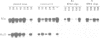Abstract
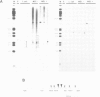
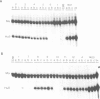
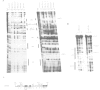
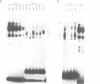
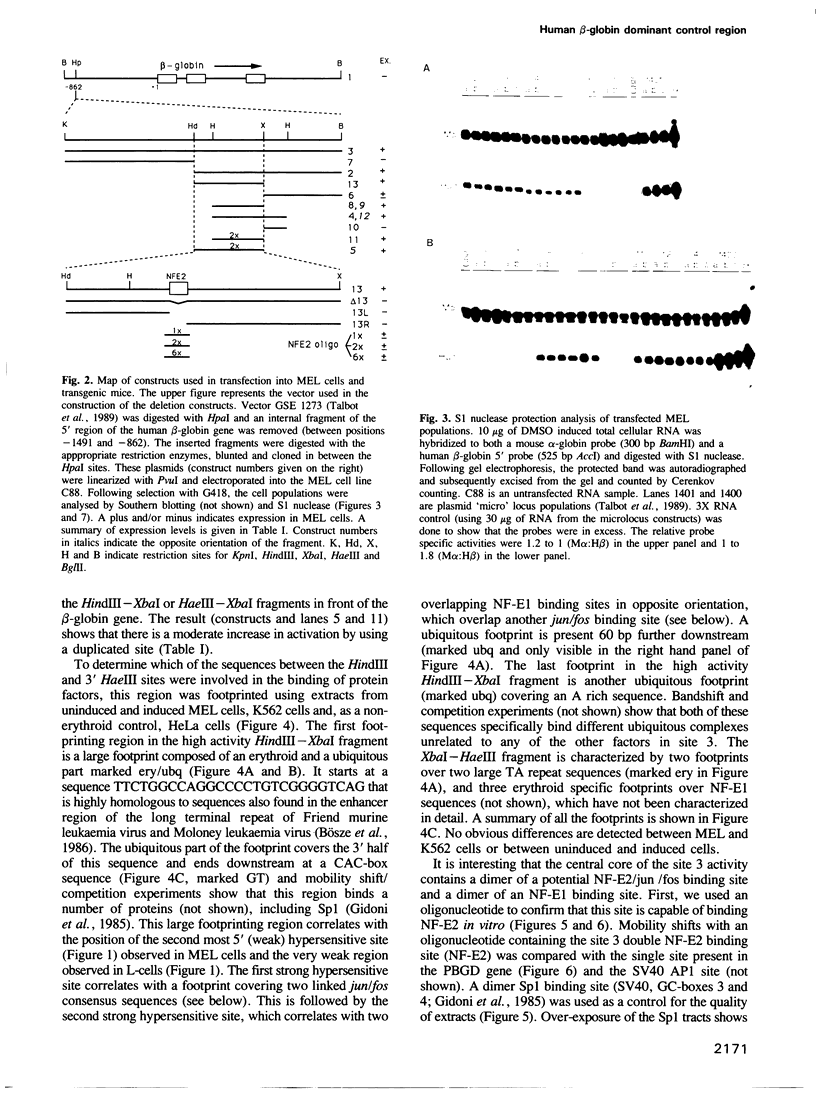
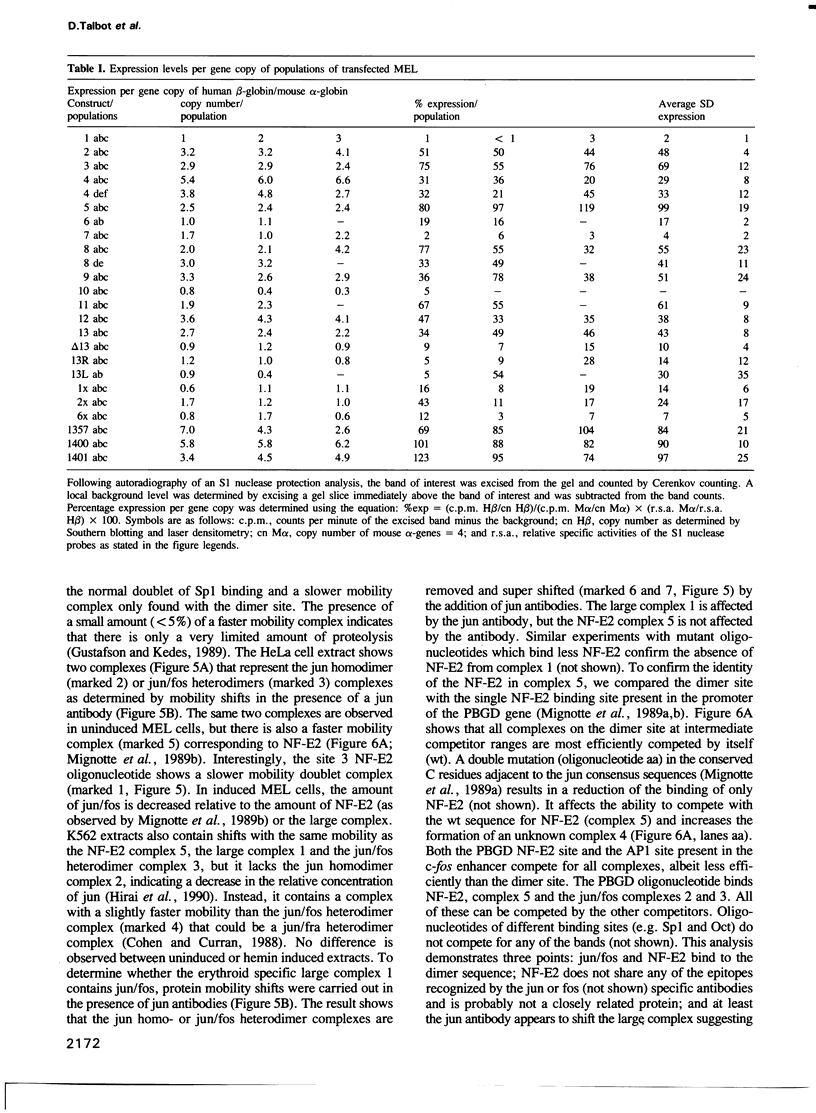
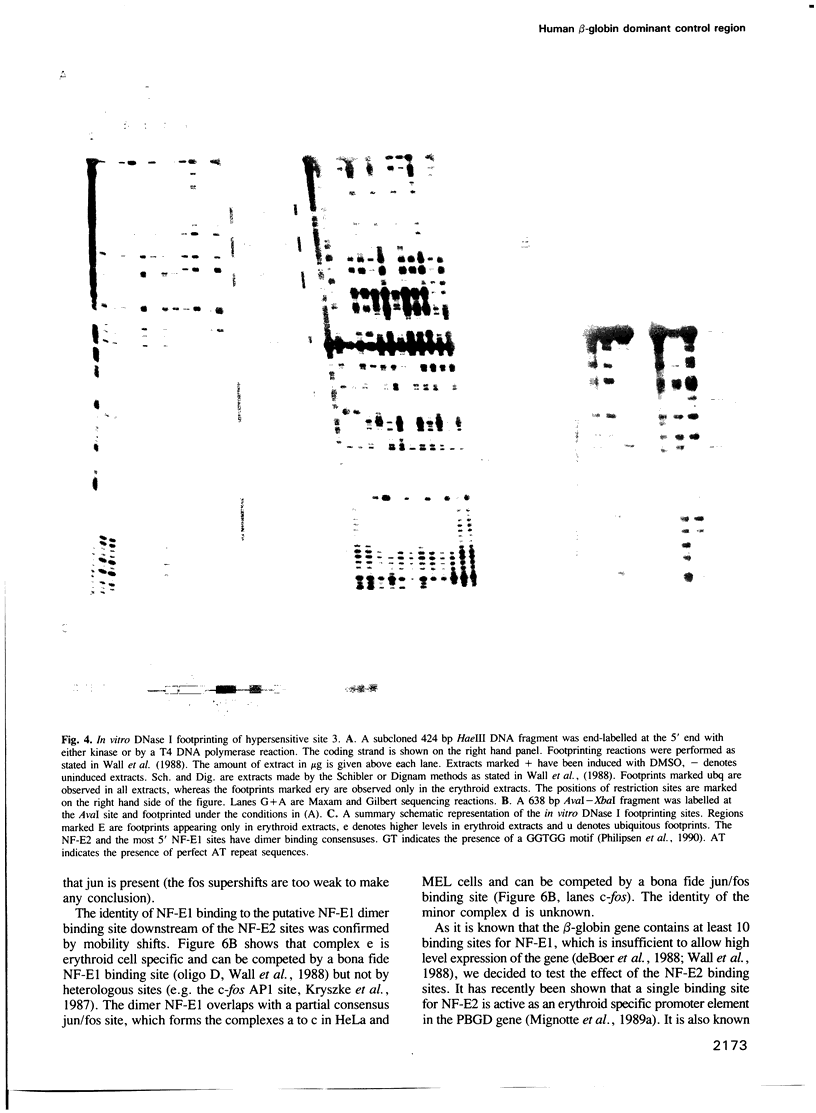
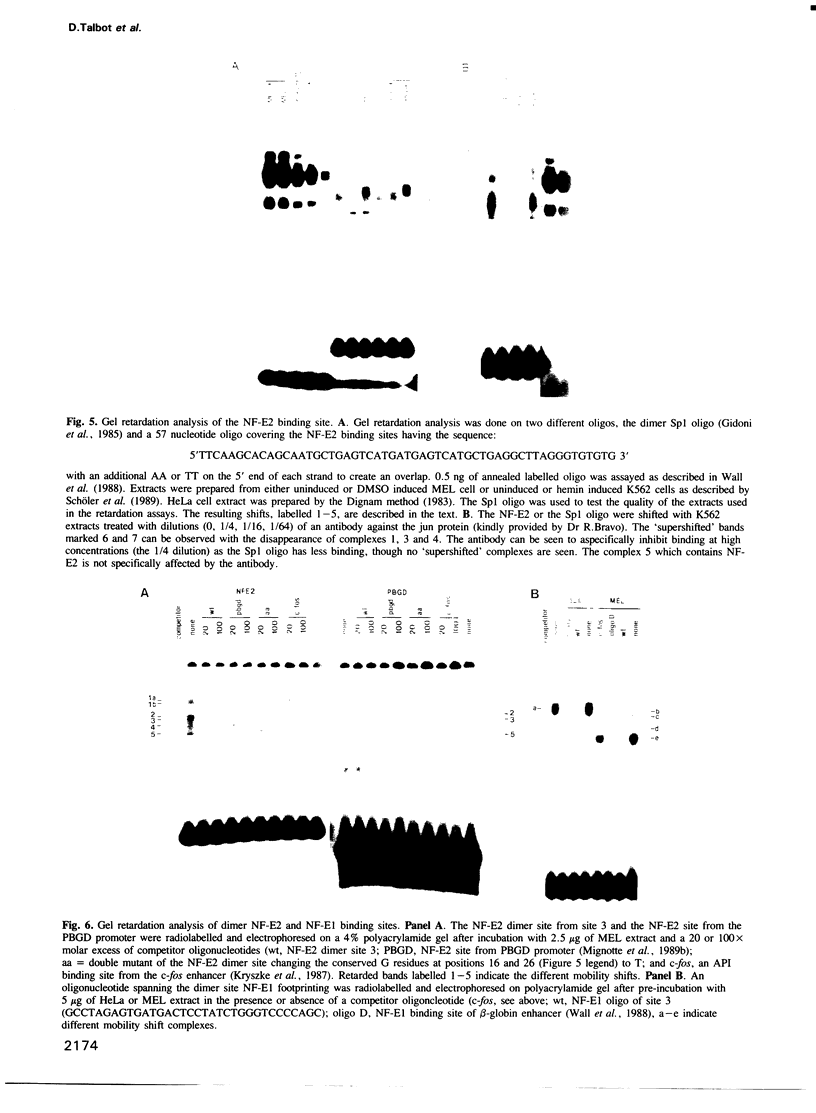
Four DNase I hypersensitive sites characterize the human beta-globin Dominant Control Region (DCR) providing position independent, high levels of erythroid specific expression to linked homologous and heterologous genes when introduced into cultured cells or in transgenic mice. We have delineated the hypersensitive site located 10.5 kbp upstream of the epsilon-globin gene by short range DNase I sensitivity mapping to a 600 bp region. Using transgenic mice and MEL cells the functional part of this region was further mapped to a 300 bp central core, which provides position independent, high level expression. It contains a number of ubiquitous and erythroid specific protein binding sites, including the previously described factors NF-E1 (GF1) and NF-E2. The latter binds to a dimer of the consensus binding sequence for jun/fos. The presence of this sequence is required for the function of the element, but single or multimerized copies of this site failed to give position independent, high levels of expression in transgenic mice or MEL cells. We therefore conclude that a combination of factor binding sites is necessary to allow site 3 to function as a strong transcriptional activator, resulting in position independent expression of the beta-globin gene.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antoniou M., deBoer E., Habets G., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene contains multiple regulatory regions: identification of one promoter and two downstream enhancers. EMBO J. 1988 Feb;7(2):377–384. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg P. E., Williams D. M., Qian R. L., Cohen R. B., Cao S. X., Mittelman M., Schechter A. N. A common protein binds to two silencers 5' to the human beta-globin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 11;17(21):8833–8852. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.21.8833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blom van Assendelft G., Hanscombe O., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. The beta-globin dominant control region activates homologous and heterologous promoters in a tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):969–977. