Abstract
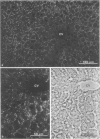
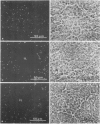
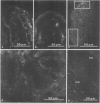
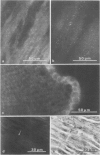
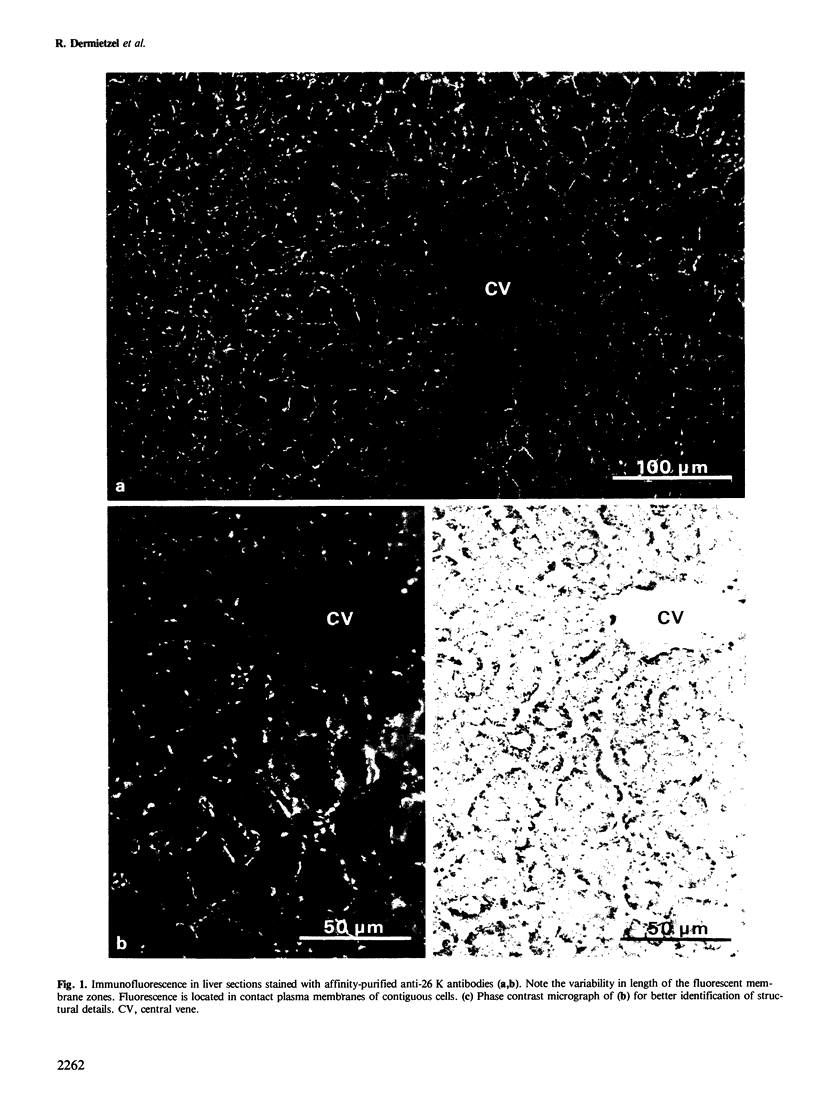
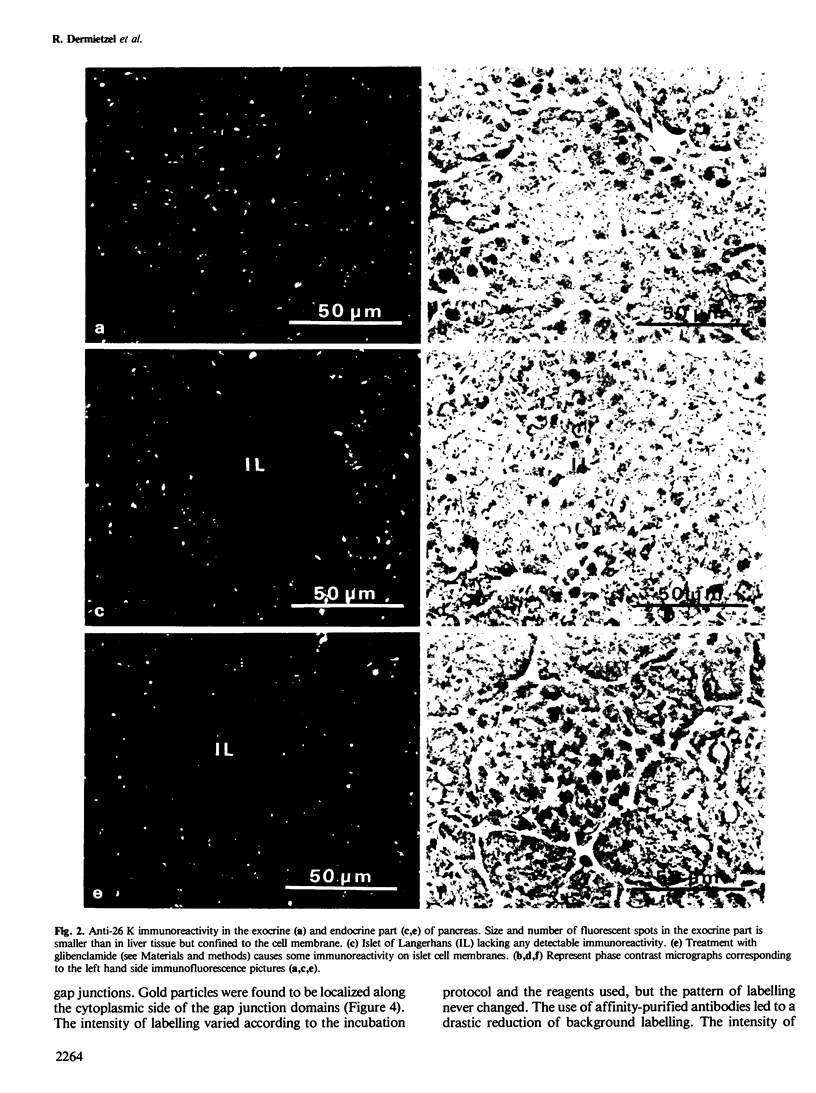
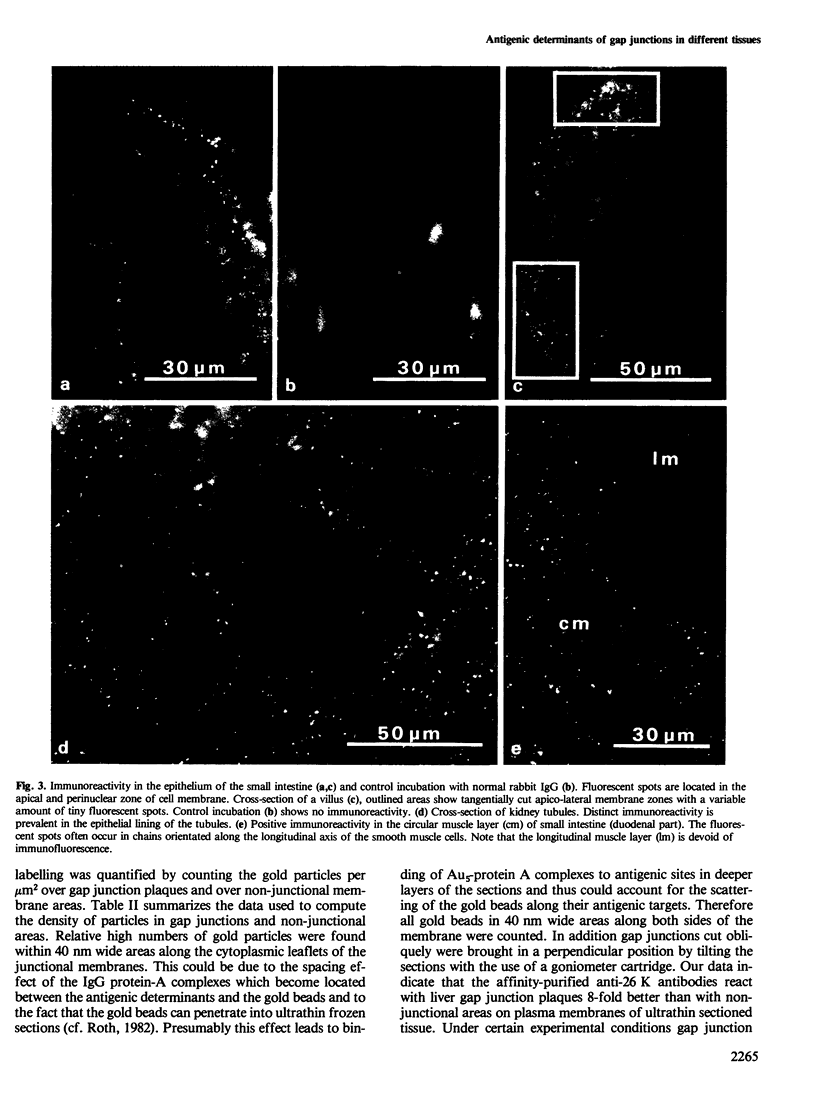
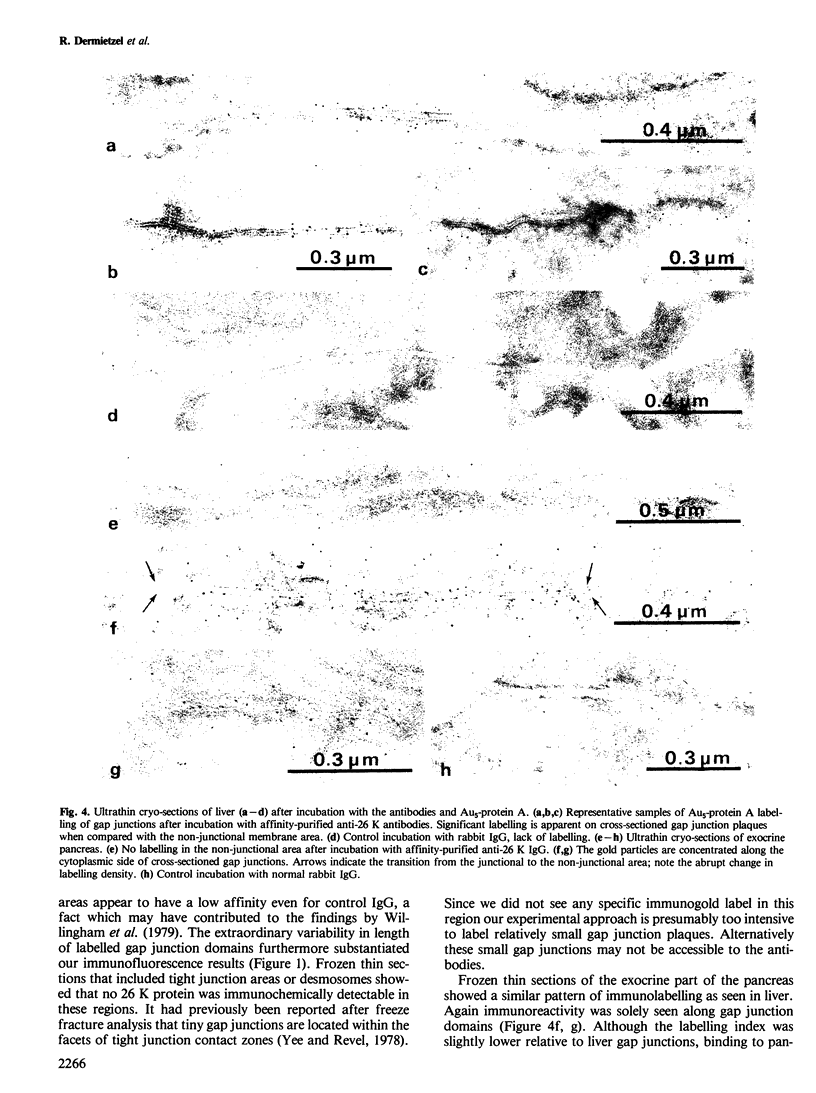
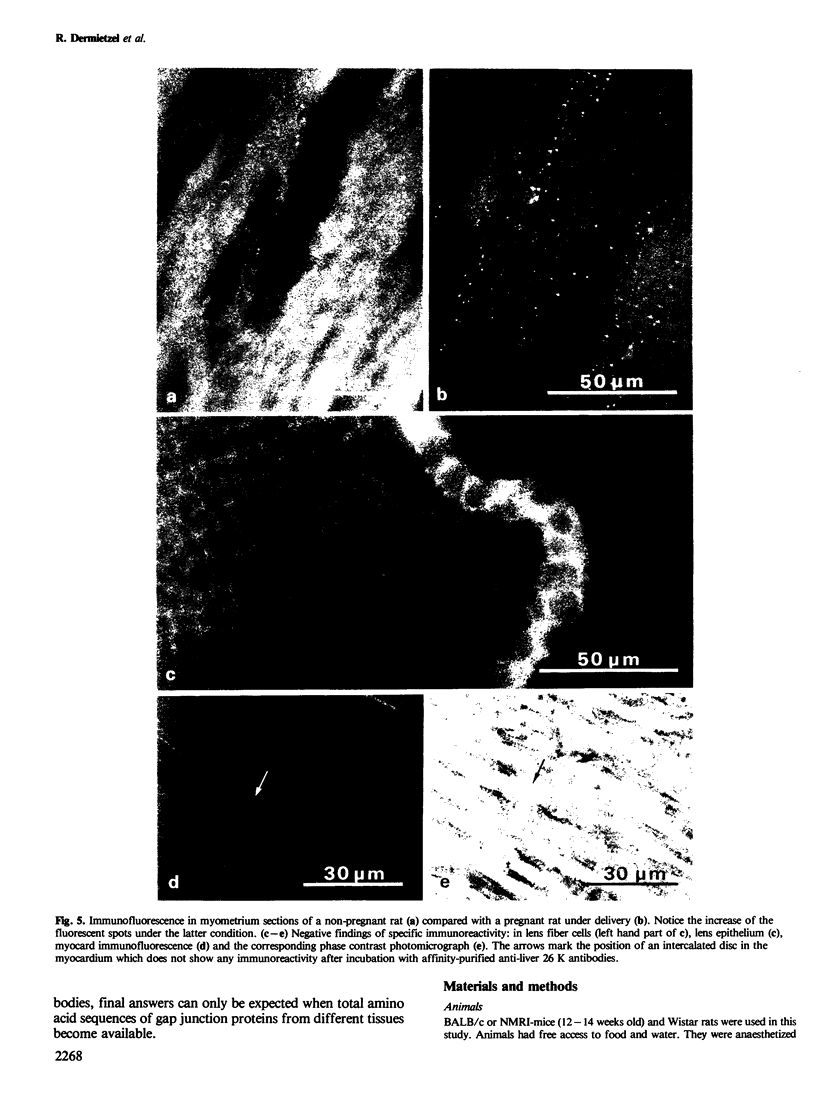
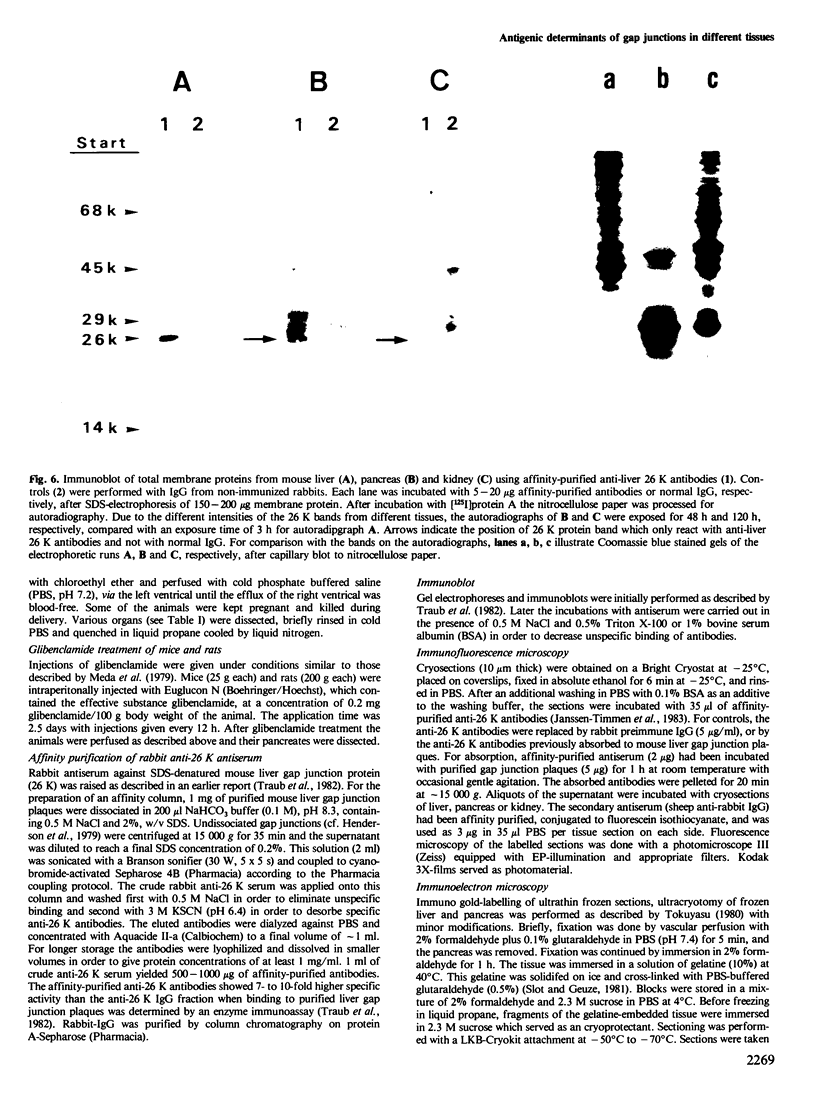
Using affinity-purified antibodies against mouse liver gap junction protein (26 K), discrete fluorescent spots were seen by indirect immunofluorescence labelling on apposed membranes of contiguous cells in several mouse and rat tissues: pancreas (exocrine part), kidney, small intestine (epithelium and circular smooth muscle), Fallopian tube, endometrium, and myometrium of delivering rats. No reaction was seen on sections of myocardium, ovaries and lens. Specific labelling of gap junction plaques was demonstrated by immunoelectron microscopy on ultrathin frozen sections through liver and the exocrine part of pancreas after treatment with gold protein A. Weak immunoreactivity was found on the endocrine part of the pancreas (i.e., Langerhans islets) after glibenclamide treatment of mice and rats, which causes an increase of insulin secretion and of the size as well as the number of gap junction plaques in cells of Langerhans