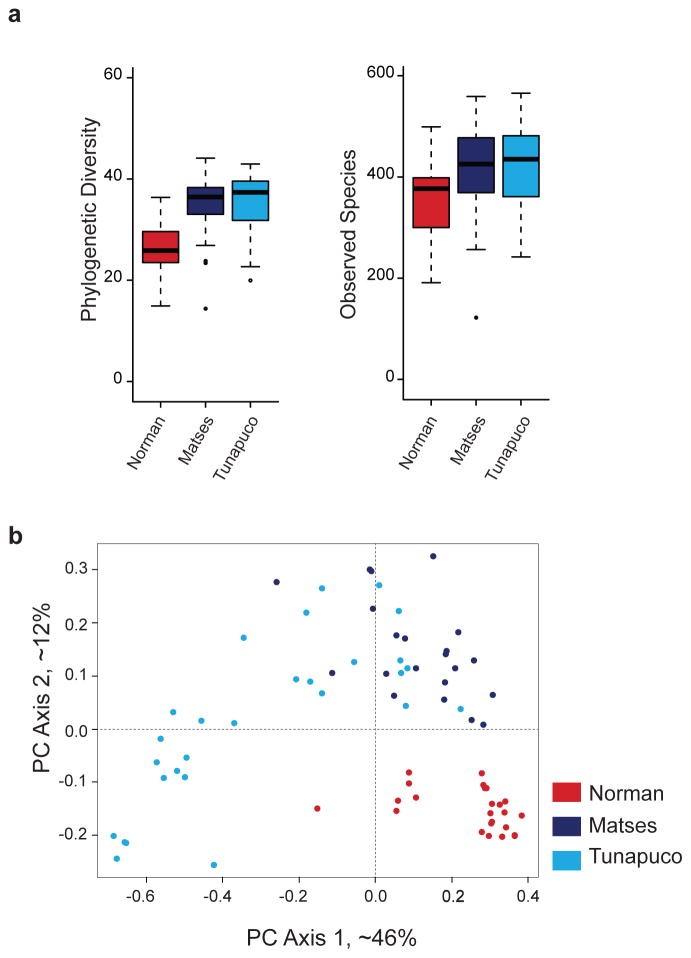
Previous reports have indicated that Western populations have lower microbial richness than non-Western populations3. Our analyses of microbial richness yielded similar results. We used targeted amplification and sequencing of the V4 region of the 16S rRNA gene (Methods), followed by clustering of sequences into Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs). We find that the Matses and Tunapuco populations have higher richness than the Norman population. The trend is observed with both phylogenetic (Faith’s PD) and non-phylogenetic (observed species) richness metrics (Fig. 1a). Further, these differences in richness between traditional and industrialized societies are robust to OTU assignment strategy (Methods) and rarefaction, being detected with as few as 5,000 reads per sample (Supplementary Fig. 2). No significant differences in richness are observed between the two traditional populations. The magnitude of difference observed between phylogenetic and non-phylogenetic richness indices indicates that the gut microbiomes of traditional societies are composed of larger numbers of phylogenetically diverse taxa, while the gut microbiomes of industrialized societies are composed of fewer closely related taxa (Fig. 1a).
Figure 1. Alpha- and beta-diversity comparisons of the gut microbiomes of the Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman populations.
Analyses were performed on 16S rRNA V4 region data, with a rarefaction depth of 10,000 reads per sample. (a) Alpha diversity comparisons based on phylogenetic and non-phylogenetic richness (Faith’s PD, observed species). The urban population has significantly lower microbial richness compared to the two rural populations. This observation is robust and observable even with less than 5,000 reads per sample (Supplementary Fig. 2). Whiskers in the boxplot represent the range of minimum and maximum alpha diversity values within a population, excluding outliers (b) Principal coordinates analysis of weighted UniFrac distances. Proportion of variance explained by each principal coordinate axis is denoted in the corresponding axis label. The rural and urban populations show clear separation.
Next, we compared microbial community structure (beta diversity) among the three populations using Principal coordinate (PCoA) transformation of weighted UniFrac6 distances (Fig. 1b). The traditional and industrialized populations show separation in PCoA space, and among the traditional populations the Matses form a separate cluster (PERMANOVA, P<0.001, and P<0.001 respectively). Further, the Tunapuco population is characterized by high interpersonal variation, evident in both PC axes 1, and 2. Supervised learning using Random Forests7, a machine learning method utilizing microbial community signatures, accurately assigned samples to their source population based on taxonomic profiles at the OTU level (100% accuracy, all populations).
