Abstract
Altered control of the rat cell cycle induced by adenovirus requires expression of transformation region E1A, but not of E1B, E2A, E2B, or late genes. We show here that neither E3 nor E4 is required, so the effect results directly from an E1A product. Mutants with defects in the 289-amino-acid (aa) E1A product had little or no effect on the rat cell cycle even at 1,000 IU per cell. A mutant (pm975) lacking the 243-aa E1A product altered cell cycle progression, but less efficiently than did wild-type virus. The 289-aa E1A protein is therefore essential for cell cycle effects; the 243-aa protein is also necessary for the full effect but cannot act alone. Mutants with altered 289-aa E1A proteins showed different extents of leak expression of viral early region E2A as the multiplicity was increased; each leaked more in human than in rat cells. dl312, with no E1A products, failed to produce E2A mRNA or protein at 1,000 IU per cell in rat cells but did so in some experiments in human cells. There appears to be a very strict dependence of viral early gene expression on E1A in rat cells, whereas dependence on E1A is more relaxed in HeLa cells, perhaps due to a cellular E1A-like function. Altered cell cycle control is more dependent on E1A function than is early viral gene expression.
Full text
PDF
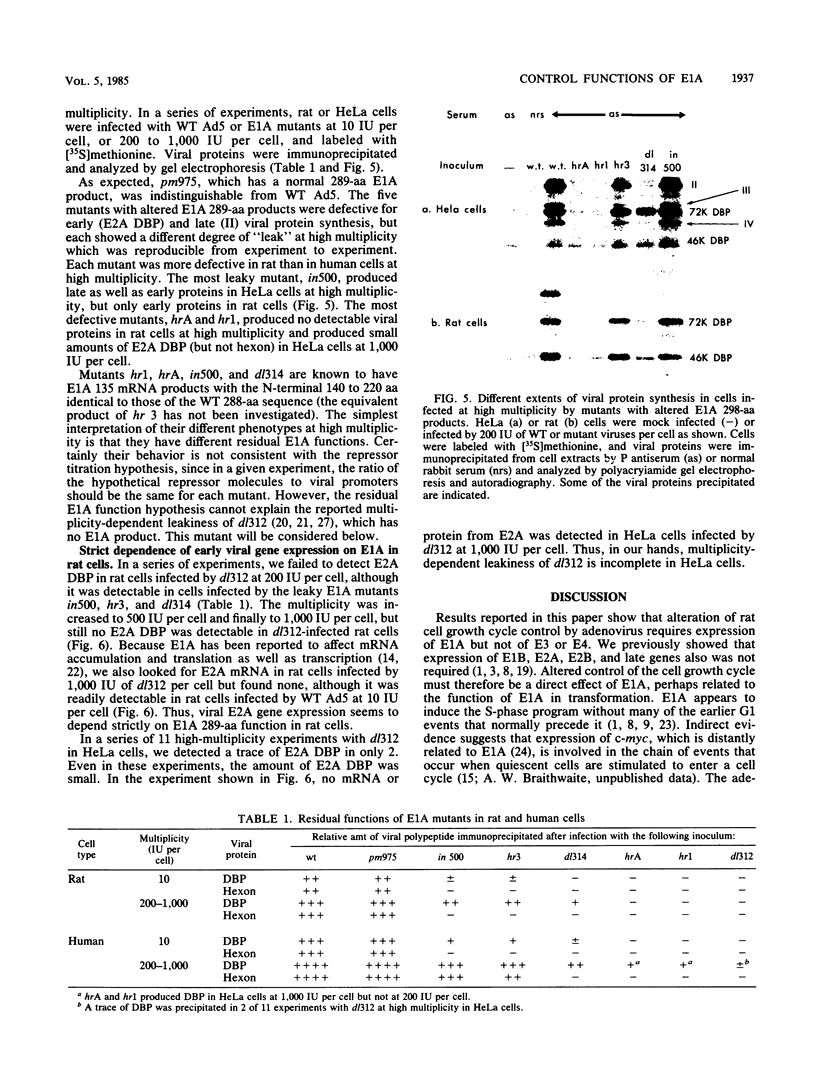
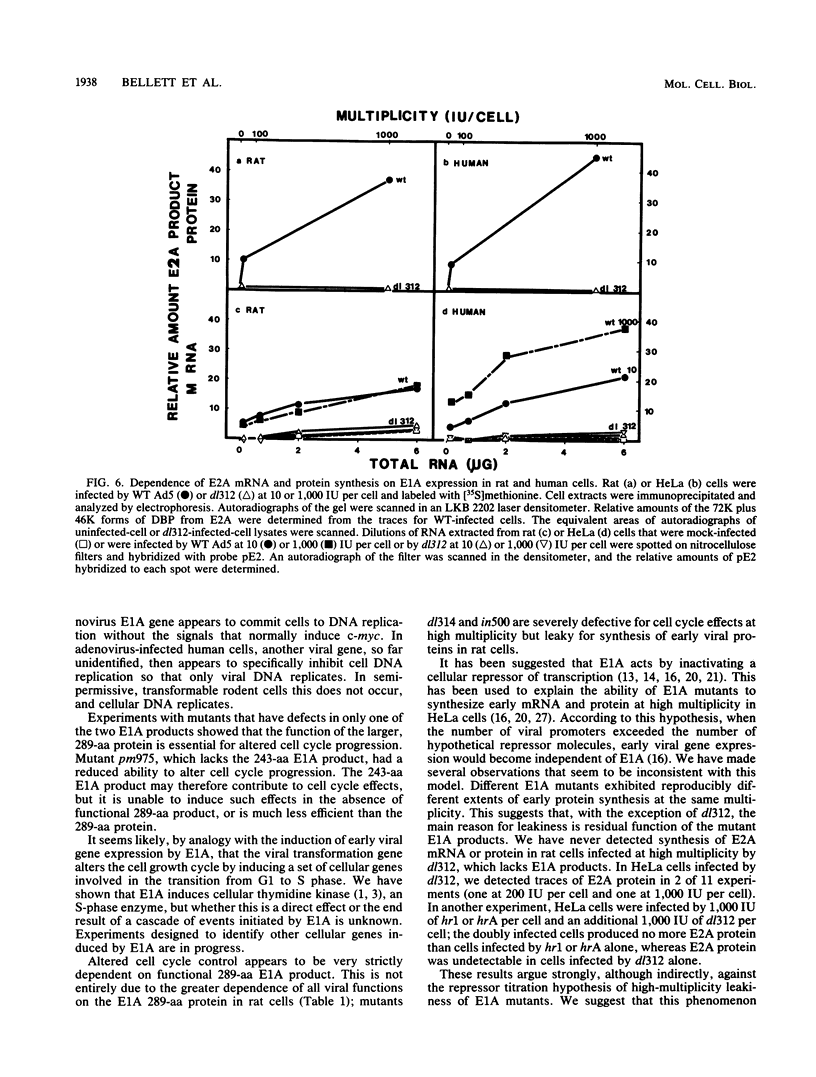

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Cheetham B. F., Li P., Parish C. R., Waldron-Stevens L. K., Bellett A. J. Adenovirus-induced alterations of the cell growth cycle: a requirement for expression of E1A but not of E1B. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):192–199. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.192-199.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Lejeune S., Naora H. Adenoviruses have homology with a reiterated sequence in genomic DNA. DNA. 1984 Jun;3(3):223–230. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1984.3.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braithwaite A. W., Murray J. D., Bellett A. J. Alterations to controls of cellular DNA synthesis by adenovirus infection. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):331–340. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.331-340.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlock L. R., Jones N. C. Transformation-defective mutant of adenovirus type 5 containing a single altered E1a mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):657–664. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.657-664.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challberg S. S., Ketner G. Deletion mutants of adenovirus 2: isolation and initial characterization of virus carrying mutations near the right end of the viral genome. Virology. 1981 Oct 15;114(1):196–209. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90265-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheetham B. F., Bellett A. J. A biochemical investigation of the adenovirus-induced G1 to S phase progression: thymidine kinase, ornithine decarboxylase, and inhibitors of polyamine biosynthesis. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Feb;110(2):114–122. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041100203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheetham B. F., Shaw D. C., Bellett A. J. Adenovirus type 5 induces progression of quiescent rat cells into S phase without polyamine accumulation. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Oct;2(10):1295–1298. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.10.1295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imperiale M. J., Kao H. T., Feldman L. T., Nevins J. R., Strickland S. Common control of the heat shock gene and early adenovirus genes: evidence for a cellular E1A-like activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):867–874. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Persson H., Johansson B. M., Philipson L. Control of adenovirus gene expression: cellular gene products restrict expression of adenovirus host range mutants in nonpermissive cells. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):50–59. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.50-59.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Persson H., Philipson L. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: posttranscriptional control mediated by both viral and cellular gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;1(9):807–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.9.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Logan J. S., Shenk T. Transcriptional and translational control of adenovirus gene expression. Microbiol Rev. 1982 Dec;46(4):377–383. doi: 10.1128/mr.46.4.377-383.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montell C., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H., Berk A. J. Resolving the functions of overlapping viral genes by site-specific mutagenesis at a mRNA splice site. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):380–384. doi: 10.1038/295380a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. D., Bellett A. J., Braithwaite A. w., Waldron L. K., Taylor I. W. Altered cell cycle progression and aberrant mitosis in adenovirus-infected rodent cells. J Cell Physiol. 1982 Apr;111(1):89–96. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041110114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray J. D., Braithwaite A. W., Taylor I. W., Bellett A. J. Adenovirus-induced alterations of the cell growth cycle: effects of mutations in early regions E2A and E2B. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1072–1075. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1072-1075.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Induction of the synthesis of a 70,000 dalton mammalian heat shock protein by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1982 Jul;29(3):913–919. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90453-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nevins J. R. Mechanism of activation of early viral transcription by the adenovirus E1A gene product. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(2 Pt 2):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90304-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Monstein H. J., Akusjärvi G., Philipson L. Adenovirus early gene products may control viral mRNA accumulation and translation in vivo. Cell. 1981 Feb;23(2):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90144-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pochron S., Rossini M., Darzynkiewicz Z., Traganos F., Baserga R. Failure of accumulation of cellular RNA in hamster cells stimulated to synthesize DNA by infection with adenovirus 2. J Biol Chem. 1980 May 25;255(10):4411–4413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ralston R., Bishop J. M. The protein products of the myc and myb oncogenes and adenovirus E1a are structurally related. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):803–806. doi: 10.1038/306803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Jones R. L., Cepko C. L., Sharp P. A., Roberts B. E. Expression of early adenovirus genes requires a viral encoded acidic polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6121–6125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruley H. E. Adenovirus early region 1A enables viral and cellular transforming genes to transform primary cells in culture. Nature. 1983 Aug 18;304(5927):602–606. doi: 10.1038/304602a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T., Jones N., Colby W., Fowlkes D. Functional analysis of adenovirus-5 host-range deletion mutants defective for transformation of rat embryo cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):367–375. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Solnick D., Anderson M. A. Transformation-deficient adenovirus mutant defective in expression of region 1A but not region 1B. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. W. A rapid single step staining technique for DNA analysis by flow microfluorimetry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Sep;28(9):1021–1024. doi: 10.1177/28.9.6157714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]