Abstract
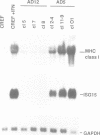
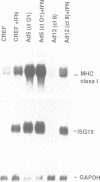
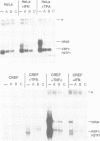
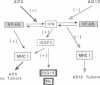
Changes in MHC class I expression are frequently observed in tumors, which represents at least one mechanism by which tumor cells escape immune surveillance. MHC class I expression is often suppressed in type 12 adenovirus (Ad12)-transformed rodent cells, but is highly induced in Ad5-transformed cells. This difference helps to explain why Ad12 but not Ad5 can induce tumors in immunocompetent syngeneic rats. In this report we demonstrate that only Ad5- but not Ad12-transformed rodent fibroblasts constitutively express beta-IFN which results in ISGF3 factor induction, and stimulation of MHC class I expression. Furthermore, we demonstrate that in contrast to Ad12-transformed cells, Ad5-transformed cells show constitutive levels of nuclear NF-kappa B-like DNA binding activity. This is of particular interest since both the beta-IFN and the MHC class I promoters contain an NF-kappa B DNA binding site. Thus, high levels of MHC class I expression in Ad5-transformed cells are due to a combinatorial stimulation of two cis-regulatory sequences of the MHC class I promoter: the NF-kappa B binding site and the interferon stimulated response element (ISRE), which binds the ISGF3 factor complex. The failure of Ad12-transformed cells to activate this pathway explains their low levels of MHC class I expression and their greater oncogenicity.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackrill A. M., Blair G. E. Nuclear proteins binding to an enhancer element of the major histocompatibility class I promoter: differences between highly oncogenic and nononcogenic adenovirus-transformed rat cells. Virology. 1989 Oct;172(2):643–646. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90207-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adami G. R., Babiss L. E. The efficiency of adenovirus transformation of rodent cells is inversely related to the rate of viral E1A gene expression. J Virol. 1990 Jul;64(7):3427–3436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.7.3427-3436.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Babiss L. E., Liaw W. S., Zimmer S. G., Godman G. C., Ginsberg H. S., Fisher P. B. Mutations in the E1a gene of adenovirus type 5 alter the tumorigenic properties of transformed cloned rat embryo fibroblast cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2167–2171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. Activation of DNA-binding activity in an apparently cytoplasmic precursor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):211–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90382-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baeuerle P. A., Baltimore D. I kappa B: a specific inhibitor of the NF-kappa B transcription factor. Science. 1988 Oct 28;242(4878):540–546. doi: 10.1126/science.3140380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, LeClair K. P., Singh H., Sharp P. A. A large protein containing zinc finger domains binds to related sequence elements in the enhancers of the class I major histocompatibility complex and kappa immunoglobulin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1406–1414. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Binding of a nuclear factor to a regulatory sequence in the promoter of the mouse H-2Kb class I major histocompatibility gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):305–313. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin A. S., Jr, Sharp P. A. Two transcription factors, NF-kappa B and H2TF1, interact with a single regulatory sequence in the class I major histocompatibility complex promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Feb;85(3):723–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.3.