Taxonomic characterization
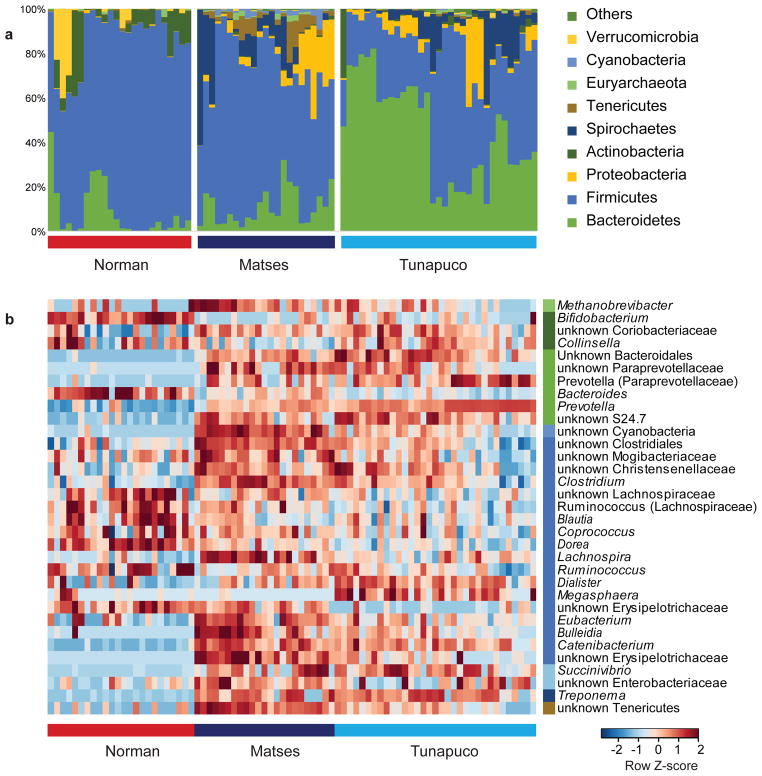
To test whether subsistence traditions harbor distinct microbial communities, we compared relative abundance of taxa between each of our populations. The three populations show differences in taxonomic distribution at the phylum level (Fig. 2a), with eight out of twenty phyla having a significant difference in abundance in at least one population (FDR-corrected Kruskal-Wallis test: P<0.0006) (Supplementary Table 4). Three of the eight phyla show a traditional/urban-industrial distribution, with the traditional populations (Matses and Tunapuco) enriched for Proteobacteria and Spirochaetes, and the urban-industrial population (Norman) enriched for Actinobacteria (Supplementary Fig. 3). Additionally, the Matses differ from the Tunapuco and Norman populations in being enriched for Cyanobacteria, Tenericutes, and Euryarchaeota (Supplementary Fig. 3). Finally, the Tunapuco population is enriched for Bacteroidetes, while the Norman and Matses populations are enriched for Firmicutes (Supplementary Fig. 3).
Figure 2. Taxonomic profile of the gut microbiomes of the Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman populations.
Analyses were performed on 16S rRNA V4 region data, rarefied to a depth of 10,000 reads per sample. (a) Relative taxa abundance plots for individuals from the three populations, summarized at the phylum level. Individuals are represented along the horizontal axis, and relative taxa frequency is denoted by the vertical axis. (b) Heatmap showing 33 genera with significant differences in abundance between populations (Kruskal-Wallis, FDR-corrected P <0.05). Individual boxplots for phyla and genera are shown in Supplementary Fig. 3. Heatmap is color-coded based on row z-scores.
To further characterize taxonomic differences, we performed Kruskal-Wallis tests on genus-level taxa and identified 33 genera showing significant differences in abundance between the three populations (FDR-corrected Kruskal-Wallis test: P<0.05) (Fig. 2b, Supplementary Table 5). The traditional/urban-industrial trends observed among Actinobacteria, Proteobacteria, and Spirochaetes are driven by the genera Bifidobacterium, Succinivibrio, and Treponema, respectively (Supplementary Fig. 3). While a high relative abundance of Bacteroidetes distinguishes Tunapuco from the Matses and Norman populations, at the genus level this is further resolved into a traditional/urban-industrial trend driven by higher levels of Prevotella among traditional gut microbiomes and Bacteroides among urban-industrial gut microbiomes. This pattern is similar to previous reports for non-Western populations1, 3 (Supplementary Fig. 3). With respect to Firmicutes, we observe a complex pattern driven by the enrichment of different genera among the three populations. Specifically, the Norman population is enriched for Ruminococcus, Blautia, Dorea, and an unknown genus in the family Lachnospiraceae (Supplementary Fig. 3). The Matses are enriched for Clostridium, Catenibacterium, Eubacterium, Lachnospira, and an unknown genus in the class Clostridiales (Supplementary Fig. 3). The Tunapuco population, while overall having lower levels of Firmicutes, is specifically enriched for the genus Dialister (Supplementary Fig. 3). Overall, these taxa distribution patterns are concordant with trends reported from previous studies on hunter-gatherer and rural agriculturalist communities1, 3.
To evaluate population discrimination, we performed supervised clustering using Random Forests on taxa tables summarized at higher taxonomic levels (genus to phylum). The Norman population consistently had a 100% classification accuracy at all taxonomic levels. In contrast, the Matses and Tunapuco populations had a 93% and 100% classification accuracy, respectively, at the genus level, reducing to 77%, and 91% at the phylum level (Supplementary Table 6). Misclassification was exclusively between the rural populations, with samples being cross-assigned between the Matses and Tunapuco, indicating shared community signatures at higher taxonomic levels between these two populations.
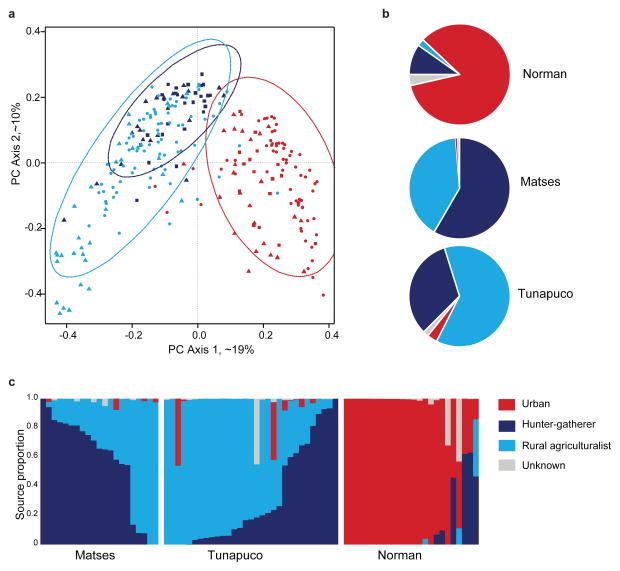
Finally, we compared genus level taxa abundance profiles between our populations, and those from two previous studies of remote agrarian and hunter-gatherer human gut microbiomes1, 3. PCoA analysis of a Bray-Curtis distance matrix generated from genus level taxa tables shows a clear separation between traditional and urban-industrial microbiomes (Fig. 3a), consistent across the three different studies. Additionally, the hunter-gatherer populations (Matses, and Hadza) form a distinct sub-cluster nested within the other traditional populations (Tunapuco, Venezuela, and Malawi). To further explore this trend, we performed Bayesian source tracking8 on the Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman samples using the previously published datasets as source populations (traditional hunter-gatherer: Hadza; rural agriculturalist: Venezuela, Malawi; and urban-industrial: USA, Italy) (Fig. 3b). Consistent with previous analyses, the urban sources formed the primary contribution (~84% average) to the Norman samples, while the combined rural and hunter-gatherer sources accounted for ~95–98% for the Tunapuco and Matses samples. Specifically, the Matses samples had a higher contribution (~58%) from the Hadza hunter-gatherer source, while the Tunapuco samples had a higher contribution (~66%) from the rural Venezuela and Malawi source. Within populations, individuals show variation (Fig. 3c), but overall between ~64–85% of individuals have profiles consistent with their subsistence strategy. Thus, while the studies were conducted with differences in sample handling (freezing, desiccation), extraction methods (MoBio PowerSoil, phenol-chloroform), and choice of PCR primers, they nevertheless show a pattern in which two hunter-gatherer populations from two separate continents (Africa and South America) have a greater affinity to each other than to other traditional or urban populations. This is similarly true for the rural agriculturalists in Africa and South America and the urban industrial populations in Europe and North America.
