Abstract
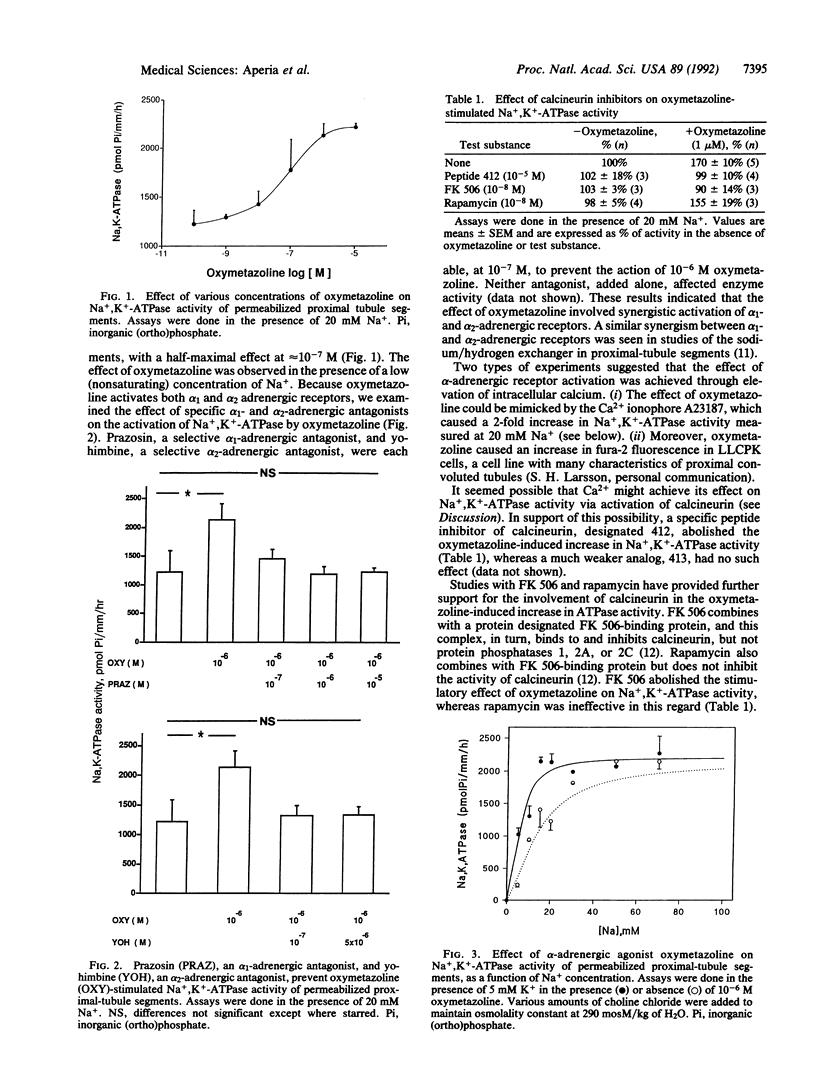
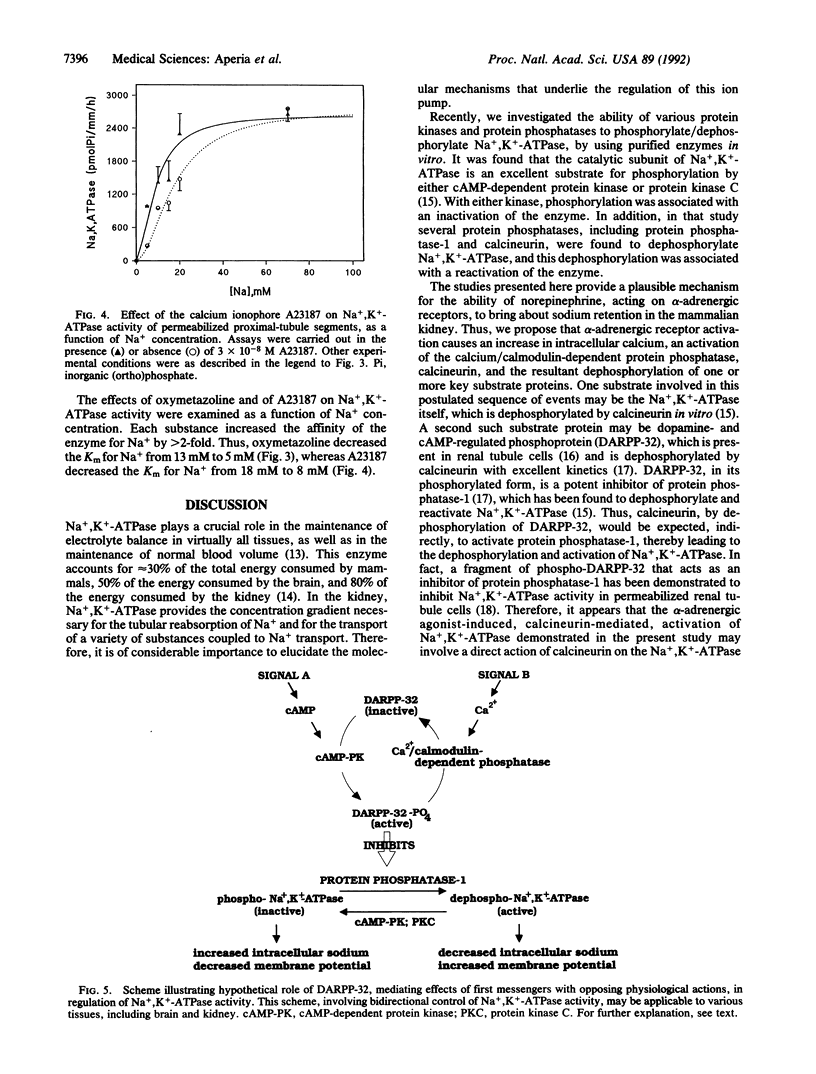
The alpha-adrenergic agonist oxymetazoline increased Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity of single proximal convoluted tubules dissected from rat kidney. Activation of the enzyme by oxymetazoline was prevented by either the alpha 1-adrenergic antagonist prazosin or the alpha 2-adrenergic antagonist yohimbine and was mimicked by the calcium ionophore A23187. The effect of oxymetazoline on Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity was prevented by a specific peptide inhibitor of calcineurin, as well as by FK 506, an immunosuppressant agent known to inhibit calcineurin; these results indicate that the action of oxymetazoline is mediated via activation of calcineurin (a calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase). Activation of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase by either oxymetazoline or A23187 was associated with a greater than 2-fold increase in its affinity for Na+. The results provide a biochemical mechanism by which norepinephrine, released from renal nerve terminals, stimulates Na+ retention.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aperia A., Fryckstedt J., Svensson L., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylated Mr 32,000 dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein inhibits Na+,K(+)-ATPase activity in renal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Apr 1;88(7):2798–2801. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.7.2798. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A. M., Aperia A., Walaas S. I., Nairn A. C., Greengard P. Phosphorylation of the catalytic subunit of Na+,K(+)-ATPase inhibits the activity of the enzyme. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11359–11362. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A. M., Hopfield J. F., Aperia A., Greengard P. Inhibition by dopamine of (Na(+)+K+)ATPase activity in neostriatal neurons through D1 and D2 dopamine receptor synergism. Nature. 1990 Sep 27;347(6291):386–388. doi: 10.1038/347386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertorello A., Aperia A. Inhibition of proximal tubule Na(+)-K(+)-ATPase activity requires simultaneous activation of DA1 and DA2 receptors. Am J Physiol. 1990 Dec;259(6 Pt 2):F924–F928. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1990.259.6.F924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal D. K., Takio K., Hansen R. S., Krebs E. G. Dephosphorylation of cAMP-dependent protein kinase regulatory subunit (type II) by calmodulin-dependent protein phosphatase. Determinants of substrate specificity. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 25;261(18):8140–8145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan Y. L. The role of norepinephrine in the regulation of fluid absorption in the rat proximal tubule. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1980 Oct;215(1):65–70. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clausen T., Van Hardeveld C., Everts M. E. Significance of cation transport in control of energy metabolism and thermogenesis. Physiol Rev. 1991 Jul;71(3):733–774. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1991.71.3.733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen H. T., Katz A. I. Adrenergic receptors and catecholamine effects on sodium transport in the mammalian nephron. Semin Nephrol. 1991 Mar;11(2):110–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gesek F. A., Cragoe E. J., Jr, Strandhoy J. W. Synergistic alpha-1 and alpha-2 adrenergic stimulation of rat proximal nephron Na+/H+ exchange. