Abstract
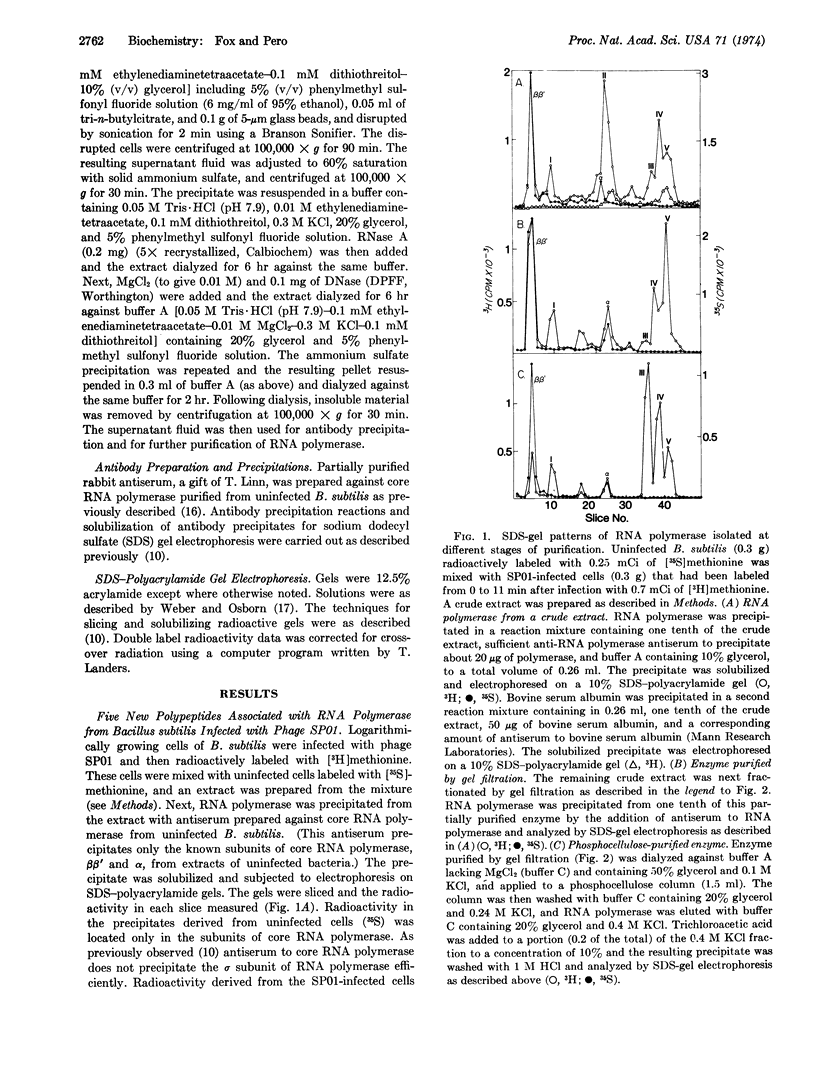
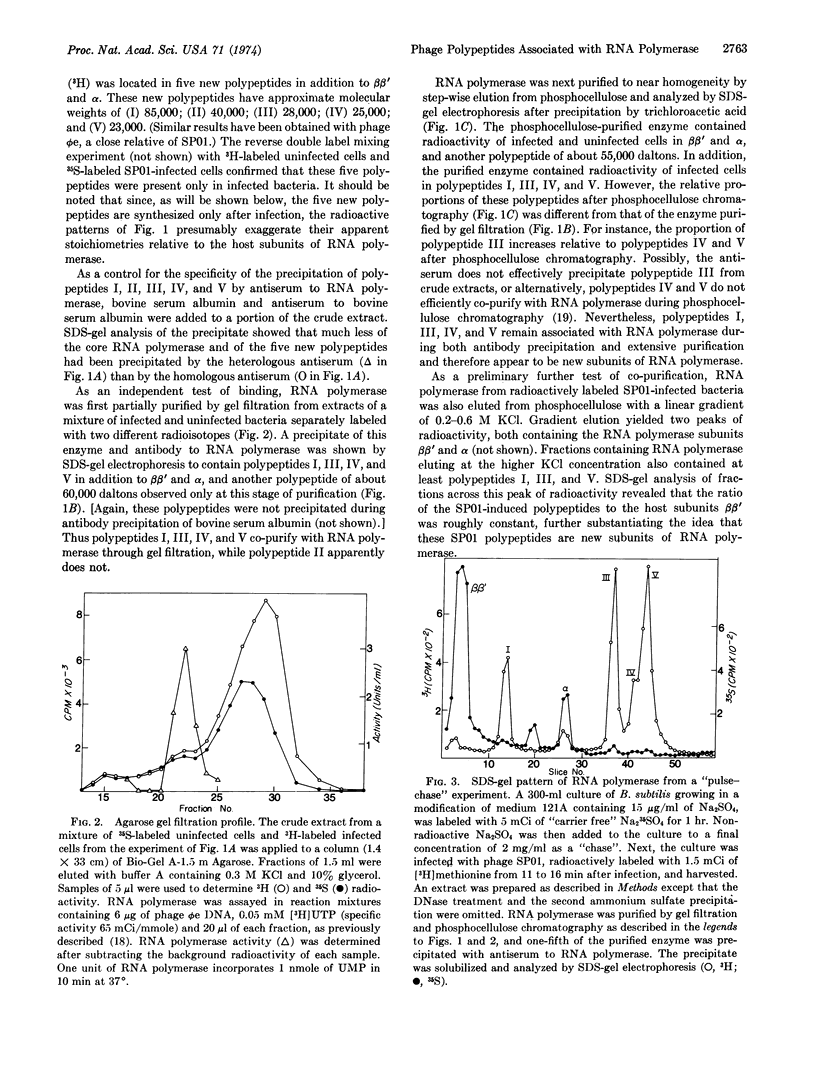
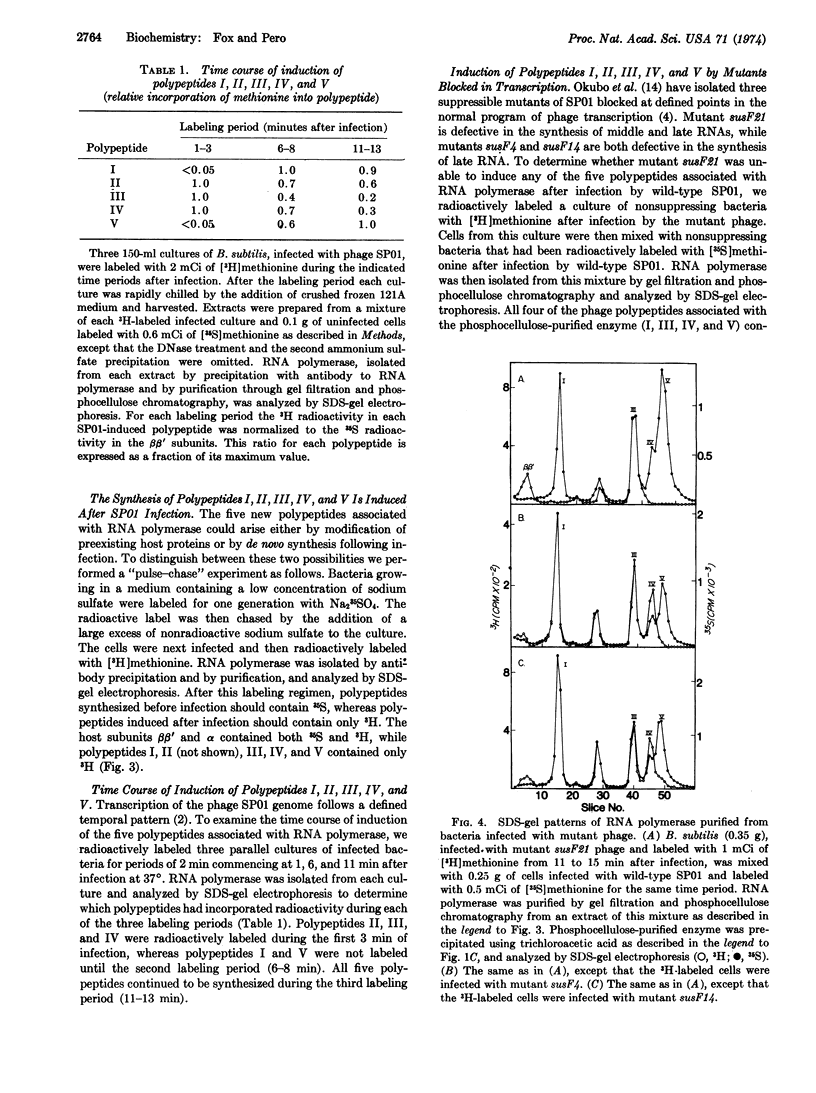
RNA polymerase was precipitated from extracts of Bacillus subtilis infected with phage SP01 by antiserum prepared against core RNA polymerase. As shown by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis, the precipitates contained at least five new polypeptides not present in uninfected bacteria, in addition to the known subunits of RNA polymerase. The molecular weights of these polypeptides are (1) 85,000; (II) 40,000; (III) 28,000; (IV) 25,000; and (V) 23,000. Four of the polypeptides (I, III, IV, and V) co-purified with RNA polymerase through gel filtration and phosphocellulose chromatography. A pulse-chase experiment indicated that all five polypeptides are synthesized de novo after infection. The synthesis of polypeptides II, III, and IV commences almost immediately after infection, while polypeptides I and V first appear several minutes later. A sus mutant blocked early in transcription, susF21 [Fujita, et al. (1971) J. Mol. Biol. 57, 301-317] failed to induce polypeptides I, IV, and V, while two other mutants, susF4 and susF14, blocked late in transcription both failed only to induce polypeptide V.
Keywords: antibody precipitation
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Gesteland R. F. Synthesis of polyoma proteins in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1973 Mar 15;74(4):627–634. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy J. J., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription specificity of an RNA polymerase fraction from bacteriophage SP01-infected B. subtilis. FEBS Lett. 1973 Aug 15;34(2):172–174. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(73)80786-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita D. J., Ohlsson-Wilhelm B. M., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription during bacteriophage SPO1 development: mutations affecting the program of viral transcription. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):301–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90348-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gage L. P., Geiduschek E. P. RNA synthesis during bacteriophage SPO1 development: six classes of SPO1 RNA. J Mol Biol. 1971 Apr 28;57(2):279–297. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Sklar J. Continual requirement for a host RNA polymerase component in a bacteriophage development. Nature. 1969 Mar 1;221(5183):833–836. doi: 10.1038/221833a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenleaf A. L., Linn T. G., Losick R. Isolation of a new RNA polymerase-binding protein from sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Feb;70(2):490–494. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.2.490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M., Whiteley H. R. RNA polymerase from Bacillus amyloliquefaciens infected with phi29 bacteriophage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Aug;70(8):2234–2237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.8.2234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horvitz H. R. Polypeptide bound to the host RNA polymerase is specified by T4 control gene 33. Nat New Biol. 1973 Aug 1;244(135):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio244137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linn T. G., Greenleaf A. L., Shorenstein R. G., Losick R. Loss of the sigma activity of RNA polymerase of Bacillus subtilis during sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jun;70(6):1865–1869. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.6.1865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losick R., Sonenshein A. L. Change in the template specificity of RNA polymerase during sporulation of Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1969 Oct 4;224(5214):35–37. doi: 10.1038/224035a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OKUBO S., STRAUSS B., STODOLSKY M. THE POSSIBLE ROLE OF RECOMBINATION IN THE INFECTION OF COMPETENT BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY BACTERIOPHAGE DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. Virology. 1964 Dec;24:552–562. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(64)90207-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okubo S., Yanagida T., Fujita D. J., Olsson-Wilhelm B. M. The genetics of bacteriophage SPO1. Biken J. 1972 Jun;15(2):81–97. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenshein A. L., Roscoe D. H. The course of phage phi-e infection in sporulating cells of Bacillus subtilis strain 3610. Virology. 1969 Oct;39(2):265–275. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90047-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. In vivo and in vitro transcription by ribonucleic acid polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1483–1489. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiegelman G. B., Whiteley H. R. Purification of ribonucleic acid polymerase from SP82-infected Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1974 Mar 10;249(5):1476–1482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. New small polypeptides associated with DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli after infection with bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):603–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Osborn M. The reliability of molecular weight determinations by dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1969 Aug 25;244(16):4406–4412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