Figure 3. Comparison of the gut microbiomes of Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman populations to published data from hunter-gatherer, rural agriculturalist and urban-industrial communities.
Analyses were performed on genus level taxa tables rarefied to 4,000 reads per sample. (a) Principal coordinate analysis of Bray-Curtis distances generated from taxa tables summarized at the genus level. Proportion of variance explained by each principal coordinate axis is denoted in the corresponding axis label. Populations are color coded by subsistence strategy. Datasets are represented by triangles (this study), circles (Yatsunenko et al. 2012), and squares (Schnorr et al. 2014), respectively. Ellipses correspond to 95% confidence boundaries for each of the three subsistence categories. (b) Results from Bayesian source-tracking analysis. Source contributions are averaged across samples within the population. (c) Results from Bayesian source-tracking for individual samples.
Functional characterization
We performed shotgun metagenome sequencing (Illumina, see Methods) to investigate whether the Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman gut microbiomes harbor differences in functional capacity. To improve annotation quality, the short reads obtained from metagenome sequencing were assembled de novo using Ray-Meta9 to generate longer contigs (Methods). Functional capacity was then inferred from annotation of open reading frames (ORFs) predicted from these contigs. We used an annotation pipeline incorporating microbial genomes (draft & complete) obtained from the HMP DACC10, IMG (v3.5, 2012)11, and NCBI GenBank databases12 as references.
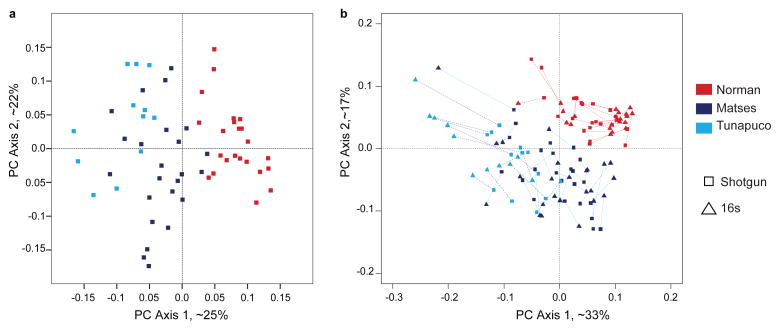
Supervised clustering using KEGG Orthology (KO)13, 14 profiles distinguished the traditional and urban-industrial populations with 100% accuracy (Supplementary Table 7). Within the traditional populations, the Matses samples had a 100% classification accuracy, while one Tunapuco sample (out of 12) was misassigned to the Matses. Beta-diversity plots generated from Bray-Curtis distance matrices (PC transformed) of KO tables showed a clear separation between the traditional and urban-industrial populations (Fig. 4a). Procrustes analyses comparing spatial fit between PC plots generated from UniFrac (taxonomic) and Bray-Curtis (functional) distances showed concordance, indicating consistency between taxonomic and functional profiles (Fig. 4b).
Figure 4. Comparison of taxonomic and functional diversity of gut microbiomes between populations.
Proportion of variance explained by each principal coordinate axis is denoted in the corresponding axis label (a) Principal Coordinates Analysis of Bray-Curtis distances generated from KEGG Ortholog tables rarefied to 200,000 counts per sample. (b) Procrustes analysis between the taxonomic and the functional datasets on paired samples from the Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman populations.
To identify KOs showing differential abundance between the three populations, we performed Kruskal-Wallis tests on KO tables. Overall, we identified 112 KOs showing a significant difference in abundance in at least one population (Supplementary Table 8). Of these, 78 KOs (69.6%) show enrichment among the traditional populations; these KOs are predominantly associated with metabolism and genetic information processing. Among the remaining KOs, 20 (17.8%) show enrichment specific to the urban-industrial population, and 14 (12.5%) show similar distributions between the urban-industrial and at least one of the two traditional populations. The KOs uniquely enriched in the urban-industrial populations are predominantly associated with membrane transport functions. Additionally, 37 of the 78 KOs enriched in the traditional populations are found at higher abundance among the residents of Tunapuco compared to the Matses.
