Abstract
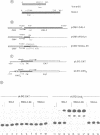
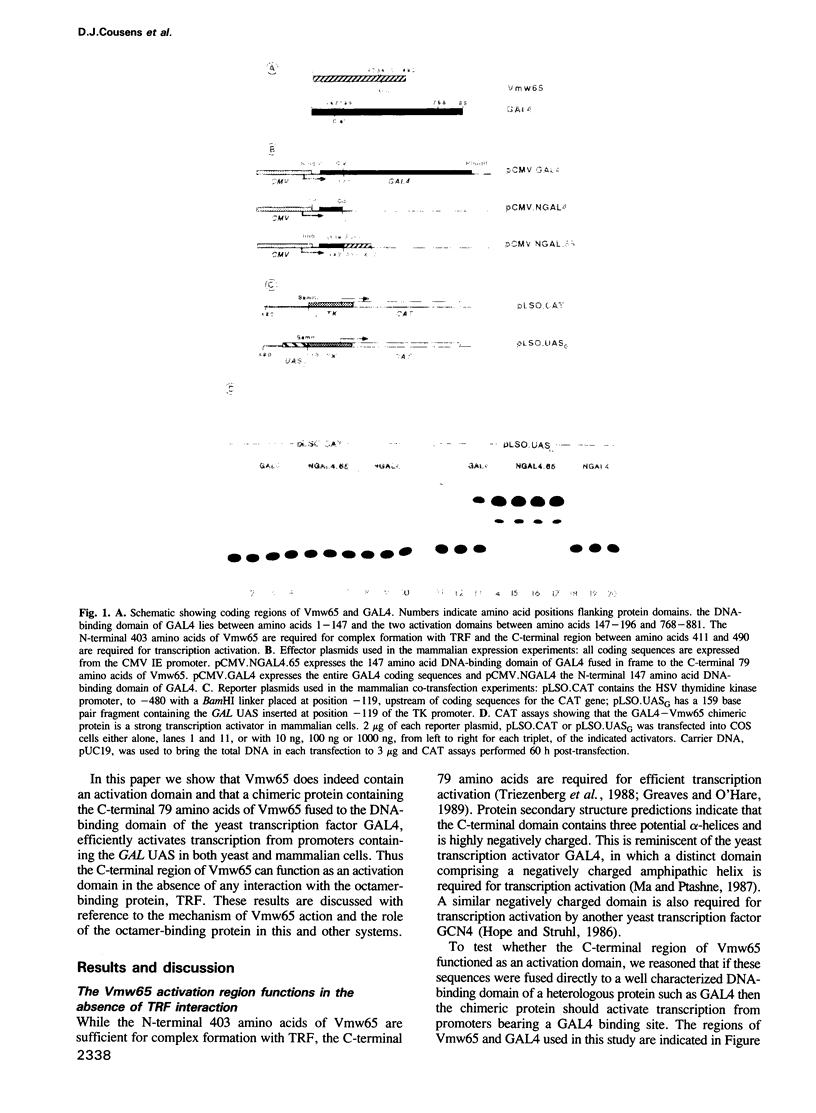
Activation of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression normally requires the formation of a ternary complex between a virus trans-activator, Vmw65, a cellular octamer-binding protein, TRF and the cis-acting target sequence, the TAATGARAT motif. We report that the C-terminal 79 amino acids of Vmw65, which contain a potential acidic amphipathic helix, can activate transcription in both yeast and mammalian cells in the absence of TRF interaction when fused to the DNA-binding domain of the yeast transcription factor, GAL4. Together with our previous report which showed that the recruitment of TRF to the DNA by Vmw65 is insufficient for transcription activation, these results indicate that the octamer binding protein may not be directly involved in transcriptional induction mediated by Vmw65. The TRF-Vmw65 complex may therefore represent a novel class of transcription activator in which the protein domain responsible for sequence-specific DNA binding, present in TRF, and that necessary for induction of transcription, within Vmw65, are located on separate proteins. These results are discussed with reference to combinatorial transcriptional control and the role of octamer-binding proteins in other systems.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr MAT alpha 1 protein, a yeast transcription activator, binds synergistically with a second protein to a set of cell-type-specific genes. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):681–691. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90326-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J., Cohen S. N. Analysis of gene control signals by DNA fusion and cloning in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1980 Apr;138(2):179–207. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90283-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Trans-activation of human immunodeficiency virus occurs via a bimodal mechanism. Cell. 1986 Sep 26;46(7):973–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90696-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dobson M. J., Tuite M. F., Mellor J., Roberts N. A., King R. M., Burke D. C., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of human interferon-alpha directed by the TRP1 5' region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2287–2302. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fletcher C., Heintz N., Roeder R. G. Purification and characterization of OTF-1, a transcription factor regulating cell cycle expression of a human histone H2b gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):773–781. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90100-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Transcription in yeast activated by a putative amphipathic alpha helix linked to a DNA binding unit. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):670–672. doi: 10.1038/330670a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves R., O'Hare P. Separation of requirements for protein-DNA complex assembly from those for functional activity in the herpes simplex virus regulatory protein Vmw65. J Virol. 1989 Apr;63(4):1641–1650. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.4.1641-1650.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Moye-Rowley W. S., Parker C. S. Transcriptional activation by the SV40 AP-1 recognition element in yeast is mediated by a factor similar to AP-1 that is distinct from GCN4. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Mahadevan S., Struhl K. Structural and functional characterization of the short acidic transcriptional activation region of yeast GCN4 protein. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):635–640. doi: 10.1038/333635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston S. A., Hopper J. E. Isolation of the yeast regulatory gene GAL4 and analysis of its dosage effects on the galactose/melibiose regulon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6971–6975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kakidani H., Ptashne M. GAL4 activates gene expression in mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):161–167. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90504-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Differentiation and DNA contact points of host proteins binding at the cis site for virion-mediated induction of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus 1. J Virol. 1988 Apr;62(4):1145–1157. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.4.1145-1157.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Host cell proteins bind to the cis-acting site required for virion-mediated induction of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(1):71–75. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.1.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Separation of sequences defining basal expression from those conferring alpha gene recognition within the regulatory domains of herpes simplex virus 1 alpha genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4065–4069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBowitz J. H., Kobayashi T., Staudt L., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. Octamer-binding proteins from B or HeLa cells stimulate transcription of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter in vitro. Genes Dev. 1988 Oct;2(10):1227–1237. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.10.1227. