Abstract
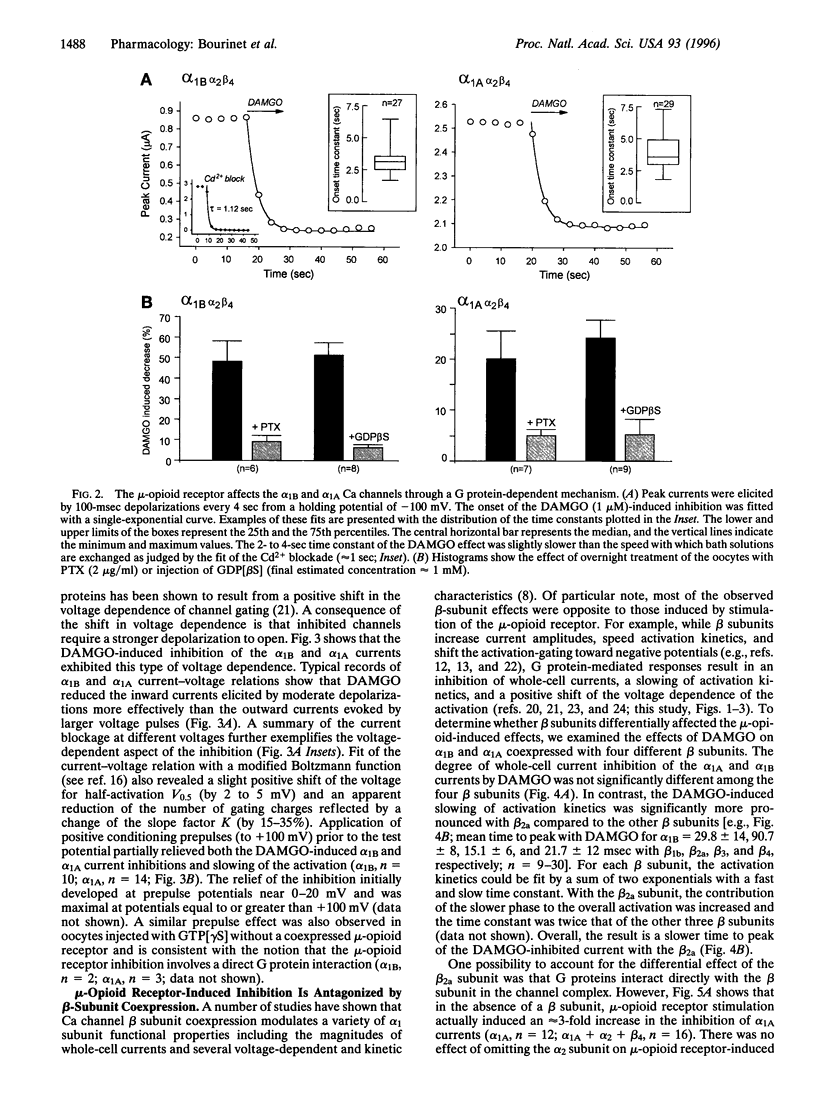
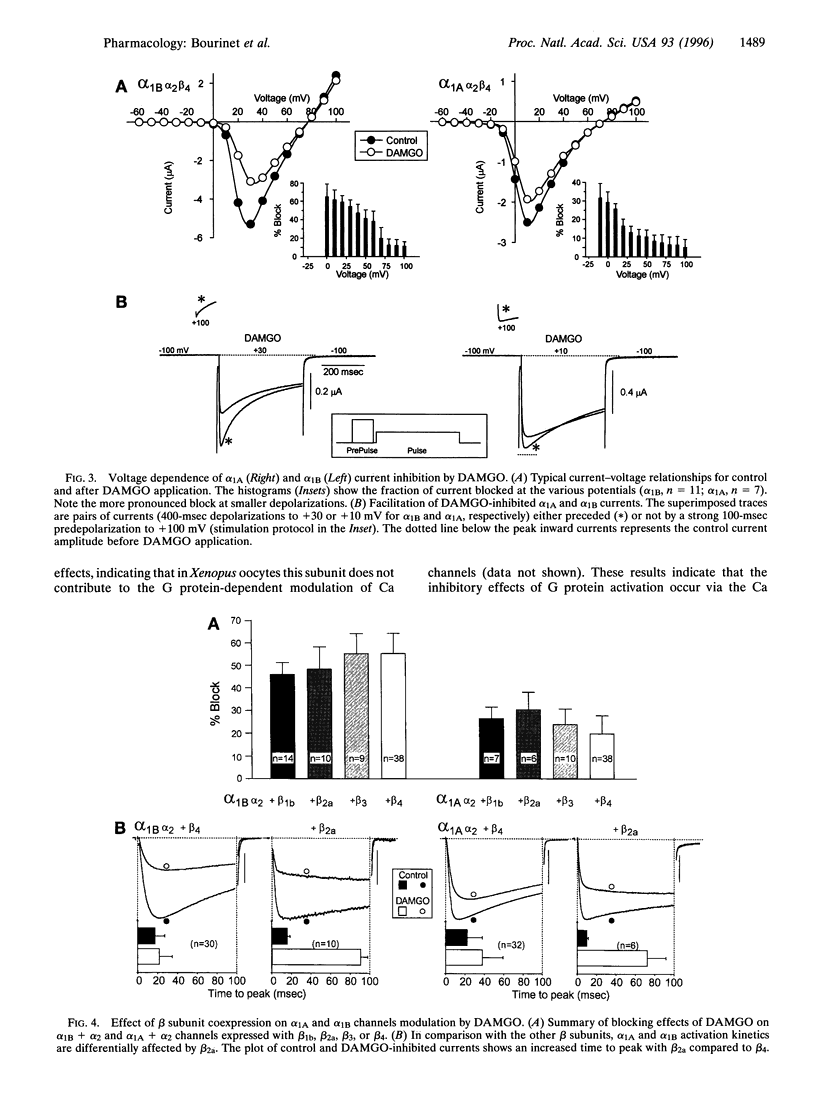
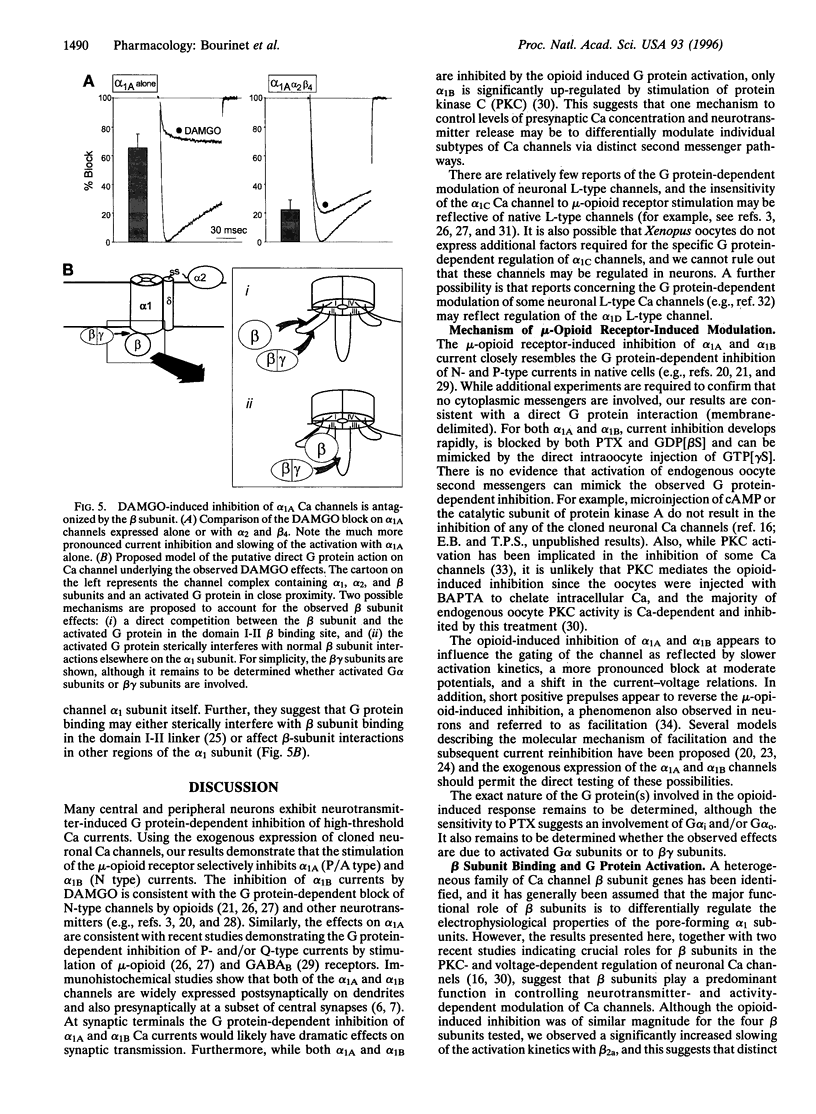
The modulation of a family of cloned neuronal calcium channels by stimulation of a coexpressed mu opioid receptor was studied by transient expression in Xenopus oocytes. Activation of the morphine receptor with the synthetic enkephalin [D-Ala2,N-Me-Phe4,Gly-ol5]enkephalin (DAMGO) resulted in a rapid inhibition of alpha1A (by approximately 20%) and alpha1B (by approximately 55%) currents while alpha1C and alpha1E currents were not significantly affected. The opioid-induced effects on alpha1A and alpha1B currents were blocked by pertussis toxin and the GTP analogue guanosine 5'-[beta-thio]diphosphate. Similar to modulation of native calcium currents, DAMGO induced a slowing of the activation kinetics and exhibited a voltage-dependent inhibition that was partially relieved by application of strong depolarizing pulses. alpha1A currents were still inhibited in the absence of coexpressed Ca channel alpha2 and beta subunits, suggesting that the response is mediated by the alpha1 subunit. Furthermore, the sensitivity of alpha1A currents to DAMGO-induced inhibition was increased approximately 3-fold in the absence of a beta subunit. Overall, the results show that the alpha1A (P/Q type) and the alpha1B (N type) calcium channels are selectively modulated by a GTP-binding protein (G protein). The results raise the possibility of competitive interactions between beta subunit and G protein binding to the alpha1 subunit, shifting gating in opposite directions. At presynaptic terminals, the G protein-dependent inhibition may result in decreased synaptic transmission and play a key role in the analgesic effect of opioids and morphine.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bean B. P. Classes of calcium channels in vertebrate cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1989;51:367–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.51.030189.002055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bean B. P. Neurotransmitter inhibition of neuronal calcium currents by changes in channel voltage dependence. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):153–156. doi: 10.1038/340153a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boland L. M., Bean B. P. Modulation of N-type calcium channels in bullfrog sympathetic neurons by luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone: kinetics and voltage dependence. J Neurosci. 1993 Feb;13(2):516–533. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-02-00516.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourinet E., Charnet P., Tomlinson W. J., Stea A., Snutch T. P., Nargeot J. Voltage-dependent facilitation of a neuronal alpha 1C L-type calcium channel. EMBO J. 1994 Nov 1;13(21):5032–5039. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1994.tb06832.