Abstract
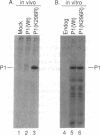
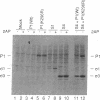
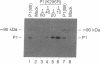
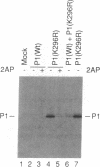
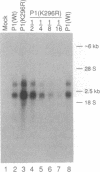
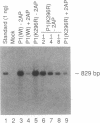
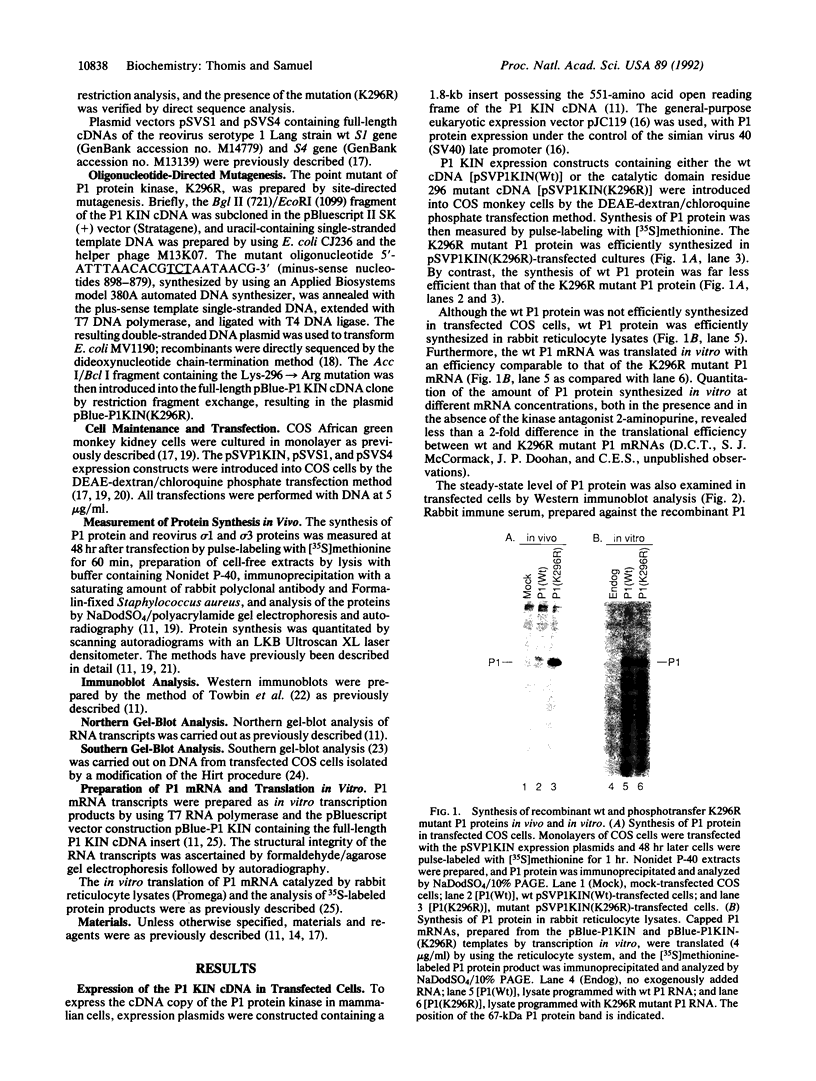
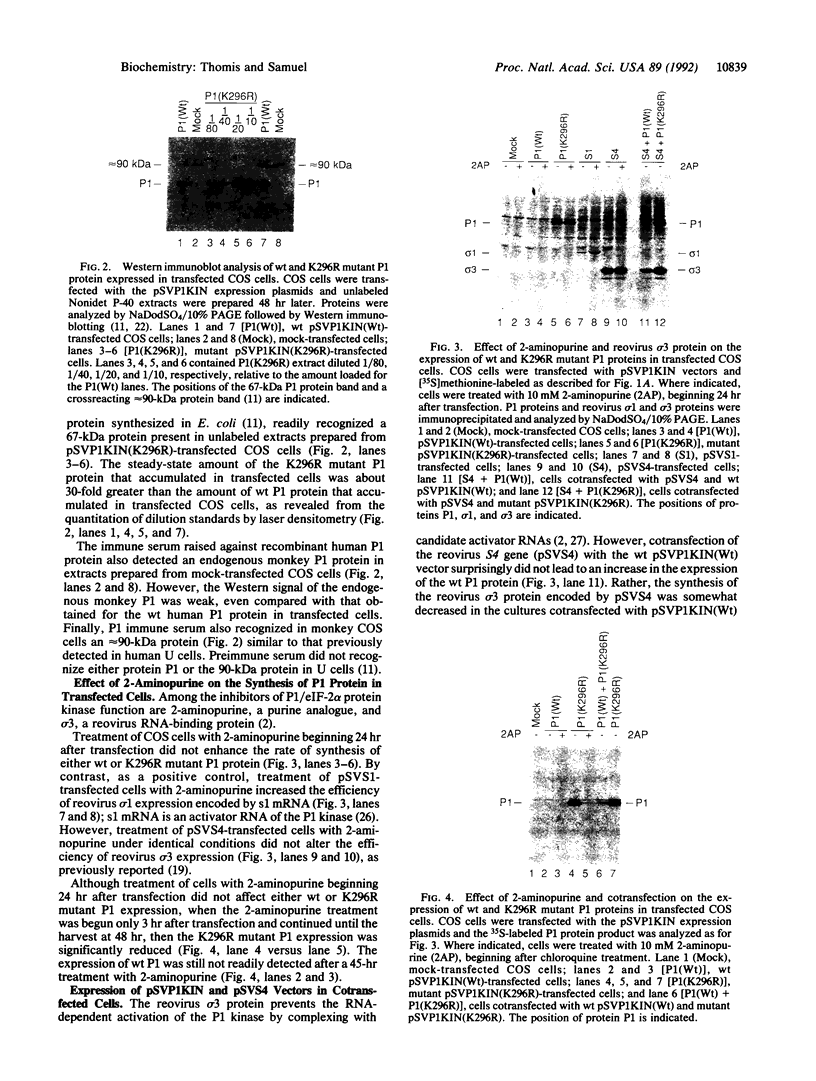
The expression of a molecular cDNA clone (P1 KIN) of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase (PKR) was examined in transfected monkey cells and in cell-free protein-synthesizing systems. Expression of the wild-type (wt) P1 KIN cDNA, which encodes an active protein kinase, was compared with that of the phosphotransfer catalytic domain II Lys-296-->Arg (K296R) mutant cDNA, which does not encode an active kinase. wt and K296R mutant P1 mRNAs prepared by transcription in vitro with T7 RNA polymerase programmed the cell-free synthesis of P1 ribosome-associated protein with comparable efficiency in the rabbit reticulocyte system. The K296R mutant P1 protein was also efficiently synthesized in vivo in transfected COS monkey cells. However, synthesis of the wt P1 protein was reduced about 30-fold in transfected COS cells as compared with the K296R mutant P1 protein. Cotransfection of wt P1 KIN cDNA with either K296R mutant P1 KIN cDNA or reovirus S4 cDNA greatly reduced the synthesis of K296R mutant P1 protein and reovirus sigma 3 protein, respectively. Although the wt and K296R mutant P1 KIN plasmid expression vectors replicated with comparable efficiencies in COS cells, the steady-state amount of P1 mRNA was about 3-fold less in COS cells transfected with the wt as compared with the K296R mutant P1 KIN cDNA. These results suggest that RNA-dependent P1 protein kinase expression is autoregulated in vivo in transfected mammalian cells primarily at the level of translation by a mechanism that is likely dependent upon catalytically active P1 kinase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atwater J. A., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. Efficiency of expression of cDNAs of the reovirus S1 and S4 genes in transfected animal cells differs at the level of translation. Virology. 1987 Aug;159(2):350–357. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90473-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Knutson G. S., Lasky S. R., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Purification and substrate specificities of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from untreated and interferon-treated mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11240–11247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Furtado M. R., Thimmappaya B. Efficient expression of small RNA polymerase III genes from a novel simian virus 40 vector and their effect on viral gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):1159–1176. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Activation of the human P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by individual reovirus s-class mRNAs: s1 mRNA is a potent activator relative to s4 mRNA. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies M. V., Elroy-Stein O., Jagus R., Moss B., Kaufman R. J. The vaccinia virus K3L gene product potentiates translation by inhibiting double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase and phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2. J Virol. 