Abstract
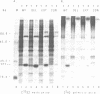
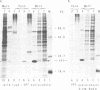
The Saccharomyces cerevisiae YPT1 gene codes for a ras-like, guanine nucleotide-binding protein which is essential for cell viability. The functional significance of two consecutive cysteines at the very carboxyl-terminal end of this protein and in ypt homologues of other eukaryotic species was examined. YPT1 gene mutations were generated that either led to substitutions by serine or the deletion of one or both C-terminal cysteines. The consequences of the mutations were checked in cells after replacing the wild type with the mutant genes. It was found that as long as one of the cysteines was retained, the protein was fully functional. The YPT1 protein could be labelled with [3H]palmitic acid that appeared to be bound in an ester linkage. The wild-type protein was evenly distributed between soluble and membrane-associated proteins, the palmitoylated form was predominantly in the crude membrane fraction. The mutant protein lacking the C-terminal cysteines was not palmitoylated and was exclusively found in the soluble fraction. The extension by three residues, -Val-Leu-Ser, generating a ras-typical C-terminal end, did not interfere with the mutant YPT1 protein's function although it resulted in a reduced labelling with palmitic acid.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbacid M. ras genes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:779–827. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.004023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Direct identification of palmitic acid as the lipid attached to p21ras. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):116–122. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capon D. J., Chen E. Y., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V. Complete nucleotide sequences of the T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene and its normal homologue. Nature. 1983 Mar 3;302(5903):33–37. doi: 10.1038/302033a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z. Q., Ulsh L. S., DuBois G., Shih T. Y. Posttranslational processing of p21 ras proteins involves palmitylation of the C-terminal tetrapeptide containing cysteine-186. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):607–612. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.607-612.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross G. A. Eukaryotic protein modification and membrane attachment via phosphatidylinositol. Cell. 1987 Jan 30;48(2):179–181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90419-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deschenes R. J., Broach J. R. Fatty acylation is important but not essential for Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS function. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2344–2351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F. Processing and fatty acid acylation of RAS1 and RAS2 proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1266–1270. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1266. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kaziro Y. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of a ras gene from Schizosaccharomyces pombe. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):687–691. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03684.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magee A. I., Gutierrez L., McKay I. A., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Dynamic fatty acylation of p21N-ras. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3353–3357. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02656.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Smith D. H., Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Structure and organization of the human Ki-ras proto-oncogene and a related processed pseudogene. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):501–506. doi: 10.1038/304501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Michaelis S., Broek D., Santa Anna S., Field J., Herskowitz I., Wigler M. RAM, a gene of yeast required for a functional modification of RAS proteins and for production of mating pheromone a-factor. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):413–422. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reymond C. D., Gomer R. H., Mehdy M. C., Firtel R. A. Developmental regulation of a Dictyostelium gene encoding a protein homologous to mammalian ras protein. Cell. 1984 Nov;39(1):141–148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90199-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
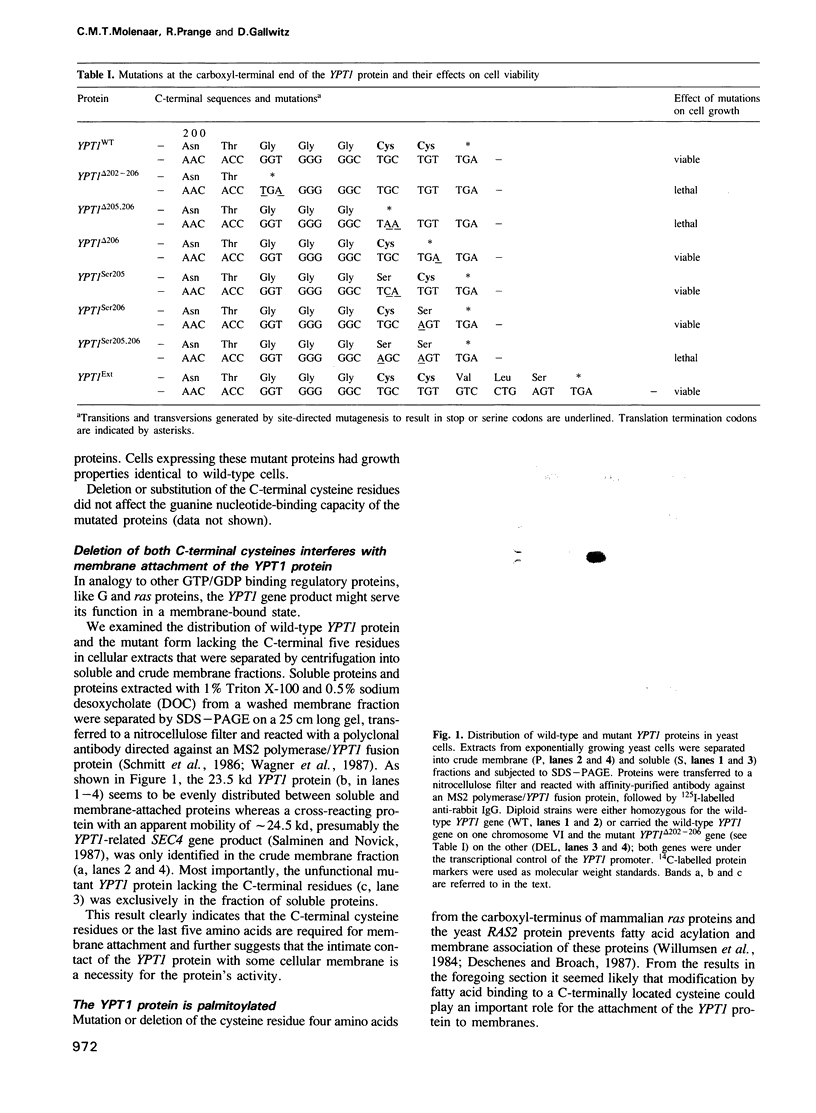
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Buss J. E. The covalent modification of eukaryotic proteins with lipid. J Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;104(6):1449–1453. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.6.1449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Weeks M. O., Gruss P., Dhar R., Oroszlan S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of a precursor in the biosynthesis of the p21 transforming protein of harvey murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):253–261. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.253-261.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Touchot N., Chardin P., Tavitian A. Four additional members of the ras gene superfamily isolated by an oligonucleotide strategy: molecular cloning of YPT-related cDNAs from a rat brain library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8210–8214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ulsh L. S., Shih T. Y. Metabolic turnover of human c-rasH p21 protein of EJ bladder carcinoma and its normal cellular and viral homologs. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1647–1652. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner P., Molenaar C. M., Rauh A. J., Brökel R., Schmitt H. D., Gallwitz D. Biochemical properties of the ras-related YPT protein in yeast: a mutational analysis. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2373–2379. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02514.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen D., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid-acylated proteins in secretory mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Apr;4(4):688–694. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.4.688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Norris K., Papageorge A. G., Hubbert N. L., Lowy D. R. Harvey murine sarcoma virus p21 ras protein: biological and biochemical significance of the cysteine nearest the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2581–2585. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02177.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]