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell V., Berrow N. S., Fitzgerald E. M., Brickley K., Dolphin A. C. Inhibition of the interaction of G protein G(o) with calcium channels by the calcium channel beta-subunit in rat neurones. J Physiol. 1995 Jun 1;485(Pt 2):365–372. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1995.sp020735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castellano A., Wei X., Birnbaumer L., Perez-Reyes E. Cloning and expression of a neuronal calcium channel beta subunit. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jun 15;268(17):12359–12366. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnet P., Bourinet E., Dubel S. J., Snutch T. P., Nargeot J. Calcium currents recorded from a neuronal alpha 1C L-type calcium channel in Xenopus oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1994 May 9;344(1):87–90. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(94)00357-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y., Mestek A., Liu J., Hurley J. A., Yu L. Molecular cloning and functional expression of a mu-opioid receptor from rat brain. Mol Pharmacol. 1993 Jul;44(1):8–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Waard M., Witcher D. R., Pragnell M., Liu H., Campbell K. P. Properties of the alpha 1-beta anchoring site in voltage-dependent Ca2+ channels. J Biol Chem. 1995 May 19;270(20):12056–12064. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.20.12056. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delcour A. H., Tsien R. W. Altered prevalence of gating modes in neurotransmitter inhibition of N-type calcium channels. Science. 1993 Feb 12;259(5097):980–984. doi: 10.1126/science.8094902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diversé-Pierluissi M., Goldsmith P. K., Dunlap K. Transmitter-mediated inhibition of N-type calcium channels in sensory neurons involves multiple GTP-binding proteins and subunits. Neuron. 1995 Jan;14(1):191–200. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90254-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolphin A. C. The G.L. Brown Prize Lecture. Voltage-dependent calcium channels and their modulation by neurotransmitters and G proteins. Exp Physiol. 1995 Jan;80(1):1–36. doi: 10.1113/expphysiol.1995.sp003825. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Jones S. W. Concentration dependence of neurotransmitter effects on calcium current kinetics in frog sympathetic neurones. J Physiol. 1994 Nov 15;481(Pt 1):35–46. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1994.sp020417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Kammermeier P. J., Jones S. W. Calcium current modulation in frog sympathetic neurones: L-current is relatively insensitive to neurotransmitters. J Physiol. 1992 Oct;456:107–123. