Abstract
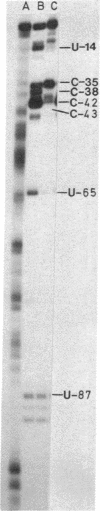
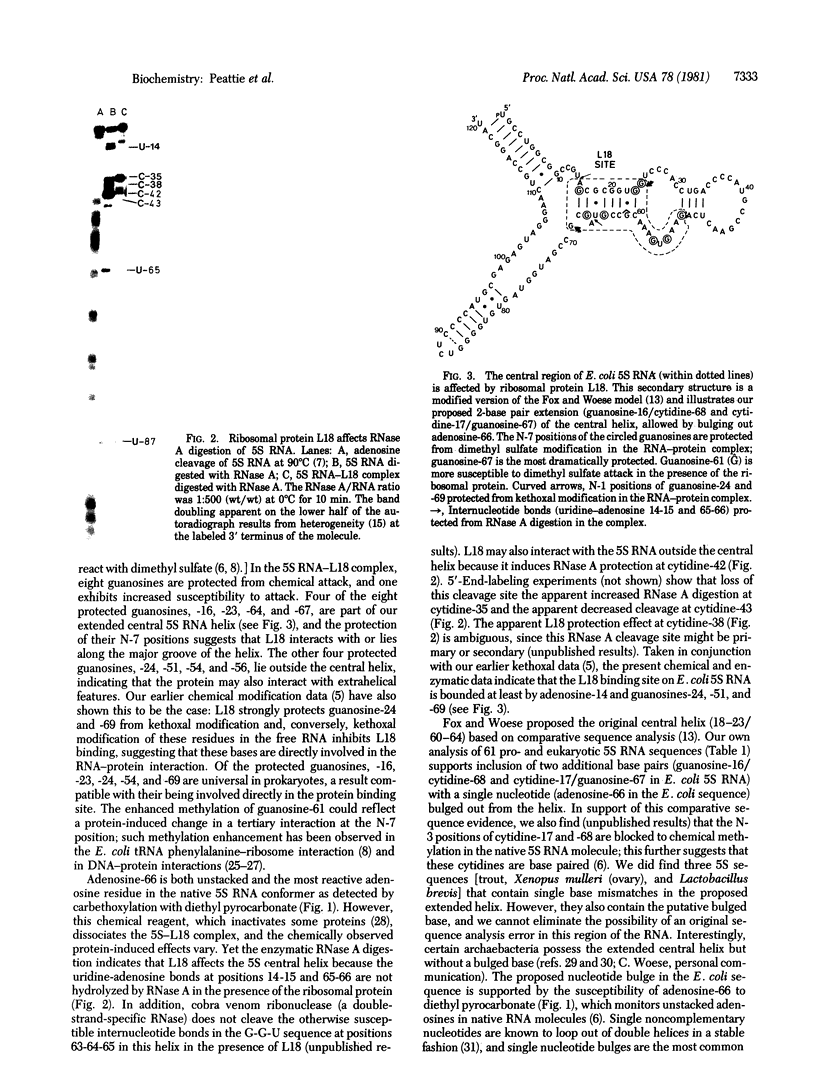
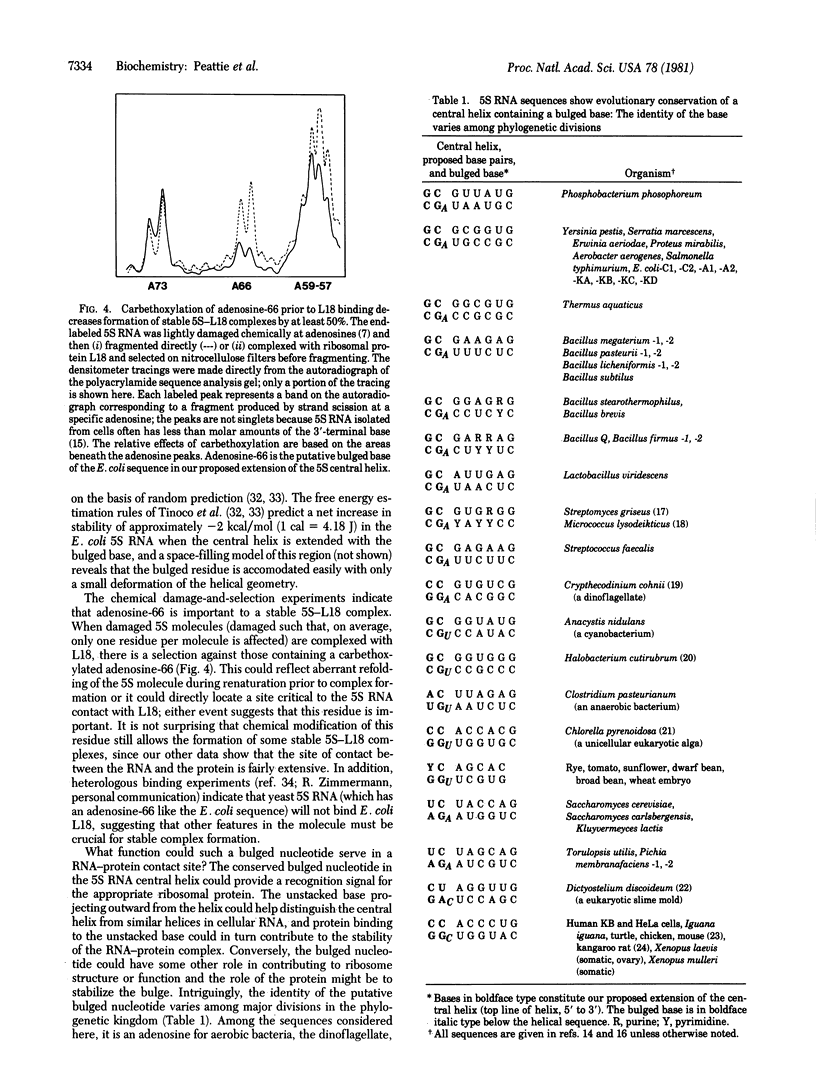
The binding of ribosomal protein L18 affects specific nucleotides in Escherichia coli 5S RNA as detected by dimethyl sulfate alkylation and RNase A digestion of the 5S-L18 complex. Most of the affected nucleotides are clustered and localize a site of RNA-protein interaction in and around the defined central helix [Fox, G. E. & Woese, C. (1975) Nature (London) 256, 505-507] of 5S RNA. Chemical carbethoxylation of the native 5S RNA with diethyl pyrocarbonate shows that a striking feature of this region is an unstacked adenosine residue at position 66. We propose that this residue exists as a singly bulged nucleotide extending the Fox and Woese central helix by two base pairs in the E. coli sequence (to positions 16-23/60-68) as well as in each of 61 (prokaryotic and eukaryotic) aligned 5S RNA sequences. In each case, the single bulged nucleotide is at the relative position of adenosine-66 in the RNA sequences. The presence of this putative bulged nucleotide appears to have been conserved in 5S RNA sequences throughout evolution, and its identity varies with major phylogenetic divisions. This residue is likely involved in specific 5S RNA-protein recognition or interaction in prokaryotic and eukaryotic ribosomes. The uridine-65 to adenosine-66 internucleotide bond is protected from RNase A digestion in the complex, and carbethoxylation of E. coli adenosine-66 prior to L18 binding affects formation of a stable RNA-protein complex. Thus, we identify a region of E. coli 5S RNA protected by the ribosomal protein L18 and propose that it contains a bulged nucleotide residue important in stable formation of this RNA-protein complex. This bulged residue appears to be evolutionarily conserved and phylogenetically defined in 5S RNA sequences in general, and consideration of other known RNA-protein binding sites shows that such a "bulged helix" may be a common feature of RNA-protein contact sites.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aubert M., Scott J. F., Reynier M., Monier R. Rearrangement of the conformation of Escherichia coli 5S RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1968 Sep;61(1):292–299. doi: 10.1073/pnas.61.1.292. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averner M. J., Pace N. R. The nucleotide sequence of marsupial 5 S ribosomal ribonucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1972 Jul 25;247(14):4491–4493. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen-Schmeisser U., Garrett R. A. A new method for the isolation of a 5 S RNA complex with proteins L5, L18 and L25 from Escherichia coli ribosomes. FEBS Lett. 1977 Mar 1;74(2):287–291. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80866-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg L., Fedorcsak I., Solymosy F. Diethyl pyrocarbonate in nucleic acid research. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;16:189–262. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60758-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein P., Reddy R., Busch H. Site-specific cleavage by T1 RNase of U-1 RNA in u-1 ribonucleoprotein particles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1562–1566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erdmann V. A. Collection of published 5S and 5.8S RNA sequences and their precursors. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):r25–r42. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.213-a. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiil N. P., Friesen J. D., Downing W. L., Dennis P. P. Post-transcriptional regulatory mutants in a ribosomal protein-RNA polymerase operon of E. coli. Cell. 1980 Apr;19(4):837–844. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90074-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. 