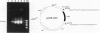Abstract
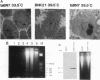
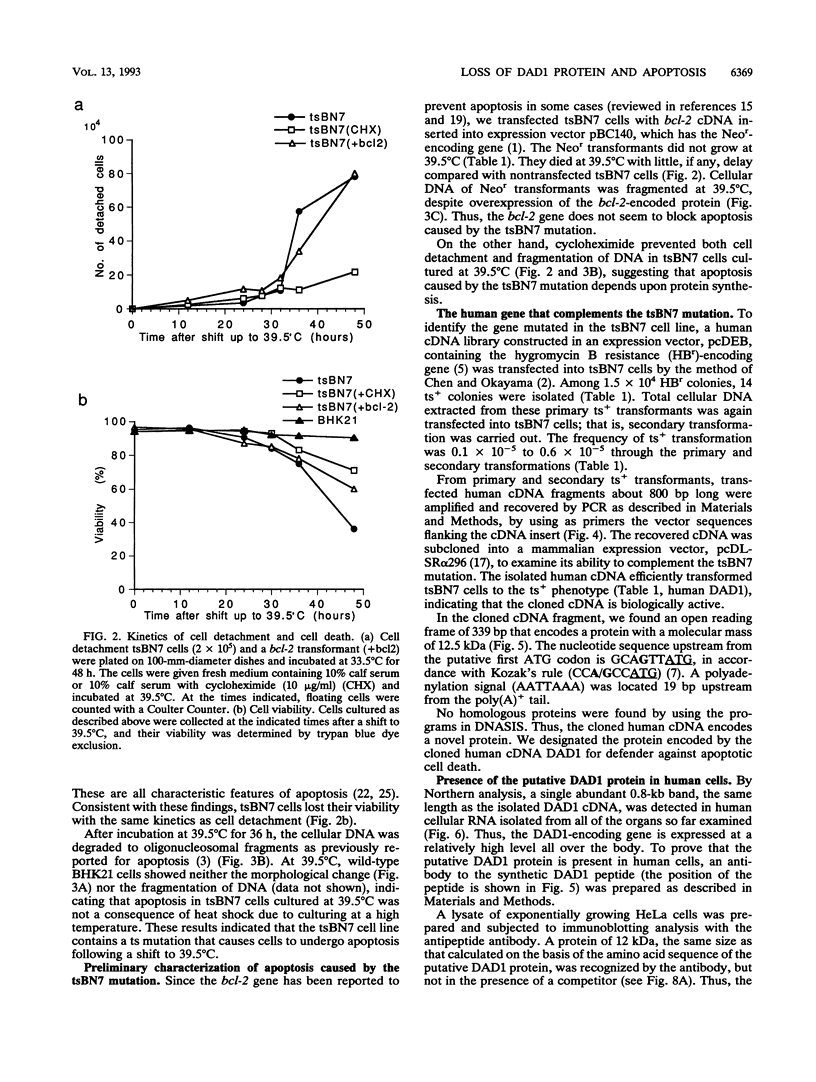
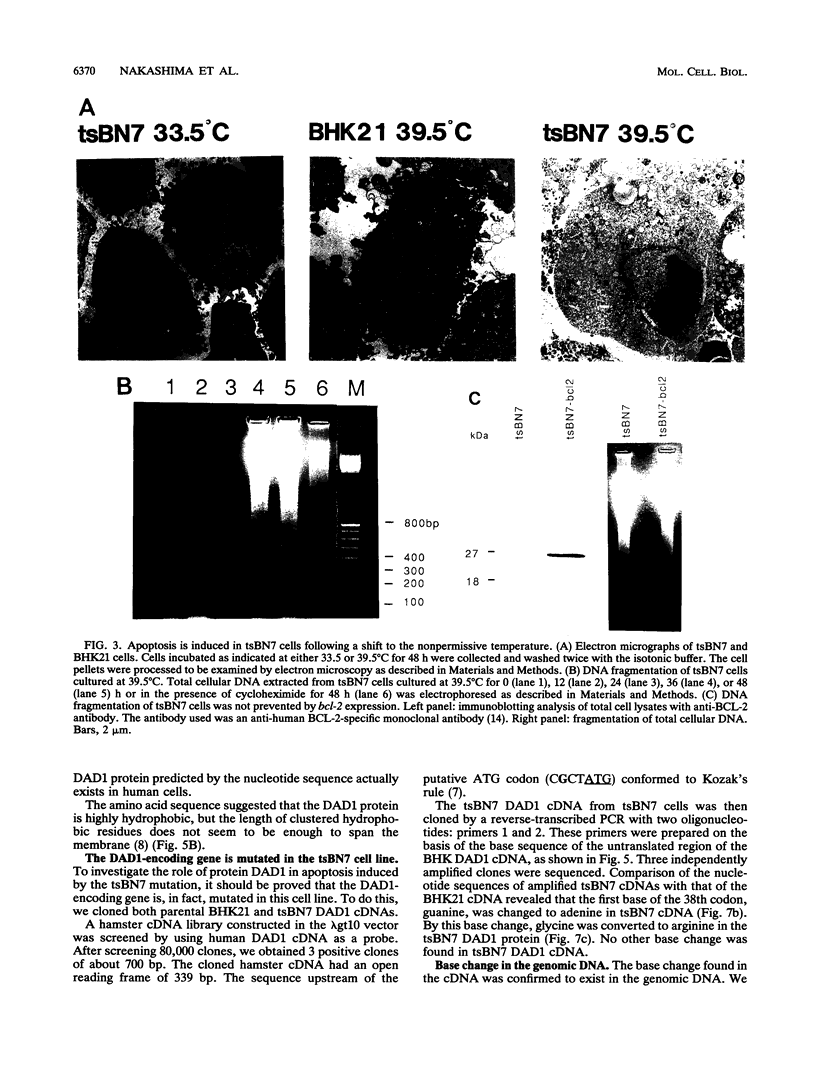
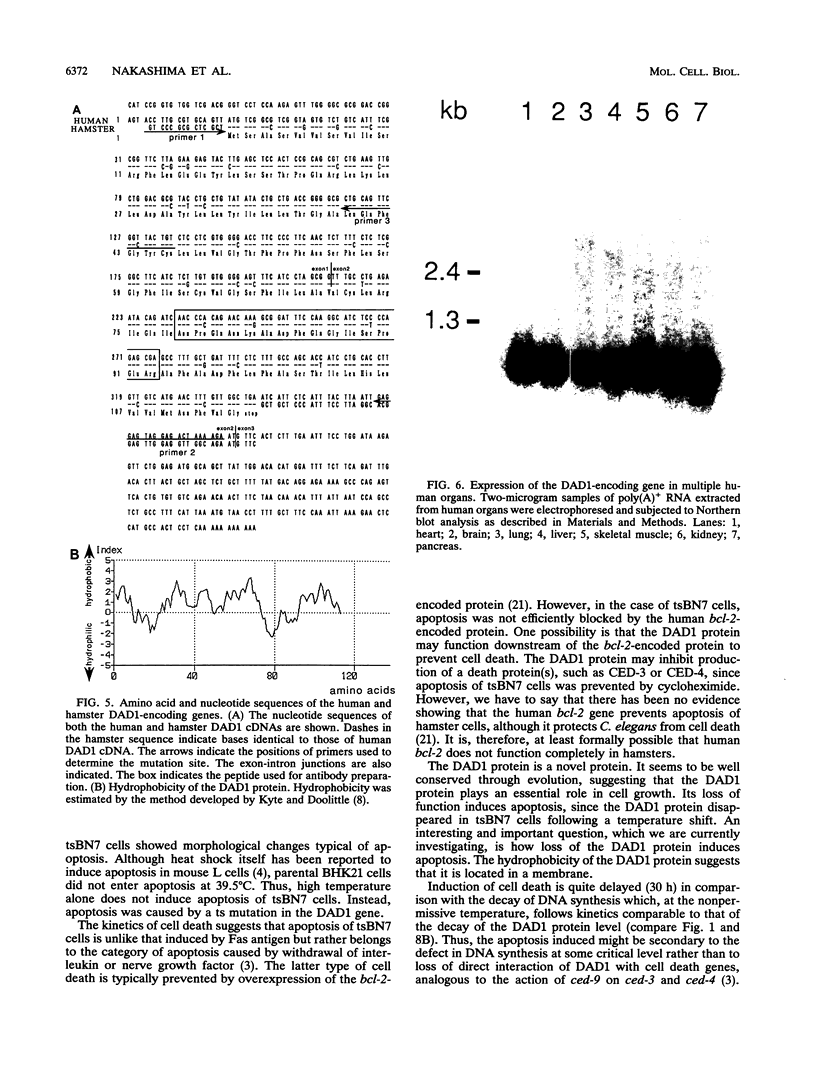
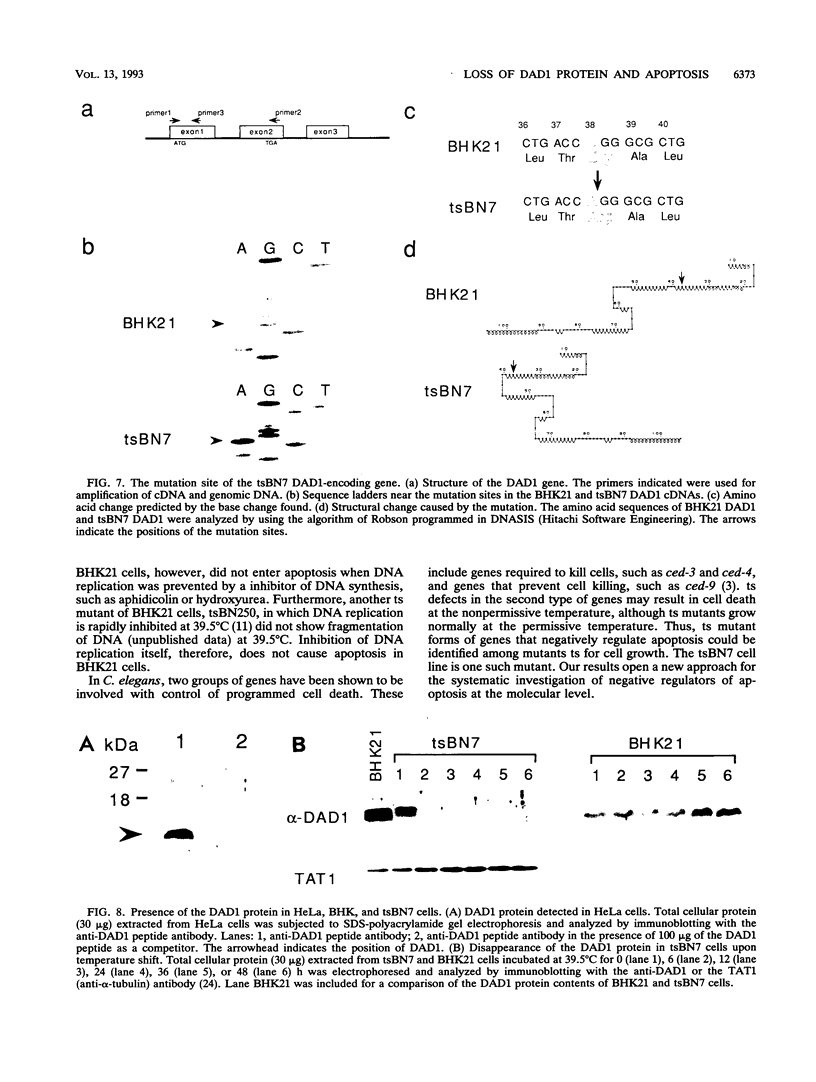
The tsBN7 cell line, one of the mutant lines temperature sensitive for growth which have been isolated from the BHK21 cell line, was found to die by apoptosis following a shift to the nonpermissive temperature. The induced apoptosis was inhibited by a protein synthesis inhibitor, cycloheximide, but not by the bcl-2-encoded protein. By DNA-mediated gene transfer, we cloned a cDNA that complements the tsBN7 mutation. It encodes a novel hydrophobic protein, designated DAD1, which is well conserved (100% identical amino acids between humans and hamsters). By comparing the base sequences of the parental BHK21 and tsBN7 DAD1 cDNAs, we found that the DAD1-encoding gene is mutated in tsBN7 cells. The DAD1 protein disappeared in tsBN7 cells following a shift to the nonpermissive temperature, suggesting that loss of the DAD1 protein triggers apoptosis.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Borzillo G. V., Endo K., Tsujimoto Y. Bcl-2 confers growth and survival advantage to interleukin 7-dependent early pre-B cells which become factor independent by a multistep process in culture. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):869–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. E., Yuan J. Y., Horvitz H. R. Mechanisms and functions of cell death. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1991;7:663–698. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.07.110191.003311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghibelli L., Nosseri C., Oliverio S., Piacentini M., Autuori F. Cycloheximide can rescue heat-shocked L cells from death by blocking stress-induced apoptosis. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Aug;201(2):436–443. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90292-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa H., Koike G., Sekiguchi M. Expression and cloning of complementary DNA for a human enzyme that repairs O6-methylguanine in DNA. J Mol Biol. 1990 Jun 20;213(4):739–747. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80260-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishida Y., Agata Y., Shibahara K., Honjo T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992 Nov;11(11):3887–3895. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05481.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Basilico C. Analysis of a method for selecting temperature-sensitive mutants of BHK cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1978 May;4(3):323–340. doi: 10.1007/BF01542846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Eilen E., Basilico C. Premature of chromosome condensation in a ts DNA- mutant of BHK cells. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):475–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90017-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishimoto T., Sekiguchi T., Kai R., Yamashita K., Takahashi T., Sekiguchi M. Large-scale selection and analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants for cell reproduction from BHK cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Nov;8(6):811–824. doi: 10.1007/BF01543021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishitani H., Ohtsubo M., Yamashita K., Iida H., Pines J., Yasudo H., Shibata Y., Hunter T., Nishimoto T. Loss of RCC1, a nuclear DNA-binding protein, uncouples the completion of DNA replication from the activation of cdc2 protein kinase and mitosis. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1555–1564. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07675.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohtsubo M., Kai R., Furuno N., Sekiguchi T., Sekiguchi M., Hayashida H., Kuma K., Miyata T., Fukushige S., Murotsu T. Isolation and characterization of the active cDNA of the human cell cycle gene (RCC1) involved in the regulation of onset of chromosome condensation. Genes Dev. 1987 Aug;1(6):585–593. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.6.585. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pezzella F., Tse A. G., Cordell J. L., Pulford K. A., Gatter K. C., Mason D. Y. Expression of the bcl-2 oncogene protein is not specific for the 14;18 chromosomal translocation. Am J Pathol. 1990 Aug;137(2):225–232. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C. Social controls on cell survival and cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 2;356(6368):397–400. doi: 10.1038/356397a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebagliati M. R., Weeks D. L., Harvey R. P., Melton D. A. Identification and cloning of localized maternal RNAs from Xenopus eggs. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):769–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90273-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takebe Y., Seiki M., Fujisawa J., Hoy P., Yokota K., Arai K., Yoshida M., Arai N. SR alpha promoter: an efficient and versatile mammalian cDNA expression system composed of the simian virus 40 early promoter and the R-U5 segment of human T-cell leukemia virus type 1 long terminal repeat. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):466–472. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.466. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida S., Sekiguchi T., Nishitani H., Miyauchi K., Ohtsubo M., Nishimoto T. Premature chromosome condensation is induced by a point mutation in the hamster RCC1 gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):577–584. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.577. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Aguila H. L., Weissman I. L. Bcl-2 prevents death of factor-deprived cells but fails to prevent apoptosis in targets of cell mediated killing. Int Immunol. 1992 Jul;4(7):821–824. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.7.821. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L. Toward an understanding of the molecular mechanisms of physiological cell death. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):786–789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.786. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Weissman I. L., Kim S. K. Prevention of programmed cell death in Caenorhabditis elegans by human bcl-2. Science. 1992 Dec 18;258(5090):1955–1957. doi: 10.1126/science.1470921. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker N. I., Harmon B. V., Gobé G. C., Kerr J. F. Patterns of cell death. Methods Achiev Exp Pathol. 1988;13:18–54. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe M., Furuno N., Goebl M., Go M., Miyauchi K., Sekiguchi T., Basilico C., Nishimito T. Molecular cloning of the human gene, CCG2, that complements the BHK-derived temperature-sensitive cell cycle mutant tsBN63: identity of CCG2 with the human X chromosomal SCAR/RPS4X gene. J Cell Sci. 1991 Sep;100(Pt 1):35–43. doi: 10.1242/jcs.100.1.35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods A., Sherwin T., Sasse R., MacRae T. H., Baines A. J., Gull K. Definition of individual components within the cytoskeleton of Trypanosoma brucei by a library of monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Sci. 1989 Jul;93(Pt 3):491–500. doi: 10.1242/jcs.93.3.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]