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Dessain S. K., Weinberg R. A. N-myc amplification causes down-modulation of MHC class I antigen expression in neuroblastoma. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):667–674. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90509-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernards R., Schrier P. I., Houweling A., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J., Zijlstra M., Melief C. J. Tumorigenicity of cells transformed by adenovirus type 12 by evasion of T-cell immunity. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):776–779. doi: 10.1038/305776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark L., Pollock R. M., Hay R. T. Identification and purification of EBP1: a HeLa cell protein that binds to a region overlapping the 'core' of the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):991–1002. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eager K. B., Williams J., Breiding D., Pan S., Knowles B., Appella E., Ricciardi R. P. Expression of histocompatibility antigens H-2K, -D, and -L is reduced in adenovirus-12-transformed mouse cells and is restored by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan C. M., Maniatis T. A DNA-binding protein containing two widely separated zinc finger motifs that recognize the same DNA sequence. Genes Dev. 1990 Jan;4(1):29–42. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.1.29. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher P. B., Babiss L. E., Weinstein I. B., Ginsberg H. S. Analysis of type 5 adenovirus transformation with a cloned rat embryo cell line (CREF). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jun;79(11):3527–3531. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.11.3527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flint J., Shenk T. Adenovirus E1A protein paradigm viral transactivator. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:141–161. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.001041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Kimura Y., Miyamoto M., Barsoumian E. L., Taniguchi T. Induction of endogenous IFN-alpha and IFN-beta genes by a regulatory transcription factor, IRF-1. Nature. 1989 Jan 19;337(6204):270–272. doi: 10.1038/337270a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H., Paraskeva C. A study to determine the reasons for differences in the tumorigenicity of rat cell lines transformed by adenovirus 2 and adenovirus 12. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):703–713. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodenow R. S., Vogel J. M., Linsk R. L. Histocompatibility antigens on murine tumors. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):777–783. doi: 10.1126/science.2997918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada H., Fujita T., Miyamoto M., Kimura Y., Maruyama M., Furia A., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Structurally similar but functionally distinct factors, IRF-1 and IRF-2, bind to the same regulatory elements of IFN and IFN-inducible genes. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90107-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrison T., Graham F., Williams J. Host-range mutants of adenovirus type 5 defective for growth in HeLa cells. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):319–329. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90428-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi H., Tanaka K., Jay F., Khoury G., Jay G. Modulation of the tumorigenicity of human adenovirus-12-transformed cells by interferon. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):263–267. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henseling U., Schmidt W., Schöler H. R., Gruss P., Hatzopoulos A. K. A transcription factor interacting with the class I gene enhancer is inactive in tumorigenic cell lines which suppress major histocompatibility complex class I genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;10(8):4100–4109. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.8.4100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Pelletier M., Boczko E. M., Babiss L. E. The state of cellular differentiation determines the activity of the adenovirus E1A enhancer element: evidence for negative regulation of enhancer function. J Virol. 1990 Jan;64(1):161–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.1.161-172.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël A., Kimura A., Kieran M., Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P. A common positive trans-acting factor binds to enhancer sequences in the promoters of mouse H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2653–2657. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kast W. M., Offringa R., Peters P. J., Voordouw A. C., Meloen R. H., van der Eb A. J., Melief C. J. Eradication of adenovirus E1-induced tumors by E1A-specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):603–614. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katoh S., Ozawa K., Kondoh S., Soeda E., Israel A., Shiroki K., Fujinaga K., Itakura K., Gachelin G., Yokoyama K. Identification of sequences responsible for positive and negative regulation by E1A in the promoter of H-2Kbm1 class I MHC gene. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):127–135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08088.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
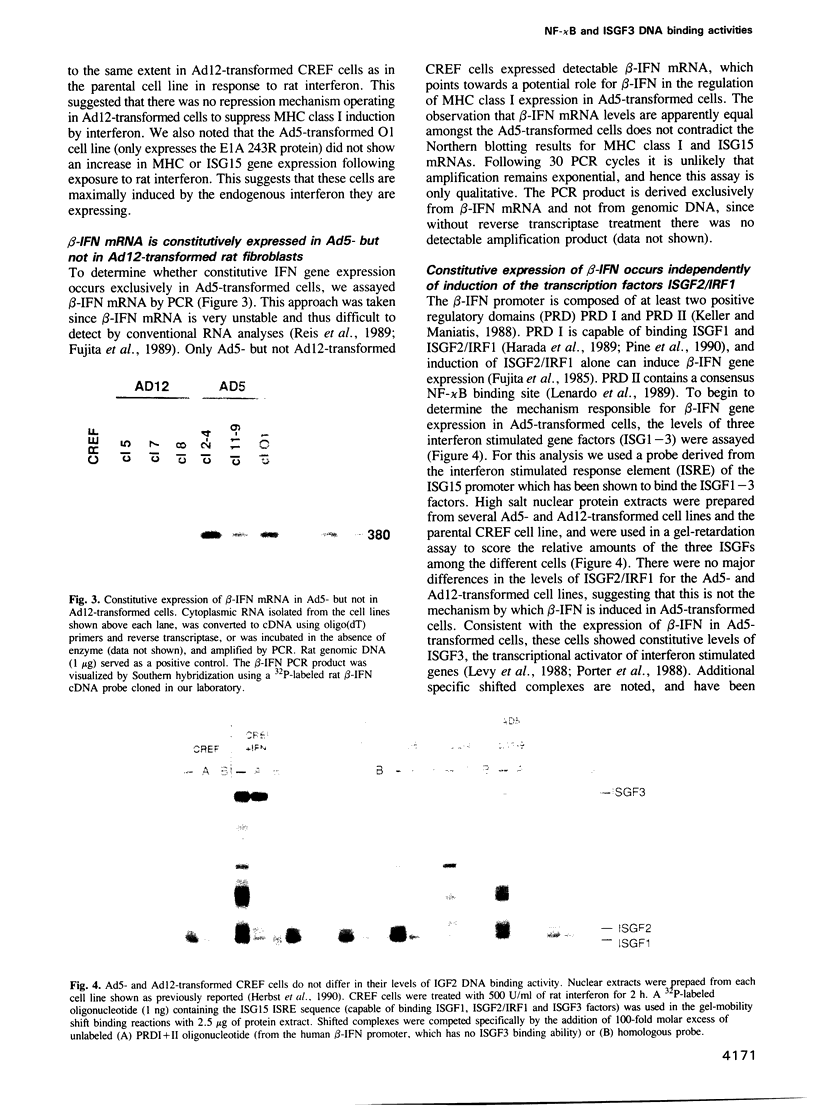
- Keller A. D., Maniatis T. Identification of an inducible factor that binds to a positive regulatory element of the human beta-interferon gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3309–3313. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieran M., Blank V., Logeat F., Vandekerckhove J., Lottspeich F., Le Bail O., Urban M. B., Kourilsky P., Baeuerle P. A., Israël A. The DNA binding subunit of NF-kappa B is identical to factor KBF1 and homologous to the rel oncogene product. Cell. 1990 Sep 7;62(5):1007–1018. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90275-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenardo M. J., Fan C. M., Maniatis T., Baltimore D. The involvement of NF-kappa B in beta-interferon gene regulation reveals its role as widely inducible mediator of signal transduction. Cell. 1989 Apr 21;57(2):287–294. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90966-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy D. E., Kessler D. S., Pine R., Reich N., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-induced nuclear factors that bind a shared promoter element correlate with positive and negative transcriptional control. Genes Dev. 1988 Apr;2(4):383–393. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.4.383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logeat F., Israël N., Ten R., Blank V., Le Bail O., Kourilsky P., Israël A. Inhibition of transcription factors belonging to the rel/NF-kappa B family by a transdominant negative mutant. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1827–1832. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07708.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mauxion F., Sen R. Alteration of a single nucleotide allows efficient binding of H2TF1/KBF1 to the immunoglobulin kappa enhancer B motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3548–3552. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3548. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meier E., Kunz G., Haller O., Arnheiter H. Activity of rat Mx proteins against a rhabdovirus. J Virol. 1990 Dec;64(12):6263–6269. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.12.6263-6269.