Abstract
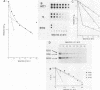
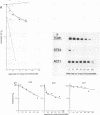
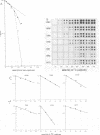
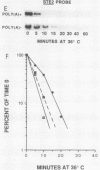
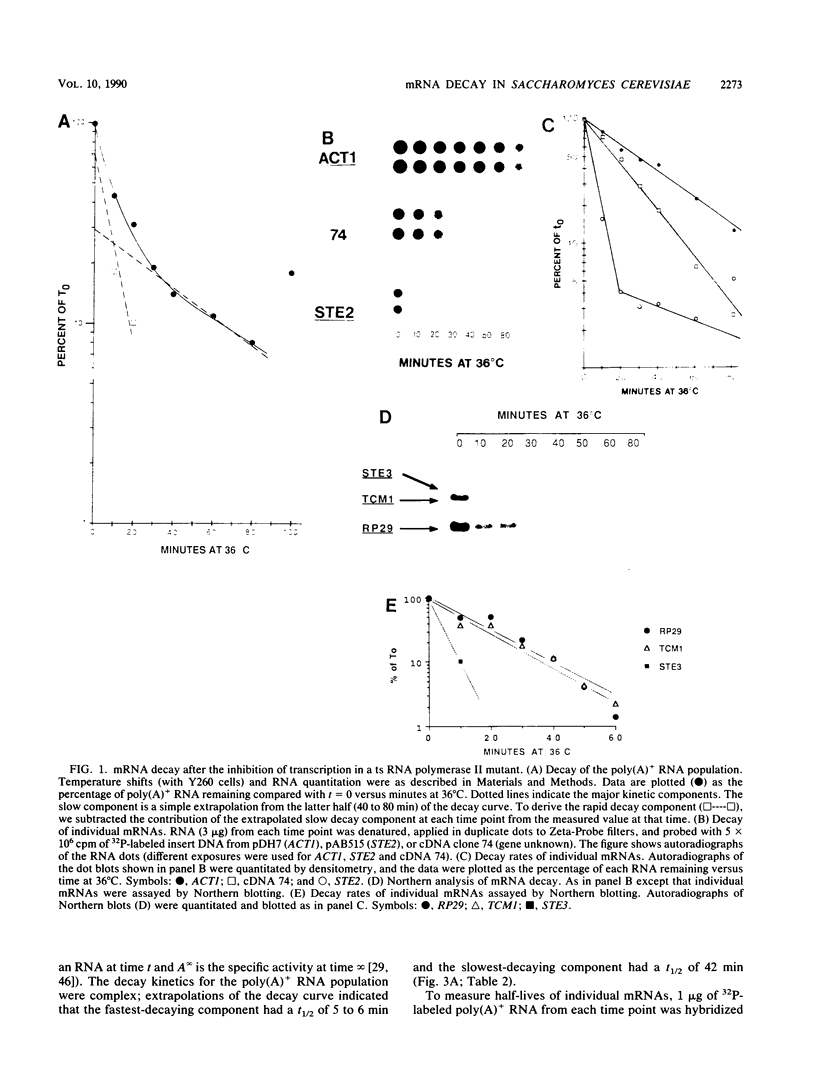
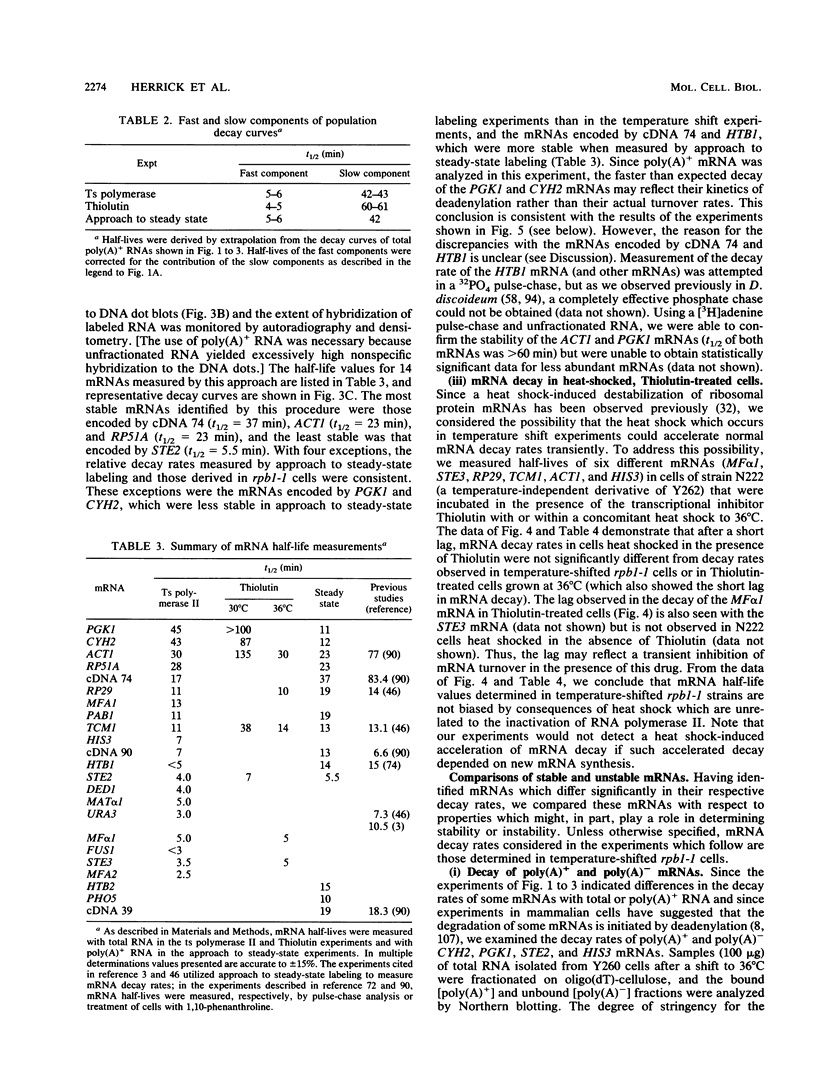
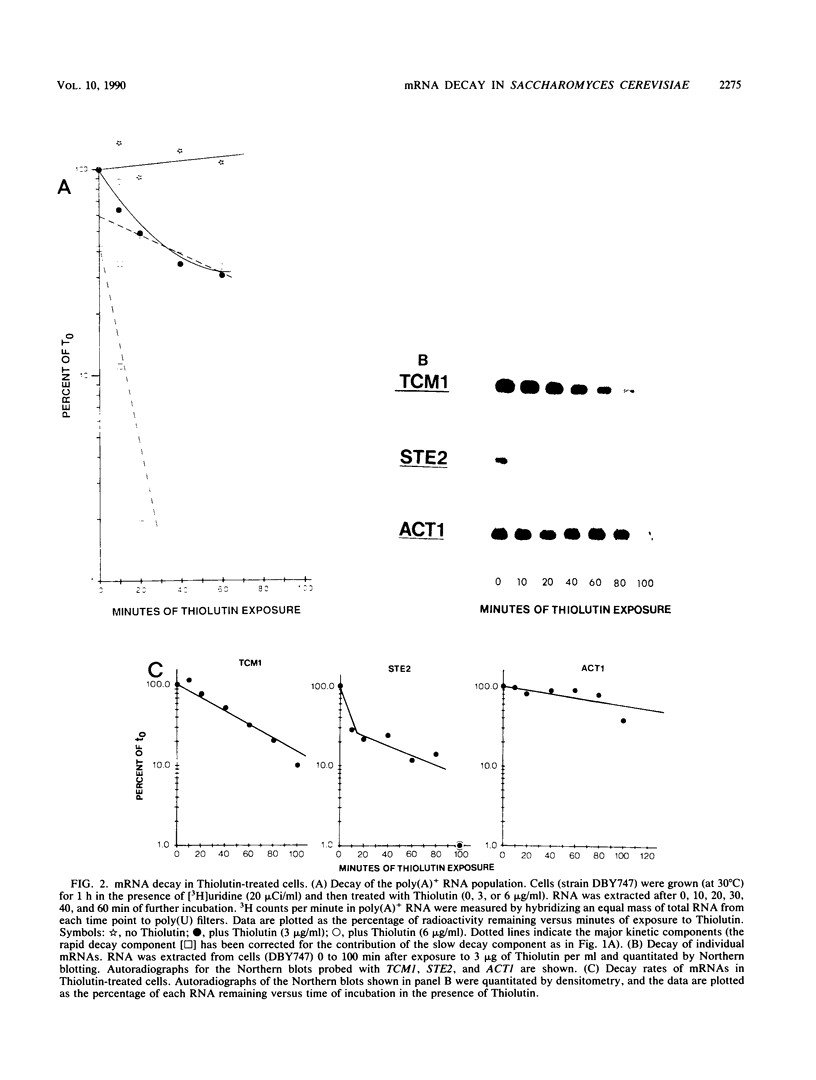
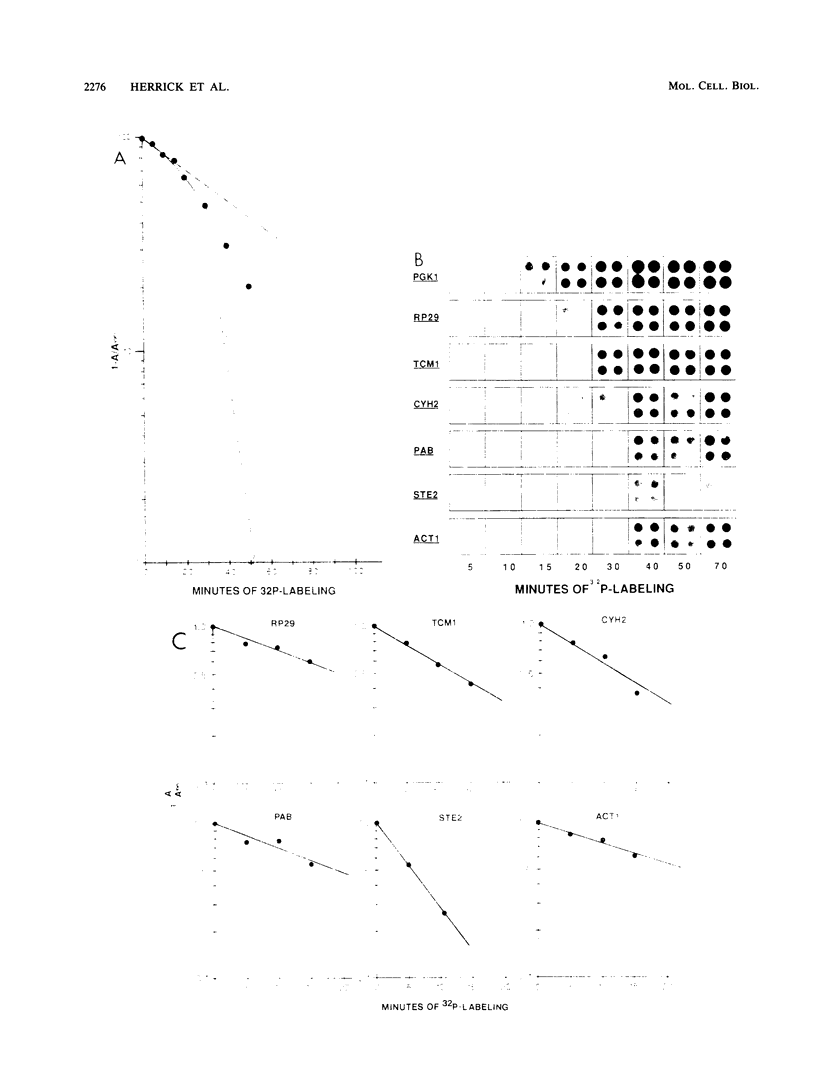
We developed a procedure to measure mRNA decay rates in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae and applied it to the determination of half-lives for 20 mRNAs encoded by well-characterized genes. The procedure utilizes Northern (RNA) or dot blotting to quantitate the levels of individual mRNAs after thermal inactivation of RNA polymerase II in an rpb1-1 temperature-sensitive mutant. We compared the results of this procedure with results obtained by two other procedures (approach to steady-state labeling and inhibition of transcription with Thiolutin) and also evaluated whether heat shock alter mRNA decay rates. We found that there are no significant differences in the mRNA decay rates measured in heat-shocked and non-heat-shocked cells and that, for most mRNAs, different procedures yield comparable relative decay rates. Of the 20 mRNAs studied, 11, including those encoded by HIS3, STE2, STE3, and MAT alpha 1, were unstable (t1/2 less than 7 min) and 4, including those encoded by ACT1 and PGK1, were stable (t1/2 greater than 25 min). We have begun to assess the basis and significance of such differences in the decay rates of these two classes of mRNA. Our results indicate that (i) stable and unstable mRNAs do not differ significantly in their poly(A) metabolism; (ii) deadenylation does not destabilize stable mRNAs; (iii) there is no correlation between mRNA decay rate and mRNA size; (iv) the degradation of both stable and unstable mRNAs depends on concomitant translational elongation; and (v) the percentage of rare codons present in most unstable mRNAs is significantly higher than in stable mRNAs.
Full text
PDF



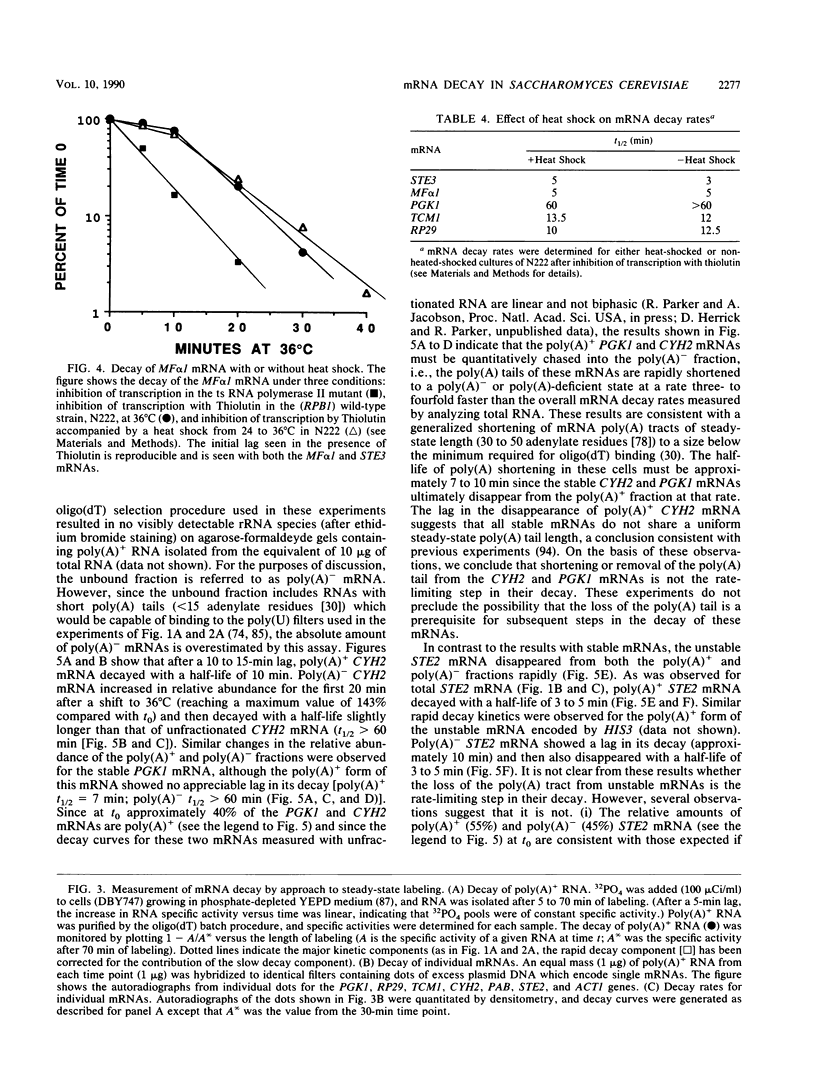
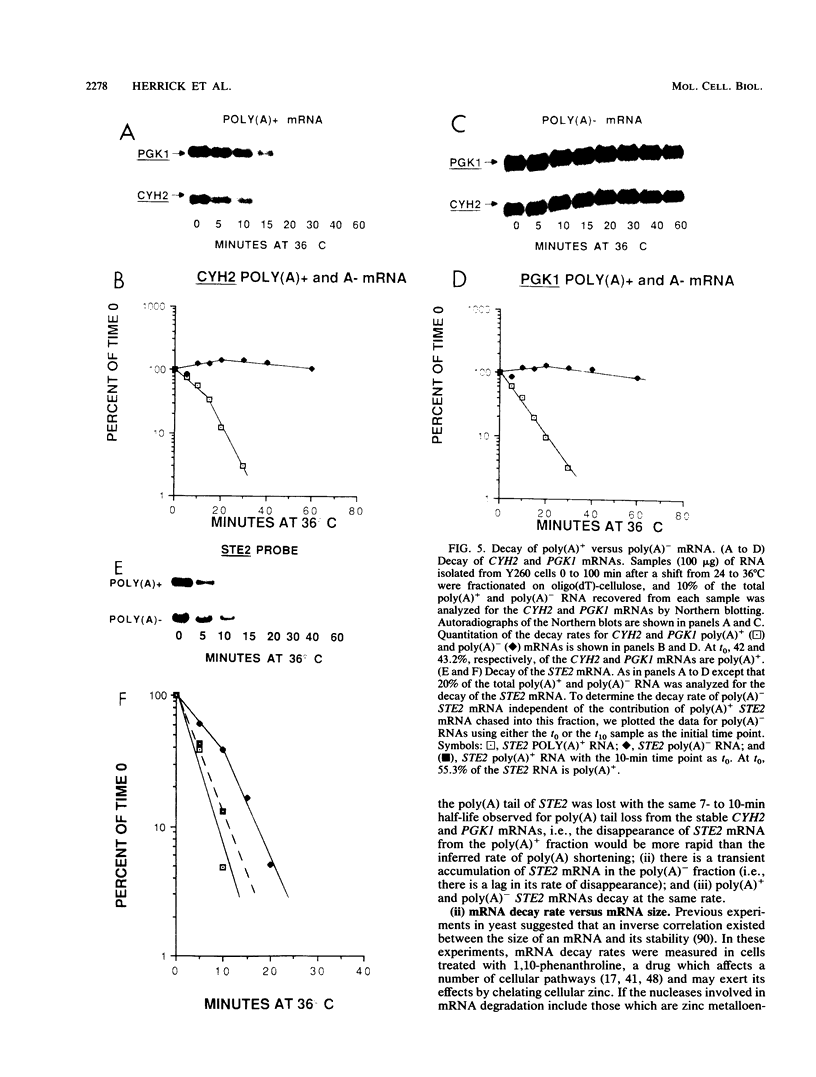
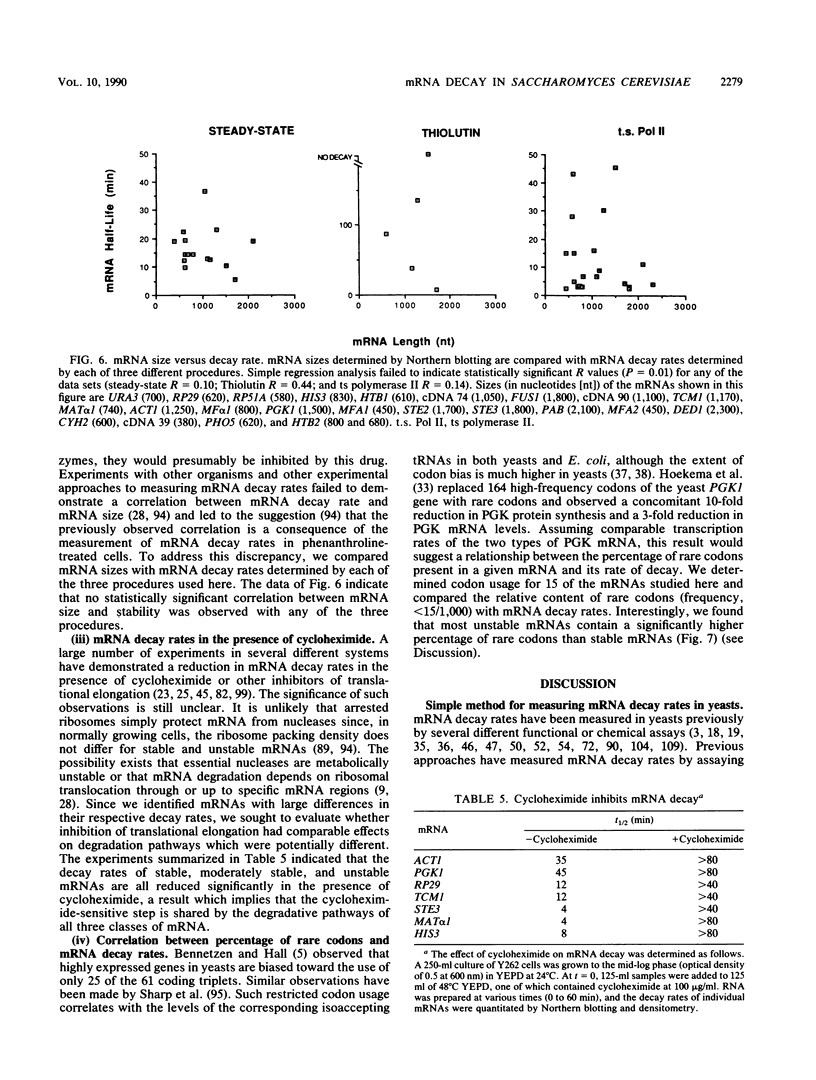
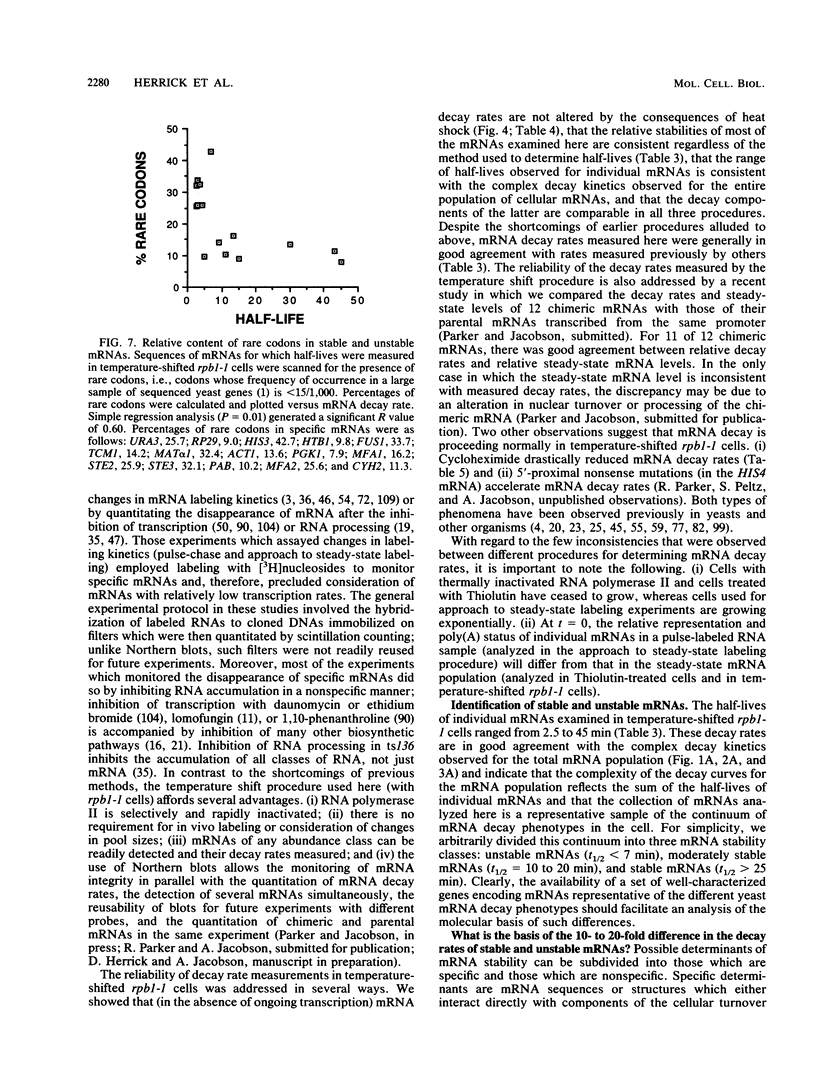




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aota S., Gojobori T., Ishibashi F., Maruyama T., Ikemura T. Codon usage tabulated from the GenBank Genetic Sequence Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988;16 (Suppl):r315–r402. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.suppl.r315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumann B., Potash M. J., Köhler G. Consequences of frameshift mutations at the immunoglobulin heavy chain locus of the mouse. EMBO J. 1985 Feb;4(2):351–359. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03636.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennetzen J. L., Hall B. D. Codon selection in yeast. J Biol Chem. 1982 Mar 25;257(6):3026–3031. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Determinants of messenger RNA stability. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):5–6. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90346-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Poly(A) shortening and degradation of the 3' A+U-rich sequences of human c-myc mRNA in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1697–1708. