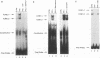Abstract
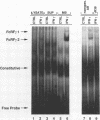
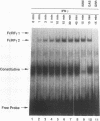
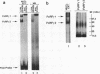
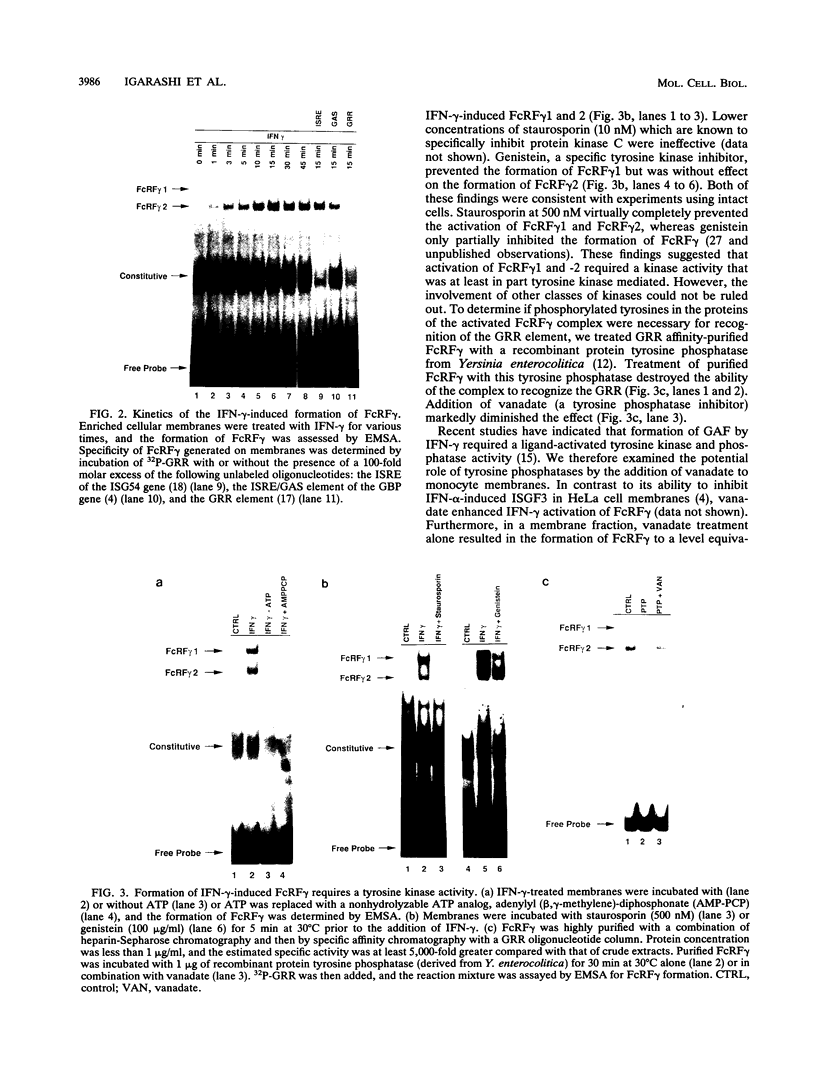
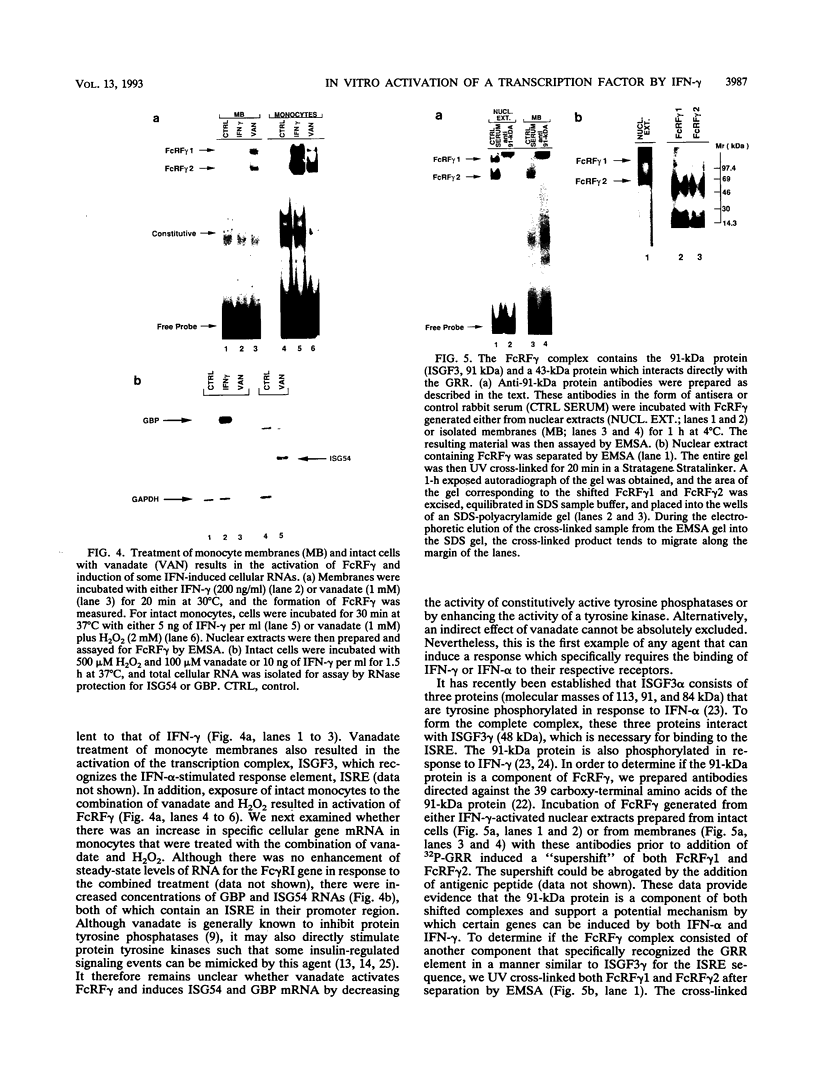
Gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) activates the formation of a DNA-binding protein complex (FcRF gamma) that recognizes the gamma response region (GRR) of the promoter for the human high-affinity Fc gamma receptor. In a membrane-enriched fraction prepared from human peripheral blood monocytes, IFN-gamma activation of FcRF gamma occurred within 1 min and was ATP dependent. Activation of FcRF gamma required a tyrosine kinase activity, and recognition of the GRR sequence by FcRF gamma could be abrogated by treatment with a tyrosine-specific protein phosphatase. Treatment of cells with vanadate alone resulted in the formation of FcRF gamma without the need for IFN-gamma. UV cross-linking and antibody competition experiments demonstrated that the FcRF gamma complex was composed of at least two components: the 91-kDa protein of the IFN-alpha-induced transcription complex ISGF3 and a 43-kDa component that bound directly to the GRR. Therefore, specificity for IFN-induced transcriptional activation of early response genes requires at least two events: (i) ligand-induced activation of membrane-associated protein by tyrosine phosphorylation and (ii) formation of a complex composed of an activated membrane protein(s) and a sequence-specific DNA-binding component.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boulet I., Ralph S., Stanley E., Lock P., Dunn A. R., Green S. P., Phillips W. A. Lipopolysaccharide- and interferon-gamma-induced expression of hck and lyn tyrosine kinases in murine bone marrow-derived macrophages. Oncogene. 1992 Apr;7(4):703–710. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Y. S., Patterson C. E., Staeheli P. Interferon-induced guanylate-binding proteins lack an N(T)KXD consensus motif and bind GMP in addition to GDP and GTP. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Sep;11(9):4717–4725. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.9.4717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Larner A. C. Activation of transcription factors by interferon-alpha in a cell-free system. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):813–815. doi: 10.1126/science.1496402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- David M., Romero G., Zhang Z. Y., Dixon J. E., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor ISGF3 by interferon alpha involves a membrane-associated tyrosine phosphatase and tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6593–6599. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker T., Lew D. J., Cheng Y. S., Levy D. E., Darnell J. E., Jr Interactions of alpha- and gamma-interferon in the transcriptional regulation of the gene encoding a guanylate-binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):2009–2014. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03608.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Larner A. C., Nakagawa Y., Hoover D. L. Culture of human monocytes with granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor results in enhancement of IFN-gamma receptors but suppression of IFN-gamma-induced expression of the gene IP-10. J Immunol. 