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1992.sp019329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elmslie K. S., Kammermeier P. J., Jones S. W. Reevaluation of Ca2+ channel types and their modulation in bullfrog sympathetic neurons. Neuron. 1994 Jul;13(1):217–228. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(94)90471-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haws C. M., Slesinger P. A., Lansman J. B. Dihydropyridine- and omega-conotoxin-sensitive Ca2+ currents in cerebellar neurons: persistent block of L-type channels by a pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein. J Neurosci. 1993 Mar;13(3):1148–1156. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.13-03-01148.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hille B. Modulation of ion-channel function by G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 1994 Dec;17(12):531–536. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(94)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai H. Tonic inhibition and rebound facilitation of a neuronal calcium channel by a GTP-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8855–8859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mintz I. M., Bean B. P. GABAB receptor inhibition of P-type Ca2+ channels in central neurons. Neuron. 1993 May;10(5):889–898. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90204-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pragnell M., De Waard M., Mori Y., Tanabe T., Snutch T. P., Campbell K. P. Calcium channel beta-subunit binds to a conserved motif in the I-II cytoplasmic linker of the alpha 1-subunit. Nature. 1994 Mar 3;368(6466):67–70. doi: 10.1038/368067a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhim H., Miller R. J. Opioid receptors modulate diverse types of calcium channels in the nucleus tractus solitarius of the rat. J Neurosci. 1994 Dec;14(12):7608–7615. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.14-12-07608.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rusin K. I., Moises H. C. mu-Opioid receptor activation reduces multiple components of high-threshold calcium current in rat sensory neurons. J Neurosci. 1995 Jun;15(6):4315–4327. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-06-04315.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sather W. A., Tanabe T., Zhang J. F., Mori Y., Adams M. E., Tsien R. W. Distinctive biophysical and pharmacological properties of class A (BI) calcium channel alpha 1 subunits. Neuron. 1993 Aug;11(2):291–303. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(93)90185-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soong T. W., Stea A., Hodson C. D., Dubel S. J., Vincent S. R., Snutch T. P. Structure and functional expression of a member of the low voltage-activated calcium channel family. Science. 