Abstract
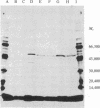
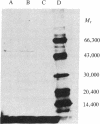
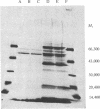
The murine lymphoma cell line LSTRA expresses high levels of a membrane-associated tyrosine protein kinase, which we now show to be acylated by [3H]myristate in vivo. This [3H]myristate-labeled tyrosine protein kinase is immunoprecipitated from detergent extracts of postnuclear particulate fractions with an antibody directed against its single site of tyrosine phosphorylation. This site has an amino acid sequence also found in the transforming proteins of the Rous sarcoma and Y73 viruses. Preincubation of the antibody with a peptide containing the same sequence completely blocks this immunoprecipitation. The [3H]myristate linkage to the protein is stable in boiling 2% NaDodSO4/0.125 M Tris Cl, pH 6.7/5% 2-mercaptoethanol, which suggests an amide rather than an ester linkage. Analogous attempts to label with [3H]palmitate show negligible incorporation into either nonnuclear particulate proteins or immunoprecipitated proteins. Chemical characterization of the immunoprecipitated protein isolated by NaDodSO4/PAGE verifies that the 3H label is in protein-associated myristate. Sonicated 5% NaDodSO4 extracts of LSTRA and YAC-1 (another murine lymphoma line) cells contain quite different distributions of myristoylated proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Agrawal H. C., Schmidt R. E., Agrawal D. In vivo incorporation of [3H]palmitic acid into PO protein, the major intrinsic protein of rat sciatic nerve myelin. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6556–6560. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken A., Cohen P., Santikarn S., Williams D. H., Calder A. G., Smith A., Klee C. B. Identification of the NH2-terminal blocking group of calcineurin B as myristic acid. FEBS Lett. 1982 Dec 27;150(2):314–318. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(82)80759-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop R., Martinez R., Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. A tumor promoter stimulates phosphorylation on tyrosine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Sep 15;115(2):536–543. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(83)80178-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolanowski M. A., Earles B. J., Lennarz W. J. Fatty acylation of proteins during development of sea urchin embryos. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4934–4940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borch R. F. Separation of long chain fatty acids as phenacyl esters by high pressure liquid chromatography. Anal Chem. 1975 Dec;47(14):2437–2439. doi: 10.1021/ac60364a037. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carr S. A., Biemann K., Shoji S., Parmelee D. C., Titani K. n-Tetradecanoyl is the NH2-terminal blocking group of the catalytic subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase from bovine cardiac muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Gentry L. E., Rohrschneider L. R., Krebs E. G. Identification of the tyrosine protein kinase from LSTRA cells by use of site-specific antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6676–6680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6676. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Hellstrom K. E., Krebs E. G. A lymphoma cell line expressing elevated levels of tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10738–10742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casnellie J. E., Harrison M. L., Hellstrom K. E., Krebs E. G. A lymphoma protein with an in vitro site of tyrosine phosphorylation homologous to that in pp60src. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):13877–13879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Regulation of cell growth and transformation by tyrosine-specific protein kinases: the search for important cellular substrate proteins. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:125–161. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69075-4_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ek B., Westermark B., Wasteson A., Heldin C. H. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation by platelet-derived growth factor. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):419–420. doi: 10.1038/295419a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garber E. A., Krueger J. G., Hanafusa H., Goldberg A. R. Only membrane-associated RSV src proteins have amino-terminally bound lipid. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):161–163. doi: 10.1038/302161a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore T., Martin G. S. Phorbol ester and diacylglycerol induce protein phosphorylation at tyrosine. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):487–490. doi: 10.1038/306487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Zeidman L., Bernstein I. D., Brown J. P. Cell-mediated reactivity to antigens shared by Moloney-virus-induced lymphomas (LSTRA) and certain 3-methylcholanthrene-induced mouse sarcomas. Int J Cancer. 1979 Apr 15;23(4):555–564. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230418. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Tyrosine protein kinases and their substrates: an overview. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Protein Phosphorylation Res. 1984;17:443–455. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs S., Kull F. C., Jr, Earp H. S., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Somatomedin-C stimulates the phosphorylation of the beta-subunit of its own receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9581–9584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasuga M., Zick Y., Blithe D. L., Crettaz M., Kahn C. R. Insulin stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of the insulin receptor in a cell-free system. Nature. 1982 Aug 12;298(5875):667–669. doi: 10.1038/298667a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krueger J. G., Garber E. A., Goldberg A. R. Subcellular localization of pp60src in RSV-transformed cells. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;107:51–124. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien P. J., Zatz M. Acylation of bovine rhodopsin by [3H]palmitic acid. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5054–5057. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Omary M. B., Trowbridge I. S. Covalent binding of fatty acid to the transferrin receptor in cultured human cells. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):4715–4718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Adams G. A., Gallione C. J. The presence of cysteine in the cytoplasmic domain of the vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is required for palmitate addition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2050–2054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. B., Shia M. A., Pilch P. F. Stimulation of tyrosine-specific phosphorylation in vitro by insulin-like growth factor I. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):438–440. doi: 10.1038/305438a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J. Proteolipids. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:193–206. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A., Oroszlan S. Myristylation of gag-onc fusion proteins in mammalian transforming retroviruses. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):431–437. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90409-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swarup G., Dasgupta J. D., Garbers D. L. Tyrosine protein kinase activity of rat spleen and other tissues. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10341–10347. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ushiro H., Cohen S. Identification of phosphotyrosine as a product of epidermal growth factor-activated protein kinase in A-431 cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Sep 25;255(18):8363–8365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]