Abstract
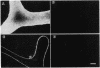
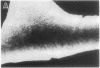
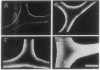
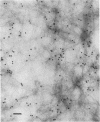
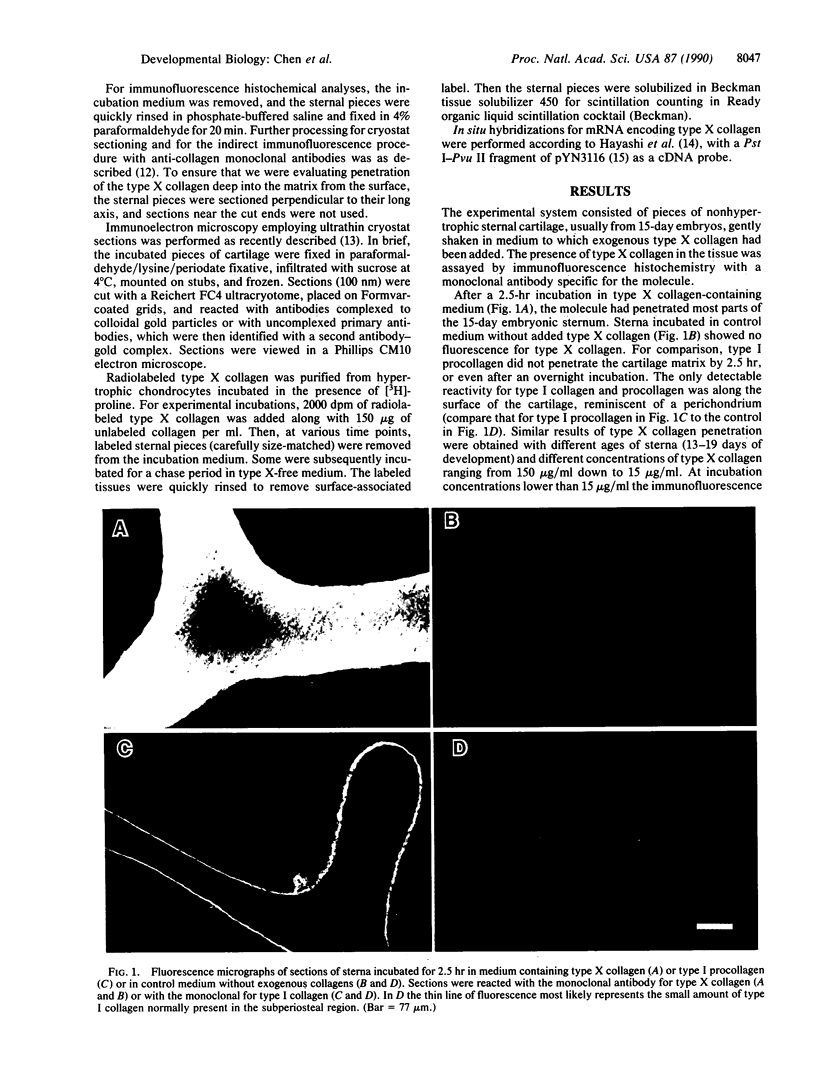
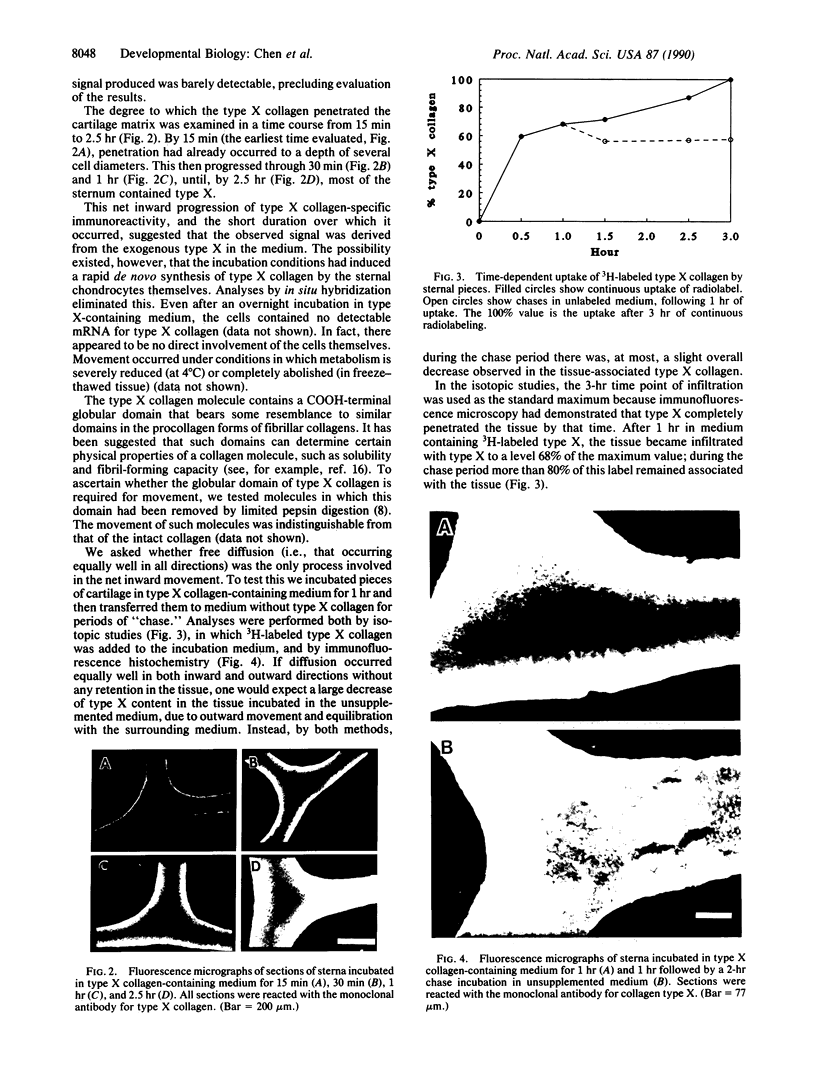
A recent immunoelectron microscopic study of type X collagen in developing cartilage gave results that could be explained by movement of the molecule from one region of the cartilage matrix to another, there becoming associated with preexisting collagen fibrils. In the present study, to test the feasibility of this model we incubated pieces of nonhypertrophic, embryonic chicken sternal cartilage (which has no endogenous type X collagen) in medium with type X collagen and then used immunofluorescence and immunoelectron microscopy to evaluate movement of the molecule through the matrix. The results show that type X collagen molecules can indeed pass through embryonic sternal cartilage matrix and subsequently become fibril-associated.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Comper W. D., Laurent T. C. Physiological function of connective tissue polysaccharides. Physiol Rev. 1978 Jan;58(1):255–315. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1978.58.1.255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumming G. J., Handley C. J., Preston B. N. Permeability of composite chondrocyte-culture-millipore membranes to solutes of varying size and shape. Biochem J. 1979 Aug 1;181(2):257–266. doi: 10.1042/bj1810257a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch J. M., Birk D. E., Linsenmayer C., Linsenmayer T. F. The spatial organization of Descemet's membrane-associated type IV collagen in the avian cornea. J Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;110(4):1457–1468. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.4.1457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fitch J. M., Gibney E., Sanderson R. D., Mayne R., Linsenmayer T. F. Domain and basement membrane specificity of a monoclonal antibody against chicken type IV collagen. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):641–647. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi M., Ninomiya Y., Parsons J., Hayashi K., Olsen B. R., Trelstad R. L. Differential localization of mRNAs of collagen types I and II in chick fibroblasts, chondrocytes, and corneal cells by in situ hybridization using cDNA probes. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;102(6):2302–2309. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.6.