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1989 Jun;249(3):694–700. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halpain S., Girault J. A., Greengard P. Activation of NMDA receptors induces dephosphorylation of DARPP-32 in rat striatal slices. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):369–372. doi: 10.1038/343369a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han C., Abel P. W., Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenoceptor subtypes linked to different mechanisms for increasing intracellular Ca2+ in smooth muscle. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):333–335. doi: 10.1038/329333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hashimoto Y., Perrino B. A., Soderling T. R. Identification of an autoinhibitory domain in calcineurin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1924–1927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmings H. C., Jr, Greengard P., Tung H. Y., Cohen P. DARPP-32, a dopamine-regulated neuronal phosphoprotein, is a potent inhibitor of protein phosphatase-1. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):503–505. doi: 10.1038/310503a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hubbard M. J., Klee C. B. Functional domain structure of calcineurin A: mapping by limited proteolysis. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 21;28(4):1868–1874. doi: 10.1021/bi00430a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingebritsen T. S., Cohen P. Protein phosphatases: properties and role in cellular regulation. Science. 1983 Jul 22;221(4608):331–338. doi: 10.1126/science.6306765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klee C. B., Krinks M. H., Manalan A. S., Cohen P., Stewart A. A. Isolation and characterization of bovine brain calcineurin: a calmodulin-stimulated protein phosphatase. Methods Enzymol. 1983;102:227–244. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)02024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Farmer J. D., Jr, Lane W. S., Friedman J., Weissman I., Schreiber S. L. Calcineurin is a common target of cyclophilin-cyclosporin A and FKBP-FK506 complexes. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):807–815. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90124-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meister B., Fryckstedt J., Schalling M., Cortés R., Hökfelt T., Aperia A., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Nairn A. C., Ehrlich M., Greengard P. Dopamine- and cAMP-regulated phosphoprotein (DARPP-32) and dopamine DA1 agonist-sensitive Na+,K+-ATPase in renal tubule cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):8068–8072. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.8068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. C., Brodde O. E., Insel P. A. Peripheral adrenergic receptors in hypertension. Hypertension. 1990 Aug;16(2):107–120. doi: 10.1161/01.hyp.16.2.107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minneman K. P. Alpha 1-adrenergic receptor subtypes, inositol phosphates, and sources of cell Ca2+. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Jun;40(2):87–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyjan A. W., Ceña V., Klein D. C., Levenson R. Differential expression and enzymatic properties of the Na+,K(+)-ATPase alpha 3 isoenzyme in rat pineal glands. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1178–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skou J. C. The Na,K-pump. Methods Enzymol. 1988;156:1–25. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(88)56004-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


