Abstract
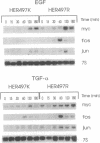
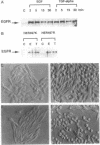
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) and type alpha transforming growth factor (TGF-alpha) bind to a specific region in subdomain III of the extracellular portion of the EGF receptor (EGFR). Binding leads to receptor dimerization, auto-and transphosphorylation on intracellular tyrosine residues, and activation of signal transduction pathways. We compared the binding and biological actions of EGF and TGF-alpha in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells expressing either wild-type human EGFR (HER497R) or a variant EGFR that has an arginine-to-lysine substitution in the extracellular domain at codon 497 (HER497K) within subdomain IV of EGFR. Both receptors exhibited two orders of binding sites with radioiodinated EGF (125I-EGF). Similar results were obtained with 125I-TGF-alpha in cells expressing HER497R. In contrast, only one order of low-affinity binding sites was seen with 125I-TGF-alpha in the case of HER497K. Although EGF and TGF-alpha enhanced tyrosine phosphorylation of both receptors, CHO cells expressing HER497K exhibited an attenuated growth response to EGF and TGF-alpha and a reduced induction of the protooncogenes FOS, JUN, and MYC. Moreover, high concentrations of TGF-alpha (5 nM) inhibited growth in these cells but not in cells expressing HER497R. These findings indicate that a region in subdomain IV of EGFR regulates signal transduction across the cell membrane and selectively modulates that binding characteristics of TGF-alpha.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aroian R. V., Lesa G. M., Sternberg P. W. Mutations in the Caenorhabditis elegans let-23 EGFR-like gene define elements important for cell-type specificity and function. EMBO J. 1994 Jan 15;13(2):360–366. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06269.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avivi A., Lax I., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Givol D., Morse B. Comparison of EGF receptor sequences as a guide to study the ligand binding site. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):673–676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Signal transmission by the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):235–238. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90281-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gan B. S., Hollenberg M. D., MacCannell K. L., Lederis K., Winkler M. E., Derynck R. Distinct vascular actions of epidermal growth factor-urogastrone and transforming growth factor-alpha. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1987 Jul;242(1):331–337. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotoh N., Tojo A., Muroya K., Hashimoto Y., Hattori S., Nakamura S., Takenawa T., Yazaki Y., Shibuya M. Epidermal growth factor-receptor mutant lacking the autophosphorylation sites induces phosphorylation of Shc protein and Shc-Grb2/ASH association and retains mitogenic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jan 4;91(1):167–171. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.1.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu C. Y., Mohammadi M., Nathan M., Honegger A., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Hurwitz D. R. Generation of recombinant cytoplasmic domain of epidermal growth factor receptor with intrinsic protein tyrosine kinase activity. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Apr;1(4):191–200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Chandrasekar B., Shah G. N. Differential binding and biological activities of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha in a human pancreatic cancer cell line. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6243–6249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Chandrasekar B., Yamanaka Y., Friess H., Buchier M., Beger H. G. Overexpression of the epidermal growth factor receptor in human pancreatic cancer is associated with concomitant increases in the levels of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha. J Clin Invest. 1992 Oct;90(4):1352–1360. doi: 10.1172/JCI116001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Finman J. E. Attenuated processing of epidermal growth factor in the face of marked degradation of transforming growth factor-alpha. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14990–14999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korc M., Haussler C. A., Trookman N. S. Divergent effects of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factors on a human endometrial carcinoma cell line. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 15;47(18):4909–4914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Burgess W. H., Bellot F., Ullrich A., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Localization of a major receptor-binding domain for epidermal growth factor by affinity labeling. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1831–1834. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1831. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lax I., Johnson A., Howk R., Sap J., Bellot F., Winkler M., Ullrich A., Vennstrom B., Schlessinger J., Givol D. Chicken epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor: cDNA cloning, expression in mouse cells, and differential binding of EGF and transforming growth factor alpha. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1970–1978. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriai T., Kobrin M. S., Korc M. Cloning of a variant epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1993 Mar 31;191(3):1034–1039. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1993.1321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Ligand: a versatile computerized approach for characterization of ligand-binding systems. Anal Biochem. 1980 Sep 1;107(1):220–239. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petch L. A., Harris J., Raymond V. W., Blasband A., Lee D. C., Earp H. S. A truncated, secreted form of the epidermal growth factor receptor is encoded by an alternatively spliced transcript in normal rat tissue. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2973–2982. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raitano A. B., Scuderi P., Korc M. Binding and biological effects of tumor necrosis factor and gamma interferon in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Pancreas. 1990 May;5(3):267–277. doi: 10.1097/00006676-199005000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron. 1992 Sep;9(3):383–391. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90177-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoelson S. E., White M. F., Kahn C. R. Tryptic activation of the insulin receptor. Proteolytic truncation of the alpha-subunit releases the beta-subunit from inhibitory control. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 5;263(10):4852–4860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorne B. A., Plowman G. D. The heparin-binding domain of amphiregulin necessitates the precursor pro-region for growth factor secretion. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Mar;14(3):1635–1646. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.3.1635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Coussens L., Hayflick J. S., Dull T. J., Gray A., Tam A. W., Lee J., Yarden Y., Libermann T. A., Schlessinger J. Human epidermal growth factor receptor cDNA sequence and aberrant expression of the amplified gene in A431 epidermoid carcinoma cells. 1984 May 31-Jun 6Nature. 309(5967):418–425. doi: 10.1038/309418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler M. E., O'Connor L., Winget M., Fendly B. Epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha bind differently to the epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6373–6378. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu D. G., Wang L. H., Chi Y., Sato G. H., Sato J. D. Human epidermal growth factor receptor residue covalently cross-linked to epidermal growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3151–3155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Schlessinger J. Epidermal growth factor induces rapid, reversible aggregation of the purified epidermal growth factor receptor. Biochemistry. 1987 Mar 10;26(5):1443–1451. doi: 10.1021/bi00379a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]