Abstract
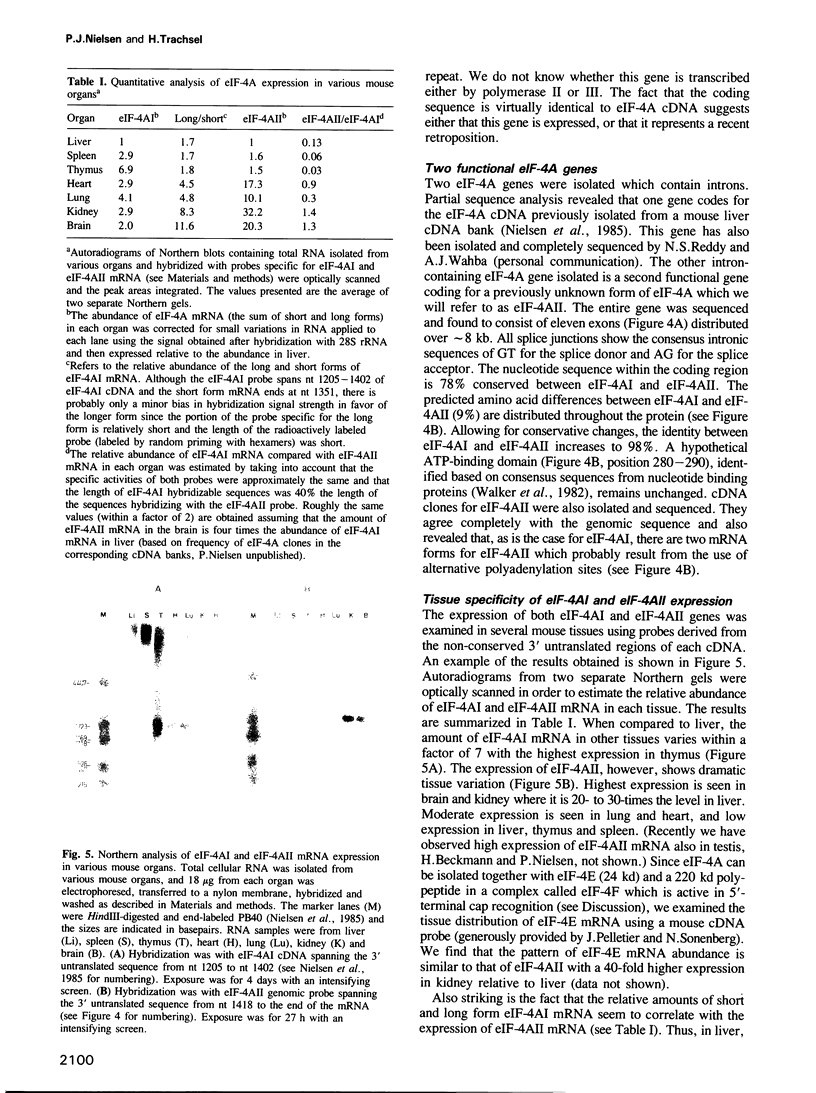
We have cloned and characterized a family of mouse genomic sequences hybridizing to mouse cDNA probes coding for eIF-4A, one of the protein synthesis initiation factors involved in the binding of mRNA to the ribosome. We estimate that there is a total of approximately 9-13 eIF-4A pseudogenes. We also found an eIF-4A intronless retroposon which, when compared to the cDNA, contains a single nucleotide difference. This possibly functional gene contains a mouse repetitive B1 element integrated in the promoter region. Furthermore, we have cloned two intron-containing eIF-4A genes (termed eIF-4AI and eIF-4AII). The eIF-4AII gene codes for a previously unknown form of eIF-4A. Northern blot hybridization with RNA from several mouse organs shows a variation in eIF-4AI expression within a factor of 7. In contrast, relative to liver, eIF-4AII expression is 20- to 30-times higher in brain and kidney, 10- to 17-fold higher in lung and heart, and is about equally abundant in liver, spleen and thymus. These data suggest that the relative efficiency of protein synthesis initiation for different mRNAs, as reflected by discrimination in messenger 5'-terminal cap recognition and binding to ribosomes, varies in different tissues.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramson R. D., Dever T. E., Lawson T. G., Ray B. K., Thach R. E., Merrick W. C. The ATP-dependent interaction of eukaryotic initiation factors with mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 15;262(8):3826–3832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birsner U., Gilles U., Nielsen P., McMaster G. K. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic system for the rapid, automated purification of oligonucleotides. J Chromatogr. 1987 Jul 31;402:381–386. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(87)80043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen M. J., Shimada T., Moulton A. D., Harrison M., Nienhuis A. W. Intronless human dihydrofolate reductase genes are derived from processed RNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7435–7439. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels-McQueen S., Detjen B. M., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Unusual requirements for optimum translation of polio viral RNA in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7195–7199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dudov K. P., Perry R. P. The gene family encoding the mouse ribosomal protein L32 contains a uniquely expressed intron-containing gene and an unmutated processed gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):457–468. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90376-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Hershey J. W. Identification and quantitation of levels of protein synthesis initiation factors in crude HeLa cell lysates by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):7228–7235. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan R., Milburn S. C., Hershey J. W. Regulated phosphorylation and low abundance of HeLa cell initiation factor eIF-4F suggest a role in translational control. Heat shock effects on eIF-4F. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 5;262(1):380–388. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edery I., Hümbelin M., Darveau A., Lee K. A., Milburn S., Hershey J. W., Trachsel H., Sonenberg N. Involvement of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A in the cap recognition process. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 25;258(18):11398–11403. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowlkes D. M., Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions of the adenovirus VAI RNA gene. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):405–413. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90351-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Abramson R. D., Satler C. A., Merrick W. C. RNA-stimulated ATPase activity of eukaryotic initiation factors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8648–8654. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Leis J. P., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. Characterization of eukaryotic initiation factor 4A, a protein involved in ATP-dependent binding of globin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5246–5252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grifo J. A., Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J., Merrick W. C. New initiation factor activity required for globin mRNA translation. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5804–5810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiremath L. S., Webb N. R., Rhoads R. E. Immunological detection of the messenger RNA cap-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7843–7849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influence of mRNA secondary structure on binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuzumaki T., Tanaka T., Ishikawa K., Ogata K. Rat ribosomal protein L35a multigene family: molecular structure and characterization of three L35a-related pseudogenes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jul 14;909(2):99–106. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(87)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P., Rosenthal N., Efstratidadis A., Gilbert W., Kolodner R., Tizard R. The structure and evolution of the two nonallelic rat preproinsulin genes. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):545–558. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90071-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maitra U., Stringer E. A., Chaudhuri A. Initiation factors in protein biosynthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:869–900. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.004253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man Y. M., Delius H., Leader D. P. Molecular analysis of elements inserted into mouse gamma-actin processed pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3291–3304. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarrey J. R., Thomas K. Human testis-specific PGK gene lacks introns and possesses characteristics of a processed gene. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):501–505. doi: 10.1038/326501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Gronenborn B., Müller-Hill B., Hans Hopschneider P. Filamentous coliphage M13 as a cloning vehicle: insertion of a HindII fragment of the lac regulatory region in M13 replicative form in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3642–3646. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moldave K. Eukaryotic protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:1109–1149. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.005333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Initiation of reovirus transcription by inosine 5'-triphosphate and properties of 7-methylinosine-capped, inosine-substituted messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1980 Dec 23;19(26):5960–5966. doi: 10.1021/bi00567a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen P. J., McMaster G. K., Trachsel H. Cloning of eukaryotic protein synthesis initiation factor genes: isolation and characterization of cDNA clones encoding factor eIF-4A. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 11;13(19):6867–6880. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.19.6867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ray B. K., Brendler T. G., Adya S., Daniels-McQueen S., Miller J. K., Hershey J. W., Grifo J. A., Merrick W. C., Thach R. E. Role of mRNA competition in regulating translation: further characterization of mRNA discriminatory initiation factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):663–667. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar G., Edery I., Gallo R., Sonenberg N. Preferential stimulation of rabbit alpha globin mRNA translation by a cap-binding protein complex. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1984 Nov 22;783(2):122–129. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(84)90003-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scarpulla R. C. Processed pseudogenes for rat cytochrome c are preferentially derived from one of three alternate mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2279–2288. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seal S. N., Schmidt A., Marcus A. Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A is the component that interacts with ATP in protein chain initiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6562–6565. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. ATP/Mg++-dependent cross-linking of cap binding proteins to the 5' end of eukaryotic mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Apr 10;9(7):1643–1656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.7.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stein J. P., Munjaal R. P., Lagace L., Lai E. C., O'Malley B. W., Means A. R. Tissue-specific expression of a chicken calmodulin pseudogene lacking intervening sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(21):6485–6489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.21.6485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tahara S. M., Morgan M. A., Shatkin A. J. Two forms of purified m7G-cap binding protein with different effects on capped mRNA translation in extracts of uninfected and poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 10;256(15):7691–7694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker J. E., Saraste M., Runswick M. J., Gay N. J. Distantly related sequences in the alpha- and beta-subunits of ATP synthase, myosin, kinases and other ATP-requiring enzymes and a common nucleotide binding fold. EMBO J. 1982;1(8):945–951. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01276.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young R. A., Davis R. W. Yeast RNA polymerase II genes: isolation with antibody probes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):778–782. doi: 10.1126/science.6356359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





