Abstract
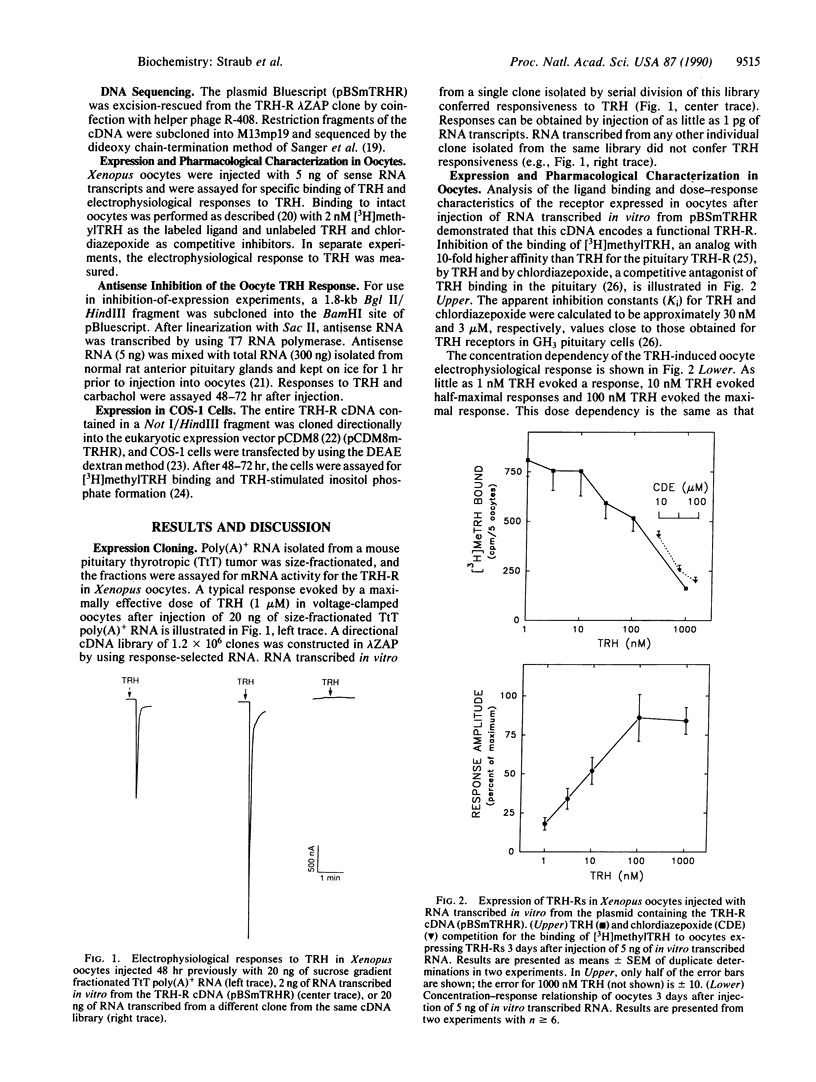
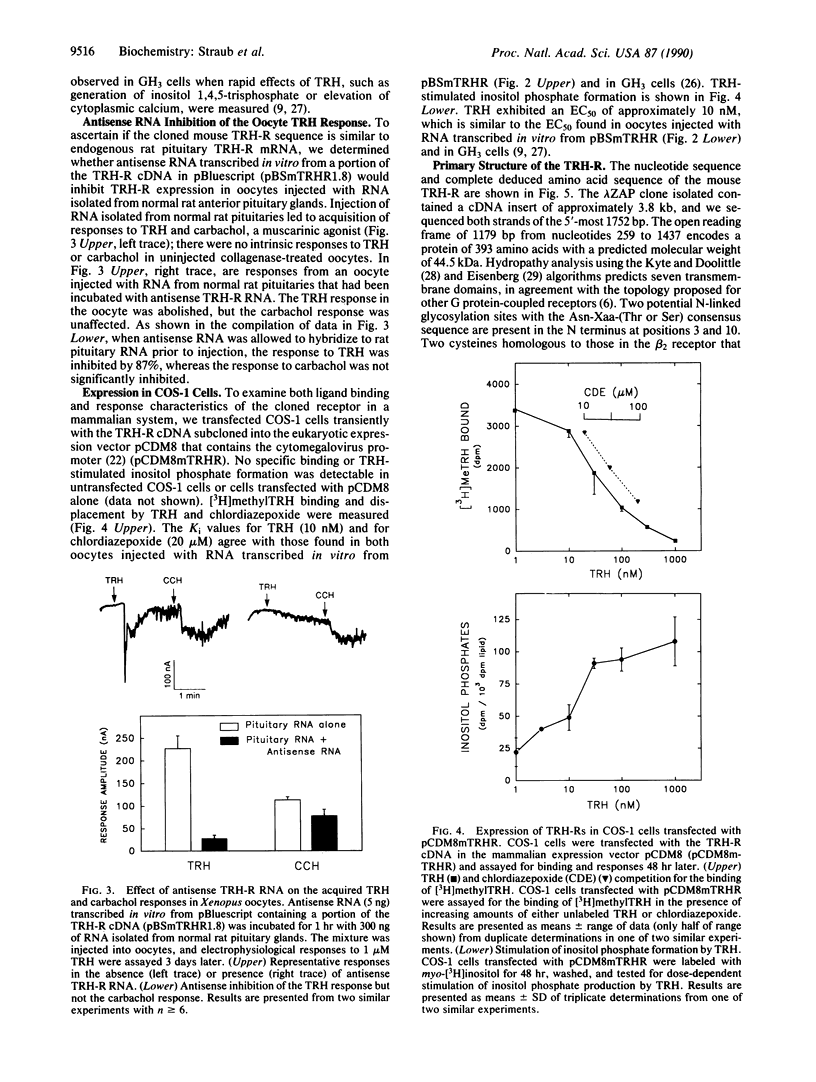
Thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) is an important extracellular regulatory molecule that functions as a releasing factor in the anterior pituitary gland and as a neurotransmitter/neuromodulator in the central and peripheral nervous systems. Binding sites for TRH are present in these tissues, but the TRH receptor (TRH-R) has not been purified from any source. Using Xenopus laevis oocytes in an expression cloning strategy, we have isolated a cDNA clone that encodes the mouse pituitary TRH-R. This conclusion is based on the following evidence. Injection of sense RNA transcribed in vitro from this cDNA into Xenopus oocytes leads to expression of cell-surface receptors that bind TRH and the competitive antagonist chlordiazepoxide with appropriate affinities and that elicit electrophysiological responses to TRH with the appropriate concentration dependency. Antisense RNA inhibits the TRH response in Xenopus oocytes injected with RNA isolated from normal rat anterior pituitary glands. Finally, transfection of COS-1 cells with this cDNA leads to expression of receptors that bind TRH and chlordiazepoxide with appropriate affinities and that transduce TRH stimulation of inositol phosphate formation. The 3.8-kilobase mouse TRH-R cDNA encodes a protein of 393 amino acids that shows similarities to other guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory protein-coupled receptors.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Tashjian A. H., Jr Thyrotropin-releasing hormone-induced spike and plateau in cytosolic free Ca2+ concentrations in pituitary cells. Relation to prolactin release. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5827–5832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunzow J. R., Van Tol H. H., Grandy D. K., Albert P., Salon J., Christie M., Machida C. A., Neve K. A., Civelli O. Cloning and expression of a rat D2 dopamine receptor cDNA. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):783–787. doi: 10.1038/336783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Use of eukaryotic expression technology in the functional analysis of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:684–704. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52074-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. The CTAB-DNA precipitation method: a common mini-scale preparation of template DNA from phagemids, phages or plasmids suitable for sequencing. Biotechniques. 1989 May;7(5):514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dohlman H. G., Caron M. G., DeBlasi A., Frielle T., Lefkowitz R. J. Role of extracellular disulfide-bonded cysteines in the ligand binding function of the beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 6;29(9):2335–2342. doi: 10.1021/bi00461a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frech G. C., Joho R. H. Construction of directional cDNA libraries enriched for full-length inserts in a transcription-competent vector. Gene Anal Tech. 1989 Mar-Apr;6(2):33–38. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(89)90024-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C. Mechanism of signal transduction by TRH. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;553:191–196. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb46641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershengorn M. C., Paul M. E. Evidence for tight coupling of receptor occupancy by thyrotropin-releasing hormone to phospholipase C-mediated phosphoinositide hydrolysis in rat pituitary cells: use of chlordiazepoxide as a competitive antagonist. Endocrinology. 