Abstract
The 4S RNA contained in RNA tumor virus particles consists of a selected population of host tRNA's. However, the mechanism by which virions select host tRNA's has not been elucidated. We have considered a model which specifies that 35S genomic RNA determines which tRNA's are to be encapsidated as well as the relative amounts of these tRNA's within the virion. The model was tested by comparing the free 4S RNA composition of normal murine leukemia virus (MuLV) particles and noninfectious virions from actinomycin D (ActD)-treated cells, which are deficient in genomic RNA (ActD virions). Viral 4S RNA was analyzed by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Surprisingly, the patterns obtained for control and ActD 4S RNA were identical to each other and were clearly distinct from the cell 4S RNA pattern. The viral patterns had three prominent areas of radioactivity. One of the spots was identified on the basis of its oligonucleotide fingerprint as tRNA Pro, the primer for MuLV RNA-directed DNA synthesis. These results were obtained with two different MuLV strains, AKR and Moloney, each grown in SC-1 cells. The demonstration that ActD virions contain primer tRNA and in general exhibit the characteristic MuLV tRNA pattern rather than the complete representation of cell 4S RNA leads to the conclusion that genomic RNA is not the major determinant in selective packaging of host tRNA's. A possible role for one or more viral proteins, including reverse transcriptase, is suggested.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluda M. A., Nayak D. P. DNA complementary to viral RNA in leukemic cells induced by avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Jun;66(2):329–336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.2.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baroudy B. M., Fournier M., Labouesse J., Papas T. S., Chirikjian J. G. tRNATrp (bovine) binding to the reverse transcriptase of avian myeloblastosis virus and function as a heterologous primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):1889–1893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.1889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bellamy A. R., Gillies S. C., Harvey J. D. Molecular weight of two oncornavirus genomes: derivation from particle molecular weights and RNA content. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1388–1393. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1388-1393.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender W., Davidson N. Mapping of poly(A) sequences in the electron microscope reveals unusual structure of type C oncornavirus RNA molecules. Cell. 1976 Apr;7(4):595–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90210-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Levinson W. E., Quintrell N., Sullivan D., Fanshier L., Jackson J. The low molecular weight RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus. I. The 4 S RNA. Virology. 1970 Sep;42(1):182–195. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90251-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Levinson W. E., Sullivan D., Fanshier L., Quintrell N., Jackson J. The low molecular weight RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus. II. The 7 S RNA. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):927–937. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90341-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonar R. A., Sverak L., Bolognesi D. P., Langlois A. J., Beard D., Beard J. W. Ribonucleic acid components of BAI strain A (myeloblastosis) avian tumor virus. Cancer Res. 1967 Jun;27(6):1138–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R. D., Armentrout R. W. Primer recognition by avian myeloblastosis virus RNA-directed DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1236–1239. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1236-1239.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Duesberg P. Role of subunits of 60 to 70S avian tumor virus ribonucleic acid in its template activity for the viral deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1972 Jul;10(1):23–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.1.23-31.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carnegie J. W., Deeney A. O., Olson K. C., Beaudreau G. S. An RNA fraction from myeloblastosis virus having properties similar to transfer RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 22;190(2):274–284. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90079-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cordell B., Stavnezer E., Friedrich R., Bishop J. M., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence that binds primer for DNA synthesis to the avian sarcoma virus genome. J Virol. 