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: the alpha 27 gene promoter-thymidine kinase chimera is positively regulated in converted L cells. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):1015–1023. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.1015-1023.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Campbell M. E., Haarr L., Frame M. C., Parris D. S., Murphy M., Hope R. G., Muller M. T., Preston C. M. The 65,000-Mr DNA-binding and virion trans-inducing proteins of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1987 Aug;61(8):2428–2437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.8.2428-2437.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight J. L., Kristie T. M., Roizman B. Binding of the virion protein mediating alpha gene induction in herpes simplex virus 1-infected cells to its cis site requires cellular proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Oct;84(20):7061–7065. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.20.7061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger D., White J. H., Chambon P. The human oestrogen receptor functions in yeast. Nature. 1988 Jul 7;334(6177):31–36. doi: 10.1038/334031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R., Haigh A. Direct combinatorial interaction between a herpes simplex virus regulatory protein and a cellular octamer-binding factor mediates specific induction of virus immediate-early gene expression. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4231–4238. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03320.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Goding C. R. Herpes simplex virus regulatory elements and the immunoglobulin octamer domain bind a common factor and are both targets for virion transactivation. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):435–445. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Hare P., Hayward G. S. Comparison of upstream sequence requirements for positive and negative regulation of a herpes simplex virus immediate-early gene by three virus-encoded trans-acting factors. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):190–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.190-199.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill E. A., Kelly T. J. Purification and characterization of nuclear factor III (origin recognition protein C), a sequence-specific DNA binding protein required for efficient initiation of adenovirus DNA replication. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 15;263(2):931–937. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Frame M. C., Campbell M. E. A complex formed between cell components and an HSV structural polypeptide binds to a viral immediate early gene regulatory DNA sequence. Cell. 1988 Feb 12;52(3):425–434. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80035-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruijn G. J., van Driel W., van der Vliet P. C. Nuclear factor III, a novel sequence-specific DNA-binding protein from HeLa cells stimulating adenovirus DNA replication. Nature. 1986 Aug 14;322(6080):656–659. doi: 10.1038/322656a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Ma J., Triezenberg S., Ptashne M. GAL4-VP16 is an unusually potent transcriptional activator. Nature. 1988 Oct 6;335(6190):563–564. doi: 10.1038/335563a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P. E., Schröter H., Nordheim A. The ability of a ternary complex to form over the serum response element correlates with serum inducibility of the human c-fos promoter. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):563–572. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90579-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. The JUN oncoprotein, a vertebrate transcription factor, activates transcription in yeast. Nature. 1988 Apr 14;332(6165):649–650. doi: 10.1038/332649a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturm R., Baumruker T., Franza B. R., Jr, Herr W. A 100-kD HeLa cell octamer binding protein (OBP100) interacts differently with two separate octamer-related sequences within the SV40 enhancer. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1147–1160. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1147. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triezenberg S. J., Kingsbury R. C., McKnight S. L. Functional dissection of VP16, the trans-activator of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene expression. Genes Dev. 1988 Jun;2(6):718–729. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.6.718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wasylyk B. Transcription elements and factors of RNA polymerase B promoters of higher eukaryotes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1988;23(2):77–120. doi: 10.3109/10409238809088317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- West R. W., Jr, Yocum R. R., Ptashne M. Saccharomyces cerevisiae GAL1-GAL10 divergent promoter region: location and function of the upstream activating sequence UASG. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Nov;4(11):2467–2478. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.11.2467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Clements J. B. Replication origins and a sequence involved in coordinate induction of the immediate-early gene family are conserved in an intergenic region of herpes simplex virus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Feb 24;12(4):2061–2079. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.4.2061. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]