1992 Apr;66(4):1943–1950. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.4.1943-1950.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of mRNA binding to ribosomes by localized activation of dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):79–81. doi: 10.1038/311079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doohan J. P., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides: ribosome pausing during the translation of reovirus S1 mRNA. Virology. 1992 Feb;186(2):409–425. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90006-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George C. X., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Expression of reovirus S3 gene in transfected COS cells and subsequent inhibition at the level of protein synthesis by type I but not by type II interferon. Virology. 1988 Oct;166(2):573–582. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90528-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Garfinkel M., Meurs E., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G., Barber G. N. Functional expression and RNA binding analysis of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated, 68,000-Mr protein kinase in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5497–5505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Davies M. V., Pathak V. K., Hershey J. W. The phosphorylation state of eucaryotic initiation factor 2 alters translational efficiency of specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;9(3):946–958. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.3.946. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr S. M., Smith G. L. Vaccinia virus DNA ligase is nonessential for virus replication: recovery of plasmids from virus-infected cells. Virology. 1991 Feb;180(2):625–632. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90076-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust B., Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Further characterization of the protein kinase activity mediated by interferon in mouse and human cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8494–8498. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky S. R., Jacobs B. L., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Characterization of sites of phosphorylation in the interferon-induced phosphoprotein P1 from mouse fibroblasts: evidence for two forms of P1. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11087–11093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luthman H., Magnusson G. High efficiency polyoma DNA transfection of chloroquine treated cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1295–1308. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack S. J., Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: identification of a RNA binding domain within the N-terminal region of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Chong K., Galabru J., Thomas N. S., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides: effect of point mutation of the sequences flanking the 5'-proximal AUG initiator codons of the reovirus S1 and S4 genes on the efficiency of mRNA translation. Virology. 