5S RNA secondary structure. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):505–507. doi: 10.1038/256505a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox G. E., Woese C. R. The architecture of 5S rRNA and its relation to function. J Mol Evol. 1975 Oct 3;6(1):61–76. doi: 10.1007/BF01732674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fresco J. R., Alberts B. M. THE ACCOMMODATION OF NONCOMPLEMENTARY BASES IN HELICAL POLYRIBONUCLEOTIDES AND DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACIDS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):311–321. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrett R. A., Noller H. F. Structures of complexes of 5S RNA with ribosomal proteins L5, L18 and L25 from Escherichia coli: identification of kethoxal-reactive sites on the 5S RNA. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):637–648. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90379-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gralla J., Steitz J. A., Crothers D. M. Direct physical evidence for secondary structure in an isolated fragment of R17 bacteriophage mRNA. Nature. 1974 Mar 15;248(445):204–208. doi: 10.1038/248204a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hindennach I., Kaltschmidt E., Wittmann H. G. Ribosomal proteins. Isolation of proteins from 50S ribosomal subunits of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Nov 11;23(1):12–16. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnebusch A. G., Klotz L. C., Blanken R. L., Loeblich A. R., 3rd An evaluation of the phylogenetic position of the dinoflagellate Crypthecodinium cohnii based on 5S rRNA characterization. J Mol Evol. 1981;17(6):334–337. doi: 10.1007/BF01734355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S. Evolutionary change in 5S RNA secondary structure and a phylogenic tree of 54 5S RNA species. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jan;76(1):381–385. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.1.381. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S., Iwabuchi M. The nucleotide sequence of 5S rRNA from a cellular slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5535–5539. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5535. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori H., Osawa S., Murao K., Ishikura H. The nucleotide sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA from Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Nov 25;8(22):5423–5426. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.22.5423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee F., Yanofsky C. Transcription termination at the trp operon attenuators of Escherichia coli and Salmonella typhimurium: RNA secondary structure and regulation of termination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4365–4369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner M. R., Boyle J. A., Mount S. M., Wolin S. L., Steitz J. A. Are snRNPs involved in splicing? Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):220–224. doi: 10.1038/283220a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Fox G. E., Kilpatrick M. W., Walker R. T., Domdey H., Krupp G., Gross H. J. The nucleotide sequence of the 5S rRNA from the archaebacterium Thermoplasma acidophilum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Feb 25;9(4):965–970. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.4.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luehrsen K. R., Fox G. E. Secondary structure of eukaryotic cytoplasmic 5S ribosomal RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2150–2154. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nazar R. N., Matheson A. T., Bellemare G. Nucleotide sequence of Halobacterium cutirubrum ribosomal 5 S ribonucleic acid. An altered secondary structure in halophilic organisms. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5464–5469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Garrett R. A. Structure of 5 S ribosomal RNA from Escherichia coli: identification of kethoxal-reactive sites in the A and B conformations. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):621–636. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90378-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noller H. F., Woese C. R. Secondary structure of 16S ribosomal RNA. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):403–411. doi: 10.1126/science.6163215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R. T., Gilbert W. DNA-binding site of lac repressor probed by dimethylsulfate methylation of lac operator. J Mol Biol. 1979 Aug 25;132(4):709–728. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90384-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A. Direct chemical method for sequencing RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Apr;76(4):1760–1764. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.4.1760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Gilbert W. Chemical probes for higher-order structure in RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4679–4682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peattie D. A., Herr W. Chemical probing of the tRNA--ribosome complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2273–2277. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Simpson R. B., Gilbert W. E. coli RNA polymerase interacts homologously with two different promoters. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):269–281. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90613-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simoncsits A. 3' Terminal labelling of RNA of RNA with beta-32P-pyrophosphate group and its application to the sequence analysis of 5S RNA from Streptomyces griseus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Sep 25;8(18):4111–4124. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.18.4111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Uhlenbeck O. C., Levine M. D. Estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nature. 1971 Apr 9;230(5293):362–367. doi: 10.1038/230362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber H. The binding site for coat protein on bacteriophage Qbeta RNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Jan 19;418(2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90067-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson R., Brownlee G. G. The sequence of 5S ribosomal RNA from two mouse cell lines. FEBS Lett. 1969 Jun;3(5):306–308. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(69)80163-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R., Magrum L. J., Gupta R., Siegel R. B., Stahl D. A., Kop J., Crawford N., Brosius J., Gutell R., Hogan J. J. Secondary structure model for bacterial 16S ribosomal RNA: phylogenetic, enzymatic and chemical evidence. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2275–2293. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wrede P., Erdmann V. A. Escherichia coli 5S RNA binding proteins L18 and L25 interact with 5.8S RNA but not with 5S RNA from yeast ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jul;74(7):2706–2709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.7.2706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmern D. The nucleotide sequence at the origin for assembly on tobacco mosaic virus RNA. Cell. 1977 Jul;11(3):463–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90065-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zurawski G., Yanofsky C. Escherichia coli tryptophan operon leader mutations, which relieve transcription termination, are cis-dominant to trp leader mutations, which increase transcription termination. J Mol Biol. 1980 Sep 5;142(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90210-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]