Abstract
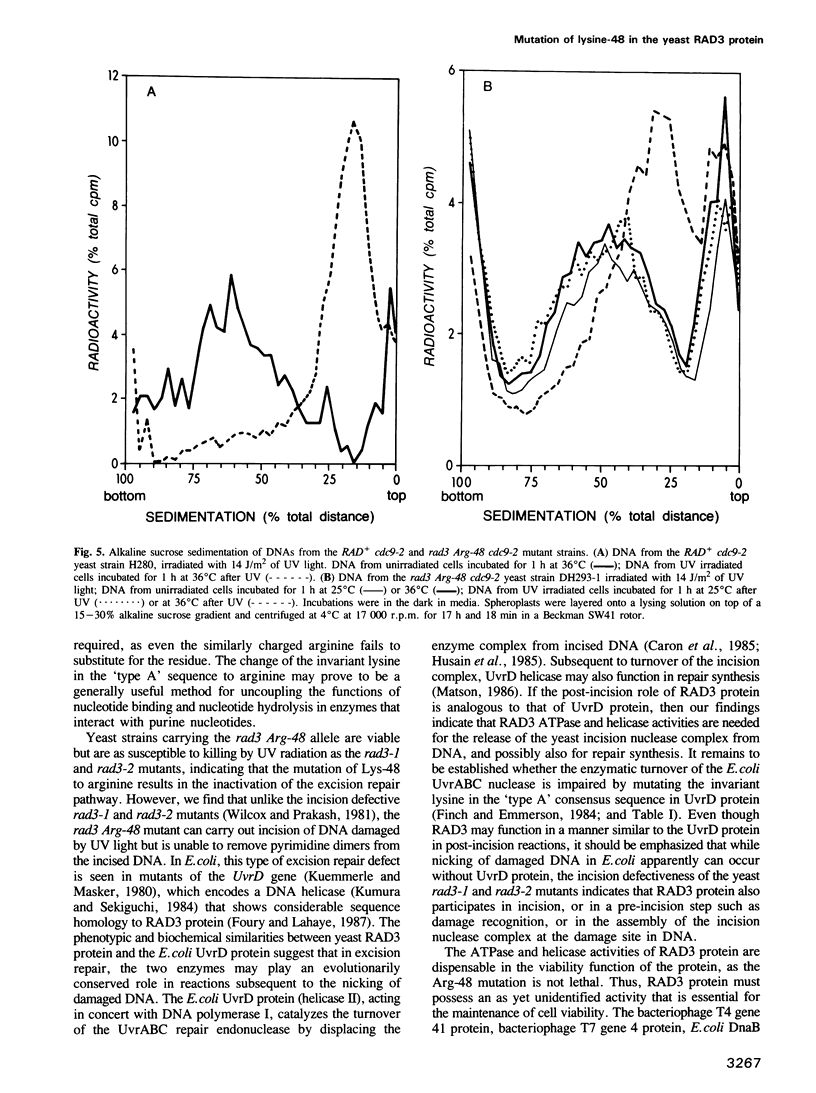
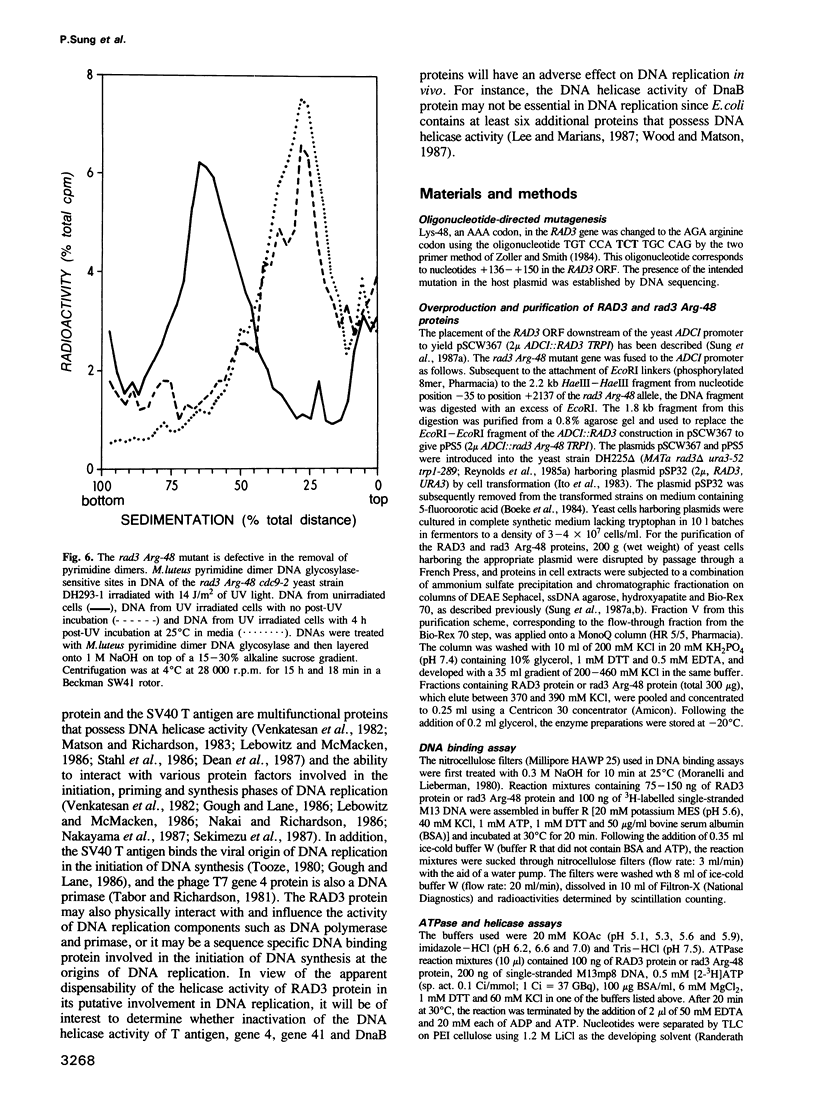
The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for excision repair of DNA damaged by UV radiation and is also essential for cell viability. The approximately 89 kd protein encoded by RAD3 possesses single-stranded DNA dependent ATPase and DNA helicase activities. The sequence Gly-X-Gly-Lys-Thr, believed to be involved in the interaction with purine nucleotides in proteins that bind and hydrolyze the nucleotides, is present in the RAD3 primary structure between amino acids 45 and 49. We report here that the point mutation of Lys-48 to arginine abolishes the RAD3 ATPase and DNA helicase activities but not the ability to bind ATP. These observations highlight the involvement of this lysine residue in the hydrolysis of ATP and indicate that the positive charge on arginine can replace that of the lysine residue in the binding of ATP but not in its hydrolysis. The rad3 Arg-48 mutant is apparently defective in a step subsequent to incision at the damage site in DNA; it can incise UV damaged DNA, but does not remove pyrimidine dimers. The role of the ATPase and DNA helicase activities of the RAD3 protein in its DNA repair and viability functions is discussed.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boeke J. D., LaCroute F., Fink G. R. A positive selection for mutants lacking orotidine-5'-phosphate decarboxylase activity in yeast: 5-fluoro-orotic acid resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):345–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00330984. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caron P. R., Kushner S. R., Grossman L. Involvement of helicase II (uvrD gene product) and DNA polymerase I in excision mediated by the uvrABC protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4925–4929. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dean F. B., Bullock P., Murakami Y., Wobbe C. R., Weissbach L., Hurwitz J. Simian virus 40 (SV40) DNA replication: SV40 large T antigen unwinds DNA containing the SV40 origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):16–20. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.16. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Emmerson P. T. The nucleotide sequence of the uvrD gene of E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5789–5799. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finch P. W., Storey A., Chapman K. E., Brown K., Hickson I. D., Emmerson P. T. Complete nucleotide sequence of the Escherichia coli recB gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8573–8582. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foury F., Lahaye A. Cloning and sequencing of the PIF gene involved in repair and recombination of yeast mitochondrial DNA. EMBO J. 1987 May;6(5):1441–1449. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02385.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fry D. C., Kuby S. A., Mildvan A. S. ATP-binding site of adenylate kinase: mechanistic implications of its homology with ras-encoded p21, F1-ATPase, and other nucleotide-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):907–911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamada M., Palmieri R. H., Russell G. A., Kuby S. A. Studies of adenosine triphosphate transphosphorylases. XIV. Equilibrium binding properties of the crystalline rabbit and calf muscle ATP--AMP transphosphorylase (adenylate kinase) and derived peptide fragments. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1979 Jun;195(1):155–177. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(79)90338-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. B., Hansen F. G., von Meyenburg K. The nucleotide sequence of the dnaA gene and the first part of the dnaN gene of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7373–7385. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash S., Reynolds P., Polakowska R., Weber S., Prakash L. Isolation and characterization of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and inviability of rad3 deletion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Abdel-Monem M., Sancar A. Effect of DNA polymerase I and DNA helicase II on the turnover rate of UvrABC excision nuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(20):6774–6778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.20.6774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Sancar A. Sequences of Escherichia coli uvrA gene and protein reveal two potential ATP binding sites. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):4895–4901. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jurnak F. Structure of the GDP domain of EF-Tu and location of the amino acids homologous to ras oncogene proteins. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):32–36. doi: 10.1126/science.3898365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight K. L., McEntee K. Nucleotide binding by a 24-residue peptide from the RecA protein of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9289–9293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuemmerle N. B., Masker W. E. Effect of the uvrD mutation on excision repair. J Bacteriol. 1980 May;142(2):535–546. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.2.535-546.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumura K., Sekiguchi M. Identification of the uvrD gene product of Escherichia coli as DNA helicase II and its induction by DNA-damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1560–1565. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., McMacken R. The Escherichia coli dnaB replication protein is a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 5;261(10):4738–4748. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Marians K. J. Escherichia coli replication factor Y, a component of the primosome, can act as a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8345–8349. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madura K., Prakash S. Nucleotide sequence, transcript mapping, and regulation of the RAD2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):914–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.914-923.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W. Escherichia coli helicase II (urvD gene product) translocates unidirectionally in a 3' to 5' direction. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 5;261(22):10169–10175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matson S. W., Richardson C. C. DNA-dependent nucleoside 5'-triphosphatase activity of the gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):14009–14016. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Defective excision of pyrimidine dimers and interstrand DNA crosslinks in rad7 and rad23 mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;188(2):235–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00332681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller R. D., Prakash L., Prakash S. Genetic control of excision of Saccharomyces cerevisiae interstrand DNA cross-links induced by psoralen plus near-UV light. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;2(8):939–948. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.8.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moranelli F., Lieberman M. W. Recognition of chemical carcinogen-modified DNA by a DNA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3201–3205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai H., Richardson C. C. Interactions of the DNA polymerase and gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Protein-protein and protein-DNA interactions involved in RNA-primed DNA synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15208–15216. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Arai N., Bond M. W., Kaziro Y., Arai K. Nucleotide sequence of dnaB and the primary structure of the dnaB protein from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):97–101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Bond M. W., Miyajima A., Kobori J., Arai K. Structure of Escherichia coli dnaC. Identification of a cysteine residue possibly involved in association with dnaB protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10475–10480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Chu G., Berg P., Friedberg E. C. RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: nucleotide sequence of wild-type and mutant alleles, transcript mapping, and aspects of gene regulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):17–26. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. A DNA repair gene required for the incision of damaged DNA is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4818–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penefsky H. S. Reversible binding of Pi by beef heart mitochondrial adenosine triphosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1977 May 10;252(9):2891–2899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perozzi G., Prakash S. RAD7 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: transcripts, nucleotide sequence analysis, and functional relationship between the RAD7 and RAD23 gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1497–1507. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RANDERATH K., RANDERATH E. ION-EXCHANGE CHROMATOGRAPHY OF NUCLEOTIDES ON POLY-(ETHYLENEIMINE)-CELLULOSE THIN LAYERS. J Chromatogr. 1964 Oct;16:111–125. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)82445-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Higgins D. R., Prakash L., Prakash S. The nucleotide sequence of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: a potential adenine nucleotide binding amino acid sequence and a nonessential acidic carboxyl terminal region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Apr 11;13(7):2357–2372. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.7.2357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Prakash L., Dumais D., Perozzi G., Prakash S. Nucleotide sequence of the RAD10 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 16;4(13A):3549–3552. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04115.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P., Prakash L., Prakash S. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis of the RAD1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1012–1020. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R. J., Friedberg E. C. Molecular mechanisms of pyrimidine dimer excision in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: incision of ultraviolet-irradiated deoxyribonucleic acid in vivo. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):692–704. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.692-704.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Stachelek C., Konigsberg W., Rupp W. D. Sequences of the recA gene and protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2611–2615. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2611. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekimizu K., Bramhill D., Kornberg A. ATP activates dnaA protein in initiating replication of plasmids bearing the origin of the E. coli chromosome. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):259–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90221-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Temeles G. L., Wolanski B. S., Socher S. H., Scolnick E. M. Mutant ras-encoded proteins with altered nucleotide binding exert dominant biological effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):952–956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stahl H., Dröge P., Knippers R. DNA helicase activity of SV40 large tumor antigen. EMBO J. 1986 Aug;5(8):1939–1944. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Matson S. W., Prakash S. RAD3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8951–8955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Weber S., Prakash S. The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA-dependent ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. Template recognition sequence for RNA primer synthesis by gene 4 protein of bacteriophage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):205–209. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesan M., Silver L. L., Nossal N. G. Bacteriophage T4 gene 41 protein, required for the synthesis of RNA primers, is also a DNA helicase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 25;257(20):12426–12434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilcox D. R., Prakash L. Incision and postincision steps of pyrimidine dimer removal in excision-defective mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1981 Nov;148(2):618–623. doi: 10.1128/jb.148.2.618-623.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood E. R., Matson S. W. Purification and characterization of a new DNA-dependent ATPase with helicase activity from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 5;262(31):15269–15276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis: a simple method using two oligonucleotide primers and a single-stranded DNA template. DNA. 1984 Dec;3(6):479–488. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]