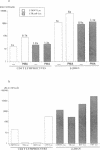
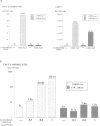
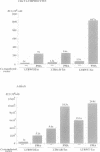
Abstract
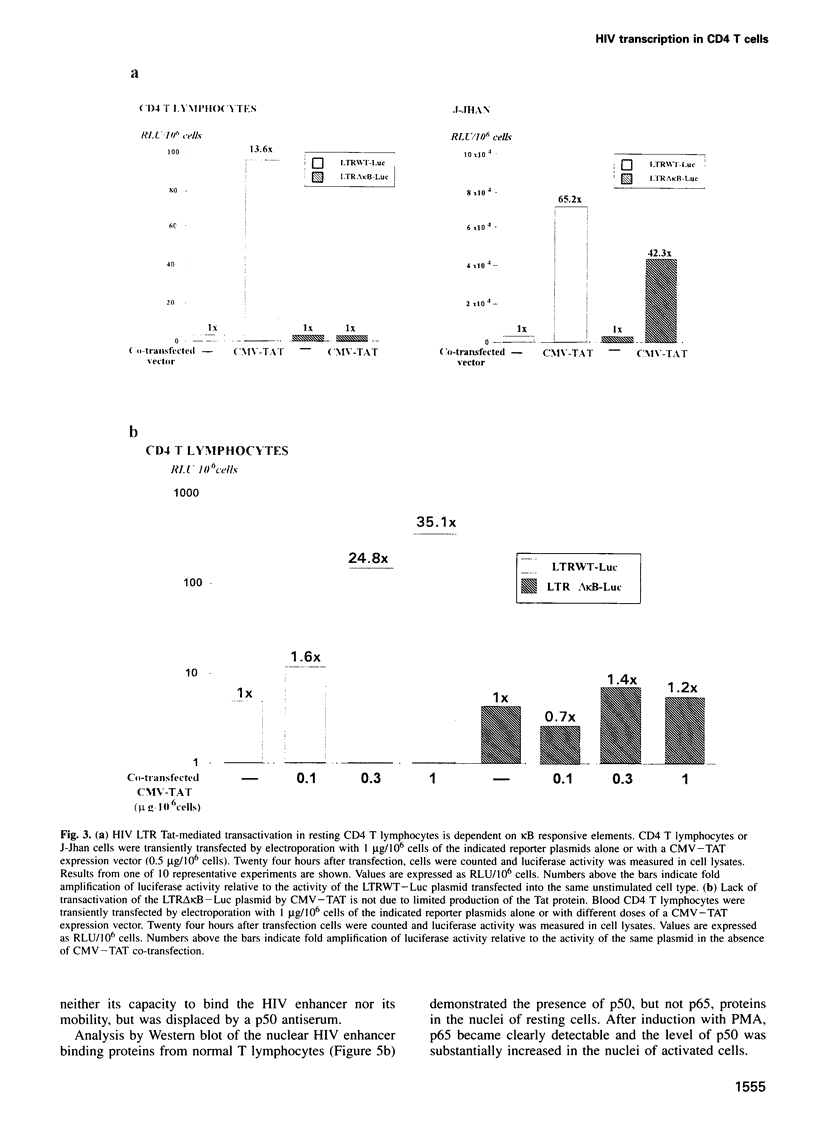
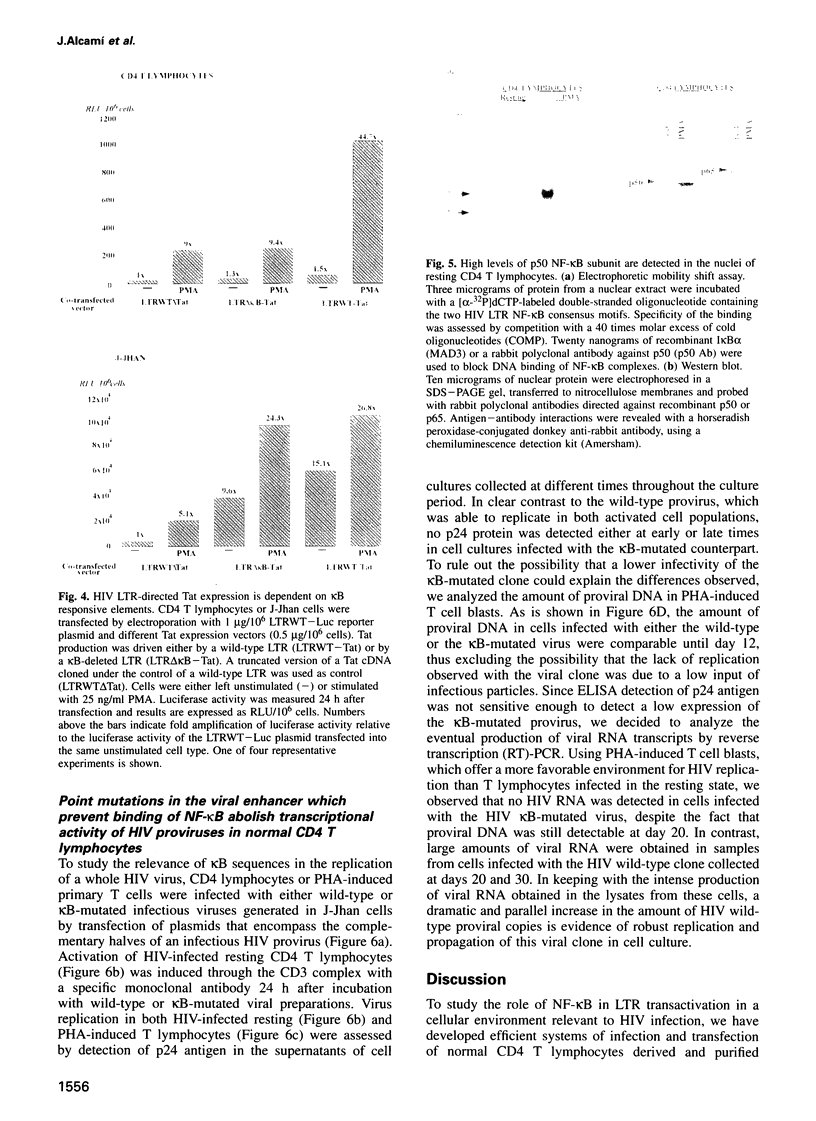
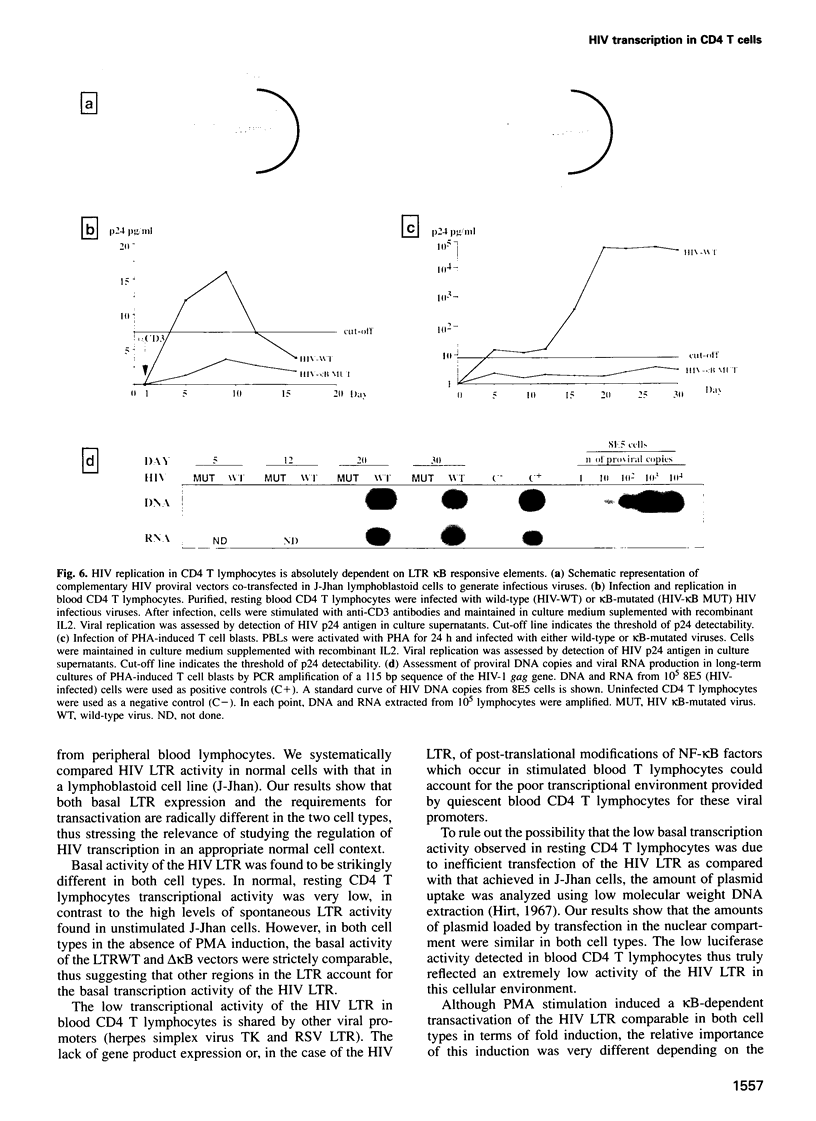
The role of NF-kappa B-dependent signals in activating the transcriptional activity of the HIV regulatory region (LTR) was analyzed by systematic comparison of HIV LTR activity in human CD4 T cells purified from peripheral blood and a transformed lymphoblastoid T cell line. In normal CD4 T cells we also analyzed the role played by the viral kappa B responsive elements in HIV replication. Analysis of nuclear extracts of resting, normal T lymphocytes revealed the presence of the p50, but not the p65, NF-kappa B subunit and the induction by phorbol esters of bona fide (p50-p65) NF-kappa B complexes. In parallel, we observed clear enhancer-dependent HIV LTR transactivation comparable in intensity with that observed in lymphoblastoid cells. We show that unstimulated CD4 T lymphocytes offer a cellular environment of very low permissivity to HIV LTR functioning. This was in sharp contrast to the high spontaneous LTR activity observed in lymphoblastoid T cells, where LTR activity was essentially independent of kappa B-responsive elements. Due to the low basal LTR activity in resting T lymphocytes, NF-kappa B-dependent transactivation was a sine qua non event for induction of the HIV LTR. Surprisingly, even the function of HIV Tat in resting CD4 T lymphocytes was found to be absolutely dependent on LTR kappa B responsive elements. The relevance of these observations obtained in transient transfections was confirmed by the incapacity of blood CD4 T lymphocytes infected with an HIV infectious provirus carrying critical point mutations in the kappa B responsive elements to show any detectable transcriptional activity upon cell activation and prolonged culture in vitro.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF
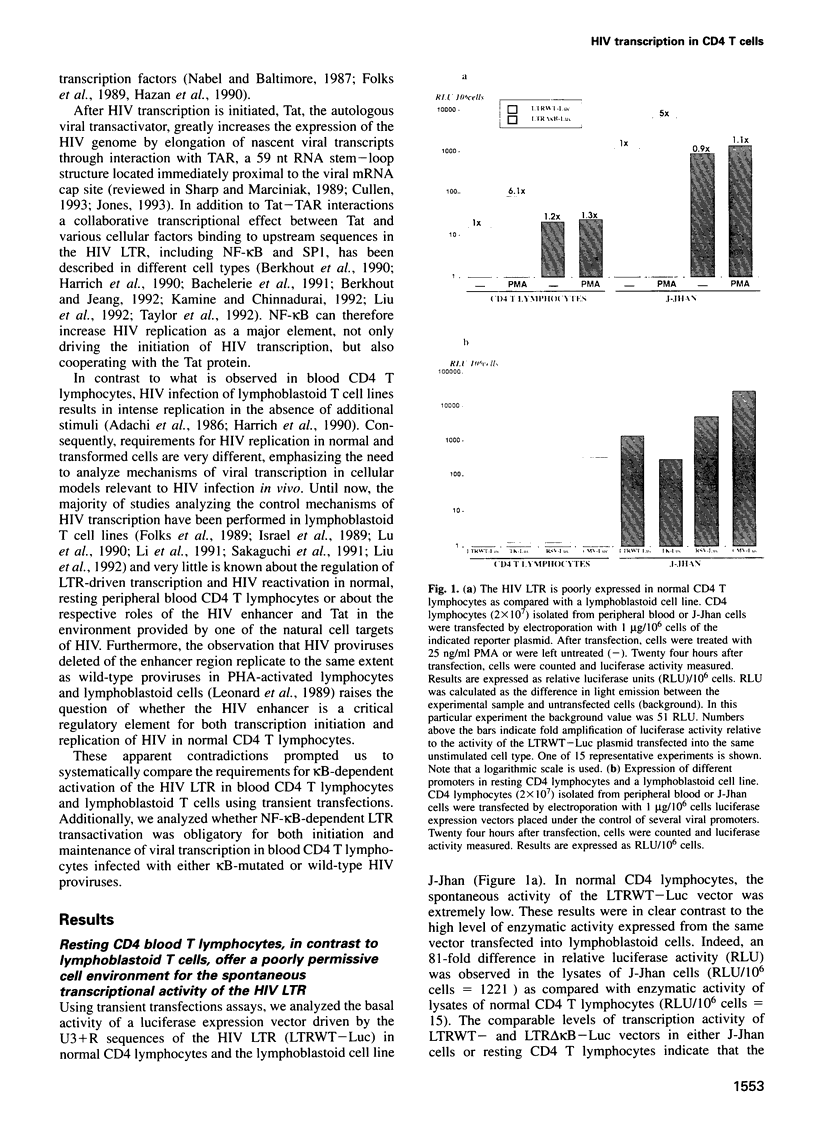




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Gendelman H. E., Koenig S., Folks T., Willey R., Rabson A., Martin M. A. Production of acquired immunodeficiency syndrome-associated retrovirus in human and nonhuman cells transfected with an infectious molecular clone. J Virol. 1986 Aug;59(2):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.2.284-291.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Fernandez B., Dominguez I., Jacqué J. M., Thomas D., Diaz-Meco M. T., Moscat J., Virelizier J. L. Phosphatidylcholine hydrolysis activates NF-kappa B and increases human immunodeficiency virus replication in human monocytes and T lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993 Nov;67(11):6596–6604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.11.6596-6604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachelerie F., Alcami J., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Virelizier J. L. HIV enhancer activity perpetuated by NF-kappa B induction on infection of monocytes. Nature. 