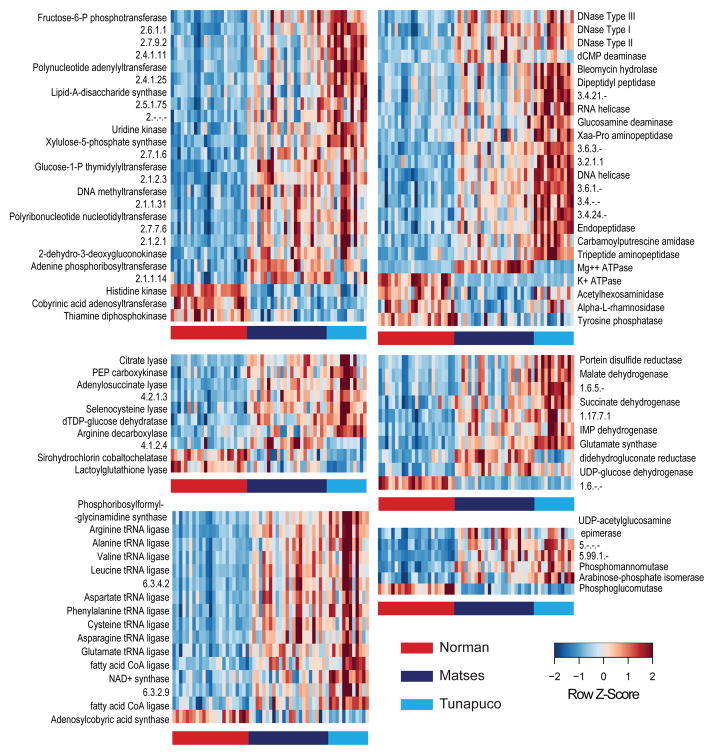
To further characterize some of these functional differences, we performed statistical analyses on ortholog tables annotated using Enzyme Commission (EC) codes15. Overall, we identified 91 ECs showing significant differences between the populations (Fig. 5, Supplementary Table 9). Of these, 79 ECs (86.8%) are enriched among the traditional populations, including several associated with the TCA cycle (e.g., succinate dehydrogenase, malate dehydrogenase), and amino acid metabolism (e.g., amino acid tRNA ligases). These pathways are related to enhanced capacity for energy production and dietary amino acid uptake. Similar to our observations with the KOs, a subset of 39 ECs show higher abundance within Tunapuco compared to the Matses. Further, a second group comprised of 34 ECs is enriched within a subset of individuals from both the Matses and Tunapuco. The remaining 12 ECs (13.2%) were enriched in the Norman population and included three ECs related to Vitamin B1 and B12 biosynthesis.
Figure 5. Heatmap of ECs showing significant differences between the gut microbiomes of Matses, Tunapuco, and Norman populations.
Enzymes are grouped based on EC class. Comparisons between populations were performed using Kruskal-Wallis tests (FDR-corrected P <0.05). Heatmap is color-coded based on row z-scores
Age stratification and Bifidobacterium
A previous study on US, Malawi, and Venezuelan populations3 found that age resulted in a significant gradient of bacterial abundances, with newborns initially showing high variation but little differentiation among populations, and eventually resembling the adults of their respective communities by three years of age3, 16. Further, this trend was shown to correlate with the abundance of Bifidobacterium, a genus thought to be associated with dietary dairy consumption. As the number of children of age under three years in our study is limited to four individuals from the Matses, we instead performed correlation analyses between age and PC axes generated from a weighted UniFrac distance matrix. A negative correlation was observed between the first PC axis and age for the Matses population (rho= −0.59, P < 0.002). While the relative abundance of Bifidobacterium in children shows no direct correlation with age, 10 out of 13 individuals (total n=25) showing presence of the genus were under the age of seven. In contrast, all individuals sampled from our Norman population showed presence of Bifidobacterium, with no correlation between age and levels of Bifidobacterium. This is consistent with regular dairy consumption self-reported by the Norman individuals.
Treponema and rural populations
Although Spirochaetes have been previously reported from the gut microbiome of non-human primates 17, 18, 19 and ancient human populations20, they have only been observed in high abundance among extant human populations with non-Western lifestyles, such as a traditional community in Burkina Faso1, and a hunter-gatherer community in Tanzania1. As such, they may represent a part of the human ancestral gut microbiome that has been lost through the adoption of industrial agriculture and/or other lifestyle changes (Supplementary Table 10). Similar to previous studies on traditional populations, we find that both the Matses and Tunapuco are enriched for Spirochaetes, specifically of the genus Treponema. Phylogenetic analysis of these Spirochaetes indicates the presence of at least five Treponema OTUs (Supplementary Table 11, Supplementary Fig. 4) found in traditional populations today. Of these, two OTUs (Greengenes 13.5 OTU ids: 300310, 338950) occur at high frequencies and are shared between the Matses and Tunapuco, and a third OTU (Greengenes 13.5 OTU id: 4307383) is present at high frequencies in the Tunapuco population but is rare among the Matses. The phylogenetic similarity of these OTUs with Treponema succinifaciens, a non-pathogenic carbohydrate metabolizer, and a member of the swine gut microbiome21, offers support to the hypothesis that these organisms might be selected for under high fiber diets.