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer G., Ross J. Regulation of c-myc mRNA stability in vitro by a labile destabilizer with an essential nucleic acid component. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1996–2006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cano F. R., Kuo S. C., Lampen J. O. Lomofungin, an inhibitor of deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):723–728. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caput D., Beutler B., Hartog K., Thayer R., Brown-Shimer S., Cerami A. Identification of a common nucleotide sequence in the 3'-untranslated region of mRNA molecules specifying inflammatory mediators. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(6):1670–1674. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.6.1670. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carneiro M., Schibler U. Accumulation of rare and moderately abundant mRNAs in mouse L-cells is mainly post-transcriptionally regulated. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):869–880. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90316-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. L., Hentze M. W., Koeller D. M., Caughman S. W., Rouault T. A., Klausner R. D., Harford J. B. Iron-responsive elements: regulatory RNA sequences that control mRNA levels and translation. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):924–928. doi: 10.1126/science.2452485. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey L., Palatnik C. M., Jacobson A. Messenger RNA half-life in Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1983 Jan;95(1):239–243. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90023-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Yarbro J. W. Comparative effects of 1,10-phenanthroline and 1,7-phenanthroline on DNA and RNA synthesis in mouse spleen. Life Sci. 1978 Mar;22(11):1007–1010. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90366-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Yarbro J. W., Mann D. E., Jr, Gautieri R. F. Effects of 1,10-phenanthroline and a zinc complex of 1,10-phenanthroline on nucleic acid synthesis in mouse liver and spleen. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1978 Apr;205(1):27–32. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevallier M. R., Bloch J. C., Lacroute F. Transcriptional and translational expression of a chimeric bacterial-yeast plasmid in yeasts. Gene. 1980 Oct;11(1-2):11–19. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90082-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Aurora V., Stern A. M., Sigman D. S. 1,10-Phenanthroline-cuprous ion complex, a potent inhibitor of DNA and RNA polymerases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Feb 28;80(4):1025–1032. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91348-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daar I. O., Maquat L. E. Premature translation termination mediates triosephosphate isomerase mRNA degradation. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Feb;8(2):802–813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.2.802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Domdey H., Apostol B., Lin R. J., Newman A., Brody E., Abelson J. Lariat structures are in vivo intermediates in yeast pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):611–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90468-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efrat S., Kaempfer R. Control of biologically active interleukin 2 messenger RNA formation in induced human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2601–2605. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Rech J., Vie A., Piechaczyk M., Bonnieu A., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Regulation of c-fos gene expression in hamster fibroblasts: initiation and elongation of transcription and mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5657–5667. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried H. M., Pearson N. J., Kim C. H., Warner J. R. The genes for fifteen ribosomal proteins of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):10176–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Sures I. Structure of a split yeast gene: complete nucleotide sequence of the actin gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2546–2550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves R. A., Pandey N. B., Chodchoy N., Marzluff W. F. Translation is required for regulation of histone mRNA degradation. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):615–626. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90240-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. High stability of messenger RNA in growing cultured cells. Nature. 1972 Nov 10;240(5376):102–104. doi: 10.1038/240102a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groner B., Hynes N., Phillips S. Length heterogeneity in the poly (adenylic acid) region of yeast messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 17;13(26):5378–5383. doi: 10.1021/bi00723a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Raué H. A., Vreken P., Wilms E., Planta R. J. Mild temperature shock affects transcription of yeast ribosomal protein genes as well as the stability of their mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 25;16(16):7917–7929. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.16.7917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekema A., Kastelein R. A., Vasser M., de Boer H. A. Codon replacement in the PGK1 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: experimental approach to study the role of biased codon usage in gene expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2914–2924. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2914. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland M. J., Holland J. P. Isolation and identification of yeast messenger ribonucleic acids coding for enolase, glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, and phosphoglycerate kinase. Biochemistry. 1978 Nov 14;17(23):4900–4907. doi: 10.1021/bi00616a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison H. T., Hartwell L. H., McLaughlin C. S. Temperature-sensitive yeast mutant defective in ribonucleic acid production. J Bacteriol. 1969 Sep;99(3):807–814. doi: 10.1128/jb.99.3.807-814.