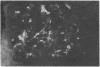
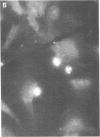
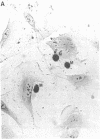
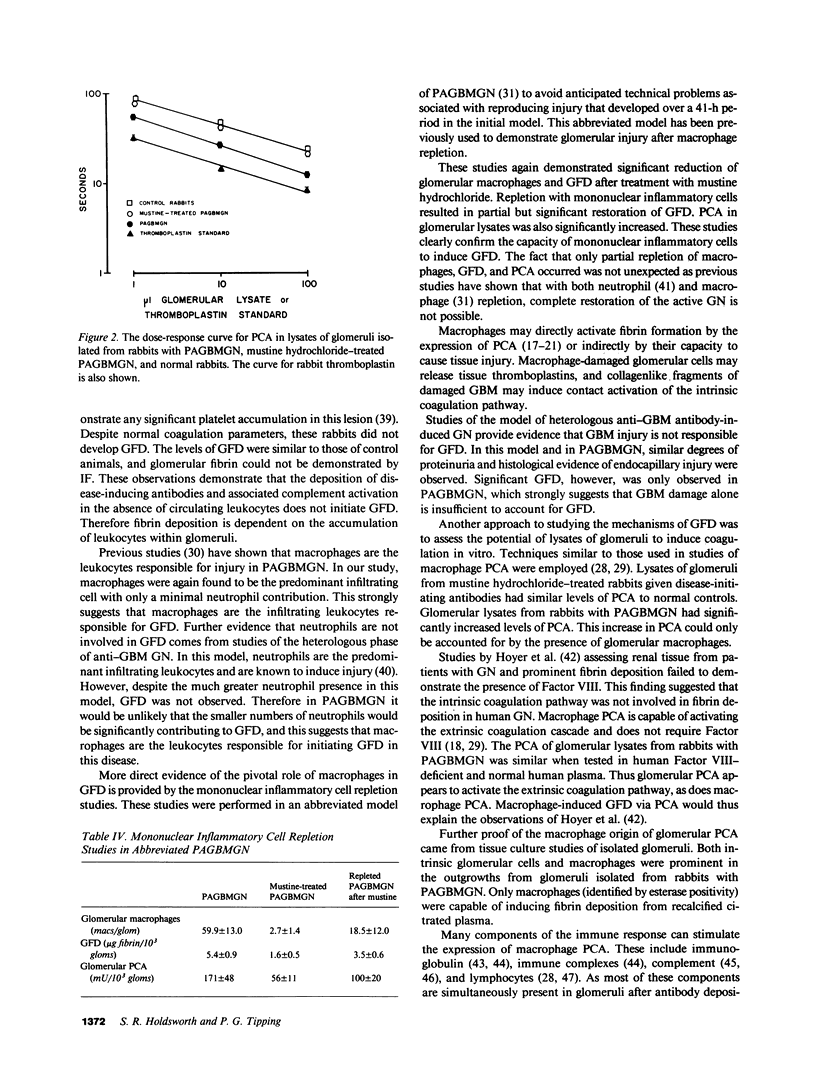
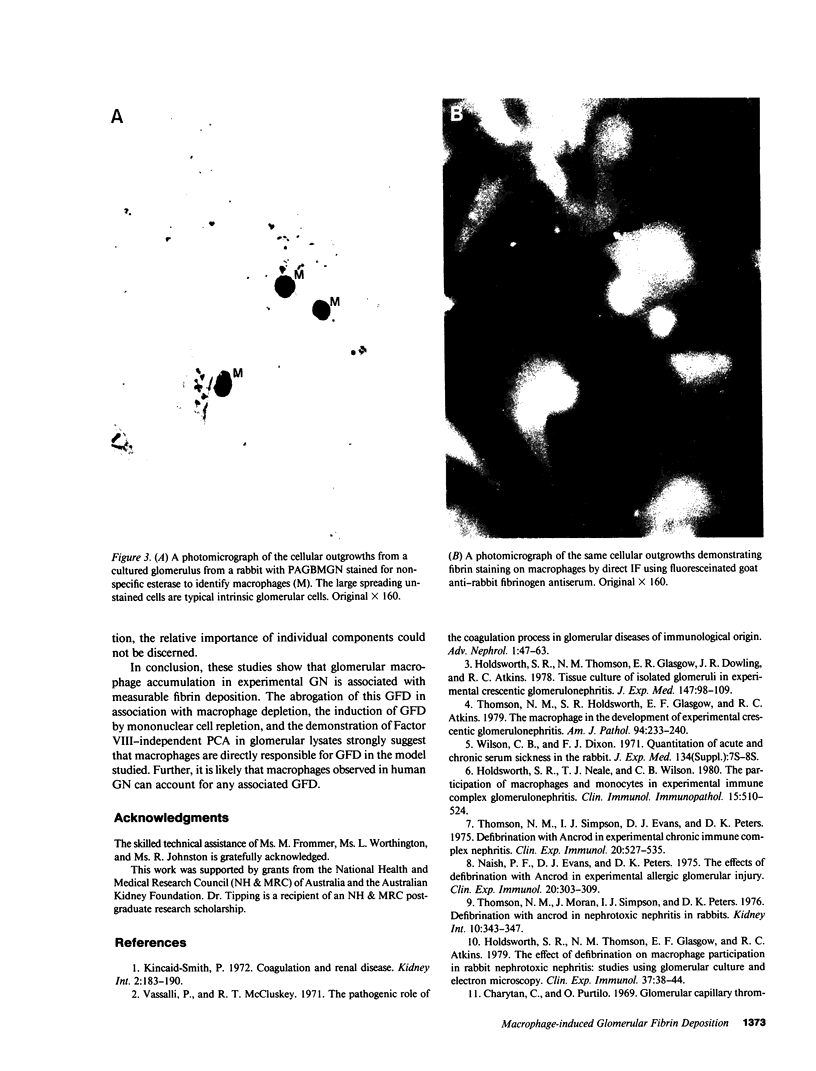
Abstract
Glomerular fibrin deposition is important in the pathogenesis of renal failure and crescent formation in glomerulonephritis. The mechanisms of glomerular fibrin deposition are unknown. The current studies explored the role of macrophages in this process. Methods were developed for measuring glomerular fibrin deposition and glomerular procoagulant activity in a passive model of the autologous phase of antiglomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis in rabbits. Significant fibrin deposition was observed to be associated with glomerular macrophage accumulation. Leukocyte ablation with mustine hydrochloride prevented both glomerular macrophage accumulation and fibrin deposition without affecting the coagulation system or the deposition of disease-inducing antibodies and complement. Repletion with mononuclear inflammatory cells produced significant fibrin deposition. To examine the role of tissue injury per se in glomerular fibrin deposition, a macrophage-independent model of glomerular injury (heterologous phase glomerulonephritis) was also studied. Although a similar degree of glomerular injury occurred, there was no significant fibrin deposition. This suggests that macrophages, rather than injury alone, are responsible for fibrin deposition. Lysates of isolated glomeruli containing macrophages demonstrated greatly enhanced procoagulant activity compared with lysates of glomeruli without macrophages. Thus macrophages appear to be directly responsible for glomerular fibrin deposition in antiglomerular basement membrane antibody-induced glomerulonephritis, and this appears to be due to their ability to express procoagulant activity rather than their propensity to cause glomerular injury.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins R. C., Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Matthews F. E. The macrophagen in human rapidly progressive glomerulonephritis. Lancet. 1976 Apr 17;1(7964):830–832. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(76)90480-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COCHRANE C. G., UNANUE E. R., DIXON F. J. A ROLE OF POLYMORPHONUCLEAR LEUKOCYTES AND COMPLEMENT IN NEPHROTOXIC NEPHRITIS. J Exp Med. 1965 Jul 1;122:99–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.122.1.99. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charytan C., Purtilo D. Glomerular capillary thrombosis and acute renal failure after epsilon-amino caproic acid therapy. N Engl J Med. 1969 May 15;280(20):1102–1104. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196905152802006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke B. E., Ham K. N., Tange J. D., Ryan G. B. Macrophages and glomerular crescent formation. Studies with rat nephrotoxic nephritis. Pathology. 1983 Jan;15(1):75–81. doi: 10.3109/00313028309061406. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. L., Rickles F. R., Bobrove A. M. Mononuclear cell tissue factor: cell of origin and requirements for activation. Blood. 1979 Aug;54(2):359–370. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards R. L., Rickles F. R. The role of human T cells (and T cell products) for monocyte tissue factor generation. J Immunol. 1980 Aug;125(2):606–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garg S. K., Niemetz J. Tissue factor activity of normal and leukemic cells. Blood. 1973 Nov;42(5):729–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. M. Pathologic mechanisms in neutrophil-mediated injury. Am J Pathol. 1972 Sep;68(3):593–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogg N. Human monocytes are associated with the formation of fibrin. J Exp Med. 1983 Feb 1;157(2):473–485. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.2.473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Thomson N. M., Atkins R. C. Tissue culture of isolated human glomeruli. Pathology. 1978 Jan;10(1):59–67. doi: 10.3109/00313027809063480. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J. Macrophage-induced glomerular injury. Cell transfer studies in passive autologous antiglomerular basement membrane antibody-initiated experimental glomerulonephritis. Lab Invest. 1984 Aug;51(2):172–180. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B. Abrogation of macrophage-dependent injury in experimental glomerulonephritis in the rabbit. Use of an antimacrophage serum. J Clin Invest. 1981 Sep;68(3):686–698. doi: 10.1172/JCI110304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Neale T. J., Wilson C. B. The participation of macrophages and monocytes in experimental immune complex glomerulonephritis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Mar;15(3):510–524. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90063-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Thomson N. M., Glasgow E. F., Atkins R. C. The effect of defibrination on macrophage participation in rabbit nephrotoxic nephritis: studies using glomerular culture and electronmicroscopy. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Jul;37(1):38–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holdsworth S. R., Thomson N. M., Glasgow E. F., Dowling J. P., Atkins R. C. Tissue culture of isolated glomeruli in experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis. J Exp Med. 1978 Jan 1;147(1):98–109. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.1.98. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyer J. R., Michael A. F., Hoyer L. W. Immunofluorescent localization of antihemophilic factor antigen and fibrinogen in human renal diseases. J Clin Invest. 1974 May;53(5):1375–1384. doi: 10.1172/JCI107686. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kincaid-Smith P. Coagulation and renal disease. Kidney Int. 1972 Oct;2(4):183–190. doi: 10.1038/ki.1972.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavelle K. J., Ransdell B. A., Kleit S. A. The influence of selective thrombocytopenia on nephrotoxic nephritis. J Lab Clin Med. 1976 Jun;87(6):967–975. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. G., Goldstein R., Cummings G., Lange K. Stimulation of human leukocyte thromboplastic activity by endotoxin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1971 Oct;138(1):145–148. doi: 10.3181/00379727-138-35848. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magil A. B., Wadsworth L. D. Monocytes in human glomerulonephritis. An electron microscopic study. Lab Invest. 1981 Jul;45(1):77–81. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R. V., Ulevitch R. J. The induction of a unique procoagulant activity in rabbit hepatic macrophages by bacterial lipopolysaccharides. J Immunol. 1981 Oct;127(4):1596–1600. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogensen C. E. The glomerular permeability determined by dextran clearance using Sephadex gel filtration. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1968;21(1):77–82. doi: 10.3109/00365516809076979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monga G., Mazzucco G., di Belgiojoso G. B., Busnach G. Monocyte infiltration and glomerular hypercellularity in human acute and persistent glomerulonephritis. Light and electron microscopic, immunofluorescence, and histochemical investigation on twenty-eight cases. Lab Invest. 1981 Apr;44(4):381–387. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhlfelder T. W., Niemetz J., Kreutzer D., Beebe D., Ward P. A., Rosenfeld S. I. C5 chemotactic fragment induces leukocyte production of tissue factor activity: a link between complement and coagulation. J Clin Invest. 1979 Jan;63(1):147–150. doi: 10.1172/JCI109269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naish P. F., Evans D. J., Peters D. K. The effects of defibrination with ancrod in experimental allergic glomerular injury. Clin Exp Immunol. 1975 May;20(2):303–309. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prydz H., Allison A. C., Schorlemmer H. U. Further link between complement activation and blood coagulation. Nature. 1977 Nov 10;270(5633):173–174. doi: 10.1038/270173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regoeczi E., Gergely J., McFarlane A. S. In vivo effects of Agkistrodon rhodostoma venom: studies with fibrinogen-131I. J Clin Invest. 1966 Jul;45(7):1202–1212. doi: 10.1172/JCI105426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Dove F. B., Lee T. K., McGee M. P., Kardon B. Procoagulant activity of lymphocyte-macrophage populations in rabbits: selective increases in marrow, blood, and spleen cells during Shwartzman reactions. Blood. 1983 Apr;61(4):712–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Lee T. K., Dunne J., Zimmerman T. S. Increases of leukocyte tissue factor activity stimulated by red cells sensitized with human blood group alloantibodies. Thromb Res. 1982 Sep 1;27(5):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(82)90300-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothberger H., Zimmerman T. S., Spiegelberg H. L., Vaughan J. H. Leukocyte procoagulant activity: enhancement of production in vitro by IgG and antigen-antibody complexes. J Clin Invest. 