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90630-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bösze Z., Thiesen H. J., Charnay P. A transcriptional enhancer with specificity for erythroid cells is located in the long terminal repeat of the Friend murine leukemia virus. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1615–1623. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04404.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen D. R., Curran T. fra-1: a serum-inducible, cellular immediate-early gene that encodes a fos-related antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2063–2069. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins F. S., Weissman S. M. The molecular genetics of human hemoglobin. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1984;31:315–462. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60382-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtin P. T., Liu D. P., Liu W., Chang J. C., Kan Y. W. Human beta-globin gene expression in transgenic mice is enhanced by a distant DNase I hypersensitive site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7082–7086. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Novak U., Gelinas R., Groudine M. Molecular analysis of the human beta-globin locus activation region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5439–5443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forrester W. C., Takegawa S., Papayannopoulou T., Stamatoyannopoulos G., Groudine M. Evidence for a locus activation region: the formation of developmentally stable hypersensitive sites in globin-expressing hybrids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 23;15(24):10159–10177. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.24.10159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerster T., Matthias P., Thali M., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Cell type-specificity elements of the immunoglobulin heavy chain gene enhancer. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1323–1330. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Kadonaga J. T., Barrera-Saldaña H., Takahashi K., Chambon P., Tjian R. Bidirectional SV40 transcription mediated by tandem Sp1 binding interactions. Science. 1985 Nov 1;230(4725):511–517. doi: 10.1126/science.2996137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmour R. S., Spandidos D. A., Vass J. K., Gow J. W., Paul J. A negative regulatory sequence near the mouse beta-maj globin gene associated with a region of potential Z-DNA. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1263–1272. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F., van Assendelft G. B., Greaves D. R., Kollias G. Position-independent, high-level expression of the human beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90584-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gustafson T. A., Kedes L. Identification of multiple proteins that interact with functional regions of the human cardiac alpha-actin promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3269–3283. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirai S., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Both Jun and Fos contribute to transcription activation by the heterodimer. Oncogene. 1990 Jan;5(1):39–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kollias G., Wrighton N., Hurst J., Grosveld F. Regulated expression of human A gamma-, beta-, and hybrid gamma beta-globin genes in transgenic mice: manipulation of the developmental expression patterns. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):89–94. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90862-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kryszke M. H., Piette J., Yaniv M. Induction of a factor that binds to the polyoma virus A enhancer on differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Nature. 1987 Jul 16;328(6127):254–256. doi: 10.1038/328254a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magram J., Chada K., Costantini F. Developmental regulation of a cloned adult beta-globin gene in transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):338–340. doi: 10.1038/315338a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
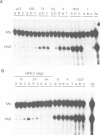
- Mignotte V., Eleouet J. F., Raich N., Romeo P. H. Cis- and trans-acting elements involved in the regulation of the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6548–6552. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mignotte V., Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F., Romeo P. H. Two tissue-specific factors bind the erythroid promoter of the human porphobilinogen deaminase gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):37–54. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philipsen S., Talbot D., Fraser P., Grosveld F. The beta-globin dominant control region: hypersensitive site 2. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2159–2167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. Mutational analysis of the chicken beta-globin enhancer reveals two positive-acting domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6267–6271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohdewohld H., Weiher H., Reik W., Jaenisch R., Breindl M. Retrovirus integration and chromatin structure: Moloney murine leukemia proviral integration sites map near DNase I-hypersensitive sites. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):336–343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.336-343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryan T. M., Behringer R. R., Townes T. M., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. High-level erythroid expression of human alpha-globin genes in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):37–41. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.37. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talbot D., Collis P., Antoniou M., Vidal M., Grosveld F., Greaves D. R. A dominant control region from the human beta-globin locus conferring integration site-independent gene expression. Nature. 1989 Mar 23;338(6213):352–355. doi: 10.1038/338352a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Townes T. M., Lingrel J. B., Chen H. Y., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. Erythroid-specific expression of human beta-globin genes in transgenic mice. EMBO J. 1985 Jul;4(7):1715–1723. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03841.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D. Y., Solomon W. B., London I. M., Lee D. P. An erythroid-specific, developmental-stage-independent enhancer far upstream of the human "beta-like globin" genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2554–2558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuan D., Solomon W., Li Q., London I. M. The "beta-like-globin" gene domain in human erythroid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6384–6388. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deBoer E., Antoniou M., Mignotte V., Wall L., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin promoter; nuclear protein factors and erythroid specific induction of transcription. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4203–4212. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03317.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]