Abstract
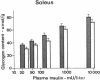
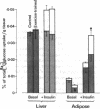
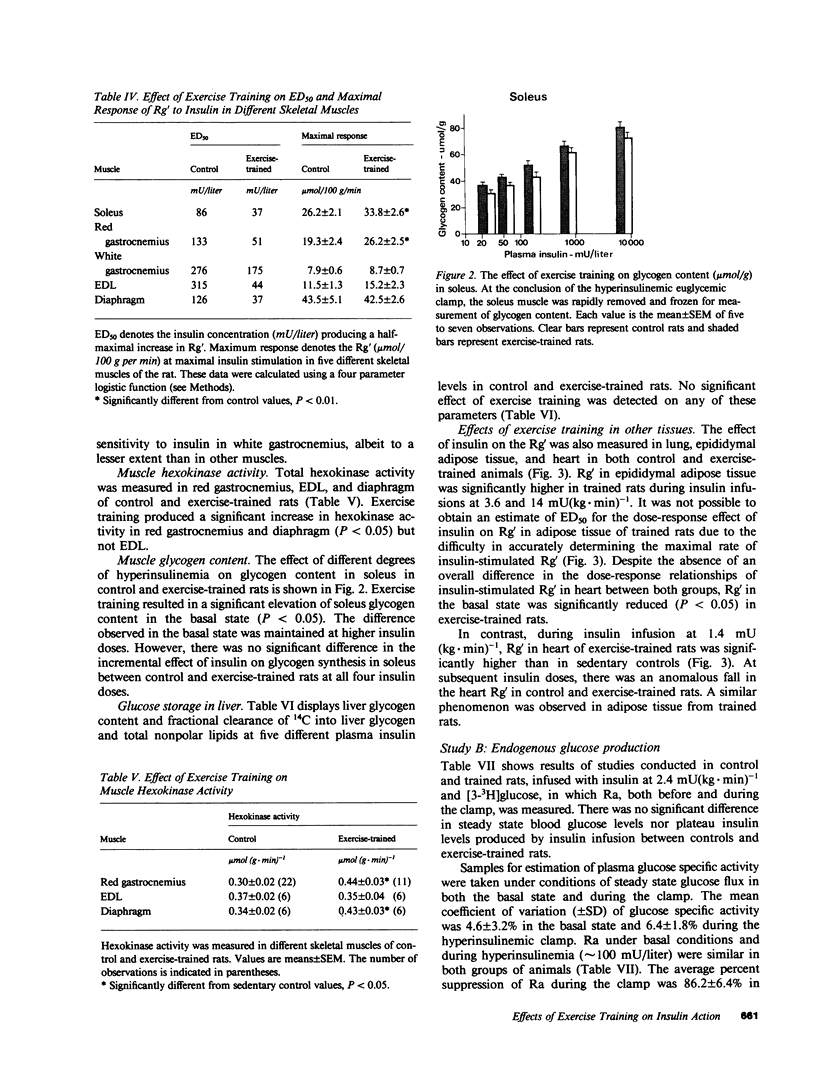
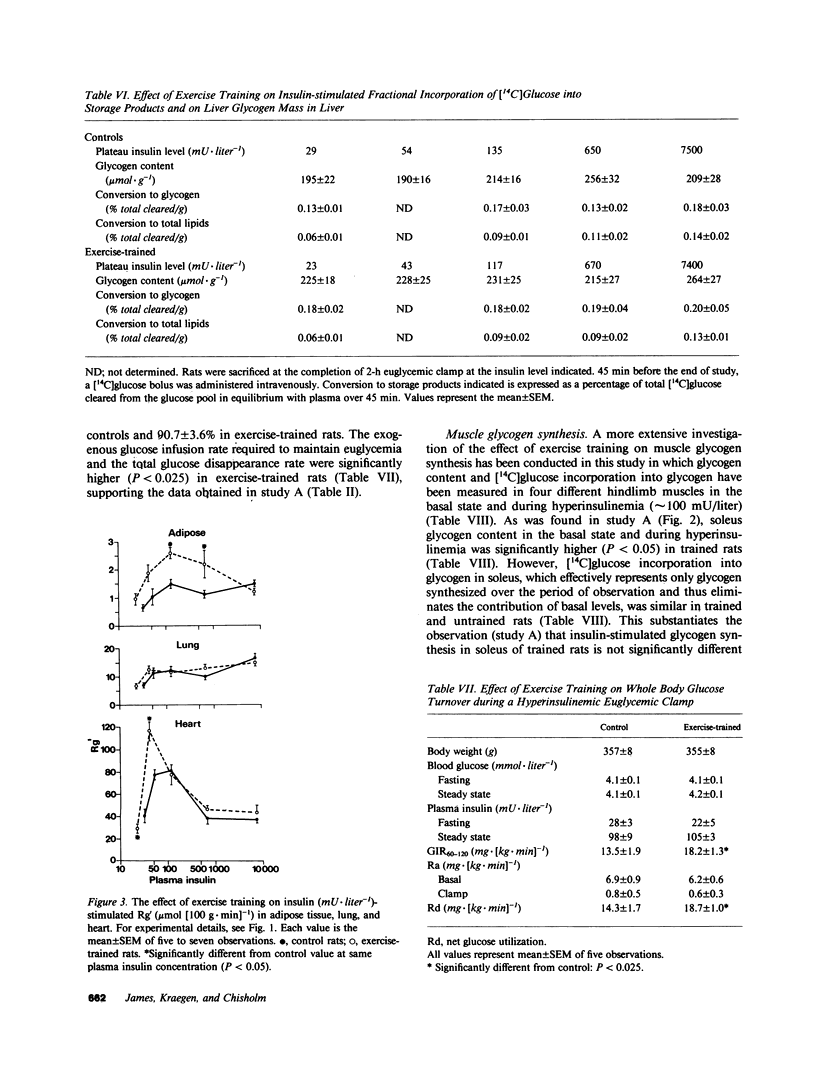
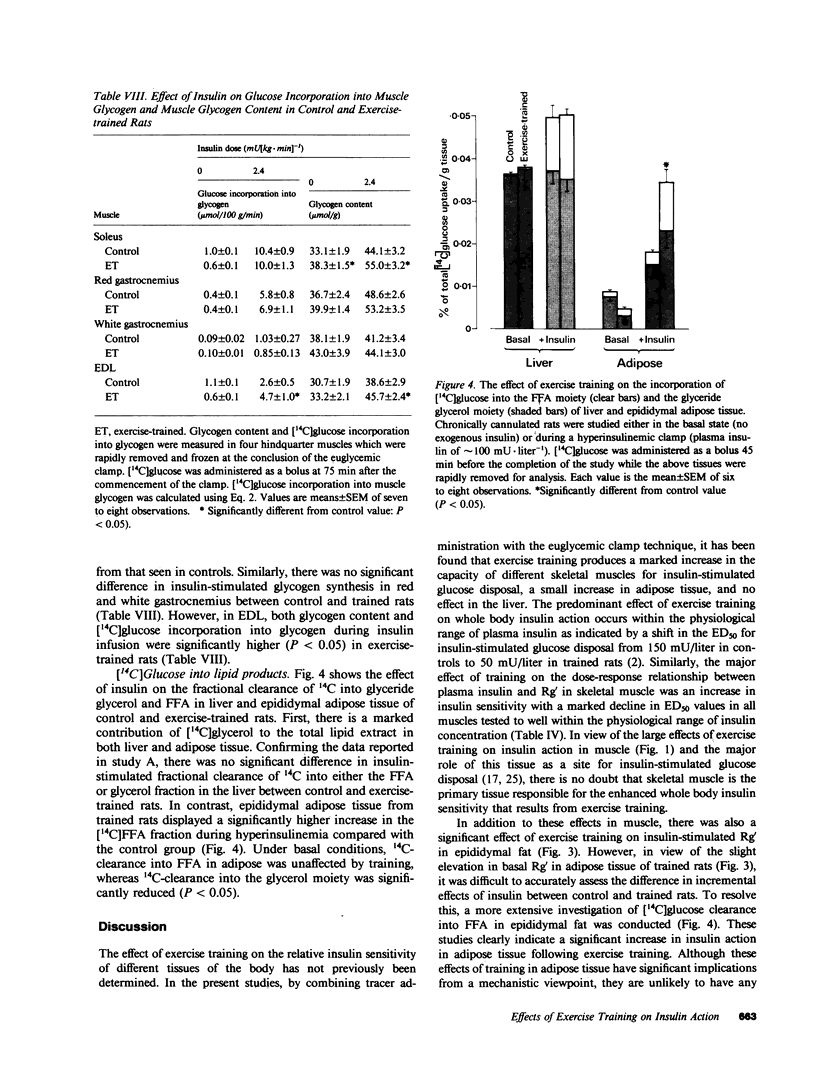
It has previously been suggested that exercise training leads to increased whole body insulin sensitivity. However, the specific tissues and metabolic pathways involved have not been examined in vivo. By combining the euglycemic clamp with administration of glucose tracers, [3H]2-deoxyglucose (2DG), [14C]glucose, and [3H]glucose, in vivo insulin action at the whole body level and within individual tissues has been assessed in exercise-trained (ET, running 1 h/d for 7 wk) and sedentary control rats at four insulin doses. Whole body insulin sensitivity was significantly increased in ET. In addition, the skeletal muscles, soleus, red and white gastrocnemius, extensor digitorum longus (EDL), and diaphragm all showed increased sensitivity of insulin-stimulated 2DG uptake with training. With the exception of EDL, no significant difference in insulin-mediated glycogen synthesis between control and ET could be found. Therefore, the increased insulin-induced 2DG uptake observed in muscle following training is apparently directed towards glucose oxidation. In ET animals, adipose tissue exhibited a significant increase in insulin-mediated 2DG uptake and [14C]glucose incorporation into free fatty acids but there was no difference from control in any parameters measured in lung or liver. EDL and white gastrocnemius, which are not primarily involved during exercise of this type, also demonstrated increased insulin sensitivity following training. In conclusion, exercise training results in a marked increase in whole body insulin sensitivity related mainly to increased glucose oxidation in skeletal muscle. This effect may be mediated by systemic as well as local factors and is likely to be of therapeutic value in pathological conditions exhibiting insulin resistance.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ariano M. A., Armstrong R. B., Edgerton V. R. Hindlimb muscle fiber populations of five mammals. J Histochem Cytochem. 1973 Jan;21(1):51–55. doi: 10.1177/21.1.51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong R. B., Laughlin M. H. Exercise blood flow patterns within and among rat muscles after training. Am J Physiol. 1984 Jan;246(1 Pt 2):H59–H68. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.1984.246.1.H59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger M., Kemmer F. W., Becker K., Herberg L., Schwenen M., Gjinavci A., Berchtold P. Effect of physical training on glucose tolerance and on glucose metabolism of skeletal muscle in anaesthetized normal rats. Diabetologia. 