1976 Aug;19(2):548–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.2.548-558.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlberg J. E., Sawyer R. C., Taylor J. M., Faras A. J., Levinson W. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Transcription of DNA from the 70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. I. Identification of a specific 4S RNA which serves as primer. J Virol. 1974 May;13(5):1126–1133. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.5.1126-1133.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis J., Scherer M., Tsai W. P., Long C. Low-molecular- weight Rauscher leukemia virus protein with preferential binding for single-stranded RNA and DNA. J Virol. 1976 May;18(2):709–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.2.709-718.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duesberg P. H., Robinson W. S. Inhibition of mouse leukemia virus (MLV) replication by actinomycin D. Virology. 1967 Apr;31(4):742–746. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(67)90211-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eiden J. J., Quade K., Nichols J. L. Interaction of tryptophan transfer RNA with Rous sarcoma virus 35S RNA. Nature. 1976 Jan 22;259(5540):245–247. doi: 10.1038/259245a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emanoil-Ravicovitch R., Larsen C. J., Bazilier M., Robin J., Périès J., Boiron M. Low-molecular-weight RNAs of murine sarcoma virus: comparative studies of free and 70S RNA-associated components. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1625–1627. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1625-1627.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Association of 4S ribonucleic acid with oncornavirus ribonucleic acids. J Virol. 1971 Aug;8(2):254–256. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.2.254-256.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Isolation of amino acid acceptor RNA from purified avian myeloblastosis virus. J Mol Biol. 1970 Sep 14;52(2):387–390. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90038-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson R. L. Studies on the RNA from avian myeloblastosis virus. Virology. 1969 Jan;37(1):124–131. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(69)90313-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faras A. J., Garapin A. C., Levinson W. E., Bishop J. M., Goodman H. M. Characterization of the low-molecular-weight RNAs associated with the 70S RNA of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):334–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.334-342.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Faras A. J., Taylor J. M., Levinson W. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. RNA-directed DNA polymerase of Rous sarcoma virus: initiation of synthesis with 70 S viral RNA as template. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 5;79(1):163–183. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90277-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folk W. R., Faras A. J. Initiation of DNA synthesis by the avian oncornavirus RNA-directed DNA polymerase: tryptophan tRNA as the major species of primer RNA. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):1049–1051. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.1049-1051.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Chromatographic analyses of isoaccepting tRNAs from avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):449–457. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.449-457.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerwin B. I., Levin J. G. Interactions of murine leukemia virus core components: characterization of reverse transcriptase packaged in the absence of 70S genomic RNA. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):478–488. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.478-488.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grandgenett D. P., Vora A. C., Faras A. J. Different states of avian myeloblastosis virus DNA polymerase and their binding capacity to primer rRNATrp. Virology. 1976 Nov;75(1):26–32. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90004-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada F., Sawyer R. C., Dahlberg J. E. A primer ribonucleic acid for initiation of in vitro Rous sarcarcoma virus deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 10;250(9):3487–3497. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Clonal cells lines from a feral mouse embryo which lack host-range restrictions for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):128–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haseltine W. A., Panet A., Smoler D., Baltimore D., Peters G., Harada F., Dahlberg J. E. Interaction of tryptophan tRNA and avian myeloblastosis virus reverse transcriptase: further characterization of the binding reaction. Biochemistry. 1977 Aug 9;16(16):3625–3632. doi: 10.1021/bi00635a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hizi A., Leis J. P., Joklik W. K. The RNA-dependent DNA polymerase of avian sarcoma virus B77. Binding of viral and nonviral ribonucleic acids to the alpha, beta2, and alphabeta forms of the enzyme. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6878–6884. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T., Dahlberg J. E. Small ribonucleic acids of Escherichia coli. I. Characterization by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jul 25;248(14):5024–5032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jamjoom G. A., Naso R. B., Arlinghaus R. B. Selective decrease in the rate of cleavage of an intracellular precursor to Rauscher leukemia virus p30 by treatment of infected cells with actinomycin D. J Virol. 1976 Sep;19(3):1054–1072. doi: 10.1128/jvi.19.3.1054-1072.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King A. M. High molecular weight RNAs from Rous sarcoma virus and Moloney murine leukemia virus contain two subunits. J Biol Chem. 1976 Jan 10;251(1):141–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
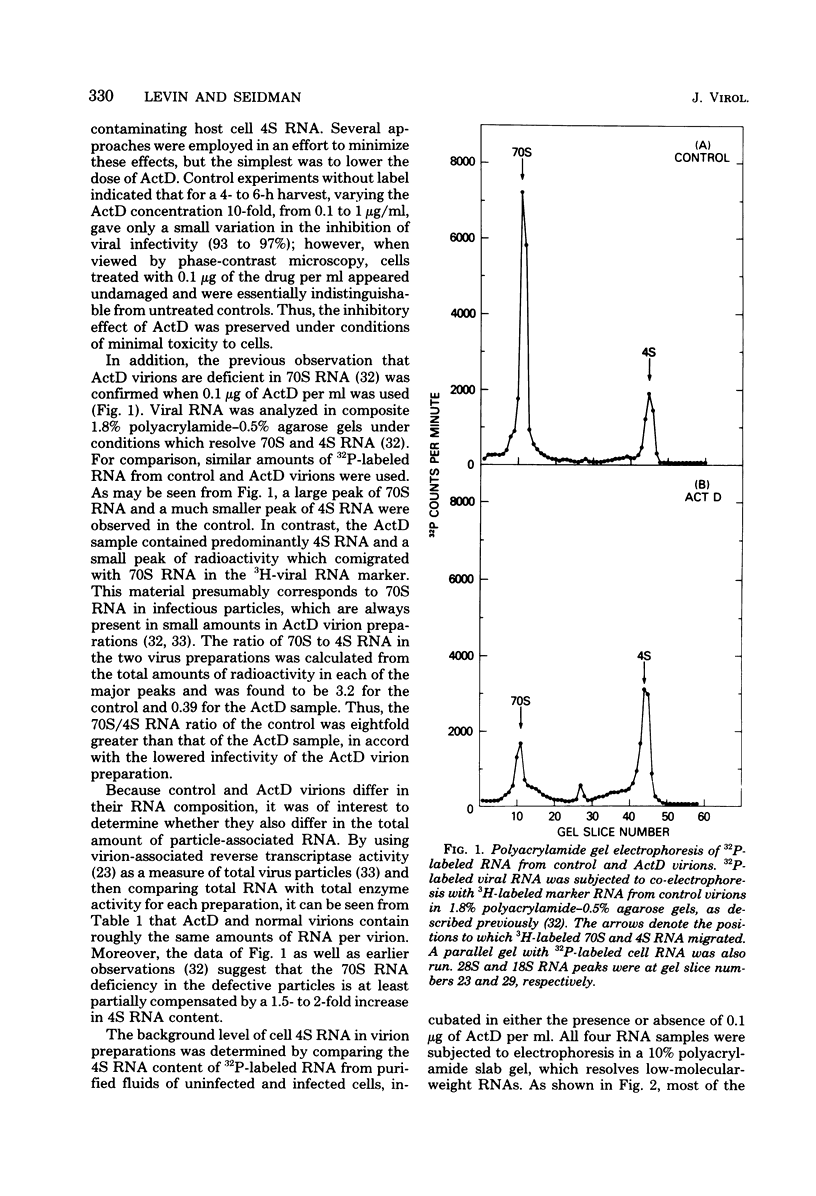
- Levin J. G., Grimley P. M., Ramseur J. M., Berezesky I. K. Deficiency of 60 to 70S RNA in murine leukemia virus particles assembled in cells treated with actinomycin D. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):152–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.152-161.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin J. G., Rosenak M. J. Synthesis of murine leukemia virus proteins associated with virions assembled in actinomycin D-treated cells: evidence for persistence of viral messenger RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Apr;73(4):1154–1158. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.4.1154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangel W. F., Delius H., Duesberg P. H. Structure and molecular weight of the 60-70S RNA and the 30-40S RNA of the Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Nov;71(11):4541–4545. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.11.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oroszlan S., Long C. W., Gilden R. V. Isolation of murine type-C virus p30 precursor protein by DNA-cellulose chromatography. Virology. 1976 Jul 15;72(2):523–526. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oskarsson M. K., Long C. W., Robey W. G., Scherer M. A., Vande Woude G. F. Phosphorylation and nucleic acid binding properties of m1 Moloney murine sarcoma virus-specific pP60gag. J Virol. 1977 Jul;23(1):196–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.1.196-204.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., Berliner H. Binding of tRNA to reverse transcriptase of RNA tumor viruses. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):214–220. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.214-220.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panet A., Haseltine W. A., Baltimore D., Peters G., Harada F., Dahlberg J. E. Specific binding of tryptophan transfer RNA to avian myeloblastosis virus RNA-dependent DNA polymerase (reverse transcriptase). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2535–2539. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paskind M. P., Weinberg R. A., Baltimore D. Dependence of Moloney murine leukemia virus production on cell growth. Virology. 1975 Sep;67(1):242–248. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
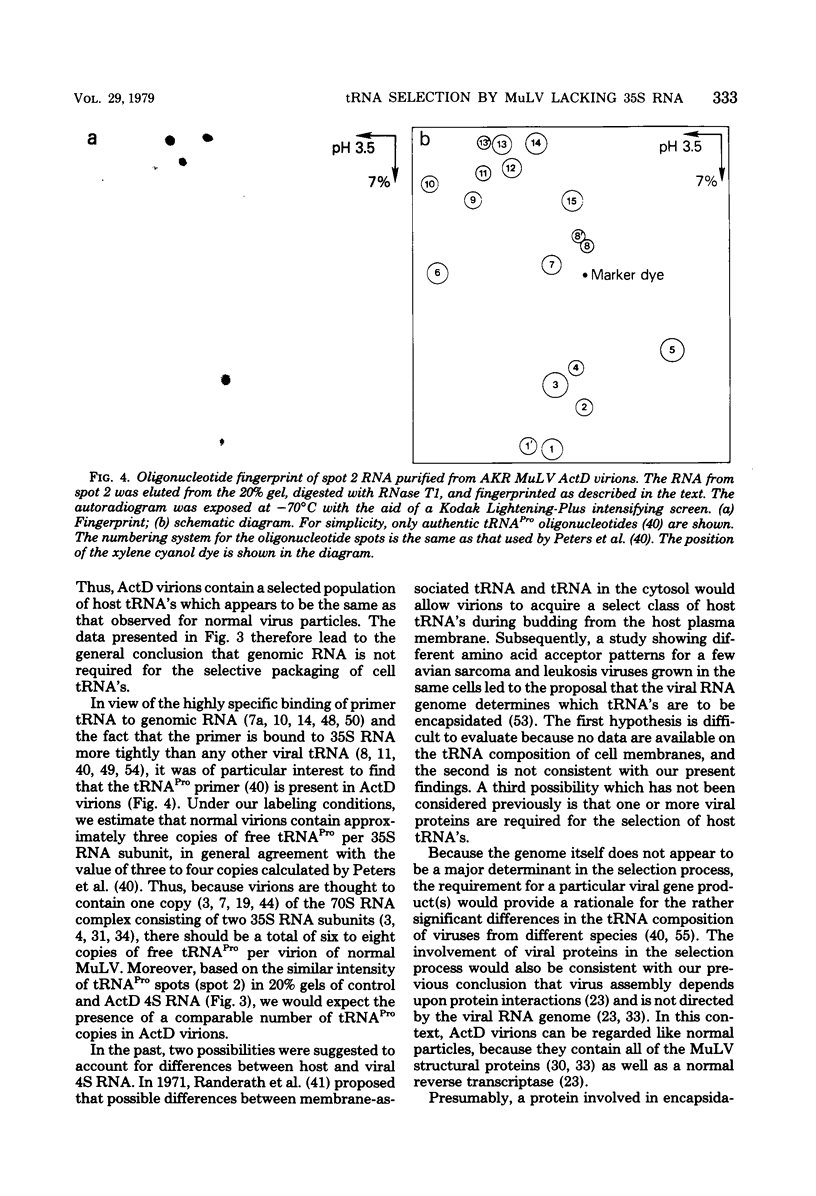
