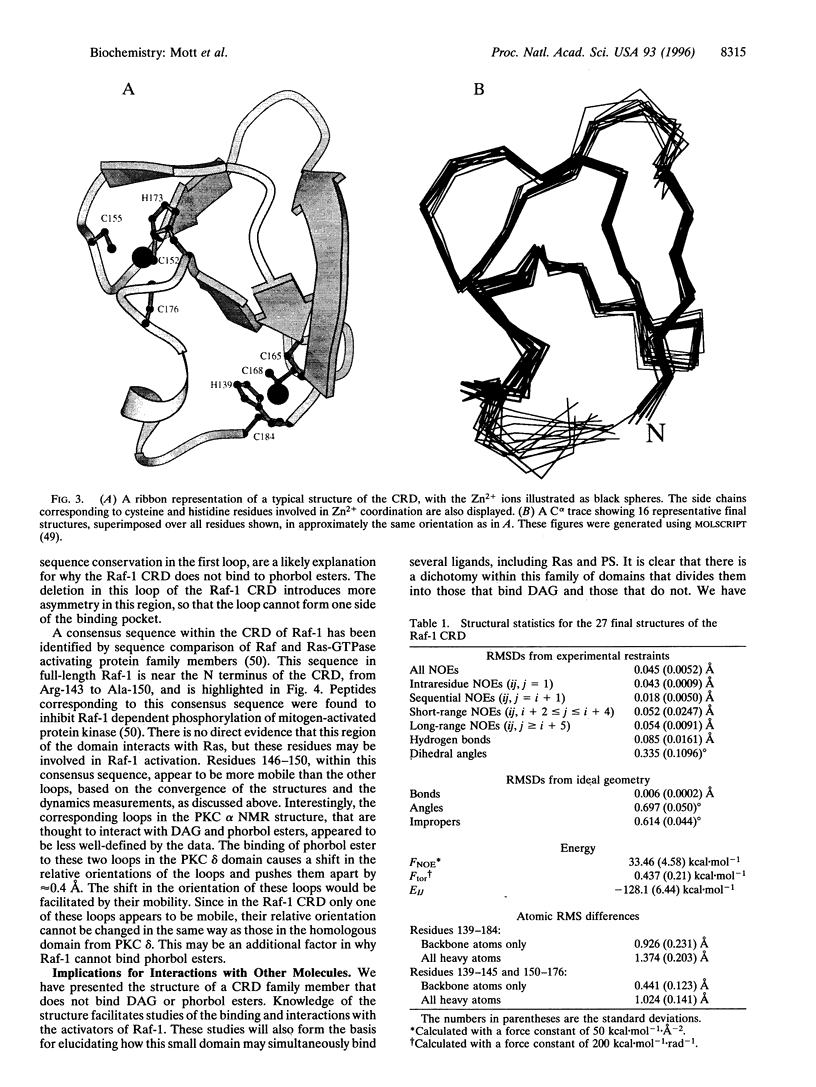
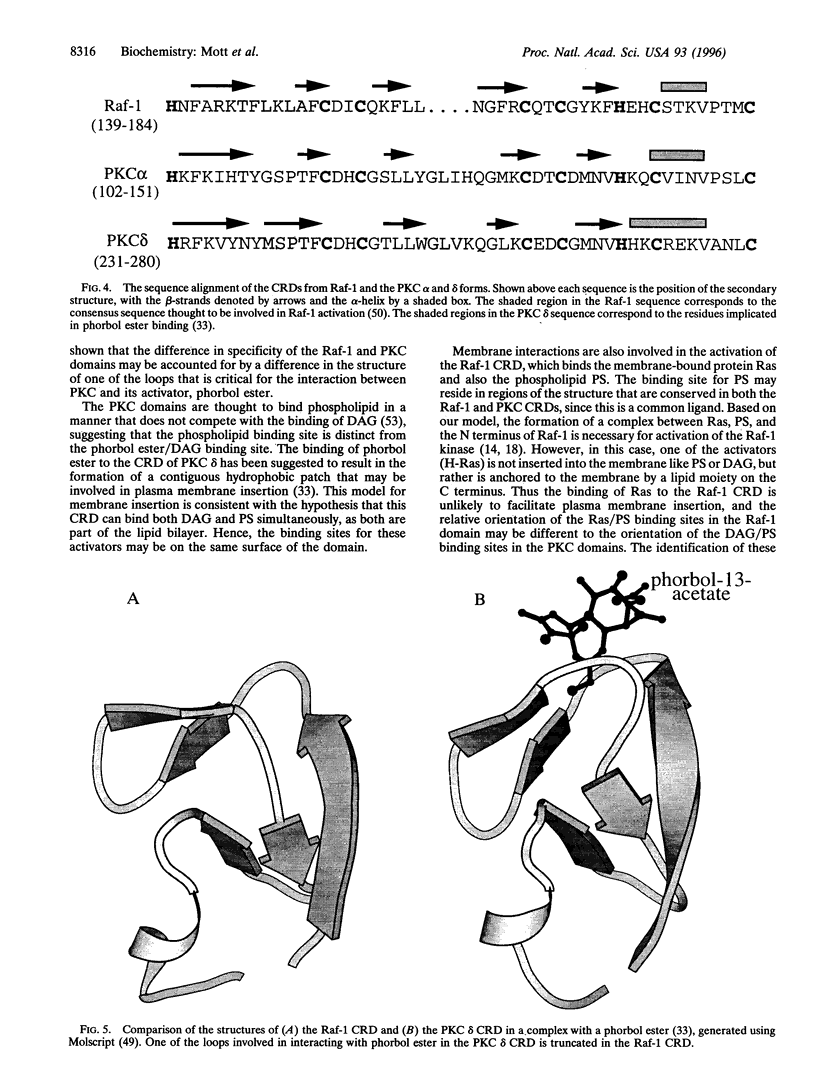
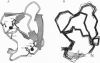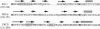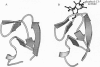Abstract
The Raf-1 protein kinase is the best-characterized downstream effector of activated Ras. Interaction with Ras leads to Raf-1 activation and results in transduction of cell growth and differentiation signals. The details of Raf-1 activation are unclear, but our characterization of a second Ras-binding site in the cysteine-rich domain (CRD) and the involvement of both Ras-binding sites in effective Raf-1-mediated transformation provides insight into the molecular aspects and consequences of Ras-Raf interactions. The Raf-1 CRD is a member of an emerging family of domains, many of which are found within signal transducing proteins. Several contain binding sites for diacylglycerol (or phorbol esters) and phosphatidylserine and are believed to play a role in membrane translocation and enzyme activation. The CRD from Raf-1 does not bind diacylglycerol but interacts with Ras and phosphatidylserine. To investigate the ligand-binding specificities associated with CRDs, we have determined the solution structure of the Raf-1 CRD using heteronuclear multidimensional NMR. We show that there are differences between this structure and the structures of two related domains from protein kinase C (PKC). The differences are confined to regions of the CRDs involved in binding phorbol ester in the PKC domains. Since phosphatidylserine is a common ligand, we expect its binding site to be located in regions where the structures of the Raf-1 and PKC domains are similar. The structure of the Raf-1 CRD represents an example of this family of domains that does not bind diacylglycerol and provides a framework for investigating its interactions with other molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed S., Kozma R., Lee J., Monfries C., Harden N., Lim L. The cysteine-rich domain of human proteins, neuronal chimaerin, protein kinase C and diacylglycerol kinase binds zinc. Evidence for the involvement of a zinc-dependent structure in phorbol ester binding. Biochem J. 1991 Nov 15;280(Pt 1):233–241. doi: 10.1042/bj2800233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avruch J., Zhang X. F., Kyriakis J. M. Raf meets Ras: completing the framework of a signal transduction pathway. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Jul;19(7):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell R. M., Burns D. J. Lipid activation of protein kinase C. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 15;266(8):4661–4664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billeter M., Neri D., Otting G., Qian Y. Q., Wüthrich K. Precise vicinal coupling constants 3JHN alpha in proteins from nonlinear fits of J-modulated [15N,1H]-COSY experiments. J Biomol NMR. 1992 May;2(3):257–274. doi: 10.1007/BF01875320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blomberg F., Maurer W., Rüterjans H. Nuclear magnetic resonance investigation of 15N-labeled histidine in aqueous solution. J Am Chem Soc. 1977 Dec 7;99(25):8149–8159. doi: 10.1021/ja00467a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brtva T. R., Drugan J. K., Ghosh S., Terrell R. S., Campbell-Burk S., Bell R. M., Der C. J. Two distinct Raf domains mediate interaction with Ras. J Biol Chem. 1995 Apr 28;270(17):9809–9812. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.17.9809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow Y. H., Pumiglia K., Jun T. H., Dent P., Sturgill T. W., Jove R. Functional mapping of the N-terminal regulatory domain in the human Raf-1 protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jun 9;270(23):14100–14106. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.23.14100. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chuang E., Barnard D., Hettich L., Zhang X. F., Avruch J., Marshall M. S. Critical binding and regulatory interactions between Ras and Raf occur through a small, stable N-terminal domain of Raf and specific Ras effector residues. Mol Cell Biol. 1994 Aug;14(8):5318–5325. doi: 10.1128/mcb.14.8.5318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark G. J., Drugan J. K., Terrell R. S., Bradham C., Der C. J., Bell R. M., Campbell S. Peptides containing a consensus Ras binding sequence from Raf-1 and theGTPase activating protein NF1 inhibit Ras function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1996 Feb 20;93(4):1577–1581. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.4.1577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppola J., Bryant S., Koda T., Conway D., Barbacid M. Mechanism of activation of the vav protooncogene. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Feb;2(2):95–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crews C. M., Erikson R. L. Extracellular signals and reversible protein phosphorylation: what to Mek of it all. Cell. 1993 Jul 30;74(2):215–217. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90411-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daum G., Eisenmann-Tappe I., Fries H. W., Troppmair J., Rapp U. R. The ins and outs of Raf kinases. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Nov;19(11):474–480. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90133-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diakun G. P., Fairall L., Klug A. EXAFS study of the zinc-binding sites in the protein transcription factor IIIA. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):698–699. doi: 10.1038/324698a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driscoll P. C., Clore G. M., Marion D., Wingfield P. T., Gronenborn A. M. Complete resonance assignment for the polypeptide backbone of interleukin 1 beta using three-dimensional heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 10;29(14):3542–3556. doi: 10.1021/bi00466a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drugan J. K., Khosravi-Far R., White M. A., Der C. J., Sung Y. J., Hwang Y. W., Campbell S. L. Ras interaction with two distinct binding domains in Raf-1 may be required for Ras transformation. J Biol Chem. 1996 Jan 5;271(1):233–237. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.1.233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson S. D., Madison V. S., Palermo R. E., Waugh D. S., Scheffler J. E., Tsao K. L., Kiefer S. E., Liu S. P., Fry D. C. Solution structure of the Ras-binding domain of c-Raf-1 and identification of its Ras interaction surface. Biochemistry. 1995 May 30;34(21):6911–6918. doi: 10.1021/bi00021a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fantl W. J., Muslin A. J., Kikuchi A., Martin J. A., MacNicol A. M., Gross R. W., Williams L. T. Activation of Raf-1 by 14-3-3 proteins. Nature. 1994 Oct 13;371(6498):612–614. doi: 10.1038/371612a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freed E., Symons M., Macdonald S. G., McCormick F., Ruggieri R. Binding of 14-3-3 proteins to the protein kinase Raf and effects on its activation. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1713–1716. doi: 10.1126/science.8085158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu H., Xia K., Pallas D. C., Cui C., Conroy K., Narsimhan R. P., Mamon H., Collier R. J., Roberts T. M. Interaction of the protein kinase Raf-1 with 14-3-3 proteins. Science. 