1979 Mar;16(3):179–184. doi: 10.1007/BF01219795. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Björntorp P., Sjöström L. Carbohydrate storage in man: speculations and some quantitative considerations. Metabolism. 1978 Dec;27(12 Suppl 2):1853–1865. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(78)80004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunengraber H., Boutry M., Lowenstein J. M. Fatty acid and 3- -hydroxysterol synthesis in the perfused rat liver. Including measurements on the production of lactate, pyruvate, -hydroxy-butyrate, and acetoacetate by the fed liver. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2656–2669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr P. J., Millar R. P., Crowley H. A simple radioimmunoassay for plasma cortisol: comparison with the fluorimetric method of determination. Ann Clin Biochem. 1977 Jul;14(4):207–211. doi: 10.1177/000456327701400157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan T. M., Exton J. H. A rapid method for the determination of glycogen content and radioactivity in small quantities of tissue or isolated hepatocytes. Anal Biochem. 1976 Mar;71(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig B. W., Hammons G. T., Garthwaite S. M., Jarett L., Holloszy J. O. Adaptation of fat cells to exercise: response of glucose uptake and oxidation to insulin. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1981 Dec;51(6):1500–1506. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1981.51.6.1500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crettaz M., Horton E. S., Wardzala L. J., Horton E. D., Jeanrenaud B. Physical training of Zucker rats: lack of alleviation of muscle insulin resistance. Am J Physiol. 1983 Apr;244(4):E414–E420. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.4.E414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Ferrannini E., Hendler R., Felig P., Wahren J. Regulation of splanchnic and peripheral glucose uptake by insulin and hyperglycemia in man. Diabetes. 1983 Jan;32(1):35–45. doi: 10.2337/diab.32.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Jacot E., Jequier E., Maeder E., Wahren J., Felber J. P. The effect of insulin on the disposal of intravenous glucose. Results from indirect calorimetry and hepatic and femoral venous catheterization. Diabetes. 1981 Dec;30(12):1000–1007. doi: 10.2337/diab.30.12.1000. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFronzo R. A., Thorin D., Felber J. P., Simonson D. C., Thiebaud D., Jequier E., Golay A. Effect of beta and alpha adrenergic blockade on glucose-induced thermogenesis in man. J Clin Invest. 