islets. Furthermore, the affinity purified anti-liver 26 K antibodies were shown by immunoblot to react with proteins of similar mol. wt. in pancreas and kidney membranes. Taken together these results suggest that gap junctions from several, morphogenetically different tissues have specific antigenic sites in common. The different extent of specific immunoreactivity of anti-liver 26 K antibodies with different tissues is likely due to differences in size and number of gap junctions although structural differences cannot be excluded.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Dahl G., Berger W. Nexus formation in the myometrium during parturition and induced by estrogen. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1978 Jul;2(4):381–387. doi: 10.1016/0309-1651(78)90024-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faulk W. P., Taylor G. M. An immunocolloid method for the electron microscope. Immunochemistry. 1971 Nov;8(11):1081–1083. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(71)90496-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitzgerald P. G., Bok D., Horwitz J. Immunocytochemical localization of the main intrinsic polypeptide (MIP) in ultrathin frozen sections of rat lens. J Cell Biol. 1983 Nov;97(5 Pt 1):1491–1499. doi: 10.1083/jcb.97.5.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabella G., Blundell D. Nexuses between the smooth muscle cells of the guinea-pig ileum. J Cell Biol. 1979 Jul;82(1):239–247. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.1.239. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenough D. A. The structure and permeability of isolated hepatocyte gap junctions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1976;40:37–43. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1976.040.01.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros D. B., Nicholson B. J., Revel J. P. Comparative analysis of the gap junction protein from rat heart and liver: is there a tissue specificity of gap junctions? Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90188-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson D., Eibl H., Weber K. Structure and biochemistry of mouse hepatic gap junctions. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 5;132(2):193–218. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90391-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Anderson D. J., Friedlander M., Gilula N. B. Comparative analysis of the major polypeptides from liver gap junctions and lens fiber junctions. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;92(1):53–59. doi: 10.1083/jcb.92.