1977 Mar;59(3):549–557. doi: 10.1172/JCI108670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salant D. J., Darby C., Couser W. G. Experimental membranous glomerulonephritis in rats. Quantitative studies of glomerular immune deposit formation in isolated glomeruli and whole animals. J Clin Invest. 1980 Jul;66(1):71–81. doi: 10.1172/JCI109837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz B. S., Edgington T. S. Immune complex-induced human monocyte procoagulant activity. I. a rapid unidirectional lymphocyte-instructed pathway. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):892–906. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sindrey M., Marshall T. L., Naish P. Quantitative assessment of the effects of platelet depletion in the autologous phase of nephrotoxic serum nephritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1979 Apr;36(1):90–96. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. M., Holdsworth S. R., Glasgow E. F., Atkins R. C. The macrophage in the development of experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis. Studies using tissue culture and electron microscopy. Am J Pathol. 1979 Feb;94(2):223–240. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomson N. M., Moran J., Simpson I. J., Peters D. K. Defibrination with ancrod in nephrotoxic nephritis in rabbits. Kidney Int. 1976 Nov;10(5):343–347. doi: 10.1038/ki.1976.120. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipping P. G., Neale T. J., Holdsworth S. R. T lymphocyte participation in antibody-induced experimental glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1985 Mar;27(3):530–537. doi: 10.1038/ki.1985.43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unanue E. R., Dixon F. J. Experimental glomerulonephritis: immunological events and pathogenetic mechanisms. Adv Immunol. 1967;6:1–90. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60521-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VASSALLI P., MCCLUSKEY R. T. THE PATHOGENIC ROLE OF THE COAGULATION PROCESS IN RABBIT MASUGI NEPHRITIS. Am J Pathol. 1964 Oct;45:653–677. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli P., McCluskey R. T. The pathogenetic role of the coagulation process in glomerular diseases of immunologic origin. Adv Nephrol Necker Hosp. 1971;1:47–63. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe T., Tanaka K. The role of coagulation and fibrinolysis in the development of rabbit Masugi nephritis. Acta Pathol Jpn. 1976 Mar;26(2):147–165. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1827.1976.tb00871.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson C. B., Dixon F. J., Fortner J. G., Cerilli G. J. Glomerular basement membrane--reactive antibody in anti-lymphocyte globulin. J Clin Invest. 1971 Jul;50(7):1525–1535. doi: 10.1172/JCI106638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yam L. T., Li C. Y., Crosby W. H. Cytochemical identification of monocytes and granulocytes. Am J Clin Pathol. 1971 Mar;55(3):283–290. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/55.3.283. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]