Abstract
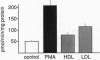
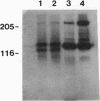
Low density lipoproteins (LDL) and high density lipoproteins (HDL) from serum stimulate signal-transduction pathways and exocytosis in rat alveolar type II cells. Both LDL and HDL stimulated primary cultures of type II cells to secrete phosphatidylcholine (PtdCho), the major phospholipid component of pulmonary surfactant. The effects on secretion were preceded temporally by stimulation of inositol phospholipid catabolism, calcium mobilization, and translocation of protein kinase C from cytosolic to membrane compartments. Heparin, which blocks the binding of ligands to the LDL receptor, completely inhibited the effects of LDL on signal transduction and PtdCho secretion but did not inhibit the effects of HDL. Unilamellar PtdCho liposomes the size of native LDL had no effect on type II cells; however, PtdCho complexes containing either apolipoproteins E or A-I stimulated both signal transduction and PtdCho secretion. LDL receptors were present in type II cell membranes by immunoblotting. In contrast to findings with hepatic membranes, type II cells exhibited two major bands of 130 kDa and 120 kDa and a minor band at 230 kDa that also was present under reducing conditions. These results are consistent with our hypothesis that the LDL-receptor pathway functions in vivo to deliver cholesterol to type II cells and that this process is coupled to surfactant assembly and secretion via signal-transduction pathway(s). HDL elicits similar responses independent of the LDL receptor, suggesting that type II cells may use the selective uptake pathway to obtain cholesterol or that HDL triggers signal transduction by mechanisms unrelated to lipid delivery.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J., Dawson R. M., Downes C. P., Heslop J. P., Irvine R. F. Changes in the levels of inositol phosphates after agonist-dependent hydrolysis of membrane phosphoinositides. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):473–482. doi: 10.1042/bj2120473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Block L. H., Knorr M., Vogt E., Locher R., Vetter W., Groscurth P., Qiao B. Y., Pometta D., James R., Regenass M. Low density lipoprotein causes general cellular activation with increased phosphatidylinositol turnover and lipoprotein catabolism. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):885–889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bochkov V. N., Voino-Yasenetskaya T. A., Tkachuk V. A. Epinephrine potentiates activation of human platelets by low density lipoproteins. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Sep 23;1097(2):123–127. doi: 10.1016/0925-4439(91)90095-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):34–47. doi: 10.1126/science.3513311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Gonzalez R. F., Marinari L. A., Mescher E. J., Hawgood S. The role of calcium in the secretion of surfactant by rat alveolar type II cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jun 27;877(2):305–313. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(86)90308-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Gonzalez R., Williams M. C. An improved method for isolating type II cells in high yield and purity. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1986 Jul;134(1):141–145. doi: 10.1164/arrd.1986.134.1.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs L. G., Mason R. J. Pulmonary alveolar type II cells isolated from rats. Release of phosphatidylcholine in response to beta-adrenergic stimulation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Mar;63(3):378–387. doi: 10.1172/JCI109313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorn C. C., Rice W. R., Singleton F. M. Calcium mobilization and response recovery following P2-purinoceptor stimulation of rat isolated alveolar type II cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1989 May;97(1):163–170. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1989.tb11938.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson S. K., Lear S. R., Barker M. E., Musliner T. A. Regulation of cholesterol metabolism in the ethionine-induced premalignant rat liver. J Lipid Res. 1990 May;31(5):933–945. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleisher L. N., Tall A. R., Witte L. D., Miller R. W., Cannon P. J. Stimulation of arterial endothelial cell prostacyclin synthesis by high density lipoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):6653–6655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilfillan A. M., Rooney S. A. Purinoceptor agonists stimulate phosphatidylcholine secretion in primary cultures of adult rat type II pneumocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jan 13;917(1):18–23. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(87)90278-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glass C., Pittman R. C., Civen M., Steinberg D. Uptake of high-density lipoprotein-associated apoprotein A-I and cholesterol esters by 16 tissues of the rat in vivo and by adrenal cells and hepatocytes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):744–750. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAVEL R. J., EDER H. A., BRAGDON J. H. The distribution and chemical composition of ultracentrifugally separated lipoproteins in human serum. J Clin Invest. 1955 Sep;34(9):1345–1353. doi: 10.1172/JCI103182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamilton R. L., Jr, Goerke J., Guo L. S., Williams M. C., Havel R. J. Unilamellar liposomes made with the French pressure cell: a simple preparative and semiquantitative technique. J Lipid Res. 1980 Nov;21(8):981–992. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass M. A., Longmore W. J. Regulation of lung surfactant cholesterol metabolism by serum lipopoteins. Lipids. 1980 Jun;15(6):401–406. doi: 10.1007/BF02534063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hass M. A., Longmore W. J. Surfactant cholesterol metabolism of the isolated perfused rat lung. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Apr 27;573(1):166–174. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(79)90183-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunt R. C., Dewey A., Davis A. A. Transferrin receptors on the surfaces of retinal pigment epithelial cells are associated with the cytoskeleton. J Cell Sci. 1989 Apr;92(Pt 4):655–666. doi: 10.1242/jcs.92.4.655. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J., Clements J. A. Surface active materials from dog lung. II. Composition and physiological correlations. Am J Physiol. 