Abstract
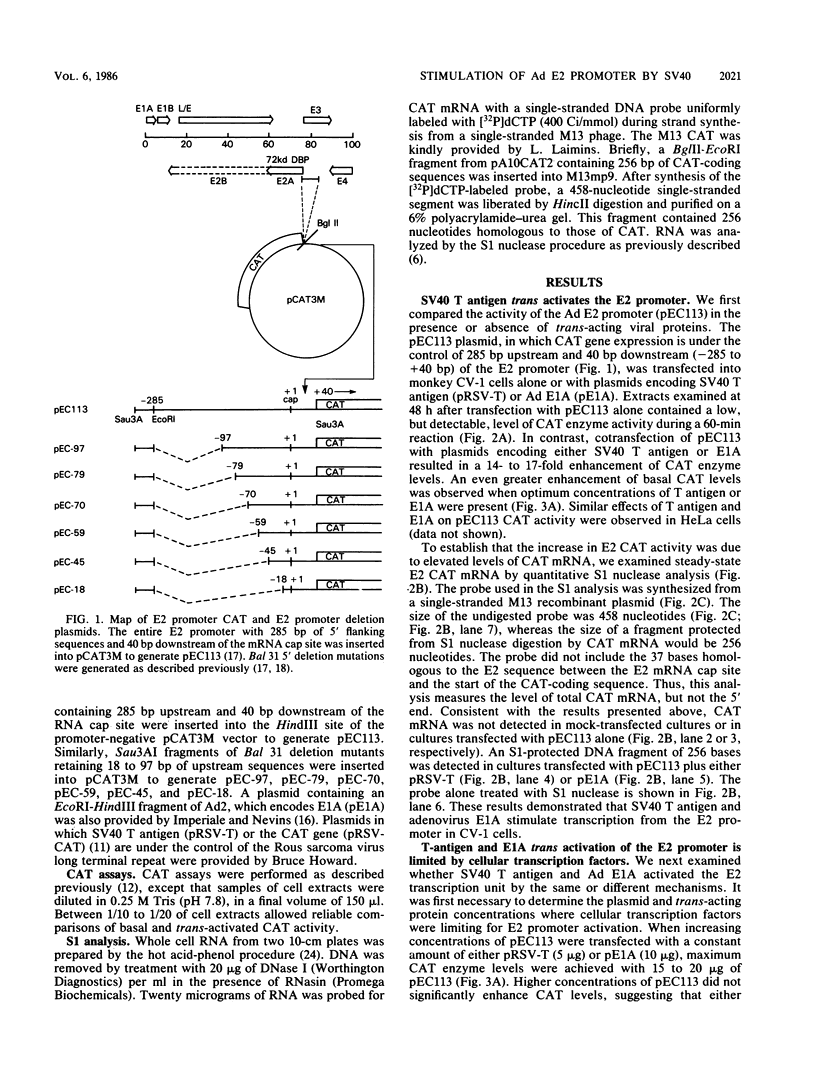
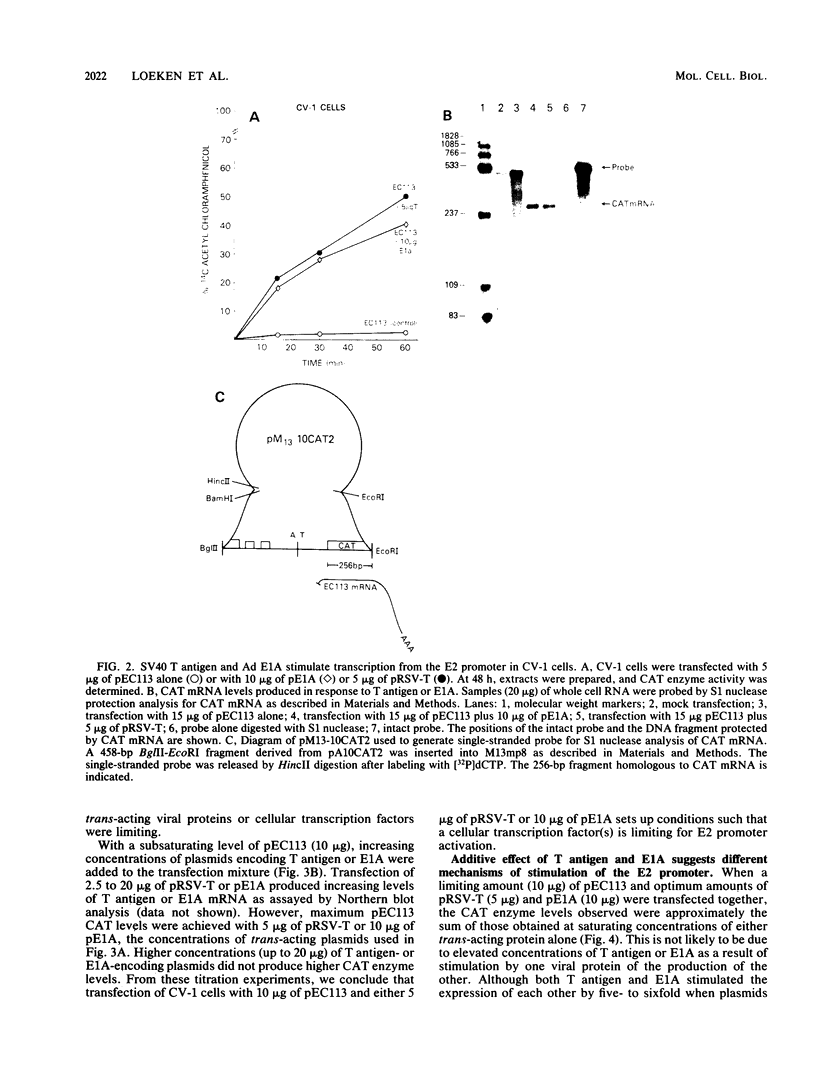
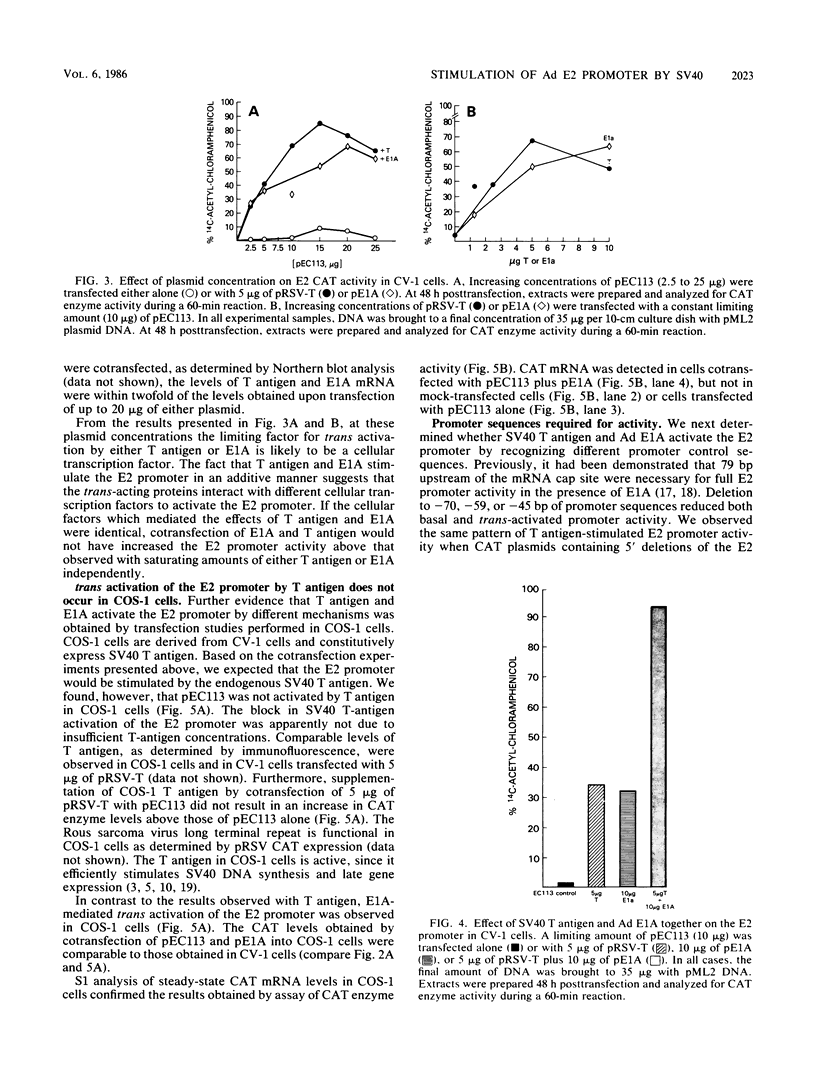
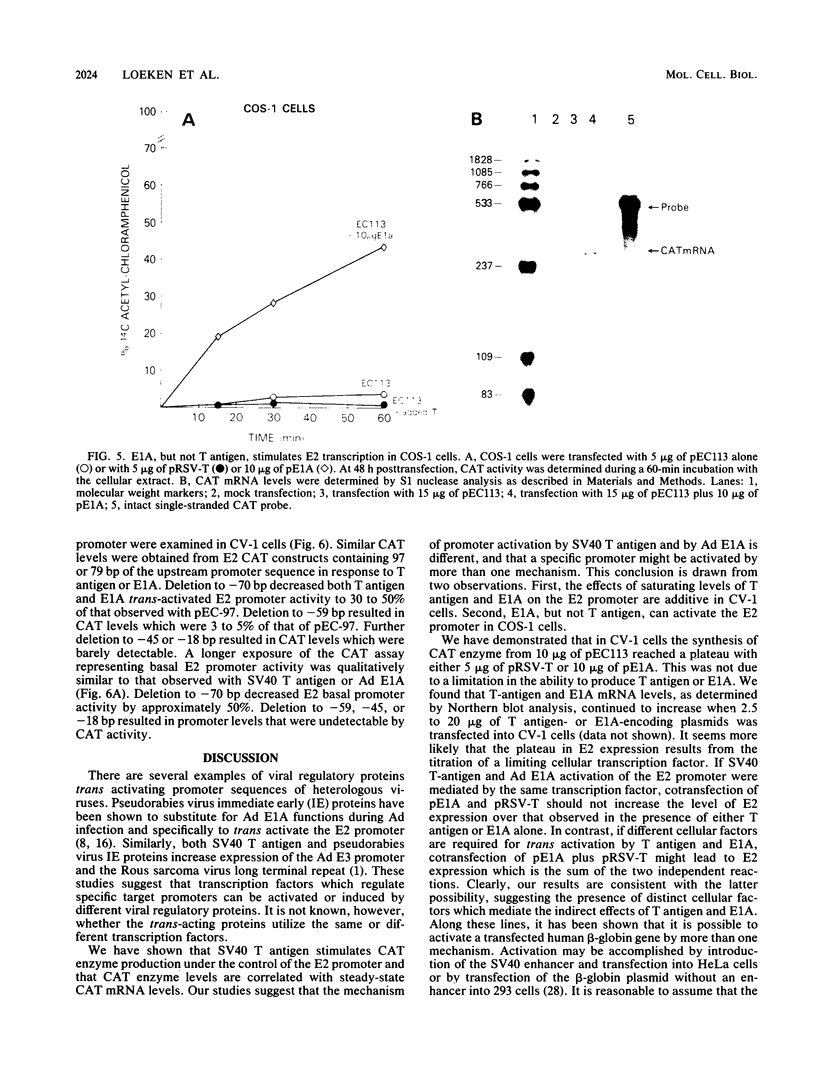
We have examined the ability of simian virus 40 T antigen to stimulate transcription from the adenovirus E2 promoter. T antigen, produced from a cotransfected plasmid, stimulated chloramphenicol acetyltransferase enzyme and mRNA production from an E2 promoter-chloramphenicol acetyltransferase fusion plasmid (pEC113) in monkey kidney CV-1 cells. The level of stimulation of E2 transcription by simian virus 40 T antigen was equal to that observed in cotransfections of pEC113 and the adenovirus E1A gene product. Deletion mutations from the 5' end of the E2 promoter were examined for their ability to express basal, T-antigen, or E1A trans-activated promoter activity. In each case, deletion of upstream promoter sequences to -70 base pairs reduced chloramphenicol acetyltransferase expression to approximately 30% of the level observed with the intact E2 promoter. Deletion to -59 base pairs resulted in chloramphenicol acetyltransferase expression that was 3 to 5% of that observed with the intact E2 promoter. At saturating levels of the stimulatory proteins, the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase levels obtained in response to T antigen and adenovirus E1A were additive. COS-1 cells, which are derived from CV-1 cells and constitutively express simian virus 40 T antigen, do not support E2 promoter trans activation by T antigen. E1A trans activation of the E2 promoter is efficient in COS-1 cells. These results suggest that although promoter sequence requirements are similar, T antigen and E1A trans activate the E2 promoter by different mechanisms.