Abstract
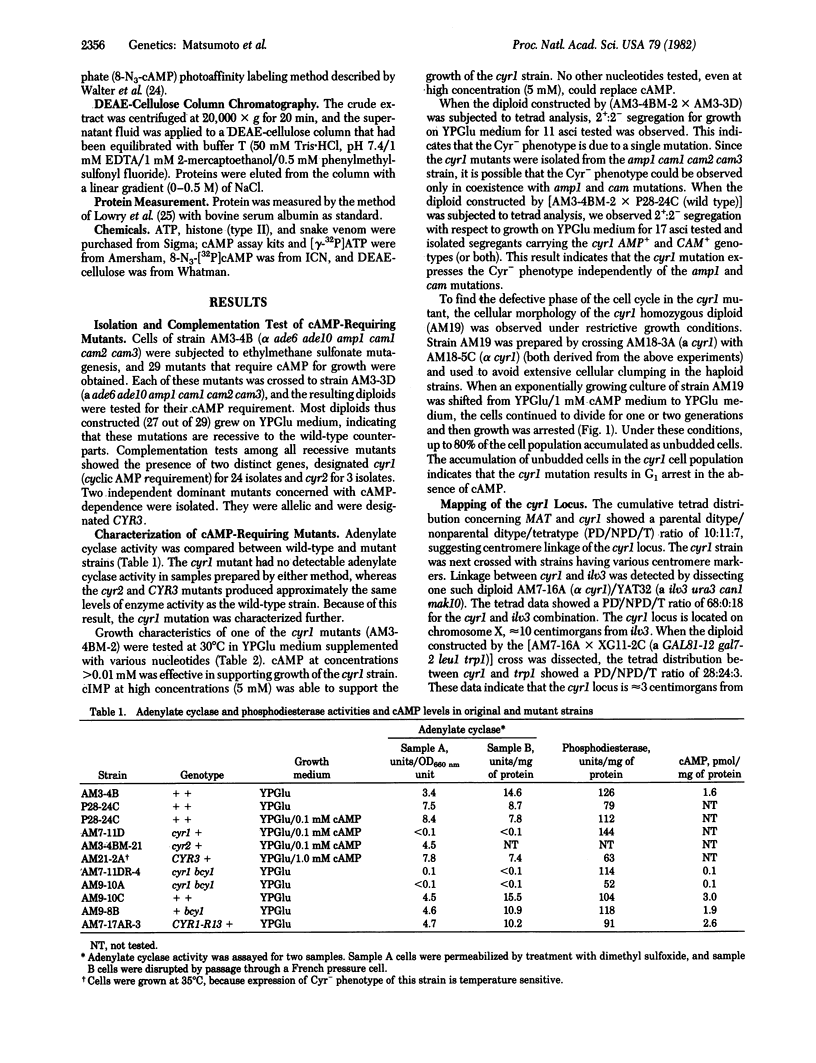
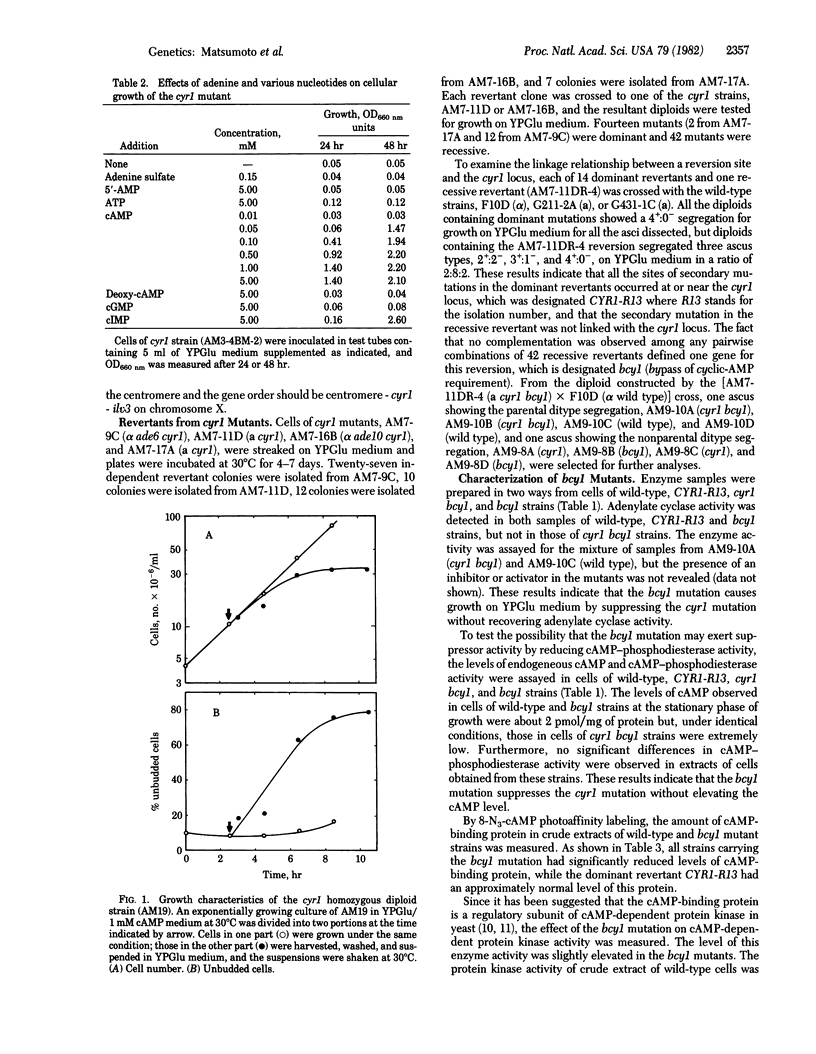
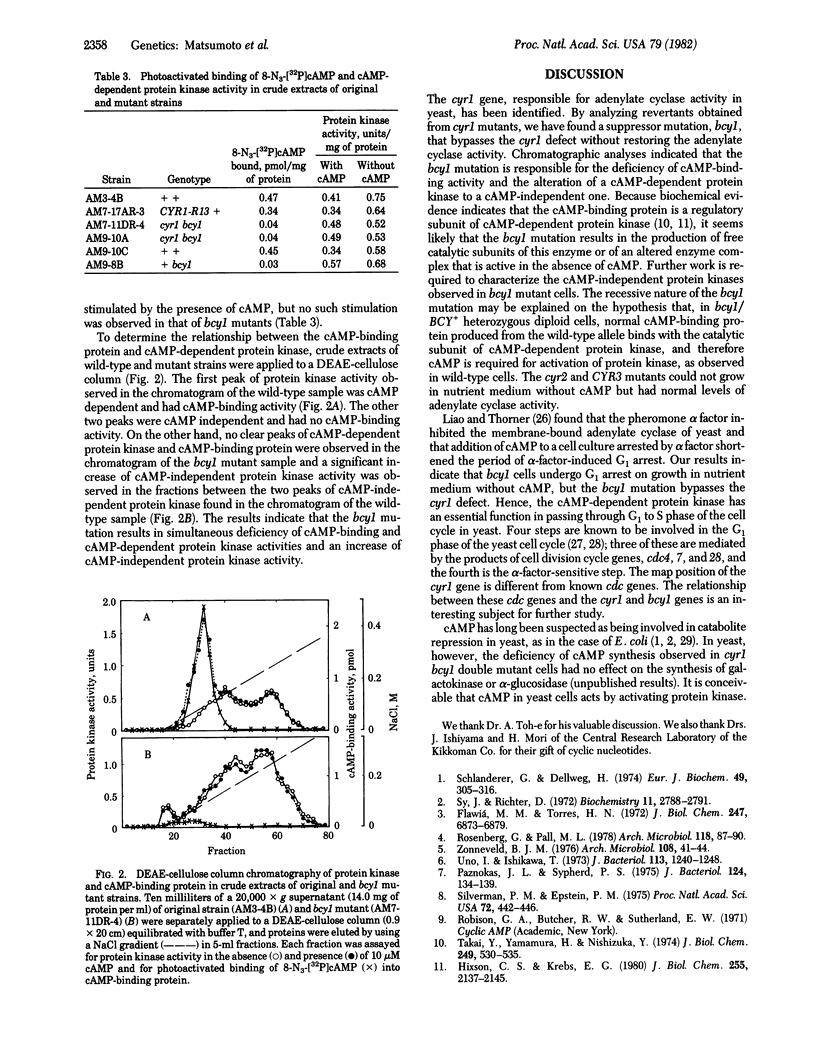
Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae that require cAMP for growth have been isolated. Some of the mutants isolated were deficient in adenylate cyclase activity and mapped at a locus, cyr1, located near the centromere of chromosome X. Growth of cells carrying the cyr1 mutation was arrested at the G1 phase of the yeast cell cycle in the absence of cAMP. The cyr1 mutation was suppressed by a secondary mutation designated bcy1. The bcy1 mutation bypassed the need for cAMP for growth. The bcy1 mutants had extremely low levels of cAMP-binding protein and cAMP-dependent protein kinase but produced a high level of cAMP-independent protein kinase. The results indicate that cAMP is an essential factor for yeast cells to proceed through the cell cycle via the activation of protein kinase.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Flawiá M. M., Torres H. N. Adenylate cyclase activity in Neurospora crassa. I. General properties. J Biol Chem. 1972 Nov 10;247(21):6873–6879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae cell cycle. Bacteriol Rev. 1974 Jun;38(2):164–198. doi: 10.1128/br.38.2.164-198.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hereford L. M., Hartwell L. H. Sequential gene function in the initiation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1974 Apr 15;84(3):445–461. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90451-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hixson C. S., Krebs E. G. Characterization of a cyclic AMP-binding protein from bakers' yeast. Identification as a regulatory subunit of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 10;255(5):2137–2145. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao H., Thorner J. Yeast mating pheromone alpha factor inhibits adenylate cyclase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1898–1902. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1898. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindegren G., Hwang Y. L., Oshima Y., Lindegren C. C. Genetical mutants induced by ethyl methanesulfonate in Saccharomyces. Can J Genet Cytol. 1965 Sep;7(3):491–499. doi: 10.1139/g65-064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahler H. R., Lin C. C. Exogenous adenosine 3': 5'-monophosphate can release yeast from catabolite repression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Aug 14;83(3):1039–1047. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91500-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Genetic control of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: evidence for constitutive expression of the positive regulatory gene gal4. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):446–457. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.446-457.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Isolation and characterization of dominant mutations resistant to carbon catabolite repression of galactokinase synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):83–93. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.83. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nogi Y., Matsumoto K., Toh-e A., Oshima Y. Interaction of super-repressible and dominant constitutive mutations for the synthesis of galactose pathway enzymes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Gen Genet. 1977 Apr 29;152(3):137–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00268810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paznokas J. L., Sypherd P. S. Respiratory capacity, cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate, and morphogenesis of Mucor racemosus. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):134–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.134-139.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg G., Pall M. L. Cyclic AMP and cyclic GMP in germinating conidia of Neurospora crassa. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jul;118(1):87–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00406079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlanderer G., Dellweg H. Cyclid AMP and catabolite repression in yeasts, In Schizosaccharomyces pombe glucose lowers both intracellular adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate levels and the activity of catabolite-sensitive enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Nov 1;49(1):305–316. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott W. A. Adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate deficiency in Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):2995–2999. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.2995. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silverman P. M., Epstein P. M. Cyclic nucleotide metabolism coupled to cytodifferentiation of Blastocladiella emersonii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Feb;72(2):442–446. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.2.442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snow R. An enrichment method for auxotrophic yeast mutants using the antibiotic 'nystatin'. Nature. 1966 Jul 9;211(5045):206–207. doi: 10.1038/211206a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sy J., Richter D. Content of cyclic 3',5'-adenosine monophosphate and adenylyl cyclase in yeast at various growth conditions. Biochemistry. 