1972 Sep;223(3):715–726. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1972.223.3.715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King R. J. The surfactant system of the lung. Fed Proc. 1974 Nov;33(11):2238–2247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. X., Stifani S., Schneider W. J., Poznansky M. J. Low density lipoprotein receptors on epithelial cell (Madin-Darby canine kidney) monolayers. Asymmetric distribution correlates with functional difference. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):9263–9270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendez A. J., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Protein kinase C as a mediator of high density lipoprotein receptor-dependent efflux of intracellular cholesterol. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jun 5;266(16):10104–10111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oram J. F., Johnson C. J., Brown T. A. Interaction of high density lipoprotein with its receptor on cultured fibroblasts and macrophages. Evidence for reversible binding at the cell surface without internalization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Feb 15;262(5):2405–2410. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pian M. S., Dobbs L. G., Düzgünes N. Positive correlation between cytosolic free calcium and surfactant secretion in cultured rat alveolar type II cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 2;960(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitas R. E., Innerarity T. L., Mahley R. W. Cell surface receptor binding of phospholipid . protein complexes containing different ratios of receptor-active and -inactive E apoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):5454–5460. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pomerantz K. B., Tall A. R., Feinmark S. J., Cannon P. J. Stimulation of vascular smooth muscle cell prostacyclin and prostaglandin E2 synthesis by plasma high and low density lipoproteins. Circ Res. 1984 May;54(5):554–565. doi: 10.1161/01.res.54.5.554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice W. R., Singleton F. M. P2-purinoceptors regulate surfactant secretion from rat isolated alveolar type II cells. Br J Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;89(3):485–491. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1986.tb11148.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruoslahti E., Hayman E. G., Pierschbacher M., Engvall E. Fibronectin: purification, immunochemical properties, and biological activities. Methods Enzymol. 1982;82(Pt A):803–831. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)82103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Effect of secretagogues on cytoplasmic free calcium in alveolar type II epithelial cells. Am J Physiol. 1987 Nov;253(5 Pt 1):C679–C686. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1987.253.5.C679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Voelker D. R., Mason R. J. Involvement of protein kinase C in pulmonary surfactant secretion from alveolar type II cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12725–12729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott-Burden T., Resink T. J., Hahn A. W., Baur U., Box R. J., Bühler F. R. Induction of growth-related metabolism in human vascular smooth muscle cells by low density lipoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12582–12589. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shariff A., Luna E. J. Diacylglycerol-stimulated formation of actin nucleation sites at plasma membranes. Science. 1992 Apr 10;256(5054):245–247. doi: 10.1126/science.1373523. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slotte J. P., Oram J. F., Bierman E. L. Binding of high density lipoproteins to cell receptors promotes translocation of cholesterol from intracellular membranes to the cell surface. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):12904–12907. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smirnov V. N., Voyno-Yasenetskaya T. A., Antonov A. S., Lukashev M. E., Shirinsky V. P., Tertov V. V., Tkachuk V. A. Vascular signal transduction and atherosclerosis. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1990;598:167–181. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1990.tb42288.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spady D. K., Turley S. D., Dietschy J. M. Receptor-independent low density lipoprotein transport in the rat in vivo. Quantitation, characterization, and metabolic consequences. J Clin Invest. 1985 Sep;76(3):1113–1122. doi: 10.1172/JCI112066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tall A. R. Plasma high density lipoproteins. Metabolism and relationship to atherogenesis. J Clin Invest. 1990 Aug;86(2):379–384. doi: 10.1172/JCI114722. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tauber J. P., Cheng J., Gospodarowicz D. Effect of high and low density lipoproteins on proliferation of cultured bovine vascular endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 1980 Oct;66(4):696–708. doi: 10.1172/JCI109907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsilibary E. C., Williams M. C. Actin and secretion of surfactant. J Histochem Cytochem. 1983 Nov;31(11):1298–1304. doi: 10.1177/31.11.6688627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turley S. D., Andersen J. M., Dietschy J. M. Rates of sterol synthesis and uptake in the major organs of the rat in vivo. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):551–569. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voyno-Yasenetskaya T. A., Dobbs L. G., Williams M. C. Regulation of ATP-dependent surfactant secretion and activation of second-messenger systems in alveolar type II cells. Am J Physiol. 1991 Oct;261(4 Suppl):105–109. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1991.261.4.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirtz H. R., Dobbs L. G. Calcium mobilization and exocytosis after one mechanical stretch of lung epithelial cells. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1266–1269. doi: 10.1126/science.2173861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wosu L., Parisella R., Kalant N. Effect of low density lipoprotein on glycosaminoglycan secretion by cultured human smooth muscle cells and fibroblasts. Influence of serum concentration and cell proliferation rate. Atherosclerosis. 1983 Sep;48(3):205–220. doi: 10.1016/0021-9150(83)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]