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Gibney E., Fitch J. M. Embryonic avian cornea contains layers of collagen with greater than average stability. J Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;103(4):1587–1593. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.4.1587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linsenmayer T. F., Gibney E., Schmid T. M. Segmental appearance of type X collagen in the developing avian notochord. Dev Biol. 1986 Feb;113(2):467–473. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90182-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A. Distribution and diffusion of solutes in articular cartilage. Biophys J. 1970 May;10(5):365–379. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(70)86307-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maroudas A. Transport of solutes through cartilage: permeability to large molecules. J Anat. 1976 Nov;122(Pt 2):335–347. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninomiya Y., Gordon M., van der Rest M., Schmid T., Linsenmayer T., Olsen B. R. The developmentally regulated type X collagen gene contains a long open reading frame without introns. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5041–5050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole A. R., Pidoux I. Immunoelectron microscopic studies of type X collagen in endochondral ossification. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2547–2554. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Linsenmayer T. F. A short chain (pro)collagen from aged endochondral chondrocytes. Biochemical characterization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 10;258(15):9504–9509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Linsenmayer T. F. Immunoelectron microscopy of type X collagen: supramolecular forms within embryonic chick cartilage. Dev Biol. 1990 Mar;138(1):53–62. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(90)90176-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Linsenmayer T. F. Immunohistochemical localization of short chain cartilage collagen (type X) in avian tissues. J Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;100(2):598–605. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.2.598. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid T. M., Mayne R., Jeffrey J. J., Linsenmayer T. F. Type X collagen contains two cleavage sites for a vertebrate collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 25;261(9):4184–4189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]