1988 Apr;163(2):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90309-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. C., Sen G. C. Identification of the double-stranded RNA-binding domain of the human interferon-inducible protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7671–7676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pathak V. K., Schindler D., Hershey J. W. Generation of a mutant form of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 lacking the site of phosphorylation by eIF-2 kinases. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):993–995. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Stark G. R., Alwine J. C. Autoregulation of simian virus 40 gene A by T antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3083–3087. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahni G., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Expression of vesicular stomatitis virus G gene in transfected COS cells is inhibited by interferon at the level of protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16764–16768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E., Brody M. S. Biosynthesis of reovirus-specified polypeptides. 2-aminopurine increases the efficiency of translation of reovirus s1 mRNA but not s4 mRNA in transfected cells. Virology. 1990 May;176(1):106–113. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(90)90235-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: phosphorylation of protein synthesis initiation factor eIF-2 in interferon-treated human cells by a ribosome-associated kinase processing site specificity similar to hemin-regulated rabbit reticulocyte kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):600–604. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.600. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Mechanisms of the antiviral action of interferons. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1988;35:27–72. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60609-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seliger L. S., Giantini M., Shatkin A. J. Translational effects and sequence comparisons of the three serotypes of the reovirus S4 gene. Virology. 1992 Mar;187(1):202–210. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90308-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theil E. C. Ferritin: structure, gene regulation, and cellular function in animals, plants, and microorganisms. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:289–315. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001445. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomis D. C., Doohan J. P., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: cDNA structure, expression, and regulation of the interferon-induced, RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase from human cells. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90732-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang X. Z., Ooi B. G., Miller L. K. Baculovirus vectors for multiple gene expression and for occluded virus production. Gene. 1991 Apr;100:131–137. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90358-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]