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Phillips S. L. Turnover of polyadenylate-containing ribonucleic acid in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1976 Feb;125(2):595–600. doi: 10.1128/jb.125.2.595-600.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):573–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez A., Tipper D. J., Davies J. Mode of action of thiolutin, an inhibitor of macromolecular synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):729–738. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston G. C., Singer R. A. RNA synthesis and control of cell division in the yeast S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1978 Aug;14(4):951–958. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90349-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. R., Cole M. D. Rapid cytoplasmic turnover of c-myc mRNA: requirement of the 3' untranslated sequences. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4513–4521. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kabnick K. S., Housman D. E. Determinants that contribute to cytoplasmic stability of human c-fos and beta-globin mRNAs are located at several sites in each mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3244–3250. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim C. H., Warner J. R. Messenger RNA for ribosomal proteins in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Mar 25;165(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klo S. C., Cano F. R., Lampen J. O. Lomofungin, an inhibitor of ribonucleic acid synthesis in yeast protoplasts: its effect on enzyme formation. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1973 Jun;3(6):716–722. doi: 10.1128/aac.3.6.716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch H., Friesen J. D. Individual messenger RNA half lives in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 26;170(2):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00337787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch H., Friesen J. D. Individual messenger RNA half lives in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Feb 26;170(2):129–135. doi: 10.1007/BF00337787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krishnamurti C., Saryan L. A., Petering D. H. Effects of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and 1,10-phenanthroline on cell proliferation and DNA synthesis of Ehrlich ascites cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Nov;40(11):4092–4099. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krowczynska A., Yenofsky R., Brawerman G. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in mouse erythroleukemia cells. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 20;181(2):231–239. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurjan J., Herskowitz I. Structure of a yeast pheromone gene (MF alpha): a putative alpha-factor precursor contains four tandem copies of mature alpha-factor. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):933–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90298-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Käufer N. F., Fried H. M., Schwindinger W. F., Jasin M., Warner J. R. Cycloheximide resistance in yeast: the gene and its protein. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 25;11(10):3123–3135. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawther R. P., Cooper T. G. Effects of inducer addition and removal upon the level of allophanate hydrolase in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1973 Dec 19;55(4):1100–1104. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(73)80008-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Fuchs R. P., Lacroute F. In vivo transcription of a eukaryotic regulatory gene. EMBO J. 1983;2(12):2179–2184. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01720.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Losson R., Lacroute F. Interference of nonsense mutations with eukaryotic messenger RNA stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5134–5137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Stauber C., Schindler R., Schümperli D. Faithful cell-cycle regulation of a recombinant mouse histone H4 gene is controlled by sequences in the 3'-terminal part of the gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4389–4393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. mRNA decay rates in late-developing Dictyostelium discoideum cells are heterogeneous, and cyclic AMP does not act directly to stabilize cell-type-specific mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4088–4097. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maquat L. E., Kinniburgh A. J., Rachmilewitz E. A., Ross J. Unstable beta-globin mRNA in mRNA-deficient beta o thalassemia. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(3 Pt 2):543–553. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90396-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marbaix G., Huez G., Burny A., Cleuter Y., Hubert E., Leclercq M., Chantrenne H., Soreq H., Nudel U., Littauer U. Z. Absence of polyadenylate segment in globin messenger RNA accelerates its degradation in Xenopus oocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3065–3067. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Clay F. J., Kelsay K., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification and regulation of a gene required for cell fusion during mating of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2680–2690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Nadal-Ginard B. Cytoplasmic processing of myosin heavy chain messenger RNA: evidence provided by using a recombinant DNA plasmid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5749–5753. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellor J., Dobson M. J., Roberts N. A., Tuite M. F., Emtage J. S., White S., Lowe P. A., Patel T., Kingsman A. J., Kingsman S. M. Efficient synthesis of enzymatically active calf chymosin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1983 Sep;24(1):1–14. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90126-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer J. F., Wake S. A. An analysis of the rate of metallothionein mRNA poly(A)-shortening using RNA blot hybridization. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Nov 25;13(22):7929–7943. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.22.7929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michaelis S., Herskowitz I. The a-factor pheromone of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is essential for mating. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1309–1318. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müllner E. W., Kühn L. C. A stem-loop in the 3' untranslated region mediates iron-dependent regulation of transferrin receptor mRNA stability in the cytoplasm. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):815–825. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90098-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R., Abelson J. Isolation and sequence of the gene for actin in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3912–3916. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3912. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nudel U., Soreq H., Littauer U. Z. Globin mRNA species containing poly(A) segments of different lengths. Their functional stability in Xenopus oocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Apr 15;64(1):115–121. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10279.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osley M. A., Hereford L. M. Yeast histone genes show dosage compensation. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):377–384. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90327-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Capone A. K., Jacobson A. Messenger RNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum: does poly(A) have a regulatory role? J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 5;141(2):99–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Jacobson A. Fractionation and functional analysis of newly synthesized and decaying messenger RNAs from vegetative cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):371–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey N. B., Marzluff W. F. The stem-loop structure at the 3' end of histone mRNA is necessary and sufficient for regulation of histone mRNA stability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4557–4559. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4557. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen S. Escherichia coli ribosomes translate in vivo with variable rate. EMBO J. 1984 Dec 1;3(12):2895–2898. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02227.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips S. L., Tse C., Serventi I., Hynes N. Structure of polyadenylic acid in the ribonucleic acid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1979 May;138(2):542–551. doi: 10.1128/jb.138.2.542-551.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poteete A. R. Location and sequence of the erf gene of phage P22. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):422–429. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90101-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmsdorf H. J., Schönthal A., Angel P., Litfin M., Rüther U., Herrlich P. Posttranscriptional regulation of c-fos mRNA expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Feb 25;15(4):1643–1659. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.4.1643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raj N. B., Pitha P. M. Analysis of interferon mRNA in human fibroblast cells induced to produce interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7426–7430. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7426. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson M., Lilley R., Little S., Emtage J. S., Yarranton G., Stephens P., Millican A., Eaton M., Humphreys G. Codon usage can affect efficiency of translation of genes in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 11;12(17):6663–6671. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.17.6663. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M., Botstein D. Structure and function of the yeast URA3 gene. Differentially regulated expression of hybrid beta-galactosidase from overlapping coding sequences in yeast. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):883–904. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Tansey T. R., Ruderman J. V. Sequence-specific adenylations and deadenylations accompany changes in the translation of maternal messenger RNA after fertilization of Spisula oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):309–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. The turnover of messenger RNA. Sci Am. 1989 Apr;260(4):48–55. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0489-48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M. Three forms of the 5.8-S ribosomal RNA species in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jan 3;41(1):197–202. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03260.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santiago T. C., Bettany A. J., Purvis I. J., Brown A. J. Messenger RNA stability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: the influence of translation and poly(A) tail length. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2417–2429. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz L. D., Friesen J. D. Nucleotide sequence of the tcml gene (ribosomal protein L3) of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):8–14. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.8-14.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sehgal P. B., Soreq H., Tamm I. Does 3'-terminal poly(A) stabilize human fibroblast interferon mRNA in oocytes of Xenopus laevis? Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):5030–5033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.5030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Blume J. E., Nielsen D. A. Regulation of messenger RNA stability in eukaryotic cells. Bioessays. 1987 May;6(5):221–226. doi: 10.1002/bies.950060507. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. A., Herrick D., Manrow R. E., Blinder D., Jacobson A. Determinants of mRNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae: differences in poly(A) tail length, ribosome loading, and mRNA size cannot account for the heterogeneity of mRNA decay rates. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Tuohy T. M., Mosurski K. R. Codon usage in yeast: cluster analysis clearly differentiates highly and lowly expressed genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 11;14(13):5125–5143. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.13.5125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G., Kamen R. A conserved AU sequence from the 3' untranslated region of GM-CSF mRNA mediates selective mRNA degradation. Cell. 1986 Aug 29;46(5):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyu A. B., Greenberg M. E., Belasco J. G. The c-fos transcript is targeted for rapid decay by two distinct mRNA degradation pathways. Genes Dev. 1989 Jan;3(1):60–72. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.1.60. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Groppi V. E., Jr, Coffino P. Inhibition of protein synthesis stabilizes histone mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2082–2090. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional mapping of the yeast pet56-his3-ded1 gene region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8587–8601. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sørensen M. A., Kurland C. G., Pedersen S. Codon usage determines translation rate in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 20;207(2):365–377. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90260-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teem J. L., Rosbash M. Expression of a beta-galactosidase gene containing the ribosomal protein 51 intron is sensitive to the rna2 mutation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4403–4407. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas P. S. Hybridization of denatured RNA and small DNA fragments transferred to nitrocellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5201–5205. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5201. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tipper D. J. Inhibition of yeast ribonucleic acid polymerases by thiolutin. J Bacteriol. 1973 Oct;116(1):245–256. doi: 10.1128/jb.116.1.245-256.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonnesen T., Friesen J. D. Inhibitors of ribonucleic acid synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: decay rate of messenger ribonucleic acid. J Bacteriol. 1973 Sep;115(3):889–896. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.3.889-896.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallis J. W., Hereford L., Grunstein M. Histone H2B genes of yeast encode two different proteins. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):799–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90556-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson T., Treisman R. Removal of poly(A) and consequent degradation of c-fos mRNA facilitated by 3' AU-rich sequences. Nature. 1988 Nov 24;336(6197):396–399. doi: 10.1038/336396a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zaret K. S., Sherman F. DNA sequence required for efficient transcription termination in yeast. Cell. 1982 Mar;28(3):563–573. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90211-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zitomer R. S., Montgomery D. L., Nichols D. L., Hall B. D. Transcriptional regulation of the yeast cytochrome c gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3627–3631. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]