1994 Oct 7;266(5182):126–129. doi: 10.1126/science.7939632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Bell R. M. Identification of discrete segments of human Raf-1 kinase critical for high affinity binding to Ha-Ras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Dec 9;269(49):30785–30788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh S., Xie W. Q., Quest A. F., Mabrouk G. M., Strum J. C., Bell R. M. The cysteine-rich region of raf-1 kinase contains zinc, translocates to liposomes, and is adjacent to a segment that binds GTP-ras. J Biol Chem. 1994 Apr 1;269(13):10000–10007. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heidecker G., Huleihel M., Cleveland J. L., Kolch W., Beck T. W., Lloyd P., Pawson T., Rapp U. R. Mutational activation of c-raf-1 and definition of the minimal transforming sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2503–2512. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hommel U., Zurini M., Luyten M. Solution structure of a cysteine rich domain of rat protein kinase C. Nat Struct Biol. 1994 Jun;1(6):383–387. doi: 10.1038/nsb0694-383. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu C. D., Kariya K., Tamada M., Akasaka K., Shirouzu M., Yokoyama S., Kataoka T. Cysteine-rich region of Raf-1 interacts with activator domain of post-translationally modified Ha-Ras. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 22;270(51):30274–30277. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.51.30274. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Irie K., Gotoh Y., Yashar B. M., Errede B., Nishida E., Matsumoto K. Stimulatory effects of yeast and mammalian 14-3-3 proteins on the Raf protein kinase. Science. 1994 Sep 16;265(5179):1716–1719. doi: 10.1126/science.8085159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa F., Sakai R., Ochiai M., Takaku F., Sugimura T., Nagao M. Identification of a transforming activity suppressing sequence in the c-raf oncogene. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):653–658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazanietz M. G., Wang S., Milne G. W., Lewin N. E., Liu H. L., Blumberg P. M. Residues in the second cysteine-rich region of protein kinase C delta relevant to phorbol ester binding as revealed by site-directed mutagenesis. J Biol Chem. 1995 Sep 15;270(37):21852–21859. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.37.21852. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Ahmed S., Kozma R., Teo M., Monfries C., Lim L. The N-terminal region of n-Chimaerin allows lipid modulation of the C-terminal p21rac-GTPase activating domain. Biochem Soc Trans. 1992 Aug;20(3):310S–310S. doi: 10.1042/bst020310s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leevers S. J., Paterson H. F., Marshall C. J. Requirement for Ras in Raf activation is overcome by targeting Raf to the plasma membrane. Nature. 1994 Jun 2;369(6479):411–414. doi: 10.1038/369411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S., Janosch P., Tanji M., Rosenfeld G. C., Waymire J. C., Mischak H., Kolch W., Sedivy J. M. Regulation of Raf-1 kinase activity by the 14-3-3 family of proteins. EMBO J. 1995 Feb 15;14(4):685–696. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb07047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu X., Chou T. B., Williams N. G., Roberts T., Perrimon N. Control of cell fate determination by p21ras/Ras1, an essential component of torso signaling in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1993 Apr;7(4):621–632. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.4.621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luo Z. J., Zhang X. F., Rapp U., Avruch J. Identification of the 14.3.3 zeta domains important for self-association and Raf binding. J Biol Chem. 1995 Oct 6;270(40):23681–23687. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.40.23681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion D., Driscoll P. C., Kay L. E., Wingfield P. T., Bax A., Gronenborn A. M., Clore G. M. Overcoming the overlap problem in the assignment of 1H NMR spectra of larger proteins by use of three-dimensional heteronuclear 1H-15N Hartmann-Hahn-multiple quantum coherence and nuclear Overhauser-multiple quantum coherence spectroscopy: application to interleukin 1 beta. Biochemistry. 1989 Jul 25;28(15):6150–6156. doi: 10.1021/bi00441a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nassar N., Horn G., Herrmann C., Scherer A., McCormick F., Wittinghofer A. The 2.2 A crystal structure of the Ras-binding domain of the serine/threonine kinase c-Raf1 in complex with Rap1A and a GTP analogue. Nature. 1995 Jun 15;375(6532):554–560. doi: 10.1038/375554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newton A. C. Protein kinase C: structure, function, and regulation. J Biol Chem. 1995 Dec 1;270(48):28495–28498. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.48.28495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono Y., Fujii T., Igarashi K., Kuno T., Tanaka C., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Phorbol ester binding to protein kinase C requires a cysteine-rich zinc-finger-like sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4868–4871. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4868. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelton J. G., Torchia D. A., Meadow N. D., Roseman S. Tautomeric states of the active-site histidines of phosphorylated and unphosphorylated IIIGlc, a signal-transducing protein from Escherichia coli, using two-dimensional heteronuclear NMR techniques. Protein Sci. 1993 Apr;2(4):543–558. doi: 10.1002/pro.5560020406. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piotto M., Saudek V., Sklenár V. Gradient-tailored excitation for single-quantum NMR spectroscopy of aqueous solutions. J Biomol NMR. 1992 Nov;2(6):661–665. doi: 10.1007/BF02192855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rance M., Sørensen O. W., Bodenhausen G., Wagner G., Ernst R. R., Wüthrich K. Improved spectral resolution in cosy 1H NMR spectra of proteins via double quantum filtering. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Dec 16;117(2):479–485. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91225-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaap D., de Widt J., van der Wal J., Vandekerckhove J., van Damme J., Gussow D., Ploegh H. L., van Blitterswijk W. J., van der Bend R. L. Purification, cDNA-cloning and expression of human diacylglycerol kinase. FEBS Lett. 1990 Nov 26;275(1-2):151–158. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81461-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton V. P., Jr, Nichols D. W., Laudano A. P., Cooper G. M. Definition of the human raf amino-terminal regulatory region by deletion mutagenesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):639–647. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stokoe D., Macdonald S. G., Cadwallader K., Symons M., Hancock J. F. Activation of Raf as a result of recruitment to the plasma membrane. Science. 1994 Jun 3;264(5164):1463–1467. doi: 10.1126/science.7811320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vojtek A. B., Hollenberg S. M., Cooper J. A. Mammalian Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell. 1993 Jul 16;74(1):205–214. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(93)90307-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang G., Kazanietz M. G., Blumberg P. M., Hurley J. H. Crystal structure of the cys2 activator-binding domain of protein kinase C delta in complex with phorbol ester. Cell. 1995 Jun 16;81(6):917–924. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(95)90011-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]