1991 Apr 25;350(6320):709–712. doi: 10.1038/350709a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ballard D. W., Dixon E. P., Peffer N. J., Bogerd H., Doerre S., Stein B., Greene W. C. The 65-kDa subunit of human NF-kappa B functions as a potent transcriptional activator and a target for v-Rel-mediated repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1875–1879. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barré-Sinoussi F., Chermann J. C., Rey F., Nugeyre M. T., Chamaret S., Gruest J., Dauguet C., Axler-Blin C., Vézinet-Brun F., Rouzioux C. Isolation of a T-lymphotropic retrovirus from a patient at risk for acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Science. 1983 May 20;220(4599):868–871. doi: 10.1126/science.6189183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beg A. A., Finco T. S., Nantermet P. V., Baldwin A. S., Jr Tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 lead to phosphorylation and loss of I kappa B alpha: a mechanism for NF-kappa B activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;13(6):3301–3310. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.6.3301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Gatignol A., Rabson A. B., Jeang K. T. TAR-independent activation of the HIV-1 LTR: evidence that tat requires specific regions of the promoter. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):757–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90120-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berkhout B., Jeang K. T. Functional roles for the TATA promoter and enhancers in basal and Tat-induced expression of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1992 Jan;66(1):139–149. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.1.139-149.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bours V., Burd P. R., Brown K., Villalobos J., Park S., Ryseck R. P., Bravo R., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. A novel mitogen-inducible gene product related to p50/p105-NF-kappa B participates in transactivation through a kappa B site. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):685–695. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukrinsky M. I., Stanwick T. L., Dempsey M. P., Stevenson M. Quiescent T lymphocytes as an inducible virus reservoir in HIV-1 infection. Science. 1991 Oct 18;254(5030):423–427. doi: 10.1126/science.1925601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R. Does HIV-1 Tat induce a change in viral initiation rights? Cell. 1993 May 7;73(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90126-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cullen B. R., Greene W. C. Regulatory pathways governing HIV-1 replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):423–426. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90420-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duh E. J., Maury W. J., Folks T. M., Fauci A. S., Rabson A. B. Tumor necrosis factor alpha activates human immunodeficiency virus type 1 through induction of nuclear factor binding to the NF-kappa B sites in the long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(15):5974–5978. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.15.5974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Embretson J., Zupancic M., Ribas J. L., Burke A., Racz P., Tenner-Racz K., Haase A. T. Massive covert infection of helper T lymphocytes and macrophages by HIV during the incubation period of AIDS. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):359–362. doi: 10.1038/362359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Clouse K. A., Justement J., Rabson A., Duh E., Kehrl J. H., Fauci A. S. Tumor necrosis factor alpha induces expression of human immunodeficiency virus in a chronically infected T-cell clone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2365–2368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T. M., Powell D., Lightfoote M., Koenig S., Fauci A. S., Benn S., Rabson A., Daugherty D., Gendelman H. E., Hoggan M. D. Biological and biochemical characterization of a cloned Leu-3- cell surviving infection with the acquired immune deficiency syndrome retrovirus. J Exp Med. 1986 Jul 1;164(1):280–290. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.1.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folks T., Kelly J., Benn S., Kinter A., Justement J., Gold J., Redfield R., Sell K. W., Fauci A. S. Susceptibility of normal human lymphocytes to infection with HTLV-III/LAV. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 1;136(11):4049–4053. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso G., Bours V., Azarenko V., Park S., Tomita-Yamaguchi M., Kanno T., Brown K., Siebenlist U. The oncoprotein Bcl-3 can facilitate NF-kappa B-mediated transactivation by removing inhibiting p50 homodimers from select kappa B sites. EMBO J. 1993 Oct;12(10):3893–3901. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06067.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franzoso G., Bours V., Park S., Tomita-Yamaguchi M., Kelly K., Siebenlist U. The candidate oncoprotein Bcl-3 is an antagonist of p50/NF-kappa B-mediated inhibition. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):339–342. doi: 10.1038/359339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Baltimore D. Independent modes of transcriptional activation by the p50 and p65 subunits of NF-kappa B. Genes Dev. 1992 May;6(5):775–787. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.5.775. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaynor R. Cellular transcription factors involved in the regulation of HIV-1 gene expression. AIDS. 1992 Apr;6(4):347–363. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199204000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrich D., Garcia J., Mitsuyasu R., Gaynor R. TAR independent activation of the human immunodeficiency virus in phorbol ester stimulated T lymphocytes. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(13):4417–4423. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07892.