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hertzberg E. L., Gilula N. B. Liver gap junctions and lens fiber junctions: comparative analysis and calmodulin interaction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1982;46(Pt 2):639–645. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1982.046.01.060. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen-Timmen U., Dermietzel R., Frixen U., Leibstein A., Traub O., Willecke K. Immunocytochemical localization of the gap junction 26 K protein in mouse liver plasma membranes. EMBO J. 1983;2(3):295–302. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01422.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Schmid E., Franke W. W., Geiger B. Different modes of internalization of proteins associated with adhaerens junctions and desmosomes: experimental separation of lateral contacts induces endocytosis of desmosomal plaque material. EMBO J. 1982;1(6):725–732. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01237.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Michaels R. L., Halban P. A., Orci L., Sheridan J. D. In vivo modulation of gap junctions and dye coupling between B-cells of the intact pancreatic islet. Diabetes. 1983 Sep;32(9):858–868. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.9.858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meda P., Perrelet A., Orci L. Increase of gap junctions between pancreatic B-cells during stimulation of insulin secretion. J Cell Biol. 1979 Aug;82(2):441–448. doi: 10.1083/jcb.82.2.441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michalke W., Loewenstein W. R. Communication between cells of different type. Nature. 1971 Jul 9;232(5306):121–122. doi: 10.1038/232121b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L. Macro- and micro-domains in the endocrine pancreas. Diabetes. 1982 Jun;31(6 Pt 1):538–565. doi: 10.2337/diab.31.6.538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orci L., Unger R. H., Renold A. E. Structural coupling between pancreatic islet cells. Experientia. 1973 Aug 15;29(8):1015–1018. doi: 10.1007/BF01930436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Preparation, characterization, and localization of antisera against bovine MP26, an integral protein from lens fiber plasma membrane. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):625–632. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. Sizing of protein A-colloidal gold probes for immunoelectron microscopy. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):533–536. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T. Immunochemistry on ultrathin frozen sections. Histochem J. 1980 Jul;12(4):381–403. doi: 10.1007/BF01011956. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub O., Drüge P. M., Willecke K. Degradation and resynthesis of gap junction protein in plasma membranes of regenerating liver after partial hepatectomy or cholestasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):755–759. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub O., Janssen-Timmen U., Drüge P. M., Dermietzel R., Willecke K. Immunological properties of gap junction protein from mouse liver. J Cell Biochem. 1982;19(1):27–44. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240190104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub O., Willecke K. Cross reaction of antibodies against liver gap junction protein (26K) with lens fiber junction protein (MIP) suggests structural homology between these tissue specific gene products. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Dec 15;109(3):895–901. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)92024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willingham M. C., Jay G., Pastan I. Localization of the ASV src gene product to the plasma membrane of transformed cells by electron microscopic immunocytochemistry. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90361-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yee A. G., Revel J. P. Loss and reappearance of gap junctions in regenerating liver. J Cell Biol. 1978 Aug;78(2):554–564. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]