1993 Mar 15;150(6):2383–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Morales P., Minami Y., Luong E., Klausner R. D., Samelson L. E. Tyrosine phosphorylation in T cells is regulated by phosphatase activity: studies with phenylarsine oxide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9255–9259. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garotta G., Ozmen L., Fountoulakis M., Dembic Z., van Loon A. P., Stüber D. Human interferon-gamma receptor. Mapping of epitopes recognized by neutralizing antibodies using native and recombinant receptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6908–6915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. A. Use of vanadate as protein-phosphotyrosine phosphatase inhibitor. Methods Enzymol. 1991;201:477–482. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(91)01043-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graber M., June C. H., Samelson L. E., Weiss A. The protein tyrosine kinase inhibitor herbimycin A, but not genistein, specifically inhibits signal transduction by the T cell antigen receptor. Int Immunol. 1992 Nov;4(11):1201–1210. doi: 10.1093/intimm/4.11.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinstein S., Furuya W., Lu D. J., Mills G. B. Vanadate stimulates oxygen consumption and tyrosine phosphorylation in electropermeabilized human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 5;265(1):318–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan K. L., Dixon J. E. Protein tyrosine phosphatase activity of an essential virulence determinant in Yersinia. Science. 1990 Aug 3;249(4968):553–556. doi: 10.1126/science.2166336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hainaut P., Giorgetti S., Kowalski A., Van Obberghen E. Insulin-like effects of vanadate on glucose uptake and on maturation in Xenopus laevis oocytes. Cell Regul. 1991 Apr;2(4):317–327. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.4.317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heffetz D., Bushkin I., Dror R., Zick Y. The insulinomimetic agents H2O2 and vanadate stimulate protein tyrosine phosphorylation in intact cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 15;265(5):2896–2902. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard O. M., Dean M., Young H., Ramsburg M., Turpin J. A., Michiel D. F., Kelvin D. J., Lee L., Farrar W. L. Characterization of a class 3 tyrosine kinase. Oncogene. 1992 May;7(5):895–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Igarashi K., David M., Finbloom D. S., Larner A. C. In vitro activation of the transcription factor gamma interferon activation factor by gamma interferon: evidence for a tyrosine phosphatase/kinase signaling cascade. Mol Cell Biol. 1993 Mar;13(3):1634–1640. doi: 10.1128/mcb.13.3.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metzger H. Fc receptors and membrane immunoglobulin. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90074-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray H. W. The interferons, macrophage activation, and host defense against nonviral pathogens. J Interferon Res. 1992 Oct;12(5):319–322. doi: 10.1089/jir.1992.12.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea J. J., McVicar D. W., Bailey T. L., Burns C., Smyth M. J. Activation of human peripheral blood T lymphocytes by pharmacological induction of protein-tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Nov 1;89(21):10306–10310. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.21.10306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse R. N., Feinman R., Ravetch J. V. Characterization of the promoter of the human gene encoding the high-affinity IgG receptor: transcriptional induction by gamma-interferon is mediated through common DNA response elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 15;88(24):11305–11309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.24.11305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petricoin E. F., 3rd, Hackett R. H., Akai H., Igarashi K., Finbloom D. S., Larner A. C. Modulation of interferon signaling in human fibroblasts by phorbol esters. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;12(10):4486–4495. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.10.4486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ravetch J. V., Kinet J. P. Fc receptors. Annu Rev Immunol. 1991;9:457–492. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.09.040191.002325. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Fu X. Y., Improta T., Aebersold R., Darnell J. E., Jr Proteins of transcription factor ISGF-3: one gene encodes the 91-and 84-kDa ISGF-3 proteins that are activated by interferon alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7836–7839. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schindler C., Shuai K., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Interferon-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of a latent cytoplasmic transcription factor. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):809–813. doi: 10.1126/science.1496401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shuai K., Schindler C., Prezioso V. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Activation of transcription by IFN-gamma: tyrosine phosphorylation of a 91-kD DNA binding protein. Science. 1992 Dec 11;258(5089):1808–1812. doi: 10.1126/science.1281555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura S., Brown T. A., Whipple J. H., Fujita-Yamaguchi Y., Dubler R. E., Cheng K., Larner J. A novel mechanism for the insulin-like effect of vanadate on glycogen synthase in rat adipocytes. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 25;259(10):6650–6658. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unkeless J. C., Scigliano E., Freedman V. H. Structure and function of human and murine receptors for IgG. Annu Rev Immunol. 1988;6:251–281. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.06.040188.001343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velazquez L., Fellous M., Stark G. R., Pellegrini S. A protein tyrosine kinase in the interferon alpha/beta signaling pathway. Cell. 1992 Jul 24;70(2):313–322. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90105-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson K. C., Finbloom D. S. Interferon gamma rapidly induces in human monocytes a DNA-binding factor that recognizes the gamma response region within the promoter of the gene for the high-affinity Fc gamma receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Dec 15;89(24):11964–11968. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.24.11964. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]