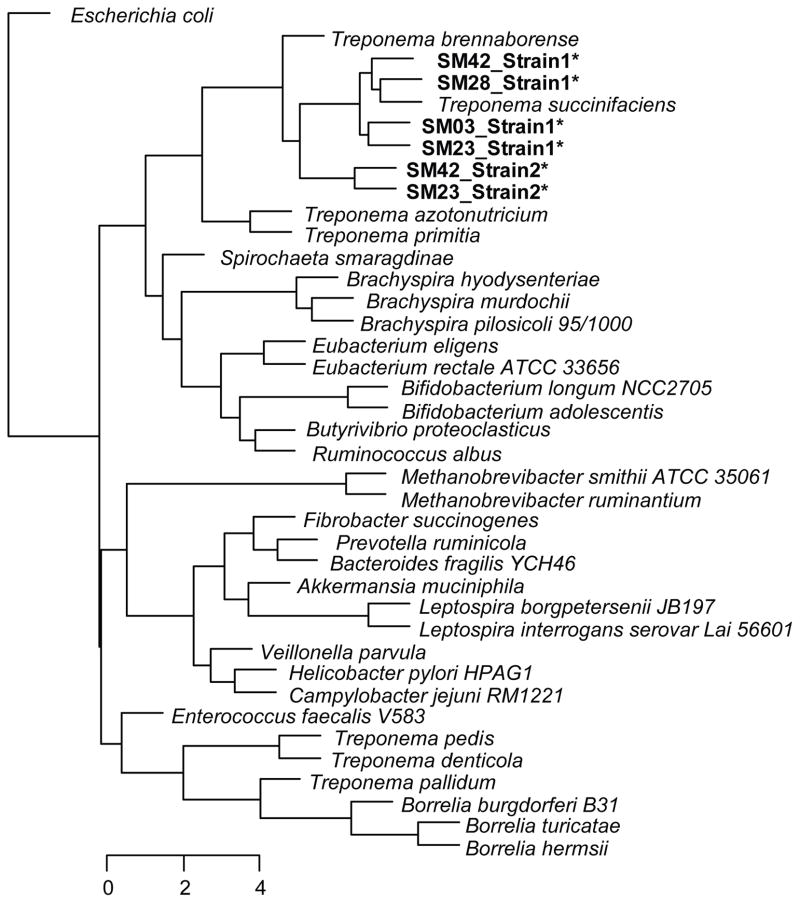
To further characterize the phylogenetic and functional relationships of the Matses gut Treponema to other currently available reference strains from this genus, we retrieved contigs matching Treponema from metagenomes assembled de novo (Methods) from four Matses samples. These samples were selected based on high frequencies of Treponema observed in their taxonomic profiles. Samples from Tunapuco were not included in this analysis as they had lower sequencing coverage and often contained multiple Treponema strains leading to poor assemblies. Phylogenetic analysis using 16S rRNA gene sequences retrieved from these contigs confirmed the presence of two distinct strains of Treponema within these samples, one with ~99% sequence similarity to T. succinifaciens (found in all four samples, referred to as Strain 1), and the other with ~90% sequence similarity to T. succinifaciens (found in two samples, referred to as Strain 2) (Fig. 6a). A second phylogenetic tree constructed using concatenated amino acid sequences from 35 single copy marker loci22 (predominantly composed of ribosomal small and large subunit proteins), showed similar topology, confirming the presence of two distinct strains of Treponema within our samples (Fig. 6b). Overall, we retrieved between 2.19 and 2.46 Mb of genome sequence data for the Treponema strains through a combination of methods, including sequence identity to the reference T. succinifaciens, GC%, and coverage statistics (Methods). We annotated these partial assemblies using the ‘prokka’ pipeline23, followed by evaluation of metabolic potential using MAPLE24. We then performed hierarchical clustering using metabolic module completion ratio (MCR) data obtained from the MAPLE pipeline (Fig. 7). Based on predicted metabolic potential, the reconstructed Treponema strains cluster most closely with T. succinifaciens, and are nested with other gut-associated treponemes reported from termites (T. azotonutricium, T. primitia)25, and a digital dermatitis associated treponeme reported from cattle (T. brennaborense)26. Additionally, these strains functionally cluster with gut-associated members of the Brachyspira clade of Spirochaetes, along with several gut-associated bacteria from other phyla, including Ruminococcus, Eubacterium, and Butyrivibrio. In contrast several pathogenic Spirochaetes including Treponema pallidum (syphilis), Borrellia burgdorferi (Lyme disease), and Treponema denticola (periodontal disease), form a functionally separate clade outside of the gut-associated bacteria. Overall, these results give further support for a potential metabolic role for the Treponema strains observed in the gut microbiomes of traditional human populations.
Figure 6. Phylogenetic trees showing relationship of Matses Treponema strains to reference Treponema species.
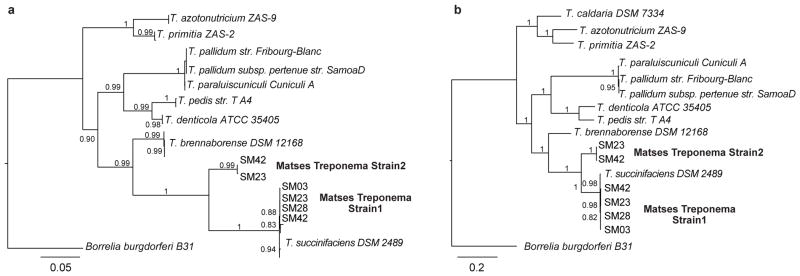
(a) Maximum likelihood tree constructed using 16S rRNA sequences from de novo assemblies of shotgun data. (b) Maximum likelihood tree constructed using concatenated amino acid sequences from 35 single copy marker loci, retrieved from de novo assemblies of shotgun data. Both trees show similar topology, with the Matses Treponema strains grouping with Treponema succinifaciens, a known carbohydrate metabolizer in the swine gut microbiome.
Figure 7. Hierarchical clustering of Matses Treponema and reference bacterial strains based on KEGG functional potential data.
Open reading frames (ORFs) predicted from reconstructed Matses Treponema genomes were annotated using the MAPLE server and compared with reference bacterial genomes (including Spirochaetes). The Matses Treponema strains share functional similarities with Treponema succinifaciens, a known carbohydrate metabolizer and apathogenic member of the swine gut microbiome.
DISCUSSION
Characterizing microbial communities and their functions in populations living relatively ancestral lifestyles is essential for understanding the coevolution of humans as a species with their microbiomes. Our results strongly support the need for human microbiome research on a larger sampling of human lifeways and traditions. Such work with vulnerable populations is challenging, especially with respect to building trust and establishing reasonable informed consent, but remains possible, even with very remote and traditional peoples. Without these insights, the benefit of research may be more applicable to the Westernized, affluent, urban populations, further exacerbating health disparities for the underrepresented. Here we present a microbiome profile that may be more consistent with the ancestral state of human biology. Such information provides a potential foundation for understanding microbiome-associated “diseases of civilization”.
Methods
Community engagement
Collaborative research with remote human communities requires careful planning and extensive outreach. As with many other indigenous populations, the Matses and Tunapuco have experienced and resent the idea of safari or helicopter research, a common model of research on indigenous populations. In addition, foreign companies’ recent attempts to extract oil from the Matses’ natural reservation have fueled the Matses’ distrust towards the outside world. To maximize protection of the communities, we consulted with colleagues at the Center for Intercultural Health of the Peruvian Institute of Health from the early stages of the study design.
