Abstract
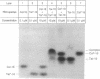
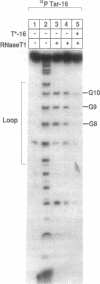
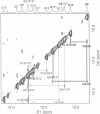
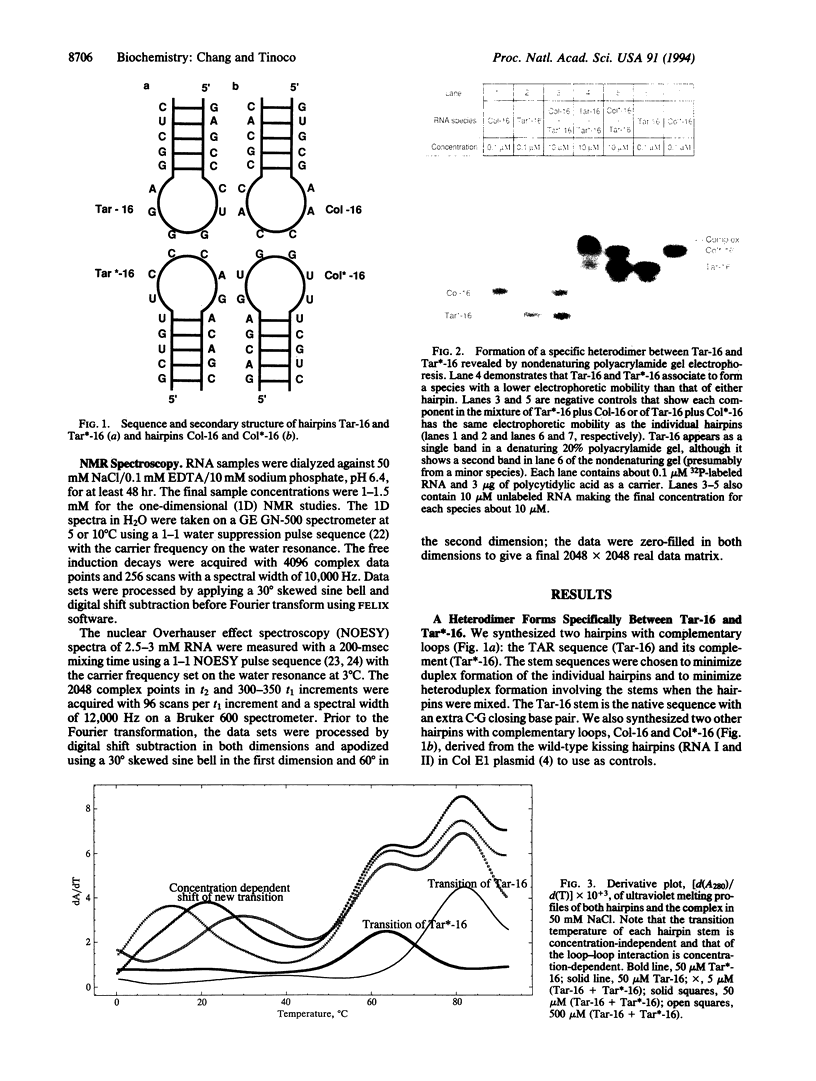
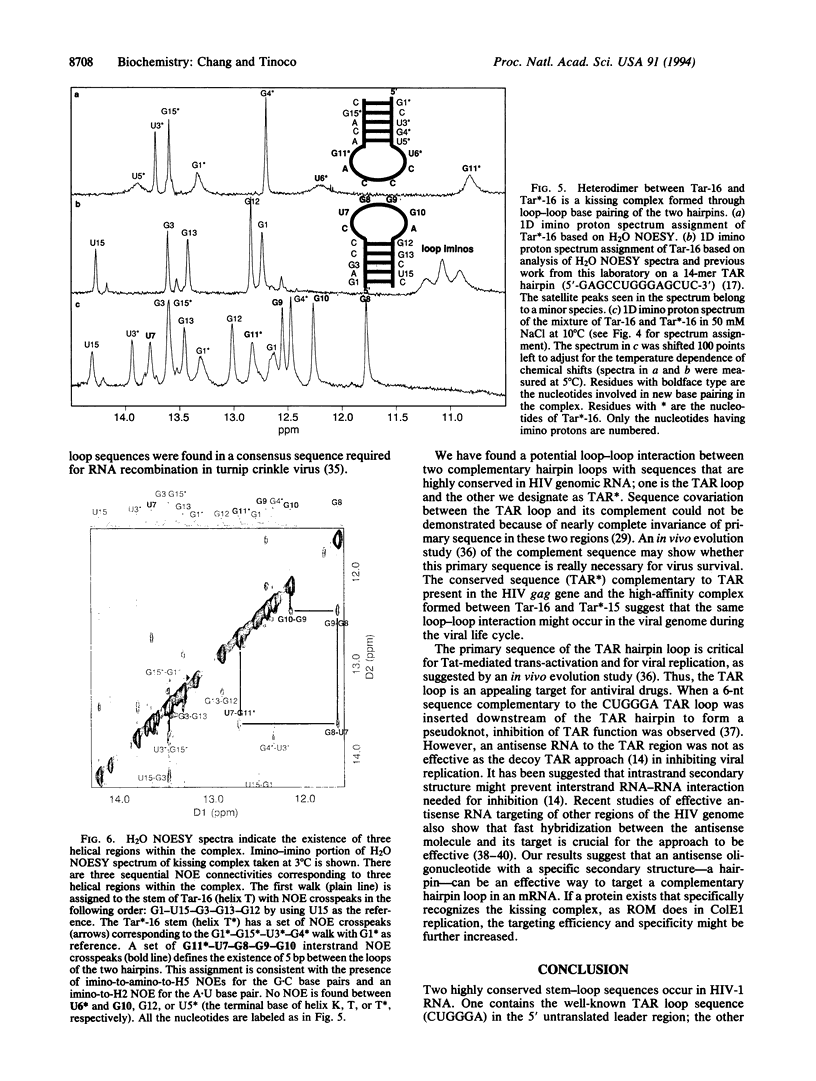
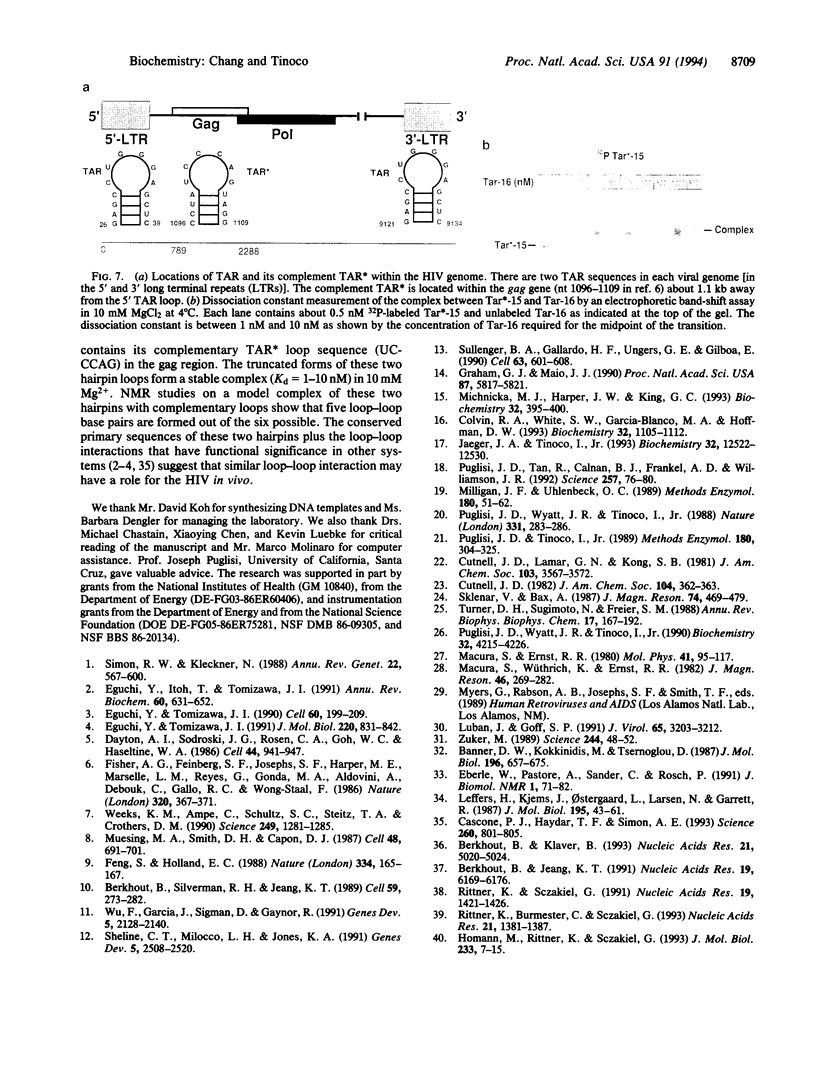
Base-pair formation between two hairpin loops--a "kissing" complex--is an RNA-folding motif that links two elements of RNA secondary structure. It is also a unique protein recognition site involved in regulation of ColE1 plasmid DNA replication. The trans-activation response element (TAR), a hairpin and bulge at the 5' end of the untranslated leader region of the human immunodeficiency virus 1 mRNA, enhances the transcription of the virus and is necessary for viral replication. Gel electrophoresis and absorbance melting curves indicate that a synthesized RNA hairpin (Tar*-16) with a loop sequence complementary to the TAR loop sequence (CUGGGA) associates specifically with a 16-nucleotide TAR hairpin (Tar-16) to form a stable complex. RNase T1 probing indicates that the three guanines in the Tar-16 loop become inaccessible in the complex. NMR imino proton spectra reveal that 5 base pairs are formed between the two hairpin loops (Tar-16 and Tar*-16); only the adenine at the 3' terminus of the TAR loop does not form a base pair with the 5'-terminal uracil of the complementary loop. A 14-nucleotide hairpin [CCUA(UCCCAG)UAGG] with a loop sequence complementary to the TAR loop is conserved within the gag gene of human immunodeficiency virus 1. A synthesized RNA hairpin corresponding to this conserved sequence also binds to the Tar-16 hairpin with high affinity. It is possible that the same RNA loop-loop interaction occurs during the viral life cycle.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banner D. W., Kokkinidis M., Tsernoglou D. Structure of the ColE1 rop protein at 1.7 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1987 Aug 5;196(3):657–675. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90039-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Detailed mutational analysis of TAR RNA: critical spacing between the bulge and loop recognition domains. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 25;19(22):6169–6176. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.22.6169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Klaver B. In vivo selection of randomly mutated retroviral genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 11;21(22):5020–5024. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.22.5020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Silverman R. H., Jeang K. T. Tat trans-activates the human immunodeficiency virus through a nascent RNA target. Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):273–282. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90289-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cascone P. J., Haydar T. F., Simon A. E. Sequences and structures required for recombination between virus-associated RNAs. Science. 1993 May 7;260(5109):801–805. doi: 10.1126/science.8484119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colvin R. A., White S. W., Garcia-Blanco M. A., Hoffman D. W. Structural features of an RNA containing the CUGGGA loop of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 trans-activation response element. Biochemistry. 1993 Feb 2;32(4):1105–1112. doi: 10.1021/bi00055a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayton A. I., Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Goh W. C., Haseltine W. A. The trans-activator gene of the human T cell lymphotropic virus type III is required for replication. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):941–947. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle W., Pastore A., Sander C., Rösch P. The structure of ColE1 rop in solution. J Biomol NMR. 1991 May;1(1):71–82. doi: 10.1007/BF01874570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi Y., Itoh T., Tomizawa J. Antisense RNA. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:631–652. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi Y., Tomizawa J. Complex formed by complementary RNA stem-loops and its stabilization by a protein: function of CoIE1 Rom protein. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90736-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eguchi Y., Tomizawa J. Complexes formed by complementary RNA stem-loops. Their formations, structures and interaction with ColE1 Rom protein. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 20;220(4):831–842. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90356-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng S., Holland E. C. HIV-1 tat trans-activation requires the loop sequence within tar. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):165–167. doi: 10.1038/334165a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher A. G., Feinberg M. B., Josephs S. F., Harper M. E., Marselle L. M., Reyes G., Gonda M. A., Aldovini A., Debouk C., Gallo R. C. The trans-activator gene of HTLV-III is essential for virus replication. 1986 Mar 27-Apr 2Nature. 