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C. Transient gene expression control: effects of transfected DNA stability and trans-activation by viral early proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 May;5(5):1034–1042. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.5.1034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Olive D. M., Hartzell S. W., Subramanian K. N. Territorial limits and functional anatomy of the simian virus 40 replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Khoury G. trans Activation of the simian virus 40 late transcription unit by T-antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1391–1399. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Loeken M. R., Khoury G. Interaction between two transcriptional control sequences required for tumor-antigen-mediated simian virus 40 late gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7299–7303. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman L. T., Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Activation of early adenovirus transcription by the herpesvirus immediate early gene: evidence for a common cellular control factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):4952–4956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.4952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gluzman Y. SV40-transformed simian cells support the replication of early SV40 mutants. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90282-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoyle R. A., Osheroff W. P., Rossini M. Two functions encoded by adenovirus early region 1A are responsible for the activation and repression of the DNA-binding protein gene. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):707–713. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03687.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell S. W., Byrne B. J., Subramanian K. N. The simian virus 40 minimal origin and the 72-base-pair repeat are required simultaneously for efficient induction of late gene expression with large tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(20):6335–6339. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.20.6335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R. Activation of gene expression by adenovirus and herpesvirus regulatory genes acting in trans and by a cis-acting adenovirus enhancer element. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):127–136. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90215-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Hart R. P., Nevins J. R. An enhancer-like element in the adenovirus E2 promoter contains sequences essential for uninduced and E1A-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Nevins J. R. Adenovirus 5 E2 transcription unit: an E1A-inducible promoter with an essential element that functions independently of position or orientation. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):875–882. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Analysis of an activatable promoter: sequences in the simian virus 40 late promoter required for T-antigen-mediated trans activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1859–1869. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kingston R. E., Kaufman R. J., Sharp P. A. Regulation of transcription of the adenovirus EII promoter by EIa gene products: absence of sequence specificity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):1970–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murthy S. C., Bhat G. P., Thimmappaya B. Adenovirus EIIA early promoter: transcriptional control elements and induction by the viral pre-early EIA gene, which appears to be sequence independent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2230–2234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D. R., Margolskee R. F., Nathans D. Mutational analysis of the simian virus 40 replicon: pseudorevertants of mutants with a defective replication origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6128–6131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shortle D., Nathans D. Regulatory mutants of simian virus 40: constructed mutants with base substitutions at the origin of DNA replication. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 15;131(4):801–817. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90202-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Treisman R., Green M. R., Maniatis T. cis and trans activation of globin gene transcription in transient assays. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7428–7432. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7428. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]