Recognizing communities’ vulnerabilities and concerns, in addition to the official efforts aiming to protect them, we initiated our work by engaging political and traditional authorities in the review of our protocol. Political authorities included regional and national authorities. The traditional authority we first approached was the Peruvian leader of the ethnic group. All concerns from these authorities were addressed in the protocol before submission to the ethics committee of the Peruvian National Institute of Health, which approved the protocol.
The protocol for the Matses community includes oversight by additional local authorities. Upon protocol approval, and with the authorization of the leader of the Matses ethnic group, we presented our project to the local authority of the District Yaquerana, who oversees all activities in the Matses reservation, and later to the leader of the Comunidad Nativa Matses Anexo San Mateo, who introduced us to the community members. Such structures are unavailable for Tunapuco. For both communities, we implemented a public meeting for community consultation and obtained community consent. In addition to community consent, all volunteer participants were individually consented when they arrived to deposit their samples.
In an effort to maximize benefits and prevent potentially coercive incentives for the community, we avoided individual presents or compensation. Instead, we offered on-site parasite screening, making a microscope available for the community to observe the analysis we performed. This experience also served to anchor the discussion about microorganisms, emphasizing the informed part of the consent process. A Matses interpreter, who was fluent in Spanish, mediated communication with the Matses community.
For both the Matses and Tunapuco communities, once preliminary results became available we returned to the community to disseminate our findings. We obtained authorization from the community for data publication and to use the community’s name in association with our findings.
Sample collection and processing
Fecal samples from participants were collected in polypropylene containers. Samples from the Matses (n=25) and Tunapuco populations (n=31) were stored in ice for up to 4 days until arriving at Lima, and they were kept frozen until DNA was extracted at the laboratory in Oklahoma. In addition, fecal samples were collected from 23 individuals from Norman, Oklahoma to serve as a comparative population with an urban-industrial lifestyle. These samples were kept on ice during transport to the laboratory and frozen within 24 hours of collection.
DNA extraction from the Matses and Tunapuco fecal samples was performed using the PowerSoil® DNA Isolation Kit (MoBio) following manufacturer’s instructions, with the addition of two heating steps: 10 minutes at 60°C before vortexing the samples with the Powerbeads, and 10 minutes at 90°C after. For the Norman fecal samples, DNA extraction was performed using the PowerMicrobiome® RNA Isolation Kit (MoBio) with the exclusion of the DNase I step. Both extraction methods included an initial bead-beating step.
To characterize the taxonomic profile of the Matses population’s gut microbiome, we amplified the V4 hypervariable region of the bacterial 16S rRNA gene using the universal bacterial/archaeal primers F515 (5′-CACGGTCGKCGGCGCCATT-3′) and R806 (5′-GGACTACHVGGGTWTCTAAT-3′)27. These same primers were used to generate 16S rRNA data in a previous study of agrarian and urban gut microbiomes3. A 12 bp GOLAY error-correcting barcode was added to the reverse primer to enable sample multiplexing. Reactions were performed in triplicate using the AccuPrime™ Taq DNA Polymerase High Fidelity system. Read statistics from the 16S V4 sequencing runs are summarized in Supplementary Table 3. To characterize gut microbiome functional potential, we performed shotgun metagenomic sequencing of fecal samples. Libraries were prepared using the Nextera DNA sample preparation kit for NGS libraries (Illumina platform).
16S sequencing data processing
The 16S rRNA sequencing data from the Illumina runs was filtered and trimmed using the program ‘sickle’ (https://github.com/najoshi/sickle) to remove bases with a quality score less than 30, followed by discarding sequences with ambiguous bases (‘N’), and a length less than 90bp. These trimmed reads were demultiplexed, chimera filtered (‘usearch’)28, and assigned to Operational Taxonomic Units (OTUs) using packages implemented in QIIME29. We initially performed closed-reference OTU assignment using ‘uclust’28 with a 97% sequence similarity threshold against the Greengenes 13.5 database30 as a reference. Overall, >95% of the total sequences were assigned to OTUs using this approach, with the urban population from Norman having ~97±2% and rural Matses and Tunapuco populations having ~96±2%, and ~95±3%, respectively, assigned to OTUs. Additionally, to document the impact of potentially novel OTUs on microbial richness, the remaining unassigned sequences were clustered de novo using a 97% sequence similarity threshold, and the resulting OTU table merged with the one generated using the closed-reference approach. Comparative 16S rRNA datasets were obtained from previously published studies1, 3, and are composed of hunter-gatherers (Hadza, n=27), rural agriculturalists (Venezuela, n=60; Malawi, n=20), and urban populations (USA, n=65; Italy, n=16). The dataset composed of Venezuela, Malawi, and USA individuals3 had been sequenced on an Illumina platform and were processed using the same quality filtering and OTU assignment criteria as employed by this study. The dataset composed of the Hadza and Italian individuals1 had been sequenced on a Roche 454 platform, and were processed using QIIME’s de novo clustering strategy using a 97% sequence similarity threshold to maximize read assignment to OTUs. All comparisons between sequences generated in this study and the two previously published datasets are limited to genus level taxa tables.