1993 May 21;260(5111):1133–1136. doi: 10.1126/science.8388125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Dubel S. J., Pragnell M., Leonard J. P., Campbell K. P., Snutch T. P. A beta-subunit normalizes the electrophysiological properties of a cloned N-type Ca2+ channel alpha 1-subunit. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1103–1116. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90005-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Soong T. W., Snutch T. P. Determinants of PKC-dependent modulation of a family of neuronal calcium channels. Neuron. 1995 Oct;15(4):929–940. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(95)90183-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stea A., Tomlinson W. J., Soong T. W., Bourinet E., Dubel S. J., Vincent S. R., Snutch T. P. Localization and functional properties of a rat brain alpha 1A calcium channel reflect similarities to neuronal Q- and P-type channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 25;91(22):10576–10580. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.22.10576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson W. J., Stea A., Bourinet E., Charnet P., Nargeot J., Snutch T. P. Functional properties of a neuronal class C L-type calcium channel. Neuropharmacology. 1993 Nov;32(11):1117–1126. doi: 10.1016/0028-3908(93)90006-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. W., Lipscombe D., Madison D. V., Bley K. R., Fox A. P. Multiple types of neuronal calcium channels and their selective modulation. Trends Neurosci. 1988 Oct;11(10):431–438. doi: 10.1016/0166-2236(88)90194-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Hell J. W., Warner C., Dubel S. J., Snutch T. P., Catterall W. A. Biochemical properties and subcellular distribution of an N-type calcium channel alpha 1 subunit. Neuron. 1992 Dec;9(6):1099–1115. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90069-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westenbroek R. E., Sakurai T., Elliott E. M., Hell J. W., Starr T. V., Snutch T. P., Catterall W. A. Immunochemical identification and subcellular distribution of the alpha 1A subunits of brain calcium channels. J Neurosci. 1995 Oct;15(10):6403–6418. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.15-10-06403.1995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Brust P. F., Feldman D. H., Patthi S., Simerson S., Maroufi A., McCue A. F., Veliçelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of an omega-conotoxin-sensitive human N-type calcium channel. Science. 1992 Jul 17;257(5068):389–395. doi: 10.1126/science.1321501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. E., Feldman D. H., McCue A. F., Brenner R., Velicelebi G., Ellis S. B., Harpold M. M. Structure and functional expression of alpha 1, alpha 2, and beta subunits of a novel human neuronal calcium channel subtype. Neuron. 1992 Jan;8(1):71–84. doi: 10.1016/0896-6273(92)90109-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]