Abstract
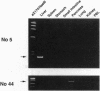
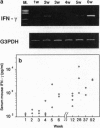
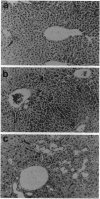
Interferon-gamma may play an important role in the immune response and in inflammatory diseases, including chronic active hepatitis. To understand the role of interferon-gamma in the regulation of inflammation and to establish a mouse model of chronic active hepatitis, we produced transgenic mice in which the mouse interferon-gamma gene was regulated by a liver-specific promoter, the serum amyloid P component gene promoter. Four transgenic mouse lines were generated, and two of these lines expressed mRNA of interferon-gamma in the liver. Levels of serum transaminases increased gradually as a function of age and were significantly higher than those of interferon-gamma-negative littermates after 4 weeks after birth. One transgenic mouse line showed a histology of chronic active hepatitis similar to that found in human patients, although cirrhotic changes such as fibrosis were scarce. Thus, the liver-specific production of interferon-gamma is sufficient to induce chronic inflammatory disease and this mouse is a transgenic model of chronic active hepatitis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Araki K., Miyazaki J., Hino O., Tomita N., Chisaka O., Matsubara K., Yamamura K. Expression and replication of hepatitis B virus genome in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):207–211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beasley R. P., Hwang L. Y., Lin C. C., Chien C. S. Hepatocellular carcinoma and hepatitis B virus. A prospective study of 22 707 men in Taiwan. Lancet. 1981 Nov 21;2(8256):1129–1133. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90585-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Ferrari C., Mondelli M. U. Hepatitis B virus structure and biology. Microb Pathog. 1989 May;6(5):311–325. doi: 10.1016/0882-4010(89)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chisari F. V., Filippi P., Buras J., McLachlan A., Popper H., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L. Structural and pathological effects of synthesis of hepatitis B virus large envelope polypeptide in transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(19):6909–6913. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.19.6909. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dienes H. P., Hess G., Wöorsdörfer M., Rossol S., Gallati H., Ramadori G., Meyer zum Büschenfelde K. H. Ultrastructural localization of interferon-producing cells in the livers of patients with chronic hepatitis B. Hepatology. 1991 Feb;13(2):321–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Mier J. W. Lymphokines. N Engl J Med. 1987 Oct 8;317(15):940–945. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198710083171506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dycaico M. J., Grant S. G., Felts K., Nichols W. S., Geller S. A., Hager J. H., Pollard A. J., Kohler S. W., Short H. P., Jirik F. R. Neonatal hepatitis induced by alpha 1-antitrypsin: a transgenic mouse model. Science. 1988 Dec 9;242(4884):1409–1412. doi: 10.1126/science.3264419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino O., Shows T. B., Rogler C. E. Hepatitis B virus integration site in hepatocellular carcinoma at chromosome 17;18 translocation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8338–8342. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hino O., Tabata S., Hotta Y. Evidence for increased in vitro recombination with insertion of human hepatitis B virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 15;88(20):9248–9252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.20.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwanaga T., Wakasugi S., Inomoto T., Uehira M., Ohnishi S., Nishiguchi S., Araki K., Uno M., Miyazaki J., Maeda S. Liver-specific and high-level expression of human serum amyloid P component gene in transgenic mice. Dev Genet. 1989;10(5):365–371. doi: 10.1002/dvg.1020100504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondelli M., Vergani G. M., Alberti A., Vergani D., Portmann B., Eddleston A. L., Williams R. Specificity of T lymphocyte cytotoxicity to autologous hepatocytes in chronic hepatitis B virus infection: evidence that T cells are directed against HBV core antigen expressed on hepatocytes. J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2773–2778. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y., Mori T., Yoshida H., Ueda S., Iesato K., Wakashin Y., Wakashin M., Okuda K. Study of cellular immunity in experimental autoimmune hepatitis in mice. Clin Exp Immunol. 1984 Jul;57(1):85–92. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moriyama T., Guilhot S., Klopchin K., Moss B., Pinkert C. A., Palmiter R. D., Brinster R. L., Kanagawa O., Chisari F. V. Immunobiology and pathogenesis of hepatocellular injury in hepatitis B virus transgenic mice. Science. 1990 Apr 20;248(4953):361–364. doi: 10.1126/science.1691527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohnishi S., Maeda S., Shimada K., Arao T. Isolation and characterization of the complete complementary and genomic DNA sequences of human serum amyloid P component. J Biochem. 1986 Oct;100(4):849–858. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picarella D. E., Kratz A., Li C. B., Ruddle N. H., Flavell R. A. Insulitis in transgenic mice expressing tumor necrosis factor beta (lymphotoxin) in the pancreas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10036–10040. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10036. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogler C. E., Sherman M., Su C. Y., Shafritz D. A., Summers J., Shows T. B., Henderson A., Kew M. Deletion in chromosome 11p associated with a hepatitis B integration site in hepatocellular carcinoma. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):319–322. doi: 10.1126/science.2996131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito I., Miyamura T., Ohbayashi A., Harada H., Katayama T., Kikuchi S., Watanabe Y., Koi S., Onji M., Ohta Y. Hepatitis C virus infection is associated with the development of hepatocellular carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(17):6547–6549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.17.6547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Palmiter R. D., Heckel J. L., Brinster R. L., Degen J. L. DNA rearrangement causes hepatocarcinogenesis in albumin-plasminogen activator transgenic mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 1;89(23):11523–11527. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.23.11523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandgren E. P., Palmiter R. D., Heckel J. L., Daugherty C. C., Brinster R. L., Degen J. L. Complete hepatic regeneration after somatic deletion of an albumin-plasminogen activator transgene. Cell. 1991 Jul 26;66(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90615-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Liggitt D., Pitts S. L., Hansen S. E., Stewart T. A. Insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus induced in transgenic mice by ectopic expression of class II MHC and interferon-gamma. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):773–782. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90414-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarvetnick N., Shizuru J., Liggitt D., Martin L., McIntyre B., Gregory A., Parslow T., Stewart T. Loss of pancreatic islet tolerance induced by beta-cell expression of interferon-gamma. Nature. 1990 Aug 30;346(6287):844–847. doi: 10.1038/346844a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shull M. M., Ormsby I., Kier A. B., Pawlowski S., Diebold R. J., Yin M., Allen R., Sidman C., Proetzel G., Calvin D. Targeted disruption of the mouse transforming growth factor-beta 1 gene results in multifocal inflammatory disease. Nature. 1992 Oct 22;359(6397):693–699. doi: 10.1038/359693a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silva A. T., Cohen J. Role of interferon-gamma in experimental gram-negative sepsis. J Infect Dis. 1992 Aug;166(2):331–335. doi: 10.1093/infdis/166.2.331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szmuness W. Hepatocellular carcinoma and the hepatitis B virus: evidence for a causal association. Prog Med Virol. 1978;24:40–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamura K., Kikutani H., Takahashi N., Taga T., Akira S., Kawai K., Fukuchi K., Kumahara Y., Honjo T., Kishimoto T. Introduction of human gamma 1 immunoglobulin genes into fertilized mouse eggs. J Biochem. 1984 Aug;96(2):357–363. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134845. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao X., Araki K., Miyazaki J., Yamamura K. Developmental and liver-specific expression directed by the serum amyloid P component promoter in transgenic mice. J Biochem. 1992 Jun;111(6):736–738. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]