Shotgun read processing
The datasets generated from shotgun metagenome sequencing were quality filtered and trimmed to remove bases with a quality score less than 30, followed by discarding sequences with ambiguous bases (‘N’) and a length less than 25bp. De novo metagenome assembly was performed on these trimmed sequences using Ray Meta9, with a k-mer length of 21. Metagenome assembly was performed on the OU Supercomputing Center for Education and Research (OSCER) platform. Open reading frame (ORF) prediction was performed on assembled contigs using ‘FragGeneScan’31. Predicted ORFs were assigned annotations through comparisons with 382 gut microbial genomes from the Human Microbiome Project (HMP DACC)10, 32. Unmapped ORFs were then compared sequentially to JGI’s Integrated Microbial Genomes dataset 11(IMG: v 3.50, October 12th, 2012), followed by sequenced microbial genomes from NCBI12. Annotations were performed using the ‘ublast’ module implemented in ‘usearch’28, with a sequence identity threshold of 60%, query coverage fraction of 50%, and e-value of 1e-5. Assembly and annotation statistics are summarized in Supplementary table 12. Depth of coverage for contigs was calculated through mapping of raw reads to assembled contigs using Bowtie233, followed by processing using ‘samtools’34 and custom R scripts. Median depth of coverage over the entire contig was then assigned as its abundance. Biological Observation Matrix (BIOM) files35 were created incorporating ORF abundance, and annotation using the KEGG Orthology (KO)13 information and Enzyme Commission (EC)15 codes. These BIOM files were subsequently used for comparisons of functional potential between the three populations.
Data analyses
Alpha diversity analyses were performed using observed species and phylogenetic diversity (PD) indices, as implemented in QIIME29. Beta diversity analyses were performed using weighted UniFrac6 (16S rRNA), and Bray-Curtis (Genus tables, shotgun KO) distance metrics, as implemented in QIIME. Statistical analyses including Principal Coordinates Analysis (PCoA), PERMANOVA tests, supervised machine learning (Random Forest)7, 36, and Bayesian source-tracking8 were performed in QIIME29. Comparison of taxonomic and functional counts data between the three populations were performed using Kruskal-Wallis tests with multiple testing correction (False Discovery Rate, FDR) implemented in R. Boxplots, heatmaps, and 2D PCoA plots were generated using R37. PERMANOVA were performed using 1,000 permutations to estimate p-values for differences among categories (i.e., country). Machine learning analyses utilized Random Forest classifiers with 10-fold cross-validation and 1,000 trees.
Treponema genome reconstruction
Contigs assembled from shotgun metagenomic reads obtained from four Matses individuals (SM03, SM23, SM28, and SM42) were screened for 16S rRNA gene sequences and 35 single copy marker loci sequences22 using a combination of NCBI-BLAST38, 39 and HMM (Hidden Markov Models)40 profile searches. Contigs with best matches within the Treponema genus were filtered. Two strains of Treponema were identified in our samples. Strain 1, found in all four samples, had a >99% sequence identity to T. succinifaciens at the 16S rRNA locus (nucleotide) and 35 single copy marker loci (average, amino acid). The second strain (Strain 2), found in samples SM23, and SM42, had ~90–91% sequence identity (nucleotide) at the 16S rRNA locus and ~88% sequence identity (average, amino acid) at the single copy marker loci, to T. succinifaciens. Several of the single copy marker loci co-assembled on contigs. Depth of coverage was consistent for marker loci on different contigs. Further, in samples with both strains (SM23, SM42), the strains were observed to have different depths of coverage, consistently observed across their respective contigs. Additional contigs were assigned to the two strains using a combination of NCBI-BLAST, depth of coverage, and GC%. Assembly evaluation was performed using the ‘reapr’ pipeline41. Assembly statistics are presented in Supplementary Table 13. Functional analysis and annotation were performed on filtered contigs using the ‘prokka’ pipeline23. Predicted Open reading frames (ORFs) were submitted through the MAPLE server24, to evaluate functional potential. The functional potential (Module completion ratio, KEGG pathways) of the Matses Treponema strains were compared using hierarchical clustering to a collection of reference genomes, including other Spirochaetes, and several gut-associated bacteria across other phyla.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
We acknowledge the collaboration of the Comunidad Nativa Matses Anexo San Mateo who open their community to our research enterprise. We recognize the contribution of Susan Polo and Maria Elena Medina during fieldwork and Alison Mann during data analysis. Research reported in this publication was primarily supported by the National Institutes of Health under award numbers R01 HG005172 and R01 GM089886. Additional support included grants from the National Institutes of Health (U54GM104938) and the National Science Foundation (#0845314). AOT was partially supported by the National Institutes of Health grant R25 CA085771 during the writing phase of this project.
Footnotes
Accession codes:
16S rRNA gene sequences from the study have been deposited in the QIIME database under study id 1448 (Illumina HiSeq V4). Shotgun sequence datasets have been deposited in the NCBI SRA database under the BioProject id PRJNA268964.