1972 Jul 18;11(15):2788–2791. doi: 10.1021/bi00765a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Yamamura H., Nishizuka Y. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase from yeast. J Biol Chem. 1974 Jan 25;249(2):530–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenzi H. F., Flawia M. M., Tellez-Inon M. T., Torres H. N. Control of Neurospora crassa morphology by cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate and dibutyryl cyclic adenosine 3', 5'-monophosphate. J Bacteriol. 1976 Apr;126(1):91–99. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.1.91-99.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenzi H. F., Flawiá M. M., Torres H. N. A Neurospora crassa morphological mutant showing reduced adenylate cyclase activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1974 Jun 18;58(4):990–996. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(74)80241-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terenzi H. F., Jorge J. A., Roselino J. E., Migliorini R. H. Adenylyl cyclase deficient cr-1 (Crisp) mutant of Neurospora crassa: cyclic AMP-dependent nutritional deficiencies. Arch Microbiol. 1979;123(3):251–258. doi: 10.1007/BF00406658. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson W. J., Terasaki W. L., Epstein P. M., Strada S. J. Assay of cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase and resolution of multiple molecular forms of the enzyme. Adv Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1979;10:69–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno I., Ishikawa T. Purification and identification of the fruiting-inducing substances in Coprinus macrorhizus. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1240–1248. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1240-1248.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uno I., Ueda T., Greengard P. Adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein system of neuronal membranes. II. Solubilization, purification, and some properties of an endogenous adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):5164–5174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter U., Uno I., Liu A. Y., Greengard P. Identification, characterization, and quantitative measurement of cyclic AMP receptor proteins in cytosol of various tissues using a photoaffinity ligand. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6494–6500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zonneveld B. J. The effect of glucose and manganese on adenosine-3',5'-monophosphate levels during growth and differentiation of Aspergillus nidulans. Arch Microbiol. 1976 May 3;108(1):41–44. doi: 10.1007/BF00425091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