320(6060):367–371. doi: 10.1038/320367a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham G. J., Maio J. J. RNA transcripts of the human immunodeficiency virus transactivation response element can inhibit action of the viral transactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5817–5821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Homann M., Rittner K., Sczakiel G. Complementary large loops determine the rate of RNA duplex formation in vitro in the case of an effective antisense RNA directed against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Mol Biol. 1993 Sep 5;233(1):7–15. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1993.1480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaeger J. A., Tinoco I., Jr An NMR study of the HIV-1 TAR element hairpin. Biochemistry. 1993 Nov 23;32(46):12522–12530. doi: 10.1021/bi00097a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffers H., Kjems J., Ostergaard L., Larsen N., Garrett R. A. Evolutionary relationships amongst archaebacteria. A comparative study of 23 S ribosomal RNAs of a sulphur-dependent extreme thermophile, an extreme halophile and a thermophilic methanogen. J Mol Biol. 1987 May 5;195(1):43–61. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luban J., Goff S. P. Binding of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) RNA to recombinant HIV-1 gag polyprotein. J Virol. 1991 Jun;65(6):3203–3212. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.6.3203-3212.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michnicka M. J., Harper J. W., King G. C. Selective isotopic enrichment of synthetic RNA: application to the HIV-1 TAR element. Biochemistry. 1993 Jan 19;32(2):395–400. doi: 10.1021/bi00053a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milligan J. F., Uhlenbeck O. C. Synthesis of small RNAs using T7 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:51–62. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80091-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muesing M. A., Smith D. H., Capon D. J. Regulation of mRNA accumulation by a human immunodeficiency virus trans-activator protein. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):691–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90247-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tan R., Calnan B. J., Frankel A. D., Williamson J. R. Conformation of the TAR RNA-arginine complex by NMR spectroscopy. Science. 1992 Jul 3;257(5066):76–80. doi: 10.1126/science.1621097. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Tinoco I., Jr Absorbance melting curves of RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1989;180:304–325. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(89)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Wyatt J. R., Tinoco I., Jr A pseudoknotted RNA oligonucleotide. Nature. 1988 Jan 21;331(6153):283–286. doi: 10.1038/331283a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puglisi J. D., Wyatt J. R., Tinoco I., Jr Solution conformation of an RNA hairpin loop. Biochemistry. 1990 May 1;29(17):4215–4226. doi: 10.1021/bi00469a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittner K., Burmester C., Sczakiel G. In vitro selection of fast-hybridizing and effective antisense RNAs directed against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Mar 25;21(6):1381–1387. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.6.1381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rittner K., Sczakiel G. Identification and analysis of antisense RNA target regions of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Apr 11;19(7):1421–1426. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.7.1421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheline C. T., Milocco L. H., Jones K. A. Two distinct nuclear transcription factors recognize loop and bulge residues of the HIV-1 TAR RNA hairpin. Genes Dev. 1991 Dec;5(12B):2508–2520. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.12b.2508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Kleckner N. Biological regulation by antisense RNA in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:567–600. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullenger B. A., Gallardo H. F., Ungers G. E., Gilboa E. Overexpression of TAR sequences renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):601–608. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90455-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner D. H., Sugimoto N., Freier S. M. RNA structure prediction. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:167–192. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weeks K. M., Ampe C., Schultz S. C., Steitz T. A., Crothers D. M. Fragments of the HIV-1 Tat protein specifically bind TAR RNA. Science. 1990 Sep 14;249(4974):1281–1285. doi: 10.1126/science.2205002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu F., Garcia J., Sigman D., Gaynor R. tat regulates binding of the human immunodeficiency virus trans-activating region RNA loop-binding protein TRP-185. Genes Dev. 1991 Nov;5(11):2128–2140. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.11.2128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M. On finding all suboptimal foldings of an RNA molecule. Science. 1989 Apr 7;244(4900):48–52. doi: 10.1126/science.2468181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]