1986 Aug;119(2):833–839. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-2-833. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey A. D., Krause J. E. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the rat substance P receptor. Science. 1990 Feb 23;247(4945):958–962. doi: 10.1126/science.2154852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M., Phillips W. J. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone stimulates GTP hydrolysis by membranes from GH4C1 rat pituitary tumor cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6183–6187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinkle P. M. Pituitary TRH receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;553:176–187. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb46639.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hökfelt T., Tsuruo Y., Ulfhake B., Cullheim S., Arvidsson U., Foster G. A., Schultzberg M., Schalling M., Arborelius L., Freedman J. Distribution of TRH-like immunoreactivity with special reference to coexistence with other neuroactive compounds. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;553:76–105. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb46633.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai A., Gershengorn M. C. Measurement of lipid turnover in response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Methods Enzymol. 1987;141:100–101. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)41059-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Nathanson N. M., Horita A. Receptor binding and characterization of TRH receptors. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;553:137–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Nathanson N. M., Horita A. Solubilization and characterization of thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors from rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4227–4231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., Huang K. N., Livelli T. J., Axel R., Jessell T. M. The 5HT2 receptor defines a family of structurally distinct but functionally conserved serotonin receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):928–932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.928. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Julius D., MacDermott A. B., Axel R., Jessell T. M. Molecular characterization of a functional cDNA encoding the serotonin 1c receptor. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):558–564. doi: 10.1126/science.3399891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family: heterogeneity and its implications. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:31–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein P. S., Sun T. J., Saxe C. L., 3rd, Kimmel A. R., Johnson R. L., Devreotes P. N. A chemoattractant receptor controls development in Dictyostelium discoideum. Science. 1988 Sep 16;241(4872):1467–1472. doi: 10.1126/science.3047871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobilka B. K., Matsui H., Kobilka T. S., Yang-Feng T. L., Francke U., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Regan J. W. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for the human platelet alpha 2-adrenergic receptor. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):650–656. doi: 10.1126/science.2823383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lechan R. M., Segerson T. P. Pro-TRH gene expression and precursor peptides in rat brain. Observations by hybridization analysis and immunocytochemistry. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;553:29–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb46630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao C. F., Themmen A. P., Joho R., Barberis C., Birnbaumer M., Birnbaumer L. Molecular cloning and expression of a fifth muscarinic acetylcholine receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7328–7337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Parmentier M., Lefort A., Dinsart C., Van Sande J., Maenhaut C., Simons M. J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Selective amplification and cloning of four new members of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 May 5;244(4904):569–572. doi: 10.1126/science.2541503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez H. M. A flexible multiple sequence alignment program. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1683–1691. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McFarland K. C., Sprengel R., Phillips H. S., Köhler M., Rosemblit N., Nikolics K., Segaloff D. L., Seeburg P. H. Lutropin-choriogonadotropin receptor: an unusual member of the G protein-coupled receptor family. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):494–499. doi: 10.1126/science.2502842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A. Injected anti-sense RNAs specifically block messenger RNA translation in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):144–148. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Dowd B. F., Hnatowich M., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J., Bouvier M. Palmitoylation of the human beta 2-adrenergic receptor. Mutation of Cys341 in the carboxyl tail leads to an uncoupled nonpalmitoylated form of the receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7564–7569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Gillo B., Straub R. E., Gershengorn M. C. Mechanism of membrane electrical response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone in Xenopus oocytes injected with GH3 pituitary cell messenger ribonucleic acid. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Dec;1(12):918–925. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-12-918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oron Y., Straub R. E., Traktman P., Gershengorn M. C. Decreased TRH receptor mRNA activity precedes homologous downregulation: assay in oocytes. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1406–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.2825350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ovchinnikov YuA, Abdulaev N. G., Zolotarev A. S., Artamonov I. D., Bespalov I. A., Dergachev A. E., Tsuda M. Octopus rhodopsin. Amino acid sequence deduced from cDNA. FEBS Lett. 1988 May 9;232(1):69–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80388-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmentier M., Libert F., Maenhaut C., Lefort A., Gérard C., Perret J., Van Sande J., Dumont J. E., Vassart G. Molecular cloning of the thyrotropin receptor. Science. 1989 Dec 22;246(4937):1620–1622. doi: 10.1126/science.2556796. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive sequence comparison with FASTP and FASTA. Methods Enzymol. 1990;183:63–98. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)83007-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips W. J., Hinkle P. M. Solubilization and characterization of pituitary thyrotropin-releasing hormone receptors. Mol Pharmacol. 1989 Apr;35(4):533–540. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popot J. L., Engelman D. M., Gurel O., Zaccaï G. Tertiary structure of bacteriorhodopsin. Positions and orientations of helices A and B in the structural map determined by neutron diffraction. J Mol Biol. 1989 Dec 20;210(4):829–847. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90111-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapiejko P. J., George S. T., Malbon C. C. Primary structure of a human protein which bears structural similarities to members of the rhodopsin/beta-adrenergic receptor family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 12;16(17):8721–8721. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.17.8721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rees D. C., DeAntonio L., Eisenberg D. Hydrophobic organization of membrane proteins. Science. 1989 Aug 4;245(4917):510–513. doi: 10.1126/science.2667138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffer M., Edmundson A. B. Use of helical wheels to represent the structures of proteins and to identify segments with helical potential. Biophys J. 1967 Mar;7(2):121–135. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(67)86579-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seed B. An LFA-3 cDNA encodes a phospholipid-linked membrane protein homologous to its receptor CD2. 1987 Oct 29-Nov 4Nature. 329(6142):840–842. doi: 10.1038/329840a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif N. A., Burt D. R. Sulfhydryl groups in receptor binding of thyrotropin-releasing hormone to rat amygdala. J Neurochem. 1984 Jan;42(1):209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb09719.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharif N. A. Quantitative autoradiography of TRH receptors in discrete brain regions of different mammalian species. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1989;553:147–175. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1989.tb46638.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Candelore M. R., Hill W. S., Sigal I. S., Dixon R. A. Identification of two serine residues involved in agonist activation of the beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 15;264(23):13572–13578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Dixon R. A., Cheung A. H., Candelore M. R., Blake A. D., Sigal I. S. Mutations that uncouple the beta-adrenergic receptor from Gs and increase agonist affinity. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 5;262(34):16439–16443. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strader C. D., Sigal I. S., Candelore M. R., Rands E., Hill W. S., Dixon R. A. Conserved aspartic acid residues 79 and 113 of the beta-adrenergic receptor have different roles in receptor function. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10267–10271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straub R. E., Gershengorn M. C. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone and GTP activate inositol trisphosphate formation in membranes isolated from rat pituitary cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2712–2717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor R. L., Burt D. R. Preparation of 3H-[3-M3-His2]TRH as an improved ligand for TRH receptors. Neuroendocrinology. 1981 May;32(5):310–316. doi: 10.1159/000123177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Rodriguez H., Wong S. K., Brandt D. R., May D. C., Burnier J., Harkins R. N., Chen E. Y., Ramachandran J., Ullrich A. The avian beta-adrenergic receptor: primary structure and membrane topology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6795–6799. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6795. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young D., O'Neill K., Jessell T., Wigler M. Characterization of the rat mas oncogene and its high-level expression in the hippocampus and cerebral cortex of rat brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5339–5342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