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Offringa R., Gebel S., van Dam H., Timmers M., Smits A., Zwart R., Stein B., Bos J. L., van der Eb A., Herrlich P. A novel function of the transforming domain of E1a: repression of AP-1 activity. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90017-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pine R., Decker T., Kessler D. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Purification and cloning of interferon-stimulated gene factor 2 (ISGF2): ISGF2 (IRF-1) can bind to the promoters of both beta interferon- and interferon-stimulated genes but is not a primary transcriptional activator of either. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2448–2457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Porter A. C., Chernajovsky Y., Dale T. C., Gilbert C. S., Stark G. R., Kerr I. M. Interferon response element of the human gene 6-16. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):85–92. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02786.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reis L. F., Ho Lee T., Vilcek J. Tumor necrosis factor acts synergistically with autocrine interferon-beta and increases interferon-beta mRNA levels in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16351–16354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rustgi A. K., Van 't Veer L. J., Bernards R. Two genes encode factors with NF-kappa B- and H2TF1-like DNA-binding properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8707–8710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada Y., Föhring B., Shenk T. E., Raska K., Jr Tumorigenicity of adenovirus-transformed cells: region E1A of adenovirus 12 confers resistance to natural killer cells. Virology. 1985 Dec;147(2):413–421. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90143-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
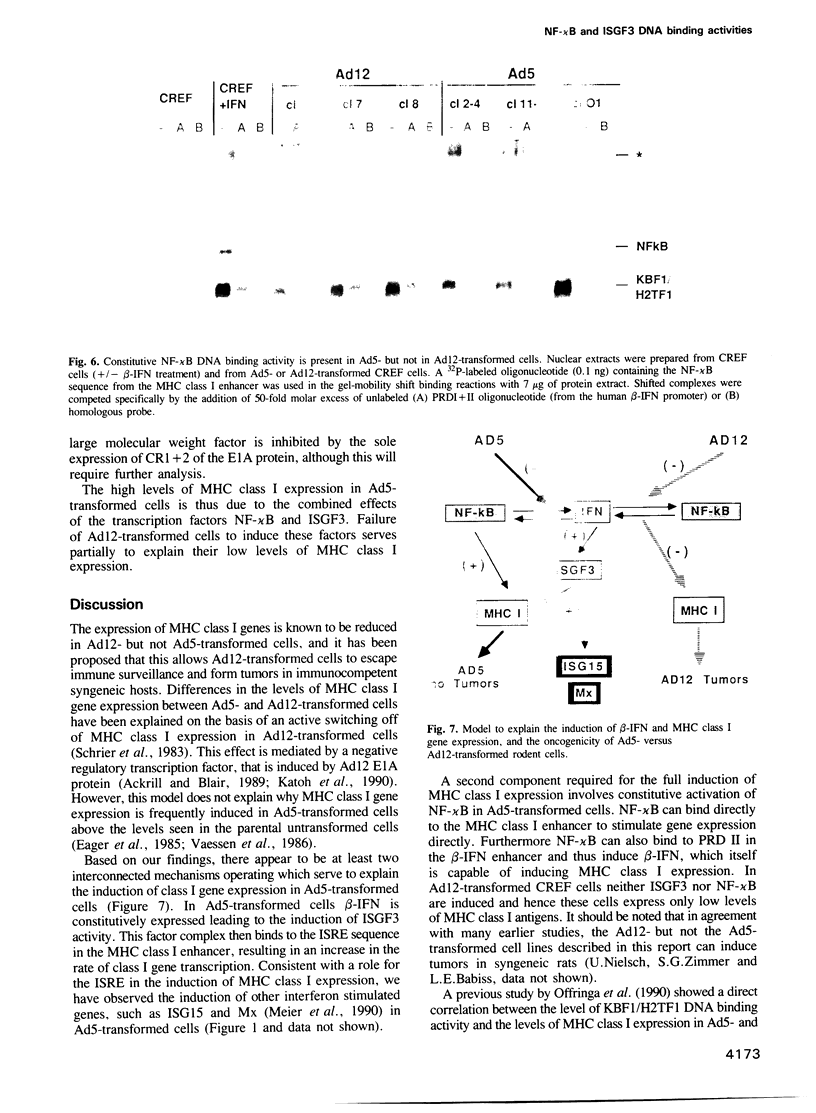
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Inducibility of kappa immunoglobulin enhancer-binding protein Nf-kappa B by a posttranslational mechanism. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):921–928. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90807-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen R., Baltimore D. Multiple nuclear factors interact with the immunoglobulin enhancer sequences. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):705–716. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90346-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Isselbacher K. J., Khoury G., Jay G. Reversal of oncogenesis by the expression of a major histocompatibility complex class I gene. Science. 1985 Apr 5;228(4695):26–30. doi: 10.1126/science.3975631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urban M. B., Schreck R., Baeuerle P. A. NF-kappa B contacts DNA by a heterodimer of the p50 and p65 subunit. EMBO J. 1991 Jul;10(7):1817–1825. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07707.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., Israel A., Kourilsky P., van der Eb A. J. Adenovirus E1A-mediated regulation of class I MHC expression. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):335–341. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04217.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallich R., Bulbuc N., Hämmerling G. J., Katzav S., Segal S., Feldman M. Abrogation of metastatic properties of tumour cells by de novo expression of H-2K antigens following H-2 gene transfection. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):301–305. doi: 10.1038/315301a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano O., Kanellopoulos J., Kieran M., Le Bail O., Israël A., Kourilsky P. Purification of KBF1, a common factor binding to both H-2 and beta 2-microglobulin enhancers. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3317–3324. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02652.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]