Abstract
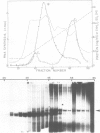
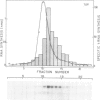
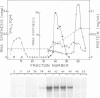
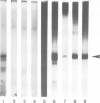
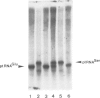
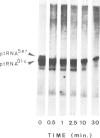
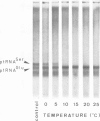
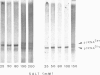
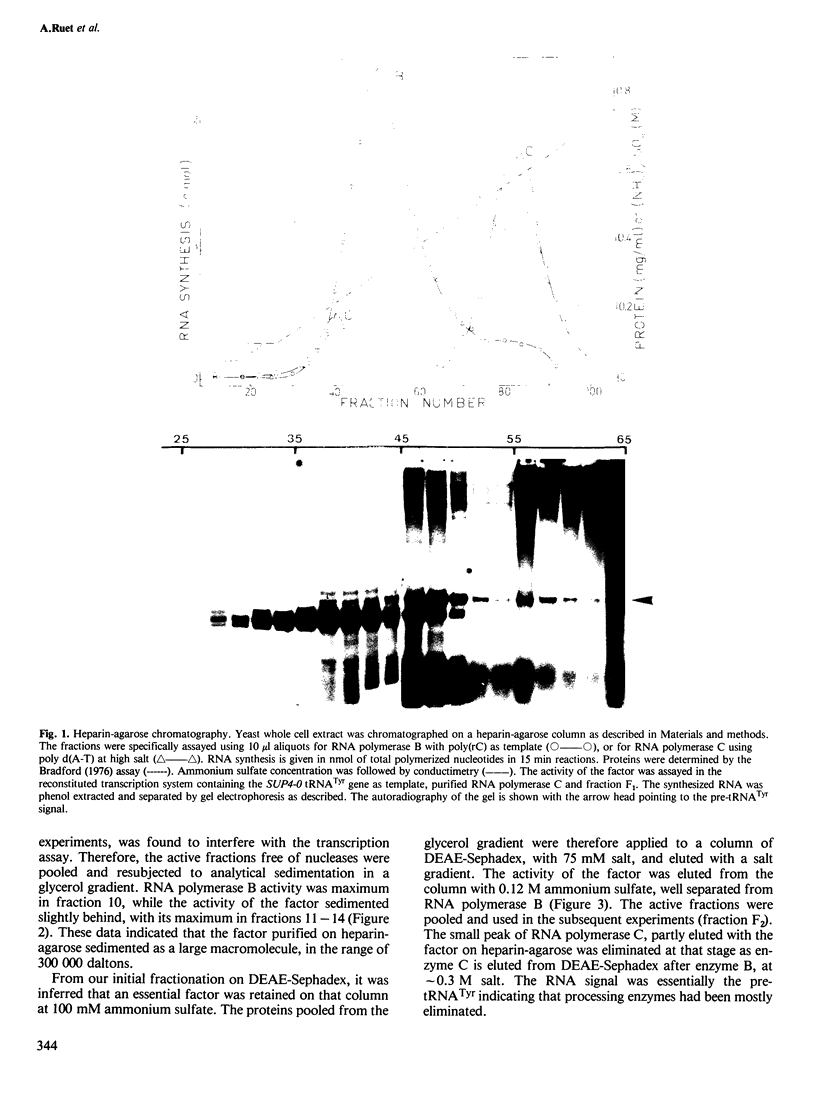
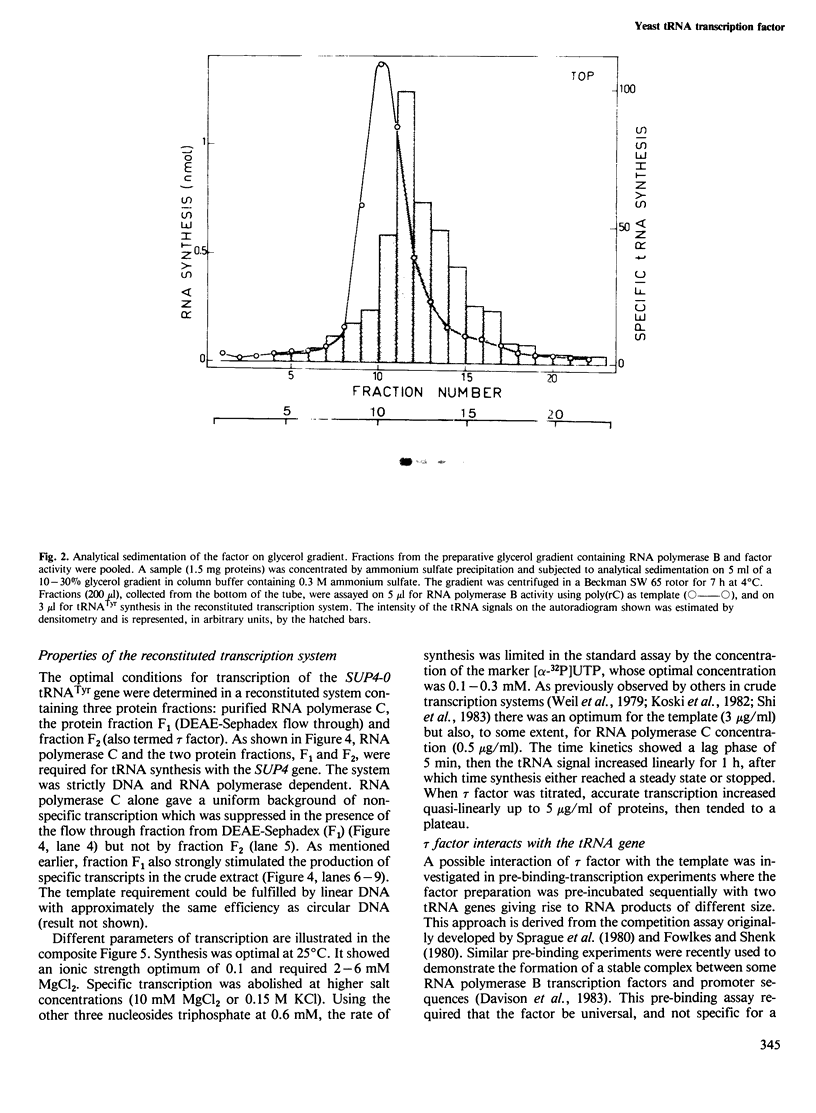
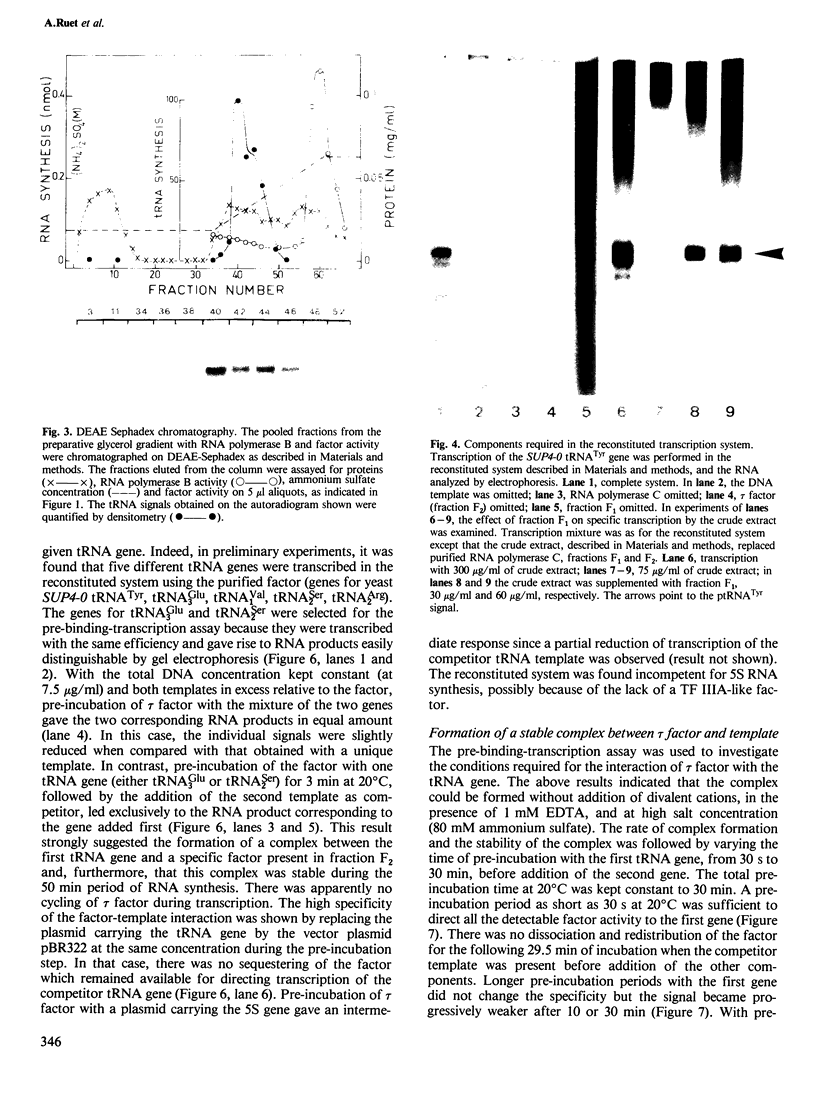
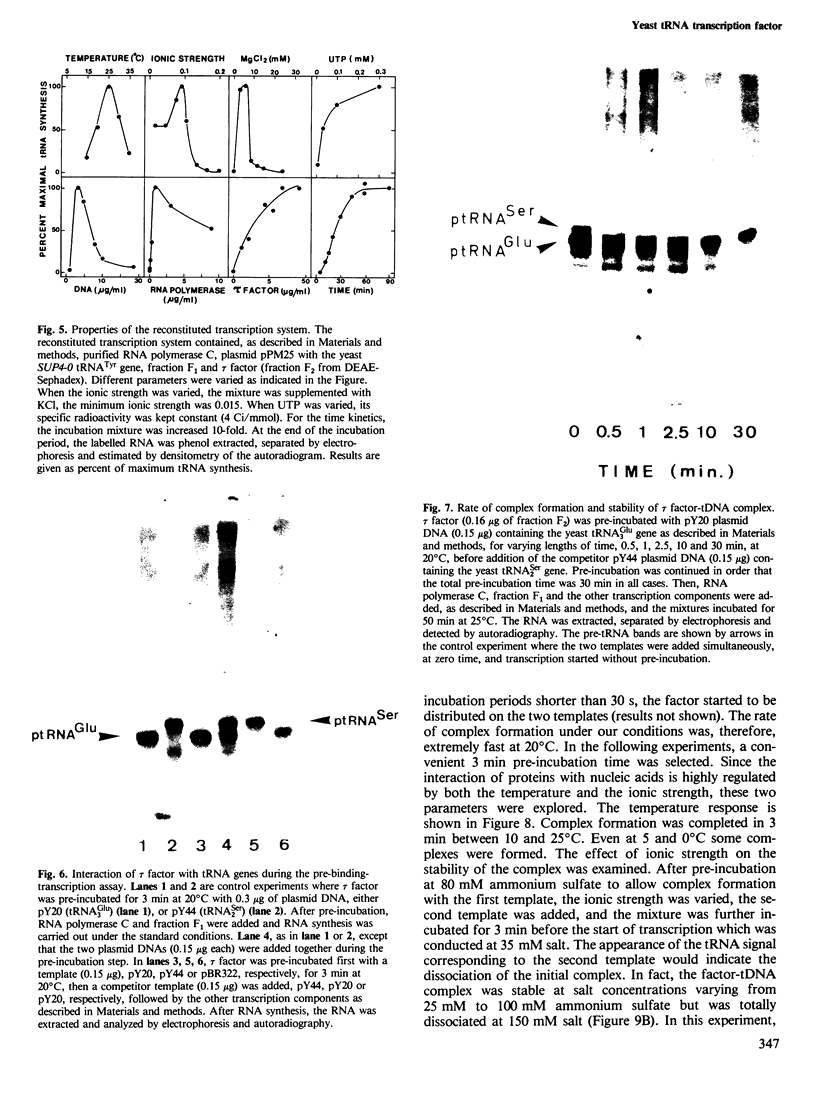
A yeast extract was fractionated to resolve the factors involved in the transcription of yeast tRNA genes. An in vitro transcription system was reconstituted with two separate protein fractions and purified RNA polymerase C (III). Optimal conditions for tRNA synthesis have been determined. One essential component, termed tau factor, was partially purified by conventional chromatographic methods on heparin-agarose and DEAE-Sephadex; it sedimented as a large macromolecule in glycerol gradients (mol. wt. approximately 300 000). tau factor was found to form a stable complex with the tRNA gene in the absence of other transcriptional components. Complex formation is very fast, is not temperature dependent between 10 degrees C and 25 degrees C and does not require divalent cations. The factor-DNA complex is stable for at least 30 min at high salt concentration (0.1 M ammonium sulfate). These results indicate that gene recognition by a specific factor is a primary event in tRNA synthesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker R. E., Eigel A., Vögtel D., Feldmann H. Nucleotide sequences of yeast genes for tRNA(2), tRNA(2) and tRNA(1): homology blocks occur in the vicinity of different tRNA genes. EMBO J. 1982;1(3):291–295. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01162.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkenmeier E. H., Brown D. D., Jordan E. A nuclear extract of Xenopus laevis oocytes that accurately transcribes 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):1077–1086. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90291-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Sakonju S., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: II. The 3' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):27–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bogenhagen D. F., Wormington W. M., Brown D. D. Stable transcription complexes of Xenopus 5S RNA genes: a means to maintain the differentiated state. Cell. 1982 Feb;28(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90359-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelke D. R., Ng S. Y., Shastry B. S., Roeder R. G. Specific interaction of a purified transcription factor with an internal control region of 5S RNA genes. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80048-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann H., Olah J., Friedenreich H. Sequence of a yeast DNA fragment containing a chromosomal replicator and a tRNA Glu 3 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2949–2959. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galli G., Hofstetter H., Birnstiel M. L. Two conserved sequence blocks within eukaryotic tRNA genes are major promoter elements. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):626–631. doi: 10.1038/294626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman H. M., Olson M. V., Hall B. D. Nucleotide sequence of a mutant eukaryotic gene: the yeast tyrosine-inserting ochre suppressor SUP4-o. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond C. I., Holland M. J. Purification of yeast RNA polymerases using heparin agarose affinity chromatography. Transcriptional properties of the purified enzymes on defined templates. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):3230–3241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klekamp M. S., Weil P. A. Specific transcription of homologous class III genes in yeast-soluble cell-free extracts. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8432–8441. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Stillman D. J., Geiduschek E. P. Specific interactions of Saccharomyces cerevisiae proteins with a promoter region of eukaryotic tRNA genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6191–6195. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Allison D. S., Worthington M., Hall B. D. An in vitro RNA polymerase III system from S. cerevisiae: effects of deletions and point mutations upon SUP4 gene transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 20;10(24):8127–8143. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.24.8127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koski R. A., Clarkson S. G., Kurjan J., Hall B. D., Smith M. Mutations of the yeast SUP4 tRNATyr locus: transcription of the mutant genes in vitro. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):415–425. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90352-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kressmann A., Hofstetter H., Di Capua E., Grosschedl R., Birnstiel M. L. A tRNA gene of Xenopus laevis contains at least two sites promoting transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Dec 11;7(7):1749–1763. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.7.1749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Brown D. D. A specific transcription factor that can bind either the 5S RNA gene or 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):4170–4174. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.4170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruet A., Sentenac A., Fromageot P. A specific assay for yeast RNA polymerases in crude cell extracts. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Oct;90(2):325–330. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12608.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Brown D. D. Contact points between a positive transcription factor and the Xenopus 5S RNA gene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90133-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaack J., Sharp S., Dingermann T., Söll D. Transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes in vitro. II. Formation of stable complexes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2447–2453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Hall B. D. Transcription in yeast: alpha-amanitin sensitivity and other properties which distinguish between RNA polymerases I and III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1029–1033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall J., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors are required for the accurate transcription of purified genes by RNA polymerase III. J Biol Chem. 1980 Dec 25;255(24):11986–11991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shastry B. S., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Multiple factors involved in the transcription of class III genes in Xenopus laevis. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):12979–12986. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X. P., Wingender E., Böttrich J., Seifart K. H. Faithful transcription of ribosomal 5-S RNA in vitro depends on the presence of several factors. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Mar 1;131(1):189–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07248.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smagowicz W., Ruet A., Camier S., Sentenac A., Fromageot P., Sternbach H. Stimulation of transcription of the yeast tRNATyr gene in cell-free extracts by tyrosyl-tRNA synthetase. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):747–749. doi: 10.1038/304747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague K. U., Larson D., Morton D. 5' flanking sequence signals are required for activity of silkworm alanine tRNA genes in homologous in vitro transcription systems. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):171–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Hager G. L., Weinberg F., Rutter W. J. Molecular structure of yeast RNA polymerase III: demonstration of the tripartite transcriptive system in lower eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1024–1028. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil P. A., Segall J., Harris B., Ng S. Y., Roeder R. G. Faithful transcription of eukaryotic genes by RNA polymerase III in systems reconstituted with purified DNA templates. J Biol Chem. 1979 Jul 10;254(13):6163–6173. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G. J. Adenovirus DNA-directed transcription of 5.5S RNA in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2175–2179. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Keulen H., Thomas D. Y. A yeast transcription system for the 5S rRNA gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5223–5238. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5223. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]