Author contributions
C.M.L. led the project and C.M.L., A.J.O-T., R.Y.T., conceived the initial project design, with input from J.M., K.S., R.K. during later phases. C.M.L., A.J.O-T., R.Y.T., L.M-R, O.T-V., A.T.O, E.G-P., L.T-C., design the field study, human subjects protocols and consent, and collected samples. C.M.L., A.J.O-T., R.Y.T., J.M., K.S., J.C.C., L.K.U., Z.Z.X., W.V.T., R.K., P.G., C.W. A.T.O. performed experiments and analyzed data. C.M.L. provided financial support for the initial project design, with additional materials and bioinformatic support provided by R.K., P.G., M.F., P.S., P.L. at later phases. C.M.L., A.J.O-T., R.Y.T. wrote the initial manuscript with significant contributions from J.M., K.S., and R.K., and critical input from all other authors. The funders had no role in this study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Schnorr SL, et al. Gut microbiome of the Hadza hunter-gatherers. Nature communications. 2014;5 doi: 10.1038/ncomms4654. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.De Filippo C, et al. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2010;107:14691–14696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005963107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yatsunenko T, et al. Human gut microbiome viewed across age and geography. Nature. 2012;486:222–227. doi: 10.1038/nature11053. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Harder JD. Matses Indian rainforest habitat classification and mammalian diversity in Amazonian Peru. Journal of Ethnobiology. 2000;20:1–36. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Israel BA, Schulz AJ, Parker EA, Becker AB. Review of community-based research: assessing partnership approaches to improve public health. Annual review of public health. 1998;19:173–202. doi: 10.1146/annurev.publhealth.19.1.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Lozupone C, Lladser ME, Knights D, Stombaugh J, Knight R. UniFrac: an effective distance metric for microbial community comparison. The ISME journal. 2011;5:169. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2010.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Breiman L. Random forests. Machine learning. 2001;45:5–32. [Google Scholar]
- 8.Knights D, et al. Bayesian community-wide culture-independent microbial source tracking. Nat Meth. 2011;8:761–763. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Boisvert S, Raymond F, Godzaridis É, Laviolette F, Corbeil J. Ray Meta: scalable de novo metagenome assembly and profiling. Genome Biol. 2012;13:R122. doi: 10.1186/gb-2012-13-12-r122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Abolude OO, Creasy HH, Mahurkar AA, White O, Giglio MG. Human Microbiome Project, Data Analysis, and Coordination Center. 2013. [Google Scholar]
- 11.Markowitz VM, et al. IMG: the integrated microbial genomes database and comparative analysis system. Nucleic acids research. 2012;40:D115–D122. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Benson DA, et al. GenBank. Nucleic acids research. 2012:gks1195. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mao X, Cai T, Olyarchuk JG, Wei L. Automated genome annotation and pathway identification using the KEGG Orthology (KO) as a controlled vocabulary. Bioinformatics. 2005;21:3787–3793. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/bti430. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kanehisa M, Goto S, Sato Y, Kawashima M, Furumichi M, Tanabe M. Data, information, knowledge and principle: back to metabolism in KEGG. Nucleic acids research. 2014;42:D199–D205. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Bairoch A. The ENZYME database in 2000. Nucleic acids research. 2000;28:304–305. doi: 10.1093/nar/28.1.304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Spor A, Koren O, Ley R. Unravelling the effects of the environment and host genotype on the gut microbiome. Nature Reviews Microbiology. 2011;9:279–290. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.McKenna P, et al. The macaque gut microbiome in health, lentiviral infection, and chronic enterocolitis. PLoS pathogens. 2008;4:e20. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0040020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ley RE, et al. Evolution of mammals and their gut microbes. Science. 2008;320:1647–1651. doi: 10.1126/science.1155725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Ochman H, et al. Evolutionary relationships of wild hominids recapitulated by gut microbial communities. PLoS biology. 2010;8:e1000546. doi: 10.1371/journal.pbio.1000546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Tito RY, et al. Insights from characterizing extinct human gut microbiomes. PLoS One. 2012;7:e51146. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0051146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Han C, et al. Complete genome sequence of Treponema succinifaciens type strain (6091T) Standards in genomic sciences. 2011;4:361. doi: 10.4056/sigs.1984594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Darling AE, Jospin G, Lowe E, Matsen FA, IV, Bik HM, Eisen JA. PhyloSift: phylogenetic analysis of genomes and metagenomes. PeerJ. 2014;2:e243. doi: 10.7717/peerj.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Seemann T. Prokka: rapid prokaryotic genome annotation. Bioinformatics. 2014:btu153. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btu153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Takami H, Taniguchi T, Moriya Y, Kuwahara T, Kanehisa M, Goto S. Evaluation method for the potential functionome harbored in the genome and metagenome. BMC genomics. 2012;13:699. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Graber JR, Leadbetter JR, Breznak JA. Description of Treponema azotonutricium sp. nov. and Treponema primitia sp. nov., the first spirochetes isolated from termite guts. Applied and environmental microbiology. 2004;70:1315–1320. doi: 10.1128/AEM.70.3.1315-1320.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Schrank K, et al. Treponema brennaborense sp. nov., a novel spirochaete isolated from a dairy cow suffering from digital dermatitis. International journal of systematic bacteriology. 1999;49:43–50. doi: 10.1099/00207713-49-1-43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Caporaso JG, et al. Ultra-high-throughput microbial community analysis on the Illumina HiSeq and MiSeq platforms. The ISME journal. 2012;6:1621–1624. doi: 10.1038/ismej.2012.8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Edgar RC. Search and clustering orders of magnitude faster than BLAST. Bioinformatics. 2010;26:2460–2461. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq461. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Caporaso JG, et al. QIIME allows analysis of high-throughput community sequencing data. Nature methods. 2010;7:335–336. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.f.303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.DeSantis TZ, et al. Greengenes, a chimera-checked 16S rRNA gene database and workbench compatible with ARB. Applied and environmental microbiology. 2006;72:5069–5072. doi: 10.1128/AEM.03006-05. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Rho M, Tang H, Ye Y. FragGeneScan: predicting genes in short and error-prone reads. Nucleic acids research. 2010;38:e191–e191. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Peterson J, et al. The NIH human microbiome project. Genome research. 2009;19:2317–2323. doi: 10.1101/gr.096651.109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Langmead B, Salzberg SL. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nature methods. 2012;9:357–359. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Li H, et al. The sequence alignment/map format and SAMtools. Bioinformatics. 2009;25:2078–2079. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btp352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.McDonald D, et al. The Biological Observation Matrix (BIOM) format or: how I learned to stop worrying and love the ome-ome. GigaScience. 2012;1:7. doi: 10.1186/2047-217X-1-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Knights D, Costello EK, Knight R. Supervised classification of human microbiota. FEMS microbiology reviews. 2011;35:343–359. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6976.2010.00251.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Team RC. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. 2012. R Foundation for Statistical Computing; Vienna, Austria: 2012. [Google Scholar]
- 38.Camacho C, et al. BLAST+: architecture and applications. BMC bioinformatics. 2009;10:421. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-10-421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of molecular biology. 1990;215:403–410. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80360-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Eddy SR. HMMER: Profile hidden Markov models for biological sequence analysis. 2001. [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hunt M, Kikuchi T, Sanders M, Newbold C, Berriman M, Otto TD. REAPR: a universal tool for genome assembly evaluation. Genome Biol. 2013;14:R47. doi: 10.1186/gb-2013-14-5-r47. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.