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hazan U., Thomas D., Alcami J., Bachelerie F., Israel N., Yssel H., Virelizier J. L., Arenzana-Seisdedos F. Stimulation of a human T-cell clone with anti-CD3 or tumor necrosis factor induces NF-kappa B translocation but not human immunodeficiency virus 1 enhancer-dependent transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7861–7865. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7861. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Israël N., Hazan U., Alcami J., Munier A., Arenzana-Seisdedos F., Bachelerie F., Israël A., Virelizier J. L. Tumor necrosis factor stimulates transcription of HIV-1 in human T lymphocytes, independently and synergistically with mitogens. J Immunol. 1989 Dec 15;143(12):3956–3960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A. HIV trans-activation and transcription control mechanisms. New Biol. 1989 Nov;1(2):127–135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A. Tat and the HIV-1 promoter. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):461–468. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90012-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamine J., Chinnadurai G. Synergistic activation of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 promoter by the viral Tat protein and cellular transcription factor Sp1. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3932–3936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3932-3936.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kashanchi F., Piras G., Radonovich M. F., Duvall J. F., Fattaey A., Chiang C. M., Roeder R. G., Brady J. N. Direct interaction of human TFIID with the HIV-1 transactivator tat. Nature. 1994 Jan 20;367(6460):295–299. doi: 10.1038/367295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard J., Parrott C., Buckler-White A. J., Turner W., Ross E. K., Martin M. A., Rabson A. B. The NF-kappa B binding sites in the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat are not required for virus infectivity. J Virol. 1989 Nov;63(11):4919–4924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.11.4919-4924.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y. C., Ross J., Scheppler J. A., Franza B. R., Jr An in vitro transcription analysis of early responses of the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 long terminal repeat to different transcriptional activators. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Apr;11(4):1883–1893. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.4.1883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Baltimore D. Regulation of the NF-kappa B/rel transcription factor and I kappa B inhibitor system. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1993 Jun;5(3):477–487. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(93)90014-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J., Perkins N. D., Schmid R. M., Nabel G. J. Specific NF-kappa B subunits act in concert with Tat to stimulate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 transcription. J Virol. 1992 Jun;66(6):3883–3887. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.6.3883-3887.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y. C., Touzjian N., Stenzel M., Dorfman T., Sodroski J. G., Haseltine W. A. Identification of cis-acting repressive sequences within the negative regulatory element of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1990 Oct;64(10):5226–5229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.64.10.5226-5229.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDougal J. S., Mawle A., Cort S. P., Nicholson J. K., Cross G. D., Scheppler-Campbell J. A., Hicks D., Sligh J. Cellular tropism of the human retrovirus HTLV-III/LAV. I. Role of T cell activation and expression of the T4 antigen. J Immunol. 1985 Nov;135(5):3151–3162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moses A. V., Ibanez C., Gaynor R., Ghazal P., Nelson J. A. Differential role of long terminal repeat control elements for the regulation of basal and Tat-mediated transcription of the human immunodeficiency virus in stimulated and unstimulated primary human macrophages. J Virol. 1994 Jan;68(1):298–307. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.1.298-307.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G., Baltimore D. An inducible transcription factor activates expression of human immunodeficiency virus in T cells. Nature. 1987 Apr 16;326(6114):711–713. doi: 10.1038/326711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan G. P., Ghosh S., Liou H. C., Tempst P., Baltimore D. DNA binding and I kappa B inhibition of the cloned p65 subunit of NF-kappa B, a rel-related polypeptide. Cell. 1991 Mar 8;64(5):961–969. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90320-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn L., Kunkel S., Nabel G. J. Tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin 1 stimulate the human immunodeficiency virus enhancer by activation of the nuclear factor kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(7):2336–2340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.7.2336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pantaleo G., Graziosi C., Demarest J. F., Butini L., Montroni M., Fox C. H., Orenstein J. M., Kotler D. P., Fauci A. S. HIV infection is active and progressive in lymphoid tissue during the clinically latent stage of disease. Nature. 1993 Mar 25;362(6418):355–358. doi: 10.1038/362355a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Popovic M., Sarngadharan M. G., Read E., Gallo R. C. Detection, isolation, and continuous production of cytopathic retroviruses (HTLV-III) from patients with AIDS and pre-AIDS. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):497–500. doi: 10.1126/science.6200935. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryseck R. P., Bull P., Takamiya M., Bours V., Siebenlist U., Dobrzanski P., Bravo R. RelB, a new Rel family transcription activator that can interact with p50-NF-kappa B. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Feb;12(2):674–684. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.2.674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakaguchi M., Zenzie-Gregory B., Groopman J. E., Smale S. T., Kim S. Y. Alternative pathway for induction of human immunodeficiency virus gene expression: involvement of the general transcription machinery. J Virol. 1991 Oct;65(10):5448–5456. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.10.5448-5456.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela K., Muchmore E., Girard M., Fultz P., Baltimore D. High viral load in lymph nodes and latent human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) in peripheral blood cells of HIV-1-infected chimpanzees. J Virol. 1993 Dec;67(12):7423–7427. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7423-7427.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmid R. M., Perkins N. D., Duckett C. S., Andrews P. C., Nabel G. J. Cloning of an NF-kappa B subunit which stimulates HIV transcription in synergy with p65. Nature. 1991 Aug 22;352(6337):733–736. doi: 10.1038/352733a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitz M. L., Baeuerle P. A. The p65 subunit is responsible for the strong transcription activating potential of NF-kappa B. EMBO J. 1991 Dec;10(12):3805–3817. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb04950.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz O., Virelizier J. L., Montagnier L., Hazan U. A microtransfection method using the luciferase-encoding reporter gene for the assay of human immunodeficiency virus LTR promoter activity. Gene. 1990 Apr 16;88(2):197–205. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90032-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A., Marciniak R. A. HIV TAR: an RNA enhancer? Cell. 1989 Oct 20;59(2):229–230. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90279-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. P., Pomerantz R., Bagasra O., Chowdhury M., Rappaport J., Khalili K., Amini S. TAR-independent transactivation by Tat in cells derived from the CNS: a novel mechanism of HIV-1 gene regulation. EMBO J. 1992 Sep;11(9):3395–3403. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05418.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong-Starkesen S. E., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Signaling through T lymphocyte surface proteins, TCR/CD3 and CD28, activates the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. J Immunol. 1989 Jan 15;142(2):702–707. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Virelizier J. L. Cellular activation and human immunodeficiency virus infection. Curr Opin Immunol. 1989;2(3):409–413. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(89)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zack J. A., Arrigo S. J., Weitsman S. R., Go A. S., Haislip A., Chen I. S. HIV-1 entry into quiescent primary lymphocytes: molecular analysis reveals a labile, latent viral structure. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):213–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90802-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]