1984 Mar;73(3):633–639. doi: 10.1172/JCI111253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLean A., Munson P. J., Rodbard D. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am J Physiol. 1978 Aug;235(2):E97–102. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1978.235.2.E97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espinal J., Dohm G. L., Newsholme E. A. Sensitivity to insulin of glycolysis and glycogen synthesis of isolated soleus-muscle strips from sedentary, exercised and exercise-trained rats. Biochem J. 1983 May 15;212(2):453–458. doi: 10.1042/bj2120453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fell R. D., Terblanche S. E., Winder W. W., Holloszy J. O. Adaptive responses of rats to prolonged treatment with epinephrine. Am J Physiol. 1981 Jul;241(1):C55–C58. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1981.241.1.C55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickson R. C., Heusner W. W., Van Huss W. D., Taylor J. F., Carrow R. E. Effects of an anabolic steroid and sprint training on selected histochemical and morphological observations in rat skeletal muscle types. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1976 Sep 23;35(4):251–259. doi: 10.1007/BF00423284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloszy J. O., Booth F. W. Biochemical adaptations to endurance exercise in muscle. Annu Rev Physiol. 1976;38:273–291. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.38.030176.001421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloszy J. O., Narahara H. T. Enhanced permeability to sugar associated with muscle contraction. Studies of the role of Ca++. J Gen Physiol. 1967 Jan;50(3):551–562. doi: 10.1085/jgp.50.3.551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Burleigh K. M., Kraegen E. W., Chisholm D. J. Effect of acute exercise and prolonged training on insulin response to intravenous glucose in vivo in rat. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1983 Dec;55(6):1660–1664. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1983.55.6.1660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Kraegen E. W. Heterogeneity of insulin action in individual muscles in vivo: euglycemic clamp studies in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E567–E574. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E567. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Kraegen E. W., Chisholm D. J. Effect of exercise training on whole-body insulin sensitivity and responsiveness. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1984 May;56(5):1217–1222. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1984.56.5.1217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Kraegen E. W., Chisholm D. J. Muscle glucose metabolism in exercising rats: comparison with insulin stimulation. Am J Physiol. 1985 May;248(5 Pt 1):E575–E580. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.5.E575. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- James D. E., Kraegen E. W. The effect of exercise training on glycogen, glycogen synthase and phosphorylase in muscle and liver. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol. 1984;52(3):276–281. doi: 10.1007/BF01015209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jansson E., Kaijser L. Muscle adaptation to extreme endurance training in man. Acta Physiol Scand. 1977 Jul;100(3):315–324. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1977.tb05956.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Bennett S. P., Chisholm D. J. In vivo insulin sensitivity in the rat determined by euglycemic clamp. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):E1–E7. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.1.E1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraegen E. W., James D. E., Jenkins A. B., Chisholm D. J. Dose-response curves for in vivo insulin sensitivity in individual tissues in rats. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):E353–E362. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1985.248.3.E353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc J., Nadeau A., Boulay M., Rousseau-Migneron S. Effects of physical training and adiposity on glucose metabolism and 125I-insulin binding. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1979 Feb;46(2):235–239. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1979.46.2.235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mondon C. E., Dolkas C. B., Reaven G. M. Site of enhanced insulin sensitivity in exercise-trained rats at rest. Am J Physiol. 1980 Sep;239(3):E169–E177. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.239.3.E169. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newsholme E. A. Substrate cycles: their metabolic, energetic and thermic consequences in man. Biochem Soc Symp. 1978;(43):183–205. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owens J. L., Fuller E. O., Nutter D. O., DiGirolamo M. Influence of moderate exercise on adipocyte metabolism and hormonal responsiveness. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1977 Sep;43(3):425–430. doi: 10.1152/jappl.1977.43.3.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richter E. A., Garetto L. P., Goodman M. N., Ruderman N. B. Muscle glucose metabolism following exercise in the rat: increased sensitivity to insulin. J Clin Invest. 