Abstract
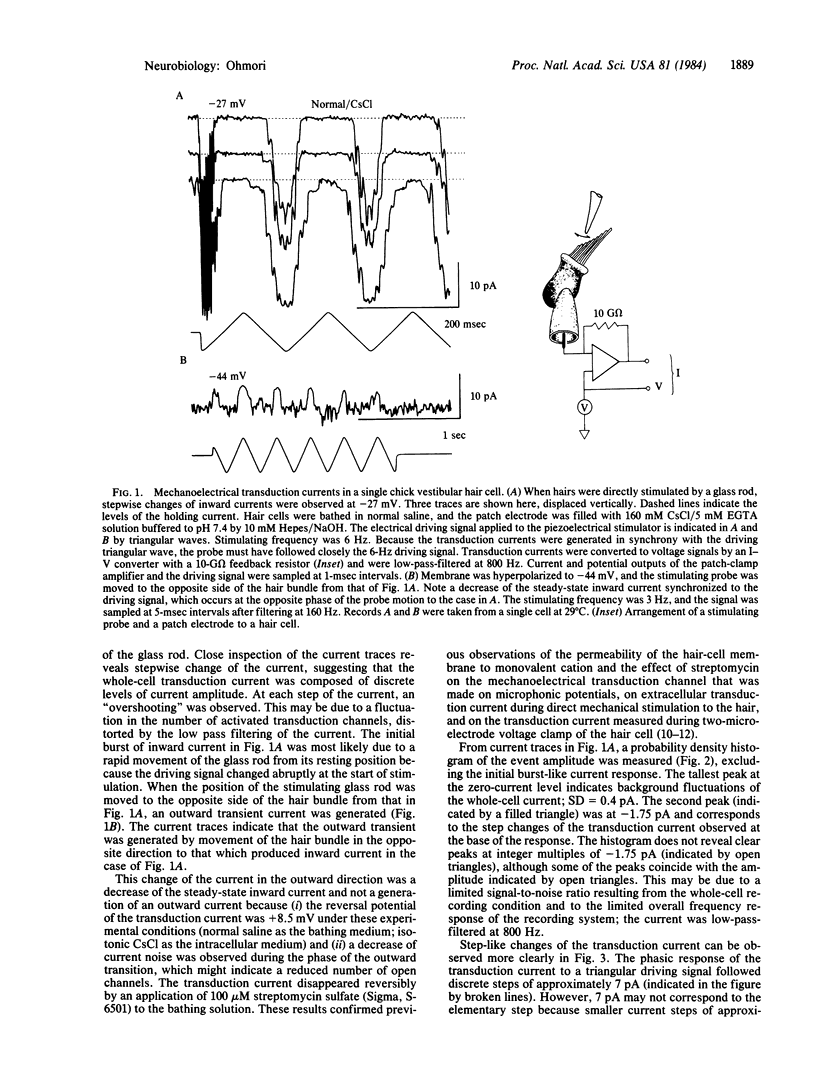
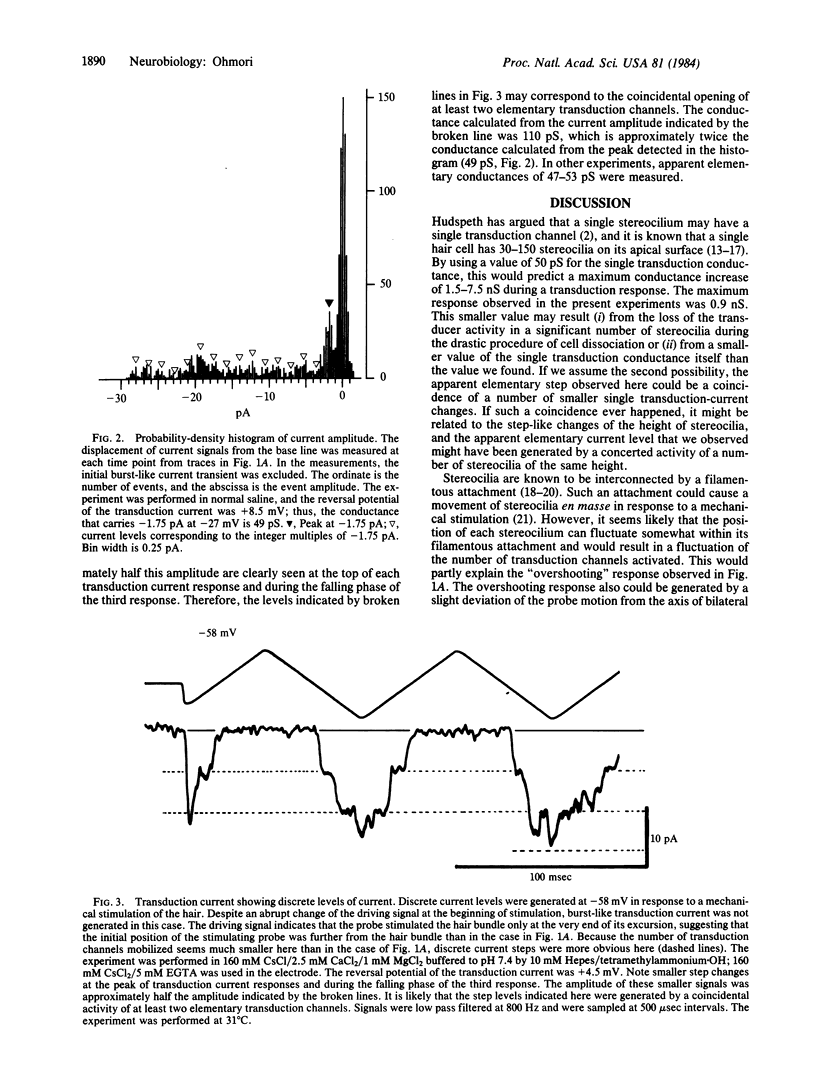
Properties of mechanoelectrical transduction were studied at the single-cell level by applying a whole-cell recording variation of the patch-clamp technique to dissociated vestibular hair cells of chicks. The hair bundle was directly stimulated by a glass rod, and transduction currents were recorded from the cell body. After a triangular movement of the stimulating probe, the transduction current was generated stepwise between discrete levels of amplitude. The minimum step amplitude was -1.8 pA at -27 mV in Na-containing normal saline.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader C. R., Bertrand D., Schwartz E. A. Voltage-activated and calcium-activated currents studied in solitary rod inner segments from the salamander retina. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:253–284. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagger-Sjöbäck D. The sensory hairs and their attachments in the lizard basilar papilla. Brain Behav Evol. 1974;10(1-3):88–94. doi: 10.1159/000124304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bagger-Sjöbäck D., Wersäll J. The sensory hairs and tectorial membrane of the basilar papilla in the lizard Calotes versicolor. J Neurocytol. 1973 Sep;2(3):329–350. doi: 10.1007/BF01104034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Hudspeth A. J. Ionic basis of the receptor potential in a vertebrate hair cell. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):675–677. doi: 10.1038/281675a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corey D. P., Hudspeth A. J. Mechanical stimulation and micromanipulation with piezoelectric bimorph elements. J Neurosci Methods. 1980 Dec;3(2):183–202. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(80)90025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagiwara S., Ohmori H. Studies of calcium channels in rat clonal pituitary cells with patch electrode voltage clamp. J Physiol. 1982 Oct;331:231–252. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1982.sp014371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. Extracellular current flow and the site of transduction by vertebrate hair cells. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):1–10. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00001.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudspeth A. J. Mechanoelectrical transduction by hair cells in the acousticolateralis sensory system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1983;6:187–215. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.06.030183.001155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura R. S. Hairs of the cochlear sensory cells and their attachment to the tectorial membrane. Acta Otolaryngol. 1966 Jan-Feb;61(1):55–72. doi: 10.3109/00016486609127043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam D. M. Biosynthesis of acetylcholine in turtle photoreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1987–1991. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. S., Hudspeth A. J. Voltage- and ion-dependent conductances in solitary vertebrate hair cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):538–541. doi: 10.1038/304538a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuura S., Ikeda K., Furukawa T. Effects of streptomycin, kanamycin, quinine, and other drugs on the microphonic potentials of goldfish sacculus. Jpn J Physiol. 1971 Oct;21(5):579–590. doi: 10.2170/jjphysiol.21.579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R. Further scanning electron microscope studies of lizard auditory papillae. J Morphol. 1978 Jun;156(3):381–417. doi: 10.1002/jmor.1051560305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaka T., Smith C. A. The structure and innervation of the pigeon's basilar papilla. J Ultrastruct Res. 1971 Apr;35(1):20–65. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(71)80141-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Düring M., Karduck A., Richter H. G. The fine structure of the inner ear in caiman crocodilus. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1974;145(1):41–65. doi: 10.1007/BF00519125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


