Abstract
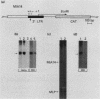
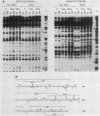
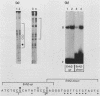
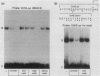
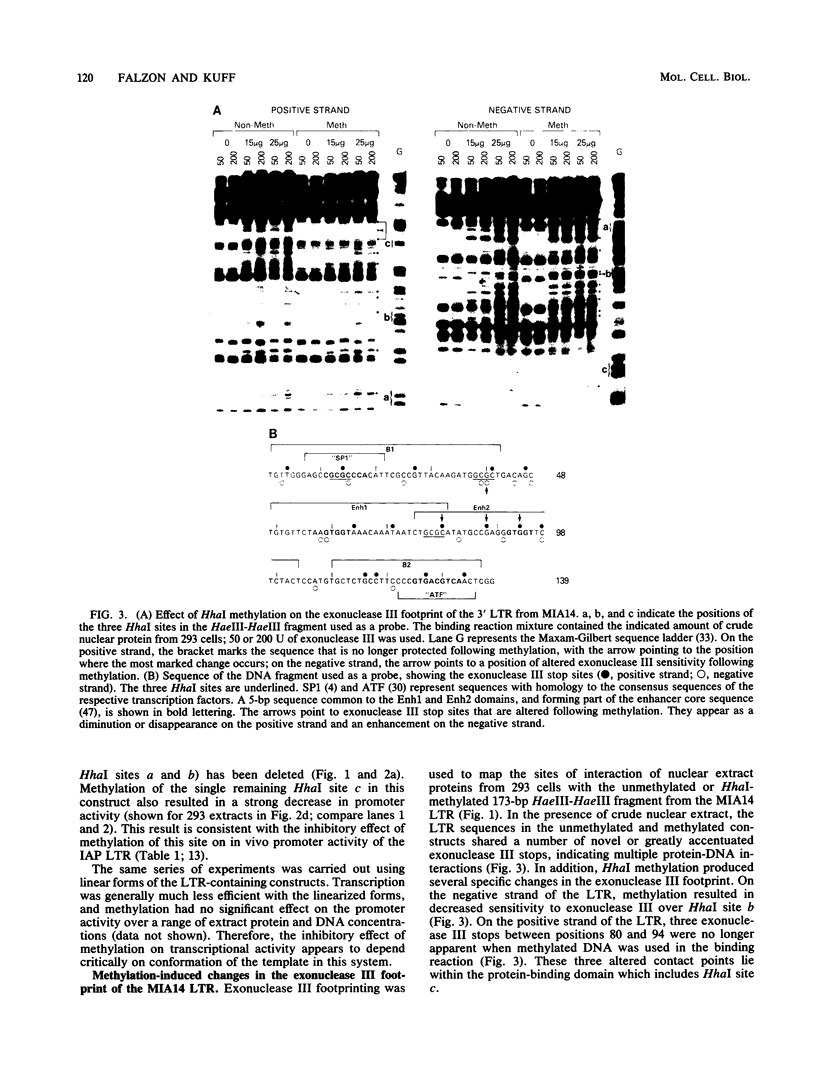
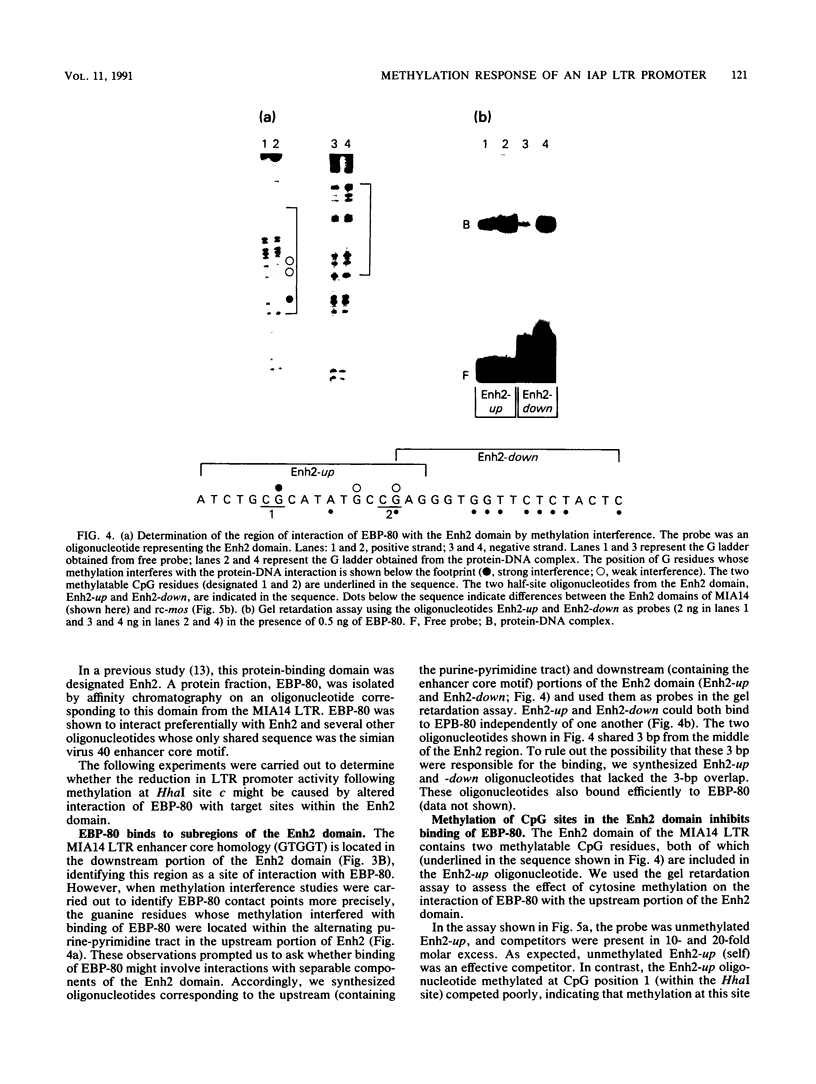
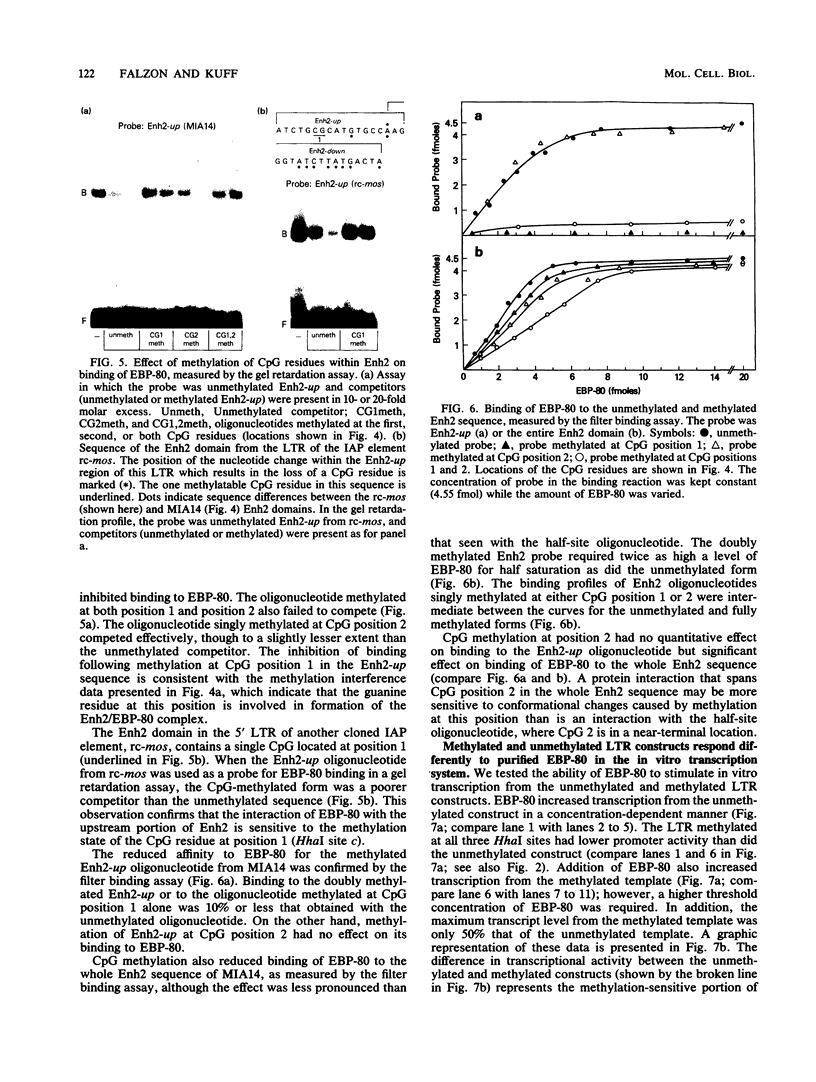
Intracisternal A-particle (IAP) expression in mouse cells has been correlated with hypomethylation of HhaI and HpaII sites in proviral long terminal repeats (LTRs). In a previous study, in vitro methylation of three HhaI sites in the U3 region of the LTR from the cloned genomic IAP element, MIA14, was shown to inhibit promoter activity in vivo. In this study, we found by site-directed mutagenesis that the two more downstream HhaI sites within this LTR were responsible for the methylation effects on promoter activity in vivo; methylation of the other (5') HhaI site, which lies within a putative SP1 binding domain, did not affect promoter activity. Methylation of the HhaI sites also inhibited promoter activity of the LTR in a cell-free transcription system. Exonuclease III footprinting demonstrated methylation-induced changes in protein binding over the region encompassing the downstream HhaI site, designated the Enh2 domain. The protein that interacts specifically with this domain, EBP-80, was characterized in a previous study (M. Falzon and E. L. Kuff, J. Biol. Chem. 264:21915-21922, 1989). We show here that the presence of methylcytosine in the HhaI site within the Enh2 domain inhibited binding of EBP-80 in vitro. The methylated MIA14 LTR construct was much less responsive to added EBP-80 in an in vitro transcription system than was the unmethylated construct. These data suggest that CpG methylation within the Enh2 domain may exert its effect on transcription in vivo by altering the interaction between EBP-80 and its cognate DNA sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bednarik D. P., Cook J. A., Pitha P. M. Inactivation of the HIV LTR by DNA CpG methylation: evidence for a role in latency. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1157–1164. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08222.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behe M., Felsenfeld G. Effects of methylation on a synthetic polynucleotide: the B--Z transition in poly(dG-m5dC).poly(dG-m5dC). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1619–1623. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Hattar J., Jiricny J. Methylation of single CpG dinucleotides within a promoter element of the Herpes simplex virus tk gene reduces its transcription in vivo. Gene. 1988 May 30;65(2):219–227. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90458-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. R., Kadonaga J. T., Bell S. P., Tjian R. Purification and biochemical characterization of the promoter-specific transcription factor, Sp1. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):47–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3529394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Inhibition of herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene expression by DNA methylation is an indirect effect. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Aug 12;13(15):5503–5513. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.15.5503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buschhausen G., Wittig B., Graessmann M., Graessmann A. Chromatin structure is required to block transcription of the methylated herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1177–1181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busslinger M., Hurst J., Flavell R. A. DNA methylation and the regulation of globin gene expression. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90150-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Huang R. C. Functional analysis of the long terminal repeats of intracisternal A-particle genes: sequences within the U3 region determine both the efficiency and direction of promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Lewis A. M., Jr Host response to adenovirus 2-transformed hamster embryo cells. Cancer Res. 1979 May;39(5):1455–1461. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doerfler W. DNA methylation and gene activity. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:93–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzon M., Kuff E. L. A variant binding sequence for transcription factor EBP-80 confers increased promoter activity on a retroviral long terminal repeat. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13084–13090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzon M., Kuff E. L. Isolation and characterization of a protein fraction that binds to enhancer core sequences in intracisternal A-particle long terminal repeats. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21915–21922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzon M., Kuff E. L. Multiple protein-binding sites in an intracisternal A particle long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4070–4077. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4070-4077.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra A., Fewell J., Lueders K., Kuff E. In vitro methylation inhibits the promotor activity of a cloned intracisternal A-particle LTR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4343–4352. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox K. R. The effect of HhaI methylation on DNA local structure. Biochem J. 1986 Feb 15;234(1):213–216. doi: 10.1042/bj2340213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., Smiley J., Russell W. C., Nairn R. Characteristics of a human cell line transformed by DNA from human adenovirus type 5. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jul;36(1):59–74. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-1-59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbers K., Schnieke A., Stuhlmann H., Jähner D., Jaenisch R. DNA methylation and gene expression: endogenous retroviral genome becomes infectious after molecular cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington M. A., Jones P. A., Imagawa M., Karin M. Cytosine methylation does not affect binding of transcription factor Sp1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2066–2070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hermann R., Hoeveler A., Doerfler W. Sequence-specific methylation in a downstream region of the late E2A promoter of adenovirus type 2 DNA prevents protein binding. J Mol Biol. 1989 Nov 20;210(2):411–415. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hojman-Montes de Oca F., Dianoux L., Peries J., Emanoil-Ravicovitch R. Intracisternal A particles: RNA expression and DNA methylation in murine teratocarcinoma cell lines. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):307–310. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.307-310.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höller M., Westin G., Jiricny J., Schaffner W. Sp1 transcription factor binds DNA and activates transcription even when the binding site is CpG methylated. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1127–1135. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Schaffner W. CpG methylation of the cAMP-responsive enhancer/promoter sequence TGACGTCA abolishes specific factor binding as well as transcriptional activation. Genes Dev. 1989 May;3(5):612–619. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.5.612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keshet I., Yisraeli J., Cedar H. Effect of regional DNA methylation on gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2560–2564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovesdi I., Reichel R., Nevins J. R. Role of an adenovirus E2 promoter binding factor in E1A-mediated coordinate gene control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2180–2184. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruczek I., Doerfler W. Expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene in mammalian cells under the control of adenovirus type 12 promoters: effect of promoter methylation on gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7586–7590. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasneret J., Canivet M., Hojman-Montes de Oca F., Tobaly J., Emanoil-Ravicovitch R., Peries J. Activation of intracisternal a particles by 5-azacytidine in mouse Ki-BALB cell line. Virology. 1983 Jul 30;128(2):485–489. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90275-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Green M. R. Interaction of a common cellular transcription factor, ATF, with regulatory elements in both E1a- and cyclic AMP-inducible promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3396–3400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Fewell J. W., Kuff E. L., Koch T. The long terminal repeat of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle gene functions as a promoter when introduced into eucaryotic cells by transfection. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2128–2135. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mays-Hoopes L. L., Brown A., Huang R. C. Methylation and rearrangement of mouse intracisternal a particle genes in development, aging, and myeloma. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1371–1380. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan R. A., Huang R. C. Correlation of undermethylation of intracisternal A-particle genes with expression in murine plasmacytomas but not in NIH/3T3 embryo fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1984 Nov;44(11):5234–5241. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E. J., Grosveld F. Site specific demethylation in the promoter of human gamma-globin gene does not alleviate methylation mediated suppression. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2329–2335. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02508.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray E., Grosveld F. Methylation and gamma-globin expression. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1985;198:157–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordheim A., Rich A. Negatively supercoiled simian virus 40 DNA contains Z-DNA segments within transcriptional enhancer sequences. Nature. 1983 Jun 23;303(5919):674–679. doi: 10.1038/303674a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohlsson H., Edlund T. Sequence-specific interactions of nuclear factors with the insulin gene enhancer. Cell. 1986 Apr 11;45(1):35–44. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90535-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rahmouni A. R., Wells R. D. Stabilization of Z DNA in vivo by localized supercoiling. Science. 1989 Oct 20;246(4928):358–363. doi: 10.1126/science.2678475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Speck N. A., Baltimore D. Six distinct nuclear factors interact with the 75-base-pair repeat of the Moloney murine leukemia virus enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1101–1110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Ott J., Eckstein F. The rapid generation of oligonucleotide-directed mutations at high frequency using phosphorothioate-modified DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8765–8785. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8765. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. W., Schmidt W., Cosstick R., Okruszek A., Eckstein F. The use of phosphorothioate-modified DNA in restriction enzyme reactions to prepare nicked DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 20;13(24):8749–8764. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.24.8749. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F., Molloy P. L. Cytosine methylation prevents binding to DNA of a HeLa cell transcription factor required for optimal expression of the adenovirus major late promoter. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1136–1143. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]