1982 Apr;69(4):785–793. doi: 10.1172/JCI110517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHONK C. E., BOXER G. E. ENZYME PATTERNS IN HUMAN TISSUES. I. METHODS FOR THE DETERMINATION OF GLYCOLYTIC ENZYMES. Cancer Res. 1964 May;24:709–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soman V. R., Koivisto V. A., Deibert D., Felig P., DeFronzo R. A. Increased insulin sensitivity and insulin binding to monocytes after physical training. N Engl J Med. 1979 Nov 29;301(22):1200–1204. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197911293012203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauffacher W., Renold A. E. Effect of insulin in vivo on diaphragm and adipose tissue of obese mice. Am J Physiol. 1969 Jan;216(1):98–105. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1969.216.1.98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiebaud D., Jacot E., DeFronzo R. A., Maeder E., Jequier E., Felber J. P. The effect of graded doses of insulin on total glucose uptake, glucose oxidation, and glucose storage in man. Diabetes. 1982 Nov;31(11):957–963. doi: 10.2337/diacare.31.11.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyama K., Okuda H. Fatty acid synthesis in adipose tissues of physically trained rats in vivo. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):E8–13. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.245.1.E8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valant P., Erlij D. K+-stimulated sugar uptake in skeletal muscle: role of cytoplasmic Ca2+. Am J Physiol. 1983 Jul;245(1):C125–C132. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1983.245.1.C125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinten J., Galbo H. Effect of physical training on transport and metabolism of glucose in adipocytes. Am J Physiol. 1983 Feb;244(2):E129–E134. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1983.244.2.E129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wardzala L. J., Crettaz M., Horton E. D., Jeanrenaud B., Horton E. S. Physical training of lean and genetically obese Zucker rats: effect on fat cell metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1982 Nov;243(5):E418–E426. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1982.243.5.E418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wirth A., Holm G., Nilsson B., Smith U., Björntorp P. Insulin kinetics and insulin binding to adipocytes in physically trained and food-restricted rats. Am J Physiol. 1980 Feb;238(2):E108–E115. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.1980.238.2.E108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]