- Peters G., Harada F., Dahlberg J. E., Panet A., Haseltine W. A., Baltimore D. Low-molecular-weight RNAs of Moloney murine leukemia virus: identification of the primer for RNA-directed DNA synthesis. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1031–1041. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1031-1041.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randerath K., Rosenthal L. J., Zamecnik P. C. Base composition differences between avian myeloblastosis virus transfer RNA and transfer RNA isolated from host cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3233–3237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pugh W. E., Hartley J. W. Plaque assay techniques for murine leukemia viruses. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):1136–1139. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90362-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Brownlee G. G., Barrell B. G. A two-dimensional fractionation procedure for radioactive nucleotides. J Mol Biol. 1965 Sep;13(2):373–398. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80104-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer R. C., Dahlberg J. E. Small RNAs of Rous sarcoma virus: characterization by two-dimensional polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and fingerprint analysis. J Virol. 1973 Dec;12(6):1226–1237. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.6.1226-1237.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulein M., Burnette W. N., August J. T. Stoichiometry and specificity of binding of Rauscher oncovirus 10,000-dalton (p10) structural protein to nucleic acids. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):54–60. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.54-60.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Barrell B. G., McClain W. H. Five steps in the conversion of a large precursor RNA into bacteriophage proline and serine transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1975 Dec 25;99(4):733–760. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen A., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Specific binding of the type C viral core protein p12 with purified viral RNA. Cell. 1976 Jan;7(1):21–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90251-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskus K. A., Collett M. S., Faras A. J. Initiation of DNA synthesis by the avian oncornavirus RNA-directed DNA polymerase: structural and functional localization of the major species of primer RNA on the oncornavirus genome. Virology. 1976 May;71(1):162–168. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Cordell-Stewart B., Rohde W., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Reassociation of 4 S and 5 S RNA's with the genome of avian sarcoma virus. Virology. 1975 May;65(1):248–259. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R. Site on the RNA of an avian sarcoma virus at which primer is bound. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):553–558. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.553-558.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trávnícek M. Some properties of amino acid-acceptor RNA isolated from avian tumour virus BAI strain A (avian myeloblastosis). Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Jun 17;182(2):427–439. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M., Meuth N. L., Bromfeld E., Manly K. F., Baltimore D. Covalently linked RNA-DNA molecule as initial product of RNA tumour virus DNA polymerase. Nat New Biol. 1971 Sep 29;233(39):131–134. doi: 10.1038/newbio233131a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang S., Kothari R. M., Taylor M., Hung P. Transfer RNA activities of Rous sarcoma and Rous associated viruses. Nat New Biol. 1973 Apr 4;242(118):133–135. doi: 10.1038/newbio242133a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Mullin B. C., Ho T., Yang W. K. Ability of tryptophan tRNA to hybridize with 35S RNA of avian myeloblastosis virus and to prime reverse transcription in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jun;72(6):2155–2159. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.6.2155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C., Mullin B. C. Transfer RNA into RNA tumor viruses. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1977;20:131–160. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60471-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waters L. C. Transfer RNAs associated with the 70S RNA of AKR murine leukemia virus. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Aug 4;65(3):1130–1136. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80503-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wollmann R. L., Kirsten W. H. Cellular origin of a mouse leukemia viral ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1968 Nov;2(11):1241–1248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.2.11.1241-1248.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaura I., Cavalieri L. F. Inhibition of reverse transcription of 70S and 35S avian myeloblastosis RNAs by nonprimer tRNA's. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):300–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.300-306.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]