Abstract
A tubulin-like protein was identified in the lower eukaryote Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The following criteria were used: (i) copolymerization of the 35S-labeled yeast protein with porcine brain tubulin; (ii) immunoprecipitation of the 35S-labeled yeast protein with antiflagellar tubulin antibody; (iii) the presence of the yeast protein as a constituent of isolated yeast nuclei; and (iv) splitting of the yeast protein in a gel electrophoretic system containing sodium dodecyl sulfate that resolved the alpha- and beta-tubulin chains from other sources. This protein did not appear to have significant affinity for the plant alkaloid, Colcemid.
Full text
PDF
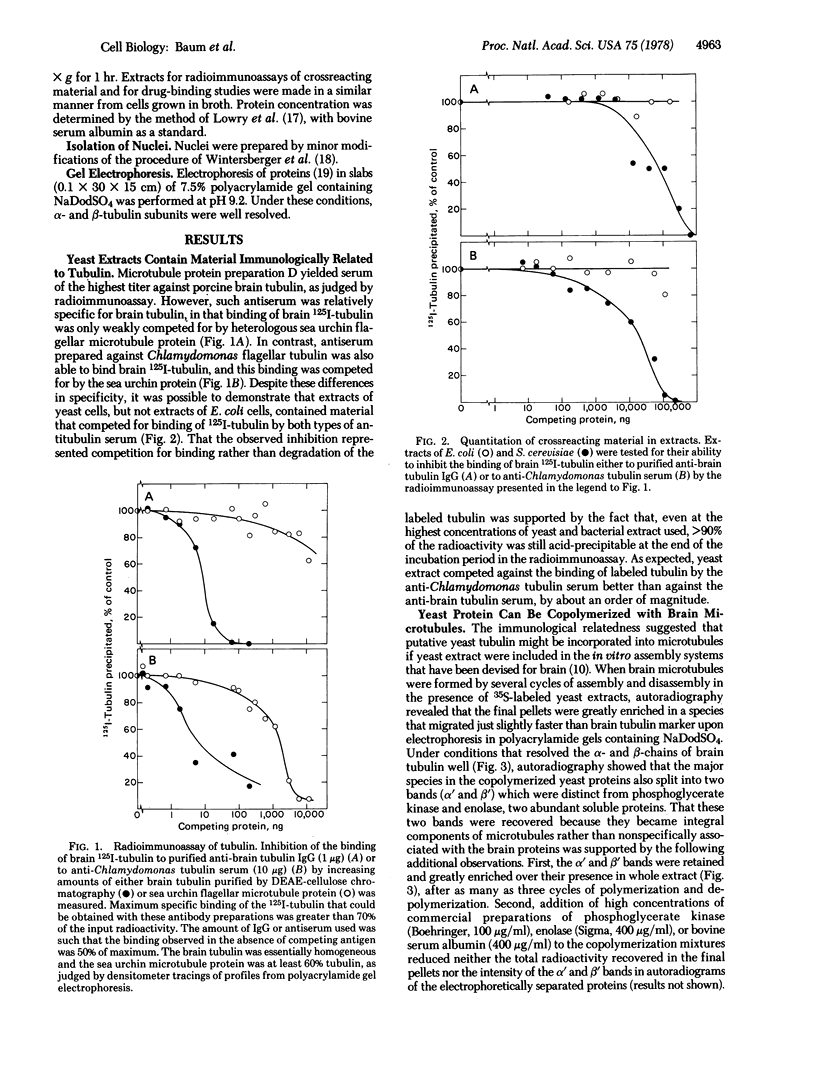

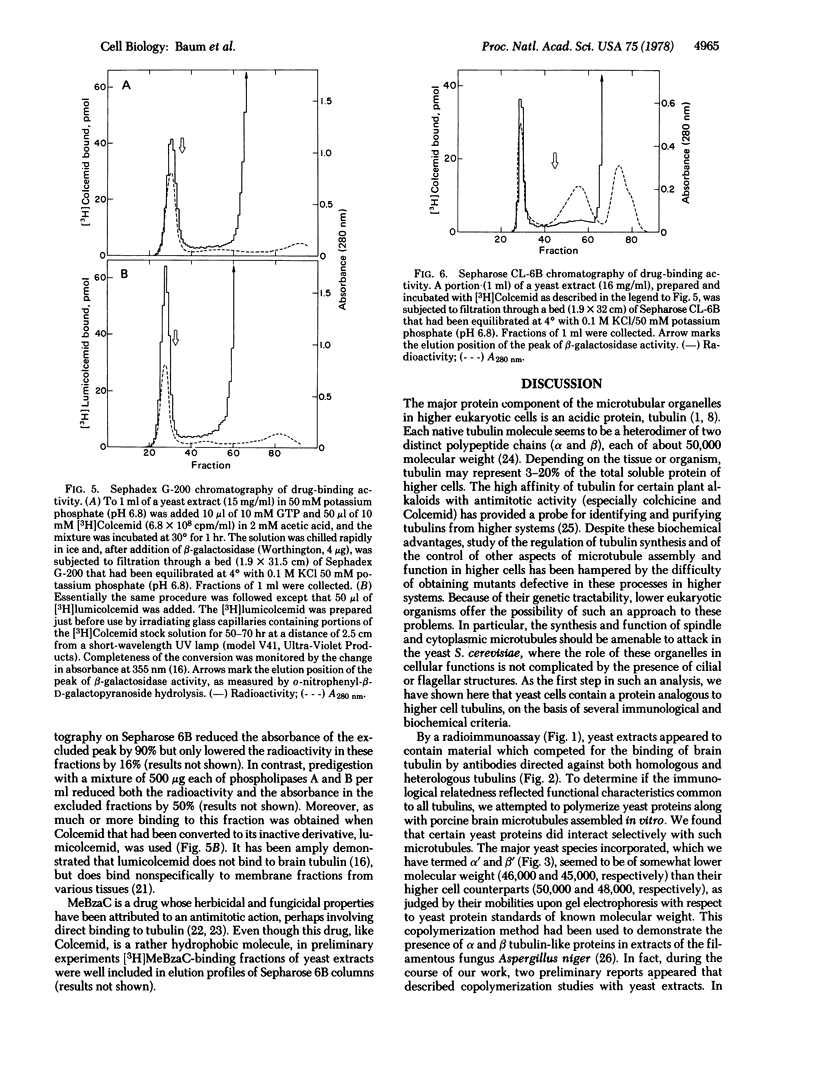

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bisson L., Thorner J. Thymidine 5'-monophosphate-requiring mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae are deficient in thymidylate synthetase. J Bacteriol. 1977 Oct;132(1):44–50. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.1.44-50.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns R. G. 3H-colcicine binding. Failure to detect any binding to soluble proteins from various lower organisms. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Oct;81(2):285–292. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90517-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Byers B., Goetsch L. Behavior of spindles and spindle plaques in the cell cycle and conjugation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):511–523. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.511-523.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidse L. C., Flach W. Differential binding of methyl benzimidazol-2-yl carbamate to fungal tubulin as a mechanism of resistance to this antimitotic agent in mutant strains of Aspergillus nidulans. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):174–193. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipper B. A. Rat brain microtubule protein: purification and determination of covalently bound phosphate and carbohydrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanagan D., Warr J. R. Colchicine binding of a high-speed supernatant of Chlamydomonas reinhardi. FEBS Lett. 1977 Aug 1;80(1):14–18. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80396-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haber J. E., Peloquin J. G., Halvorson H. O., Borisy G. G. Colcemid inhibition of cell growth and the characterization of a colcemid-binding activity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Biol. 1972 Nov;55(2):355–367. doi: 10.1083/jcb.55.2.355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludueńa R. F., Shooter E. M., Wilson L. Structure of the tubulin dimer. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 25;252(20):7006–7014. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchison J. M., Carter B. L. Cell cycle analysis. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;11:201–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mortimer R. K., Hawthorne D. C. Genetic mapping in yeast. Methods Cell Biol. 1975;11:221–233. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)60325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B., Borisy G. G. Microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1973;42:507–540. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.42.070173.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson J. B., Ris H. Electron-microscopic study of the spindle and chromosome movement in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Cell Sci. 1976 Nov;22(2):219–242. doi: 10.1242/jcs.22.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piperno G., Luck D. J. Microtubular proteins of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. An immunochemical study based on the use of an antibody specific for the beta-tubulin subunit. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 10;252(1):383–391. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheir-Neiss G., Nardi R. V., Gealt M. A., Morris N. R. Tubulin-like protein from Aspergillus nidulans. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Mar 22;69(2):285–290. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder J. A., McIntosh J. R. Biochemistry and physiology of microtubules. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:699–720. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.003411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stadler J., Franke W. W. Characterization of the colchicine binding of membrane fractions from rat and mouse liver. J Cell Biol. 1974 Jan;60(1):297–303. doi: 10.1083/jcb.60.1.297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Water R. D., Kleinsmith L. J. Identification of alpha and beta tubulin in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Jun 7;70(3):704–708. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90649-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber K., Wehland J., Herzog W. Griseofulvin interacts with microtubules both in vivo and in vitro. J Mol Biol. 1976 Apr 25;102(4):817–829. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90293-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Suter M. M., Littman D. R., Kirschner M. W. Properties of the depolymerization products of microtubules from mammalian brain. Biochemistry. 1974 Dec 31;13(27):5529–5537. doi: 10.1021/bi00724a012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Cole R. D. An improved preparation of highly specific tublin antibodies. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Apr;99(1):15–22. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90674-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L., Bamburg J. R., Mizel S. B., Grisham L. M., Creswell K. M. Interaction of drugs with microtubule proteins. Fed Proc. 1974 Feb;33(2):158–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintersberger U., Smith P., Letnansky K. Yeast chromatin. Preparation from isolated nuclei, histone composition and transcription capacity. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Feb 15;33(1):123–130. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02663.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]